A Novel Non-contact AC Voltage Detector Based on Concentric Double-layer Spherical Shell Structure
-
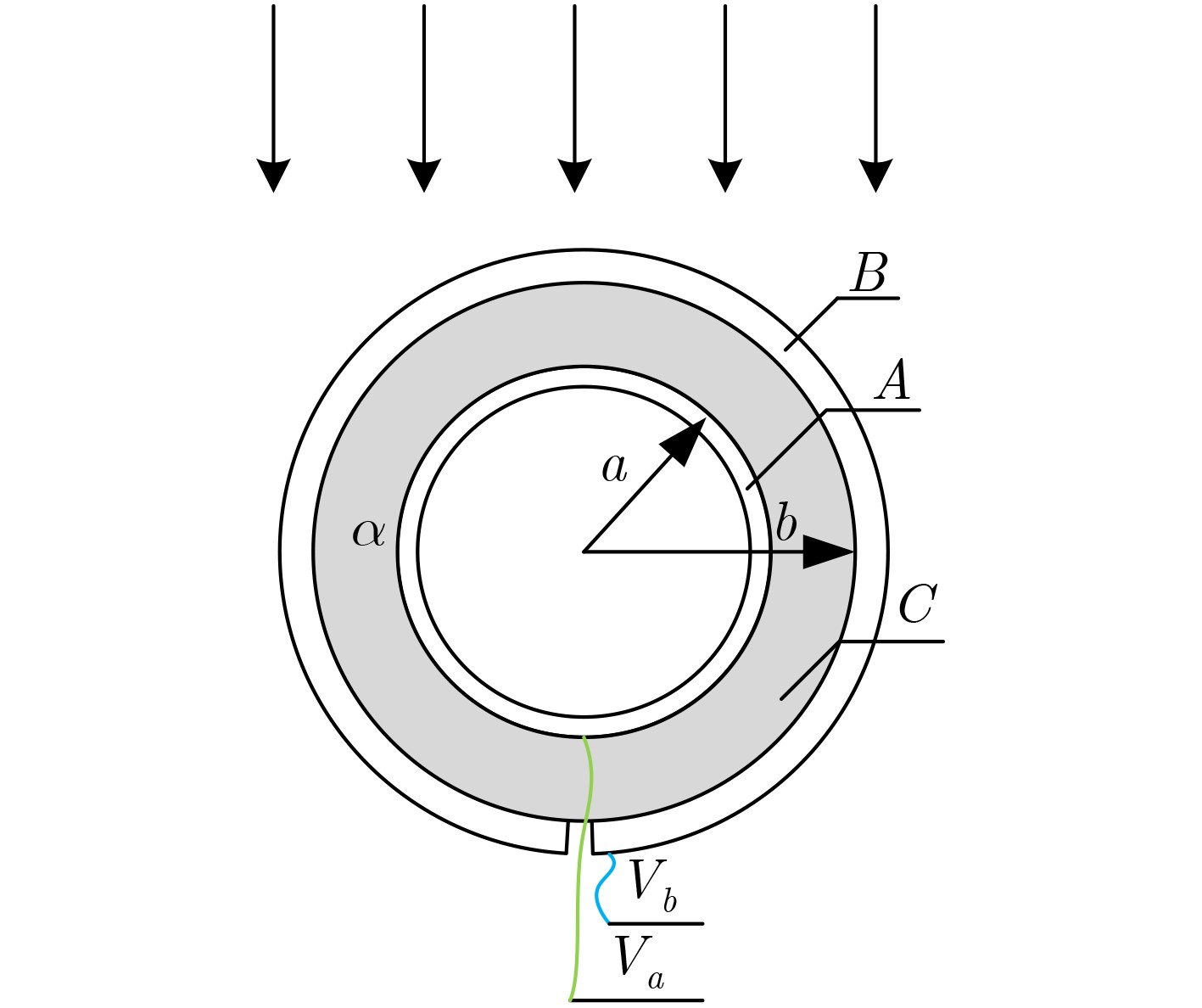
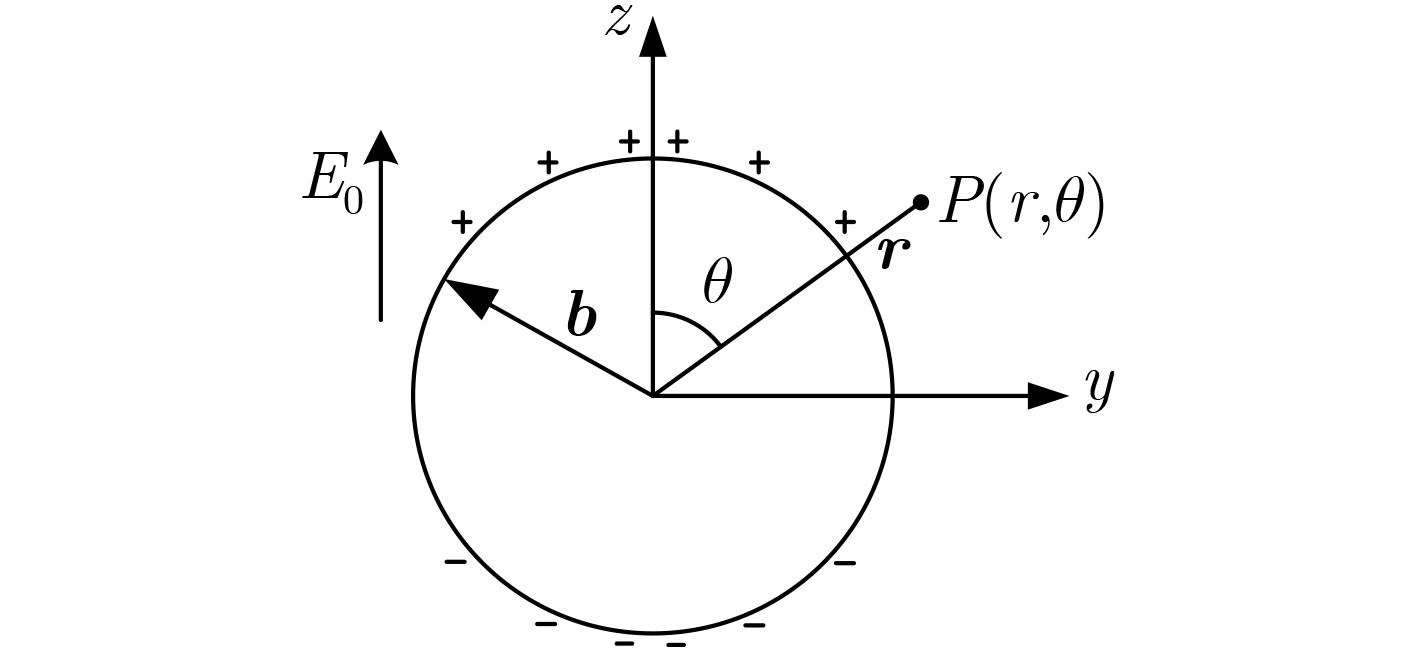
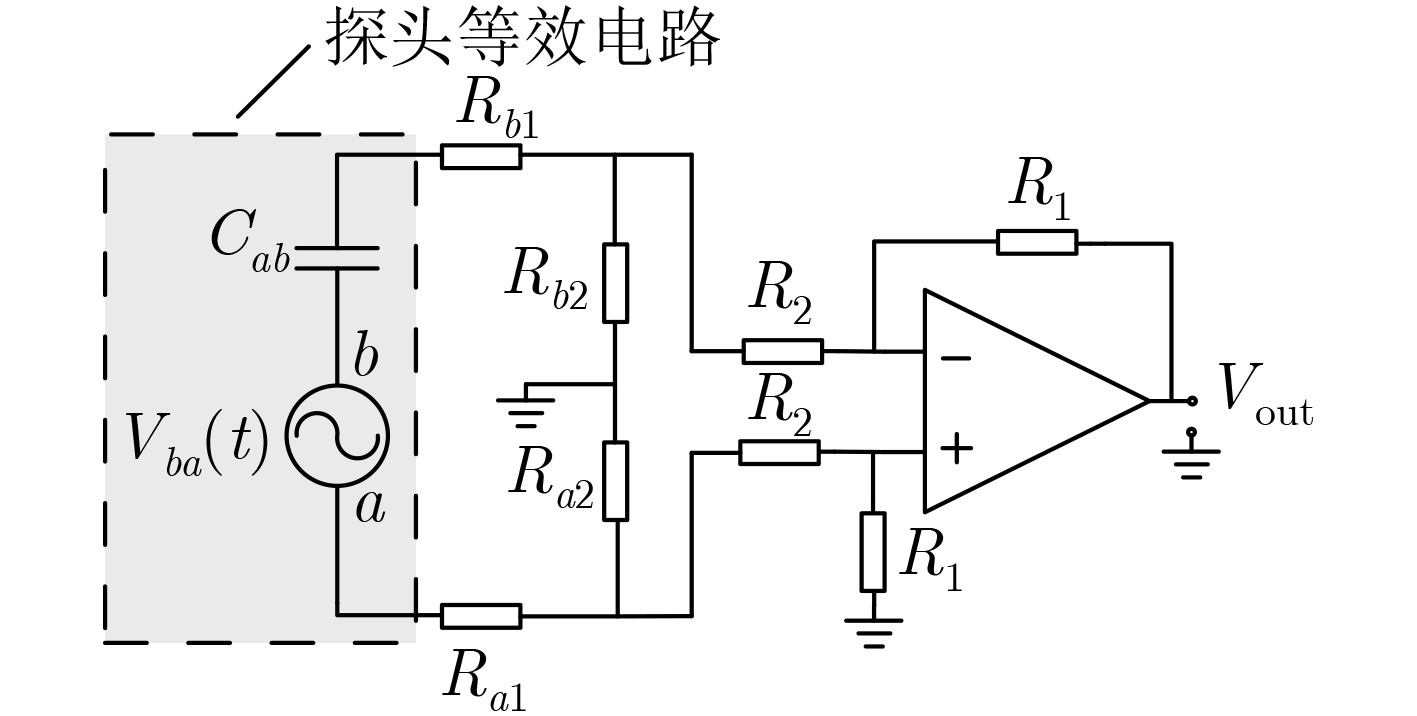
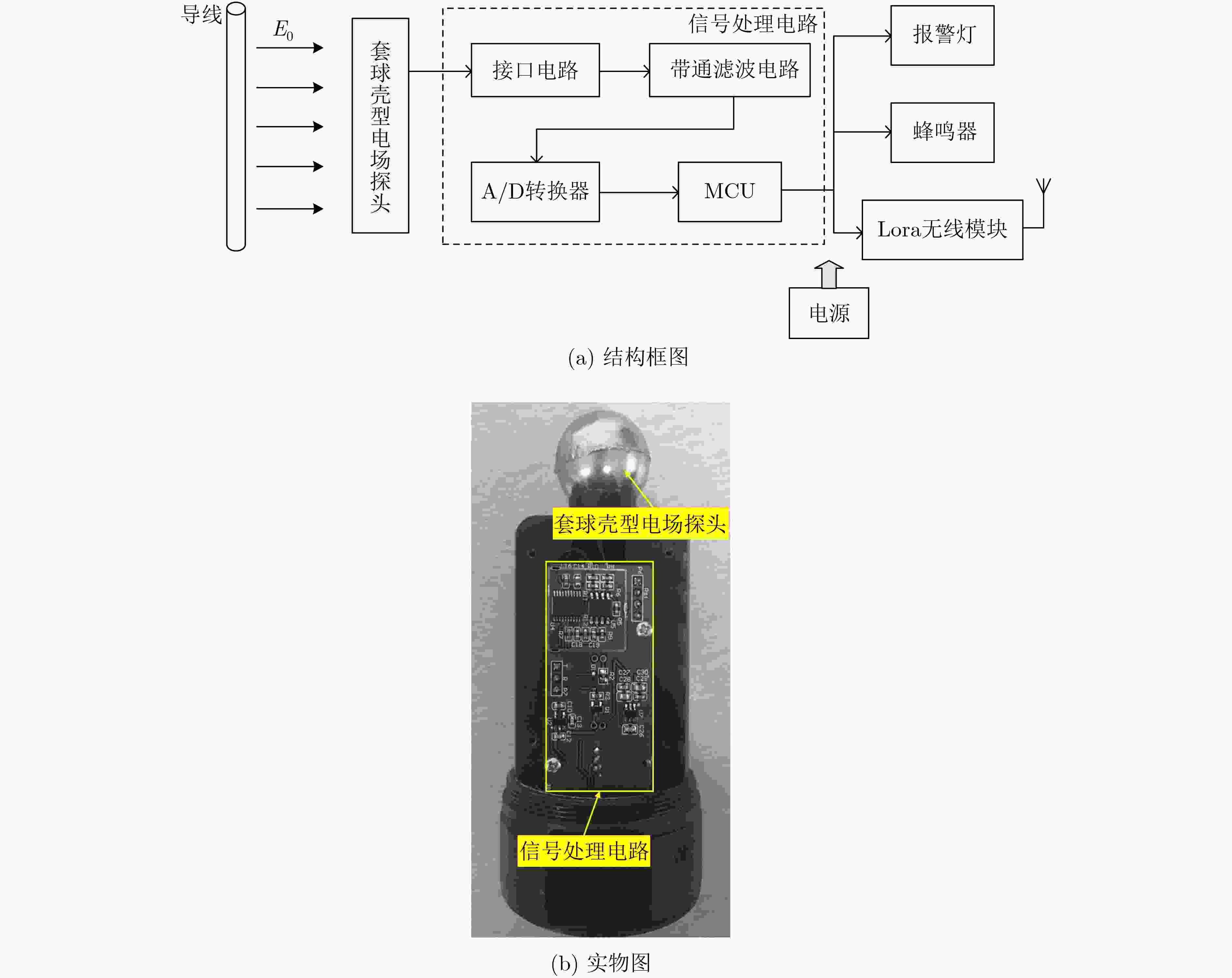
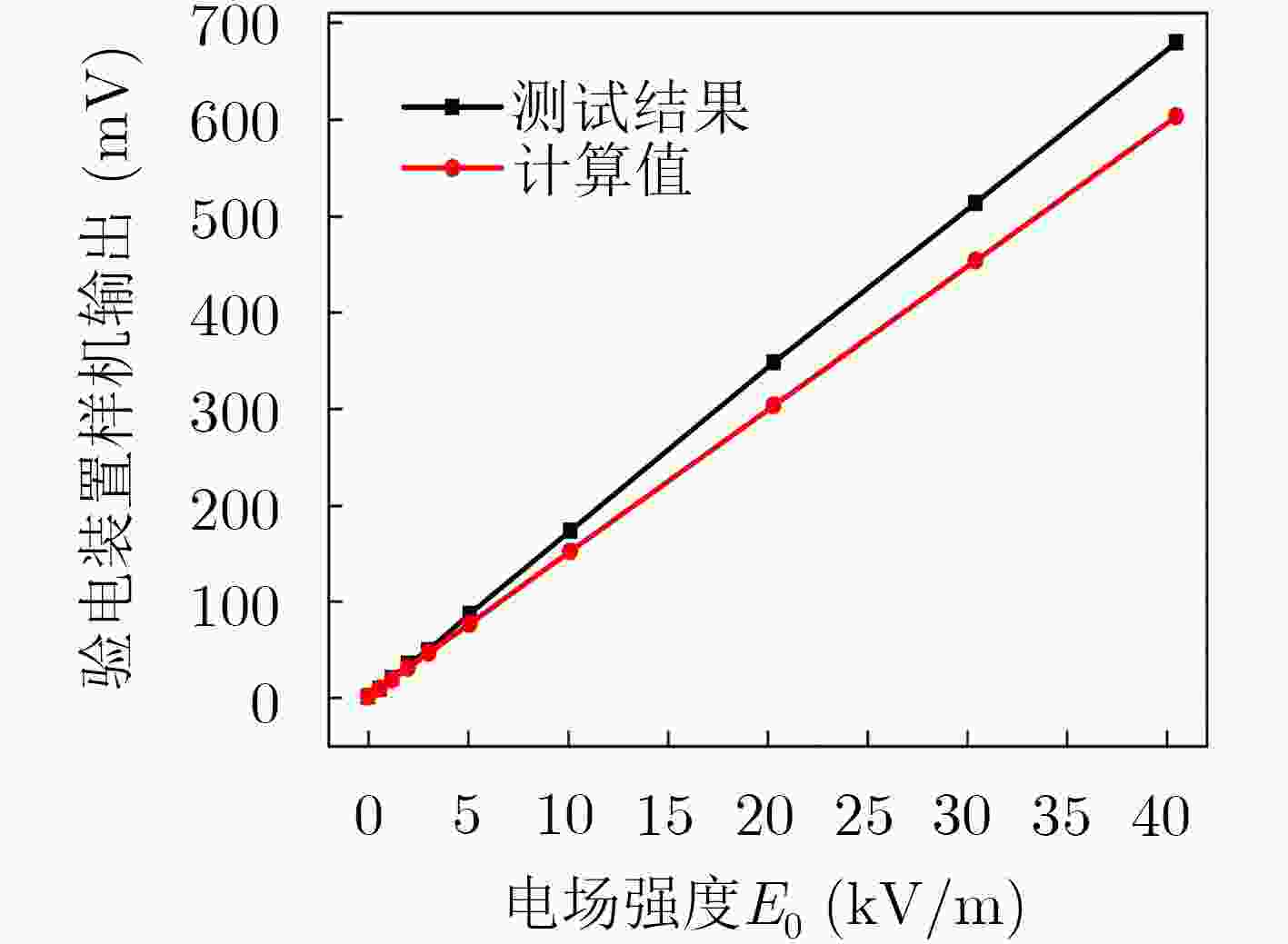
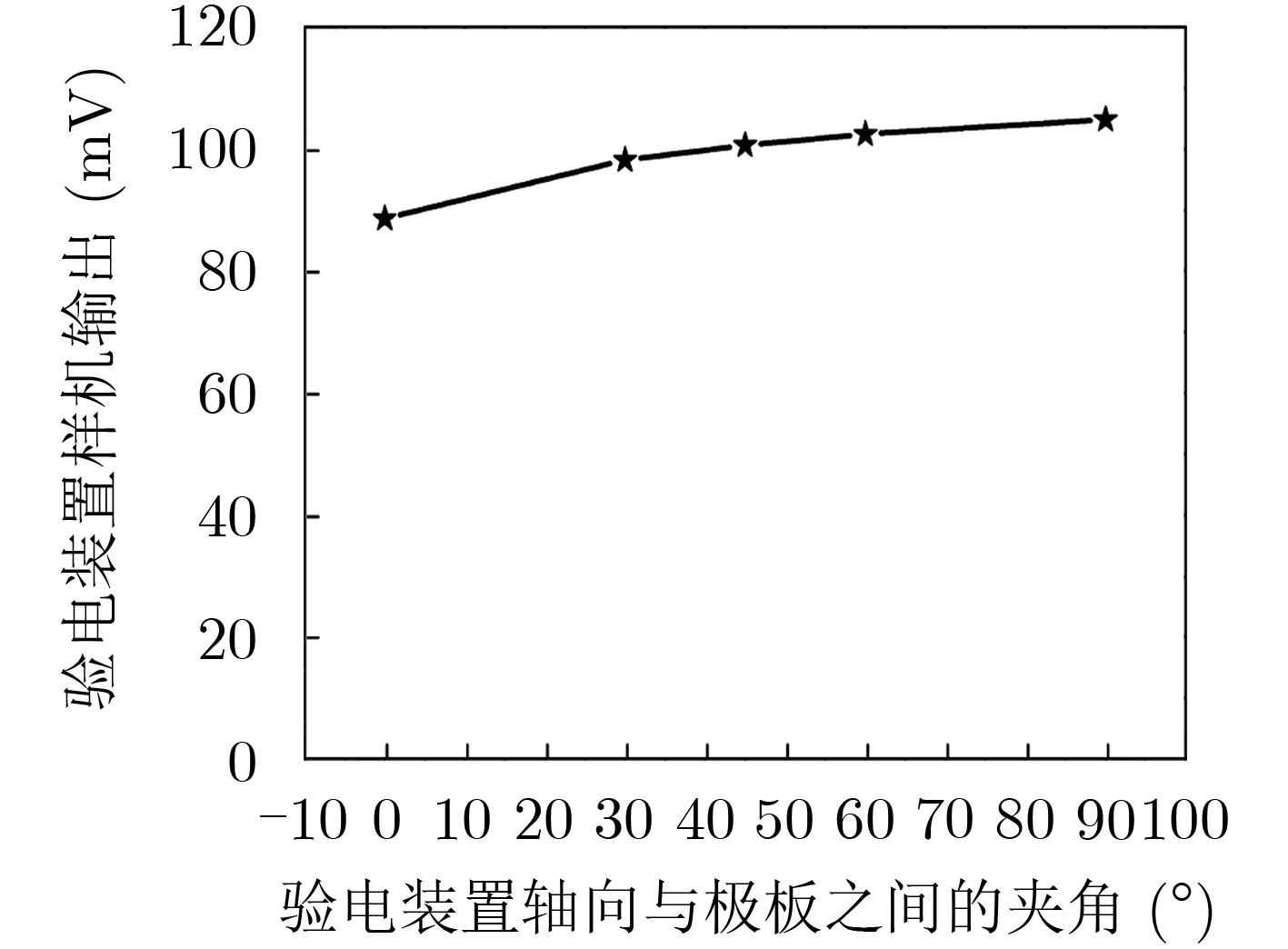
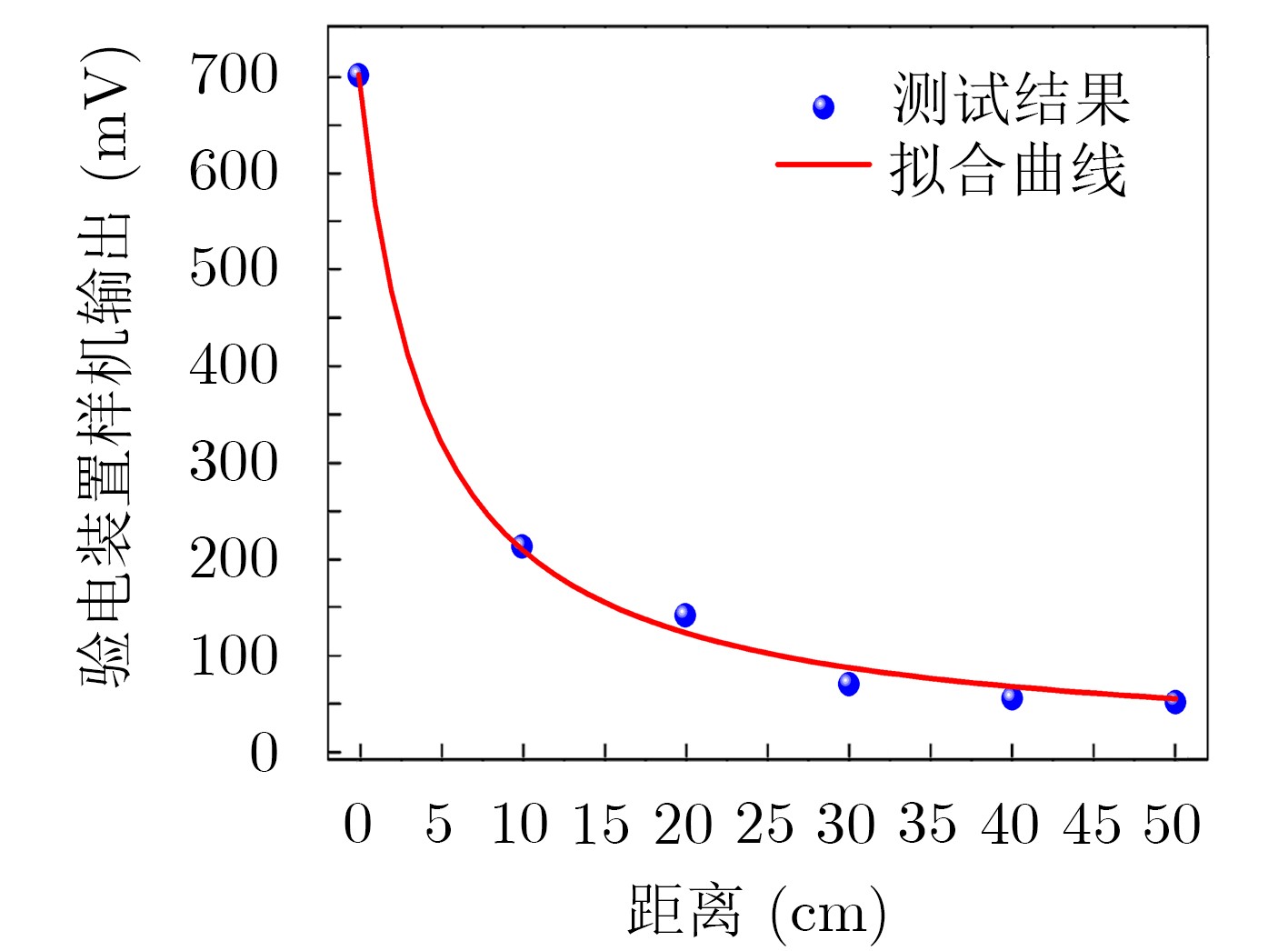
摘要: 该文提出一种基于套球壳型电场探头的非接触式交流验电装置。套球壳型结构类似差分结构,可消除共模干扰噪声的影响。建立套球壳型结构的电场分布理论模型,得到外球壳表面的感应电荷密度和电场探头的灵敏度表达式。提出电场探头的等效电路模型,并设计了接口电路,最终成功研制出非接触式交流验电装置样机。测试结果表明:已研制样机的电压输出与施加电场之间有良好的线性关系,线性度达到0.66%,并且测试结果与计算结果有较好的一致性;当样机在0~45°范围内转动时,其输出的电压值仅降低了4.0%,说明验电装置的小角度旋转基本上不影响验电的准确性;越接近输电线路,样机输出的电压值的增大速度越快,阈值易于识别,说明越容易验电。Abstract: A novel non-contact AC voltage detector based on the electric field probe of concentric double-layer spherical shell structure is presented. The concentric double-layer spherical shell structure is similar to the differential structure, which can eliminate the influence of common mode interference noise. The theoretical model of the electric field distribution of the double-layer spherical shell structure is established, and the induced charge density of the outer spherical shell surface is analyzed. Then the sensitivity expression of the electric field probe is obtained. Furthermore, the equivalent circuit model of the electric field probe is proposed and the interface circuit is designed. Finally, a prototype of the not-contact AC voltage detector is successfully developed. The test results show that there is a good linear relationship between the output of the prototype and the applied electric field, with a linearity of 0.66%, and the test results are in good agreement with the calculated results. Additionally, when the prototype rotates within the range of 0~45°, the output voltage is only reduced by a maximum of 4.0%, which indicates that the small angle rotation of the AC voltage detector does not affect the accuracy of electricity testing. Besides, the closer to the transmission line, the faster the output voltage of the prototype increases, and the threshold is easy to identify, suggesting that it is easier to verify the electricity.
-
表 1 匀强电场中的标定测试数据与理论计算结果
预设电压
值(V)实际施加
电压值(V)电场
值(kV/m)验电器样机
输出(mV)计算
结果(mV)0 0 0 0 0 500 576 0.576 8.0 8.6 1000 1198 1.198 19.4 17.9 2000 1992 1.992 34.0 29.7 3000 3030 3.030 48.2 45.1 5000 5080 5.080 86.0 75.7 10000 10120 10.120 172.4 150.8 20000 20300 20.300 347.4 302.5 30000 30400 30.400 512.8 452.9 40000 40450 40.450 679.8 602.7 表 2 与高压极板间不同夹角验电装置样机输出及相对误差计算结果
验电装置轴向与极板
之间的夹角(°)0 30 45 60 90 验电装置输出(mV) 88.65 98.25 100.65 102.45 104.85 相对误差(%) 15.4 6.3 4.0 2.2 0 -
[1] 吴龙锋, 黄胜, 胡礼军, 等. 高压验电器的研究综述及展望[J]. 智慧电力, 2018, 46(6): 61–67, 94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7598.2018.06.010WU Longfeng, HUANG Sheng, HU Lijun, et al. Summary and prospect of high voltage electroscope[J]. Smart Power, 2018, 46(6): 61–67, 94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7598.2018.06.010 [2] 张忠宝, 姚玉永. 35 kV高压验电器的数显改进与开发[J]. 电工电气, 2009(7): 19–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3175.2009.07.006ZHANG Zhongbao and YAO Yuyong. Digital-displayed improvement and exploitation of 35 kV high-voltage electroscope[J]. Electrotechnics Electric, 2009(7): 19–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3175.2009.07.006 [3] 廖文强. 浅析电容型验电器在使用中的缺陷及对策[J]. 通信电源技术, 2013, 30(2): 79–80.LIAO Wenqiang. Analysis of capacitance electroscope with defects and its countermeasures[J]. Telecom Power Technology, 2013, 30(2): 79–80. [4] 冯锟, 阮江军, 杜晟磊, 等. 电容型高压验电器故障分析与灵敏度改进[J]. 机电元件, 2014, 34(3): 42–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6133.2014.03.011FENG Kun, RUAN Jiangjun, DU Shenglei, et al. A fault analysis and sensitivity improvement of capacitive high voltage electroscope[J]. Electromechanical Components, 2014, 34(3): 42–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6133.2014.03.011 [5] KHAN T H, KABIR S M L, HUSSAIN S, et al. Design and implementation of a low cost electricity meter testing bench[C]. 2010 IEEE Symposium on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Penang, Malaysia, 2010: 34–39. doi: 10.1109/ISIEA.2010.5679499. [6] 李禾, 邓志祥, 王闯, 等. 电容型验电器验电盲区问题的研究[J]. 电器与能效管理技术, 2014(15): 10–13. doi: 10.16628/j.cnki.2095-8188.2014.15.004LI He, DENG Zhixiang, WANG Chuang, et al. Study on electrical inspection’s dead zone of capacitive detector[J]. Electrical &Energy Management Technology, 2014(15): 10–13. doi: 10.16628/j.cnki.2095-8188.2014.15.004 [7] 高桂华. 基于场强分布的非接触式超高压验电器设计[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2014.GAO Guihua. The design of non-contact electroscope of ultra-high voltage based on field intensity distribution[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2014. [8] ZHOU Momo and LI Chunmao. Development of non-contact electroscope[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on High Voltage Engineering and Application, Chendu, China, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICHVE.2016.7800630. [9] KURRER R and FESER K. The application of ultra-high-frequency partial discharge measurements to gas-insulated substations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 1998, 13(3): 777–782. doi: 10.1109/61.686974 [10] KOYAMA T, YOSHIDA T, and IDENO I. Development of a non-contact direct-voltage detector[J]. JR East Technical Review, 2012(22): 23–26. [11] 胡泽文, 何为, 姚德贵, 等. 高压工频电场警示仪的研究[J]. 电测与仪表, 2009, 46(9): 45–48.HU Zewen, HE Wei, YAO Degui, et al. Research of high-voltage power frequency electric field warning instrument[J]. Electrical Measurement &Instrumentation, 2009, 46(9): 45–48. [12] 谭毓苗. 非接触式高压直流验电器的研究与实现[D]. [硕士论文], 重庆理工大学, 2018.TAN Yumiao. Research and implementation of non-contact high voltage DC electroscope[D]. [Master dissertation], Chongqing University of Technology, 2018. [13] HORTON R, HALPIN M, and WALLACE K. Induced voltage in parallel transmission lines caused by electric field induction[C]. 2006 IEEE 11th International Conference on Transmission & Distribution Construction, Operation and Live-Line Maintenance, Albuquerque, USA, 2006: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/TDCLLM.2006.340720. [14] TSANG K M and CHAN W L. Dual capacitive sensors for non-contact AC voltage measurement[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2011, 167(2): 261–266. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2011.02.019 [15] ZHANG Xuemin, ZHANG Peng, SHI Yuqing, et al. Hardware design of non-contact voltage detector based on STM32 microcontroller[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 768: 062036. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/768/6/062036 [16] ZHU Jianjun, LEI Xinglie, SU Ziming, et al. Study of non-contact voltage detector of 1000 kV UHV AC based on MEMS electric field sensor[J]. MATEC Web of Conferences, 2018, 160: 02001. doi: 10.1051/matecconf/201816002001 [17] 仝杰, 雷煜卿, 刘国华, 等. 微型电场传感器在工频电场测量中的应用研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(12): 3036–3041. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180217TONG Jie, LEI Yuqing, LIU Guohua, et al. Power-frequency electric field measurement using a micromachined electric field sensor[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(12): 3036–3041. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180217 [18] ZHANG Zhanlong, LI Lin, XIE Xuemei, et al. Optimization design and research character of the passive electric field sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2014, 14(2): 508–513. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2013.2284201 [19] 陈国文. 球形二维工频电场测量系统研究[D]. [硕士论文], 华北电力大学, 2012.CHEN Guowen. Research on two-dimensional spherical power frequency electric field measurement system[D]. [Master dissertation], North China Electric Power University, 2012. [20] 毕德显. 电磁场理论[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 1985.BI Dexian. Electromagnetic Field Theory[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 1985. [21] 杨文翰, 吕英华. 用模拟电荷法求解高压输电线附近电磁场[J]. 电网技术, 2008, 32(2): 47–50, 55.YANG Wenhan and LÜ Yinghua. Application of emulation charge method in calculation of electromagnetic environment near to HV transmission lines[J]. Power System Technology, 2008, 32(2): 47–50, 55. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
