Image Segmentation Algorithm Based on Context Fuzzy C-Means Clustering
-
摘要: 像素间的上下文相关信息对图像分割算法的抗噪性和准确性具有重要意义,现有的模糊C均值(FCM)聚类算法对此缺乏充分考虑。该文基于对空间上下文的可靠性度量,提出一种模糊C均值聚类算法(RSFCM)应用于图像分割:通过对空间上下文有效建模来提高聚类算法的抗噪声干扰性能,并研究了一种新的可靠性模糊度量指标,使聚类算法能更好地平衡细节保留和去噪,从而获得更加准确的分割结果。实验选取人工合成图像、交通标志图像和遥感图像3类数据测试聚类算法性能,结果表明,RSFCM在图像分割过程中能有效地抑制椒盐噪声和高斯噪声引起的类内异构及类间同构问题,能提高图像的像素可分性,并有效地保留了图像的边缘细节。Abstract: The correlation information between pixels is of great significance for image segmentation. The existing Fuzzy C-Means (FCM) clustering algorithm lacks sufficient consideration for it. Based on the reliability measure of spatial context, this paper proposes a Reliability-based Spatial context Fuzzy C-Means (RSFCM) clustering algorithm: The clustering algorithm anti-noise performance is improved by effectively modeling the spatial neighborhood; A new reliability fuzzy metric is proposed, which balances the relationship between detail retention and anti-noise, so that the clustering results are more accurate. A synthetic image, a traffic sign image and a remote sensing image are used to test the algorithms performance. The results show, compared with the existing FCM algorithm, RSFCM can effectively suppress heterogeneity of intra-class objects caused by Salt & Pepper noise and Gaussian noise for the image segmentation, improve pixels separability and preserve the edge details of the image greatly.
-
Key words:
- Image segmentation /
- Clustering /
- Fuzzy C-Means (FCM) /
- Spatial context
-
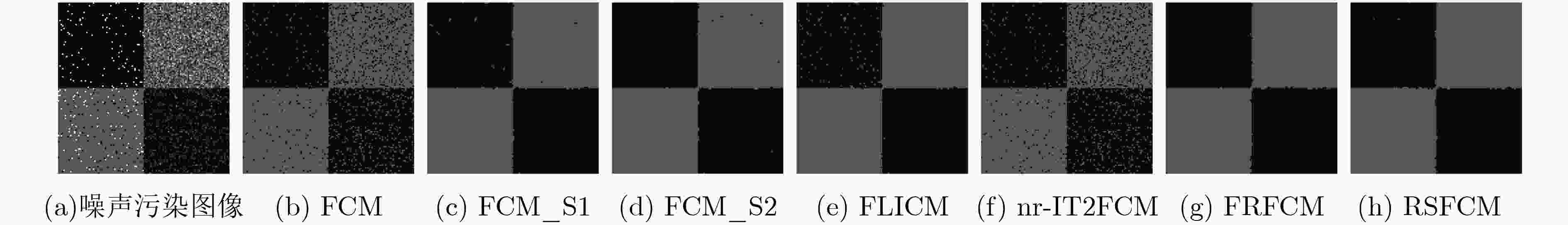
表 1 合成图像分割结果的PSNR比较(dB)
算法 FCM FCM_S1 FCM_S2 FLICM nr-IT2FCM FRFCM RSFCM PSNR 18.8293 25.8502 25.0842 24.6283 18.6673 24.2498 26.0099 表 2 不同噪声级别下合成图像分割结果的JS系数比较
算法 FCM FCM_S1 FCM_S2 FLICM nr-IT2FCM FRFCM RSFCM Gaussian 8% 74.517 96.436 35.773 96.820 74.011 83.179 97.015 Gaussian 10% 72.729 94.489 37.830 96.954 72.217 72.278 95.673 Gaussian 15% 68.671 90.356 38.300 89.435 68.427 70.465 91.817 Salt &Pepper 8% 95.599 98.627 49.780 97.333 95.599 58.044 99.237 Salt &Pepper 10% 94.519 97.882 96.478 96.289 94.519 85.925 98.743 Salt &Pepper 15% 92.609 96.619 49.689 94.763 92.609 74.500 97.882 表 3 交通标志图像分割结果的PSNR比较 (dB)
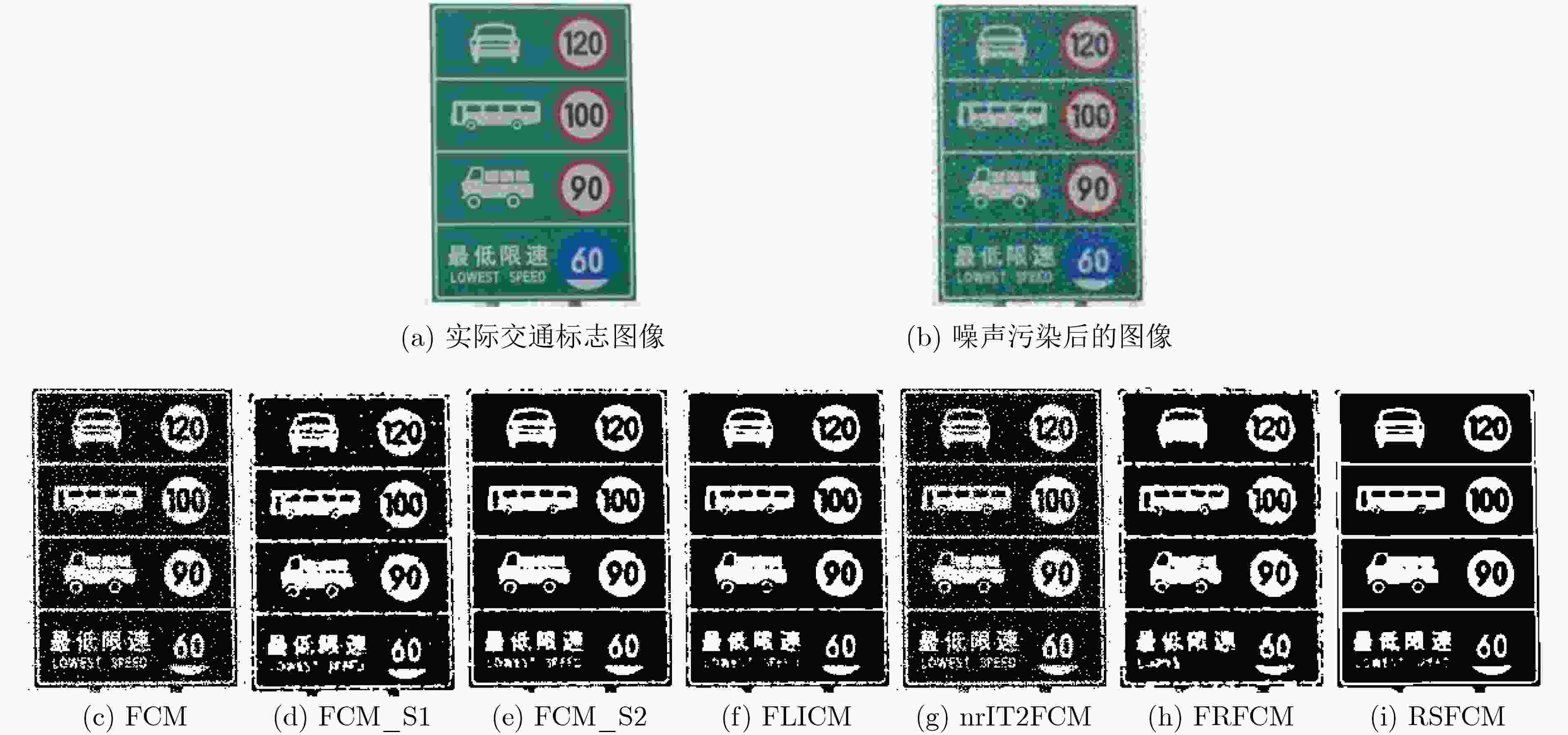
算法 FCM FCM_S1 FCM_S2 FLICM nr-IT2FCM FRFCM RSFCM PSNR 21.4062 27.7089 27.0842 24.6283 18.6752 24.2498 29.6100 表 4 遥感图像分割结果的OA(%)和Kappa系数比较
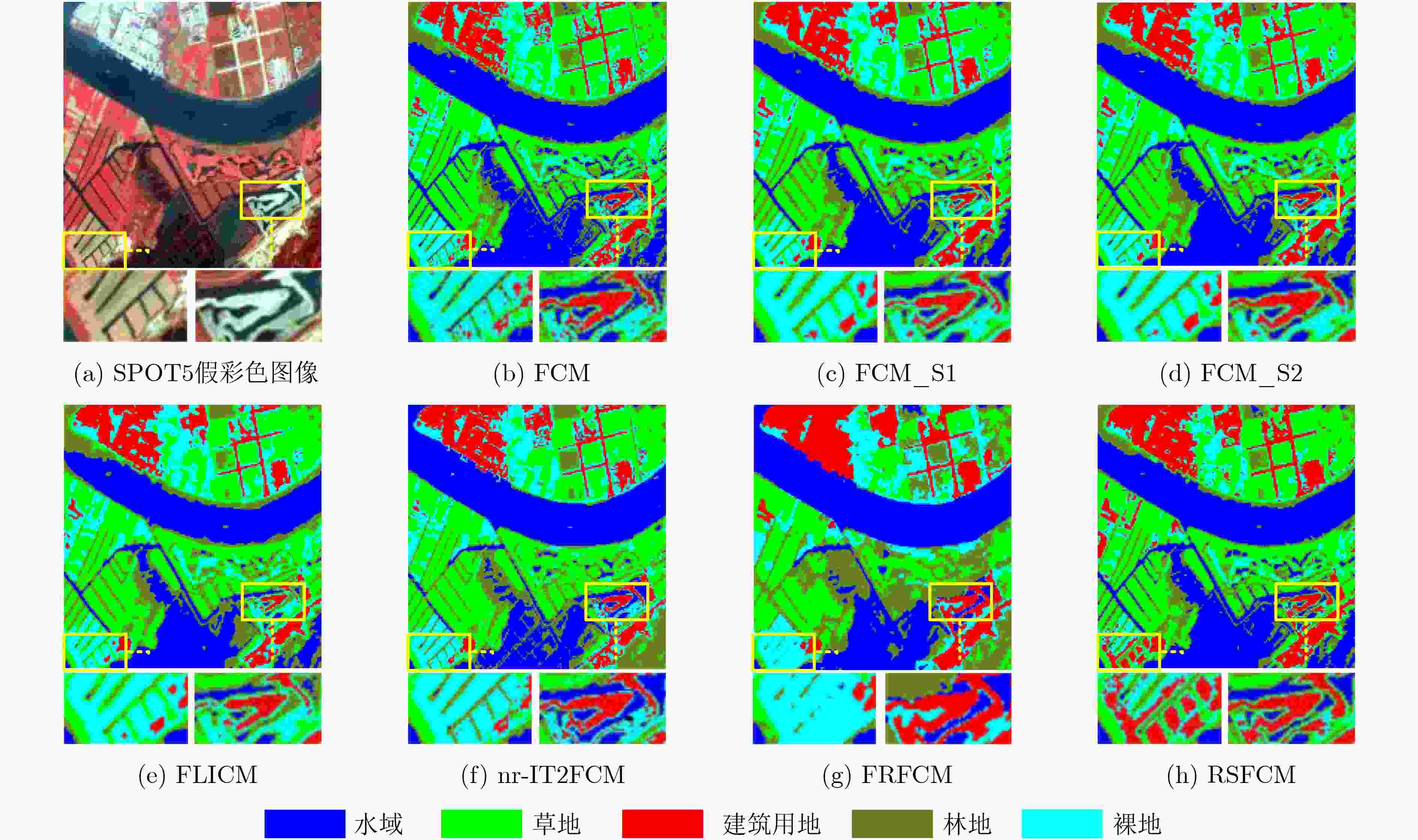
类别 算法 样本点 FCM FCM_S1 FCM_S2 FLICM nr-IT2FCM FRFCM RSFCM 水域 16029 95.63 96.56 96.45 92.76 91.15 94.78 97.61 草地 2216 96.79 97.29 97.83 97.96 98.28 58.39 97.79 林地 2449 62.07 72.02 68.31 62.18 43.98 34.46 67.95 裸地 1140 74.82 82.33 80.79 84.14 72.91 59.06 71.74 建筑工地 4333 69.91 72.79 72.63 70.92 72.79 84.35 84.47 OA 总体 87.44 89.78 89.32 86.35 83.52% 82.81 91.57 Kappa 总体 0.7884 0.8279 0.8201 0.7751 0.7263 0.7078 0.8562 -
[1] LU Zhenyu, QIU Yunan, and ZHAN Tianming. Neutrosophic C-means clustering with local information and noise distance-based kernel metric image segmentation[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2019, 58: 269–276. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2018.11.045 [2] SOOMRO S, MUNIR A, and CHOI K N. Fuzzy c-means clustering based active contour model driven by edge scaled region information[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2019, 120: 387–396. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2018.10.052 [3] 施伟锋, 卓金宝, 兰莹. 一种基于属性空间相似性的模糊聚类算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(11): 2722–2728. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180974SHI Weifeng, ZHUO Jinbao, and LAN Ying. A novel fuzzy clustering algorithm based on similarity of attribute space[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(11): 2722–2728. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180974 [4] 吴志勇, 丁香乾, 许晓伟, 等. 基于深度学习和模糊C均值的心电信号分类方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(10): 1913–1920. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170417WU Zhiyong, DING Xiangqian, XU Xiaowei, et al. A method for ECG classification using deep learning and fuzzy C-means[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(10): 1913–1920. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170417 [5] BEZDEK J C. Pattern Recognition with Fuzzy Objective Function Algorithms[M]. Boston: Springer, 1981: 203–239. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0450-1. [6] ZHANG Tong, SU Guoxi, QING Chunmei, et al. Hierarchical lifelong learning by sharing representations and integrating hypothesis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(12): 1004–1014. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2018.2884996 [7] SINGH C and BALA A. A local Zernike moment-based unbiased nonlocal means fuzzy C-Means algorithm for segmentation of brain magnetic resonance images[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2019, 118: 625–639. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2018.10.023 [8] 费博雯, 邱云飞, 刘万军, 等. 距离决策下的模糊聚类集成模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(8): 1895–1903. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171065FEI Bowen, QIU Yunfei, LIU Wanjun, et al. Fuzzy clustering ensemble model based on distance decision[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(8): 1895–1903. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171065 [9] AHMED M N, YAMANY S M, MOHAMED N, et al. A modified fuzzy c-means algorithm for bias field estimation and segmentation of MRI data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2002, 21(3): 193–199. doi: 10.1109/42.996338 [10] CHEN Songcan and ZHANG Daoqiang. Robust image segmentation using FCM with spatial constraints based on new kernel-induced distance measure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics) , 2004, 34(4): 1907–1916. doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2004.831165 [11] ZHANG Hua, WANG Qunming, SHI Wenzhong, et al. A novel adaptive fuzzy local information C-means clustering algorithm for remotely sensed imagery classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(9): 5057–5068. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2702061 [12] KRINIDIS S and CHATZIS V. A robust fuzzy local information C-means clustering algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(5): 1328–1337. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2040763 [13] LEI Tao, JIA Xiaohong, ZHANG Yanning, et al. Significantly fast and robust fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm based on morphological reconstruction and membership filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(5): 3027–3041. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2796074 [14] XING Haihua, HE Hui, HU Dan, et al. An interval Type-2 fuzzy sets generation method for remote sensing imagery classification[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2019, 133: 104287. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2019.06.008 [15] CHEN C L P, ZHANG Tong, CHEN Long, et al. I-ching divination evolutionary algorithm and its convergence analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(1): 2–13. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2512286 [16] ZHANG Tong, CHEN C L P, CHEN Long, et al. Design of highly nonlinear substitution boxes based on I-ching operators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(12): 3349–3358. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2846186 [17] NEWTON I. Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy[M]. London: Benjamin Motte Publishing, 1687. [18] 徐超, 詹天明, 孔令成, 等. 基于学生t分布的鲁棒分层模糊算法及其在图像分割中的应用[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(7): 1695–1700. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.07.020XU Chao, ZHAN Tianming, KONG Lingcheng, et al. A robust hierarchical fuzzy algorithm with student’s t-distribution for image segmentation application[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(7): 1695–1700. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.07.020 [19] 赵凤, 张咪咪, 刘汉强. 区域信息驱动的多目标进化半监督模糊聚类图像分割算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1106–1113. doi: 10.12000/JRIT180605ZHAO Feng, ZHANG Mimi, and LIU Hanqiang. Multi-objective evolutionary semi-supervised fuzzy clustering image segmentation motivated by region information[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1106–1113. doi: 10.12000/JRIT180605 [20] CAO Changyu, ZHENG Jiachun, HUANG Yiqi, et al. Investigation of a promoted you only look once algorithm and its application in traffic flow monitoring[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(17): 3619. doi: 10.3390/app9173619 [21] ZHANG Lefei, ZHANG Liangpei, DU Bo, et al. Hyperspectral image unsupervised classification by robust manifold matrix factorization[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 485: 154–169. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.02.008 -





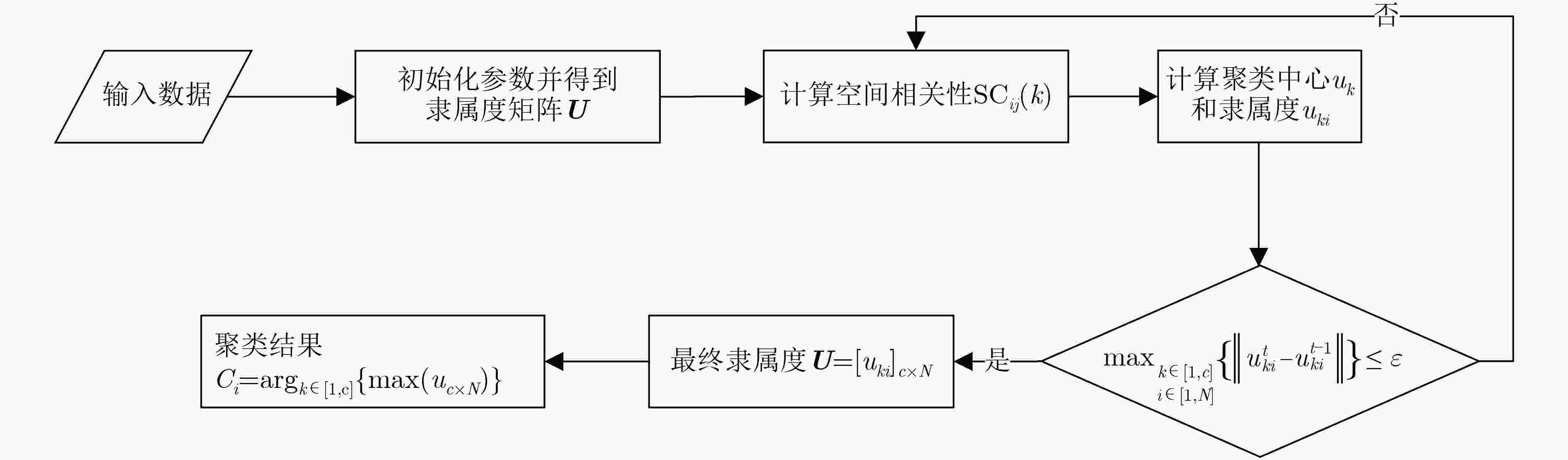
 下载:
下载:
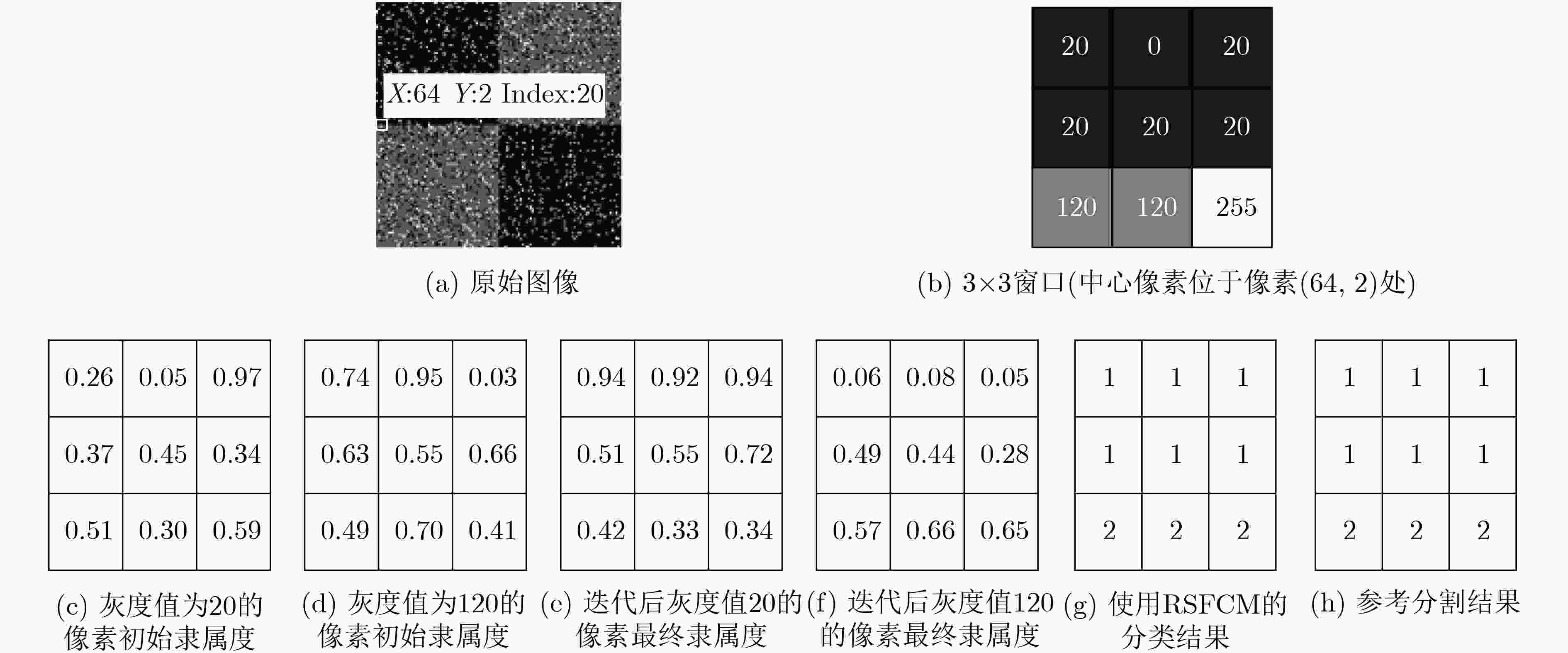
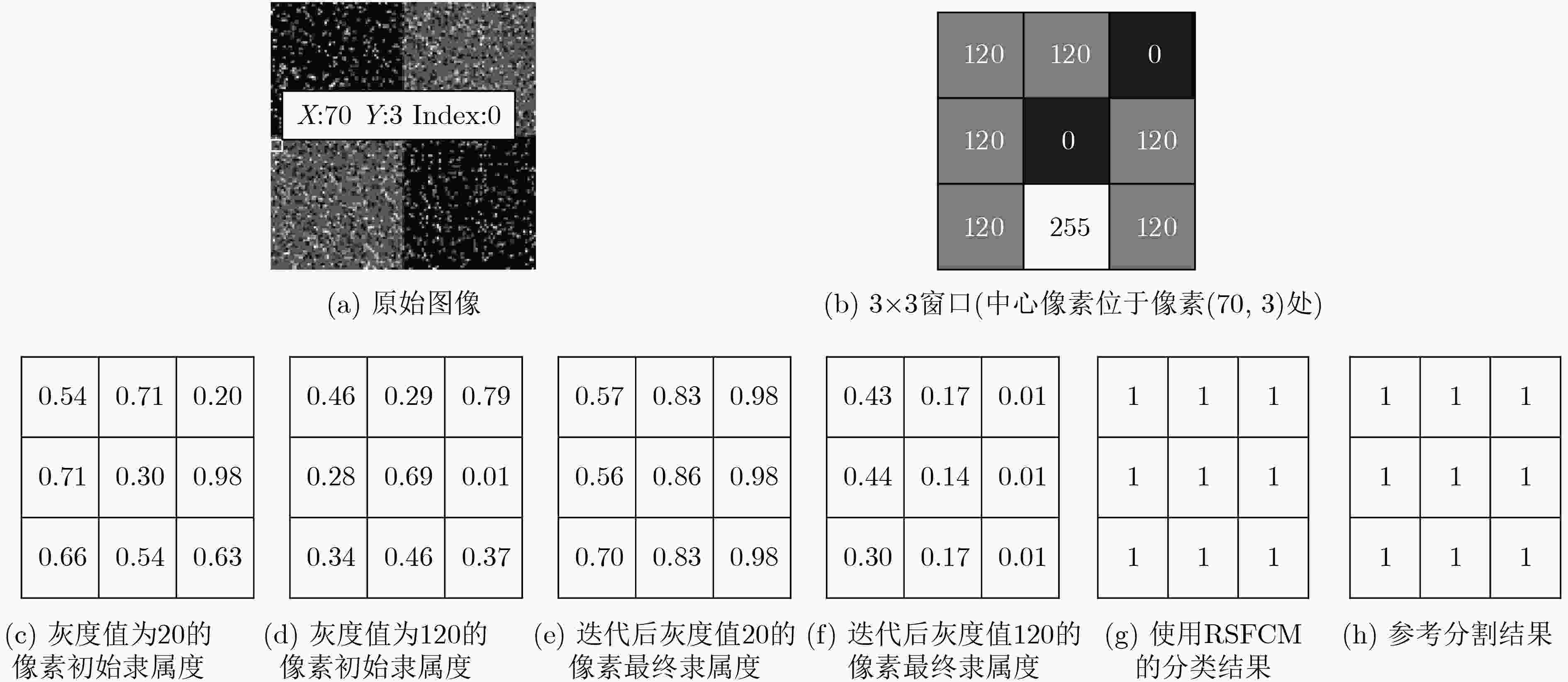


 下载:
下载:
