Research on Resource Allocation and Offloading Decision Based on Multi-agent Architecture in Cloud-fog Hybrid Network
-
摘要: 针对D2D辅助的云雾混合架构下资源分配及任务卸载决策优化问题,该文提出一种基于多智能体架构深度强化学习的资源分配及卸载决策算法。首先,该算法考虑激励约束、能量约束以及网络资源约束,联合优化无线资源分配、计算资源分配以及卸载决策,建立了最大化系统总用户体验质量(QoE)的随机优化模型,并进一步将其转化为MDP问题。其次,该算法将原MDP问题进行因式分解,并建立马尔可夫博弈模型。然后,基于行动者-评判家(AC)算法提出一种集中式训练、分布式执行机制。在集中式训练过程中,多智能体通过协作获取全局信息,实现资源分配及任务卸载决策策略优化,在训练过程结束后,各智能体独立地根据当前系统状态及策略进行资源分配及任务卸载。最后,仿真结果表明,该算法可以有效提升用户QoE,并降低了时延及能耗。Abstract: To optimize strategy of resource allocation and task offloading decision on D2D-assisted cloud-fog architecture, a joint resource allocation and offloading decision algorithm based on a multi-agent architecture deep reinforcement learning method is proposed. Firstly, considering incentive constraints, energy constraints, and network resource constraints, the algorithm jointly optimizes wireless resource allocation, computing resource allocation, and offloading decisions. Further, the algorithm establishes a stochastic optimization model that maximizes the total user Quality of Experience (QoE) of the system, and transfers it into an MDP problem. Secondly, the algorithm factorizes the original MDP problem and models a Markov game. Then, a centralized training and distributed execution mechanism based on the Actor-Critic (AC) algorithm is proposed. In the centralized training process, multi-agents obtains the global information through cooperation to optimize the resource allocation and task offloading decision strategies. After the training process, each agent performs independently resource allocation and task offloading based on the current system state and strategy. Finally, the simulation results demonstrate that the algorithm can effectively improve user QoE, and reduce delay and energy consumption.
-
Key words:
- Cloud-fog hybrid network /
- D2D /
- Multi-agent /
- Resource allocation /
- Computation offloading
-
表 1 仿真参数
参数 数值 参数 数值 信道带宽B 1 MHz 噪声功率 –100 dBm 路径损耗模型 128.1+37.6lg (d) ${\kappa _{{K_{n,m}}}},\forall {K_{n,m}} \in {{\boldsymbol{N}}_m}$ 10–28 Watt×s2 cycles3 子信道数量 10 ${R_m}(t),\forall m \in {\boldsymbol{M}}$ 1 Mbps $f_{{K_{n,m}}}^l,\forall {K_{n,m}} \in {{\boldsymbol{N}}_m}$ Uniform[0.5–1.5]×109 CPU cycles/s $f_{{K_{n,m}}}^{{C}},\forall {K_{n,m}} \in {{\boldsymbol{N}}_m}$ 4 GHz ${D_{{K_{n,m}}}}(t),\forall {K_{n,m}} \in {{\boldsymbol{N}}_m}$ Uniform[0.1–1] Mbit $\xi _{{K_{n,m}}}^c$, $\zeta _{{K_{n,m}}}^c$ 0.5, 0.01 ${C_{{K_{n,m}}}}(t),\forall {K_{n,m}} \in {{\boldsymbol{N}}_m}$ Uniform[500–1500] cycles/bit $E_{{K_{n,m}}}^b$ 0.25 J 最大用户传输功率 300 mW ${f_{m,\max }}$ 2 GHz -
[1] ARJOUNE Y and FARUQUE S. Artificial intelligence for 5G wireless systems: Opportunities, challenges, and future research direction[C]. 2020 10th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference(CCWC), Las Vegas, USA, 2020: 1023–1028. doi: 10.1109/CCWC47524.2020.9031117. [2] LI Zhuo, ZHOU Xu, and QIN Yifang. A survey of mobile edge computing in the industrial internet[C]. The 7th International Conference on Information, Communication and Networks (ICICN), Macao, China, 2019: 94–98. doi: 10.1109/ICICN.2019.8834959. [3] SHAH-MANSOURI H and WONG V W S. Hierarchical fog-cloud computing for IoT systems: A computation offloading game[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(4): 3246–3257. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2838022 [4] HE Yinghui, REN Jinke, Yu Guanding, et al. D2D communications meet mobile edge computing for enhanced computation capacity in cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(3): 1750–1763. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2896999 [5] YI Changyan, HUANG Shiwei, and CAI Jun. Joint resource allocation for device-to-device communication assisted fog computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2021, 20(3): 1076–1091. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2019.2952354 [6] DINH T Q, LA Q D, QUEK T Q S, et al. Learning for computation offloading in mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2018, 66(12): 6353–6367. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2866572 [7] LIU Yiming, YU F R, LI Xi, et al. Distributed resource allocation and computation offloading in fog and cloud networks with non-orthogonal multiple access[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(12): 12137–12151. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2872912 [8] 向旭东. 云计算性能与节能的动态优化研究[D]. [博士论文], 北京科技大学, 2015.XIANG Xudong. Dynamic optimization of performance and energy consumption in cloud computing[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2015. [9] MIN Minghui, XIAO Liang, CHEN Ye, et al. Learning-based computation offloading for IoT devices with energy harvesting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(2): 1930–1941. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2890685 [10] LI Zheng and GUO Caili. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning based spectrum allocation for D2D underlay communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(2): 1828–1840. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2961405 [11] ZHONG Chen, GURSOY M C, and VELIPASALAR S. Deep multi-agent reinforcement learning based cooperative edge caching in wireless networks[C]. The ICC 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Shanghai, China, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2019.8762084. [12] NGUYEN K K, DUONG T Q, VIEN N A, et al. Distributed deep deterministic policy gradient for power allocation control in D2D-based V2V communications[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 164533–164543. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2952411 [13] DU Jianbo, ZHAO Liqiang, FENG Jie, et al. Computation offloading and resource allocation in mixed fog/cloud computing systems with min-max fairness guarantee[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2018, 66(4): 1594–1608. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2017.2787700 [14] AMIRI R., ALMASI M A, ANDREWS J G, et al. Reinforcement learning for self organization and power control of two-tier heterogeneous networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(8): 3933–3947. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2919611 [15] LOWE R, WU Yi, TAMAR A, et al. Multi-agent actor-critic for mixed cooperative-competitive environments[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6379–6390. [16] YANG Bo, SHEN Yanyan, HAN Qiaoni, et al. Energy-efficient resource allocation for time-varying OFDMA relay systems with hybrid energy supplies[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2018, 12(1): 702–713. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2016.2551319 [17] MAO Yuyi, YOU Changsheng, ZHANG Jun, et al. A survey on mobile edge computing: The communication perspective[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(4): 2322–2358. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2745201 -






 下载:
下载:
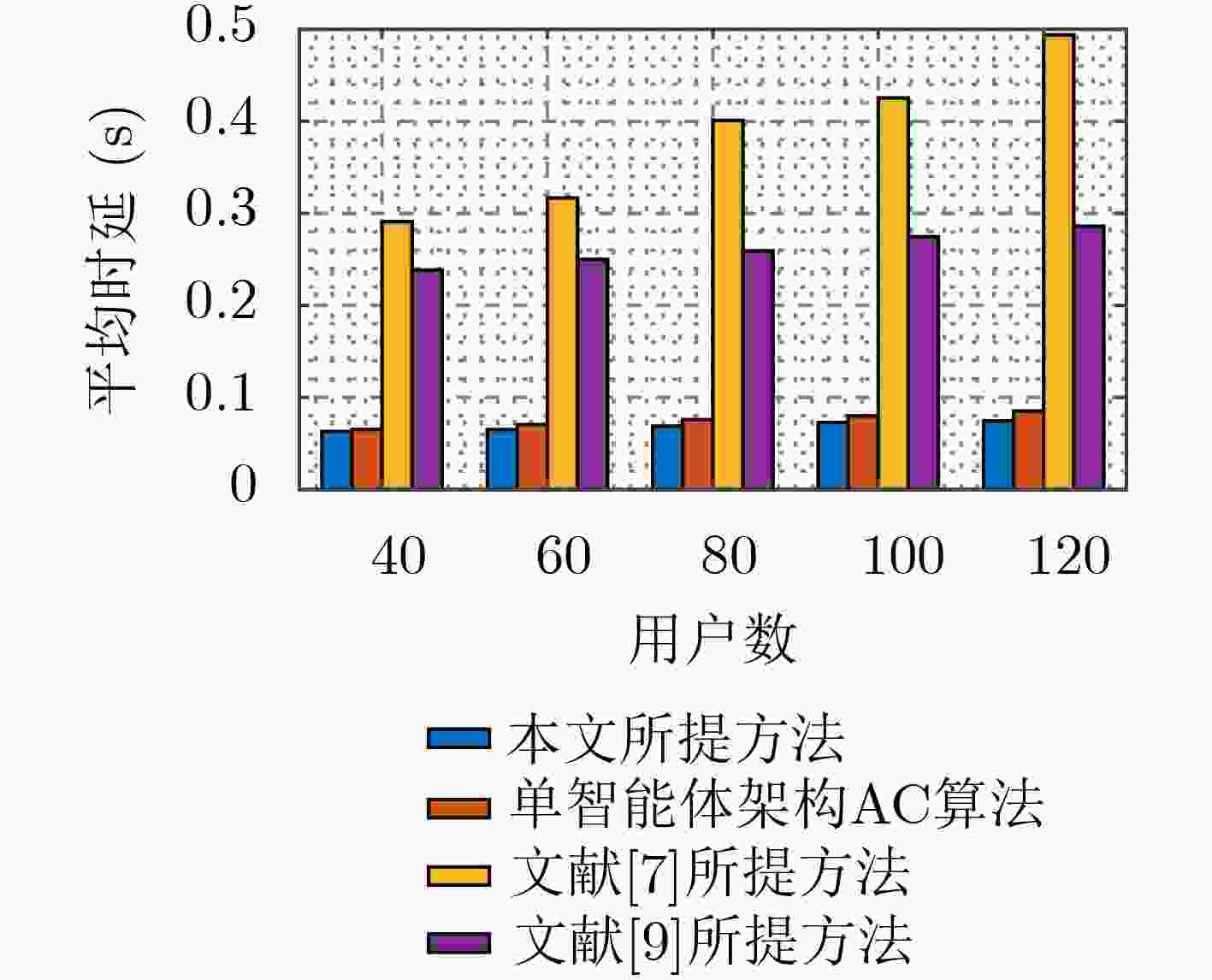
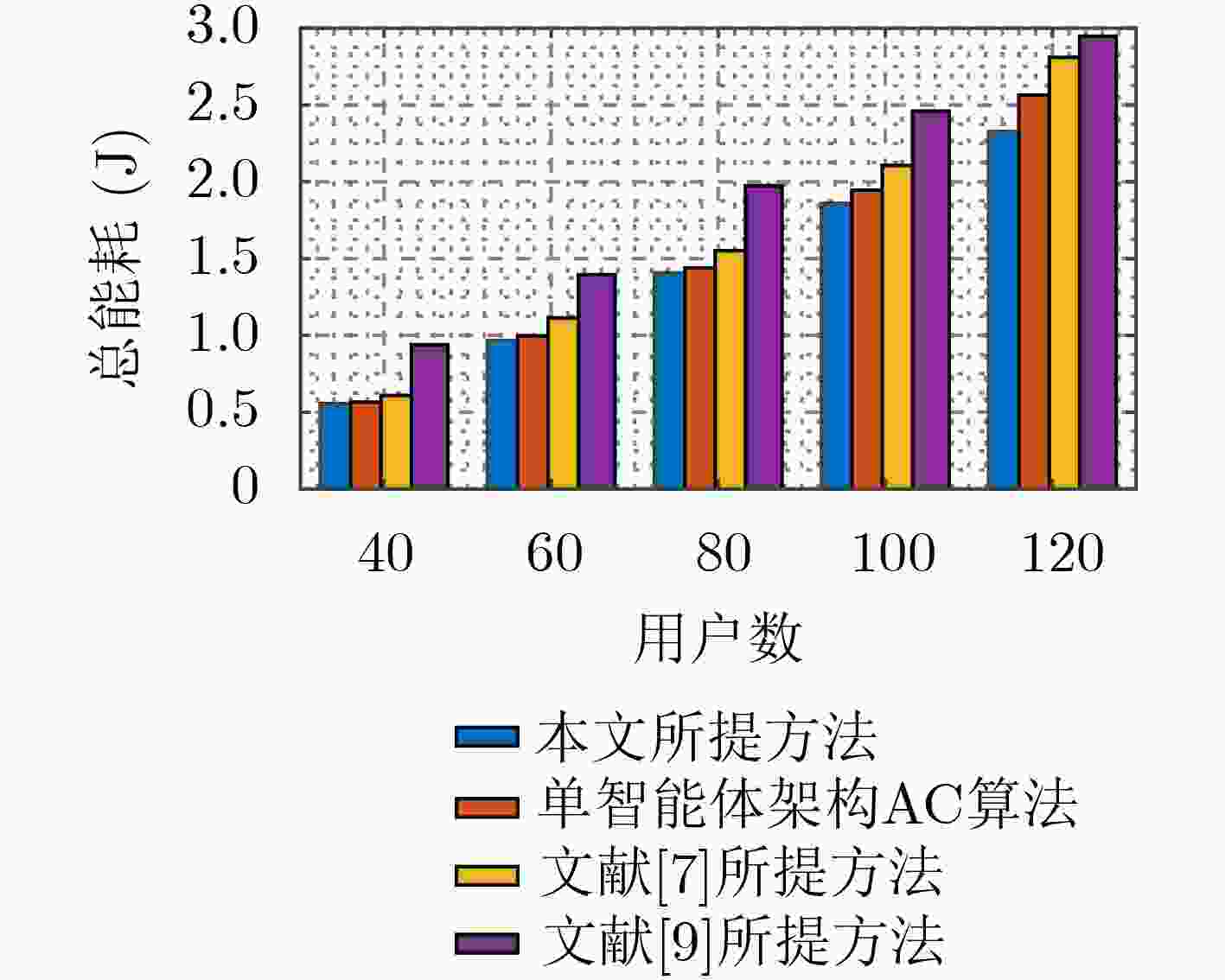
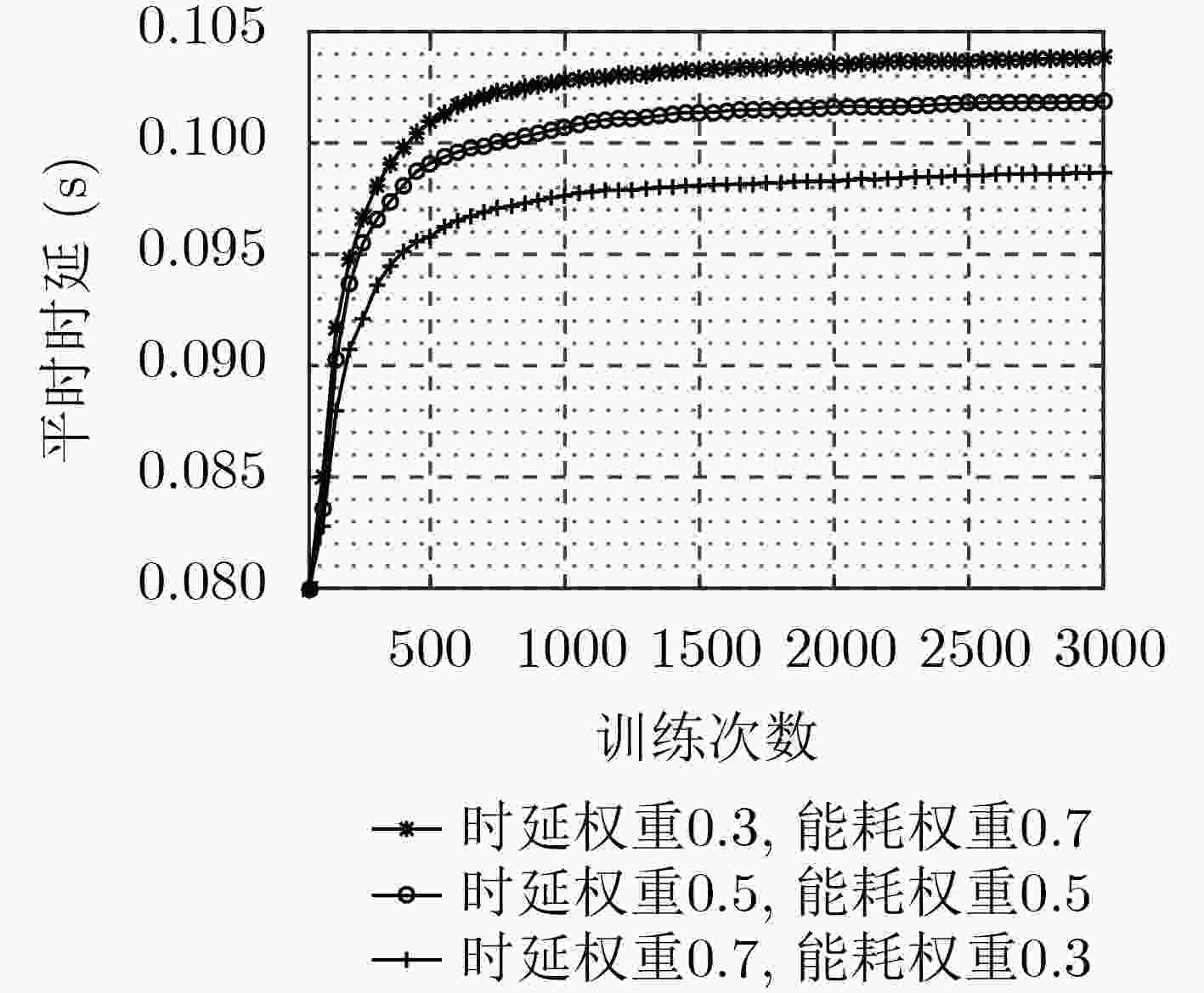
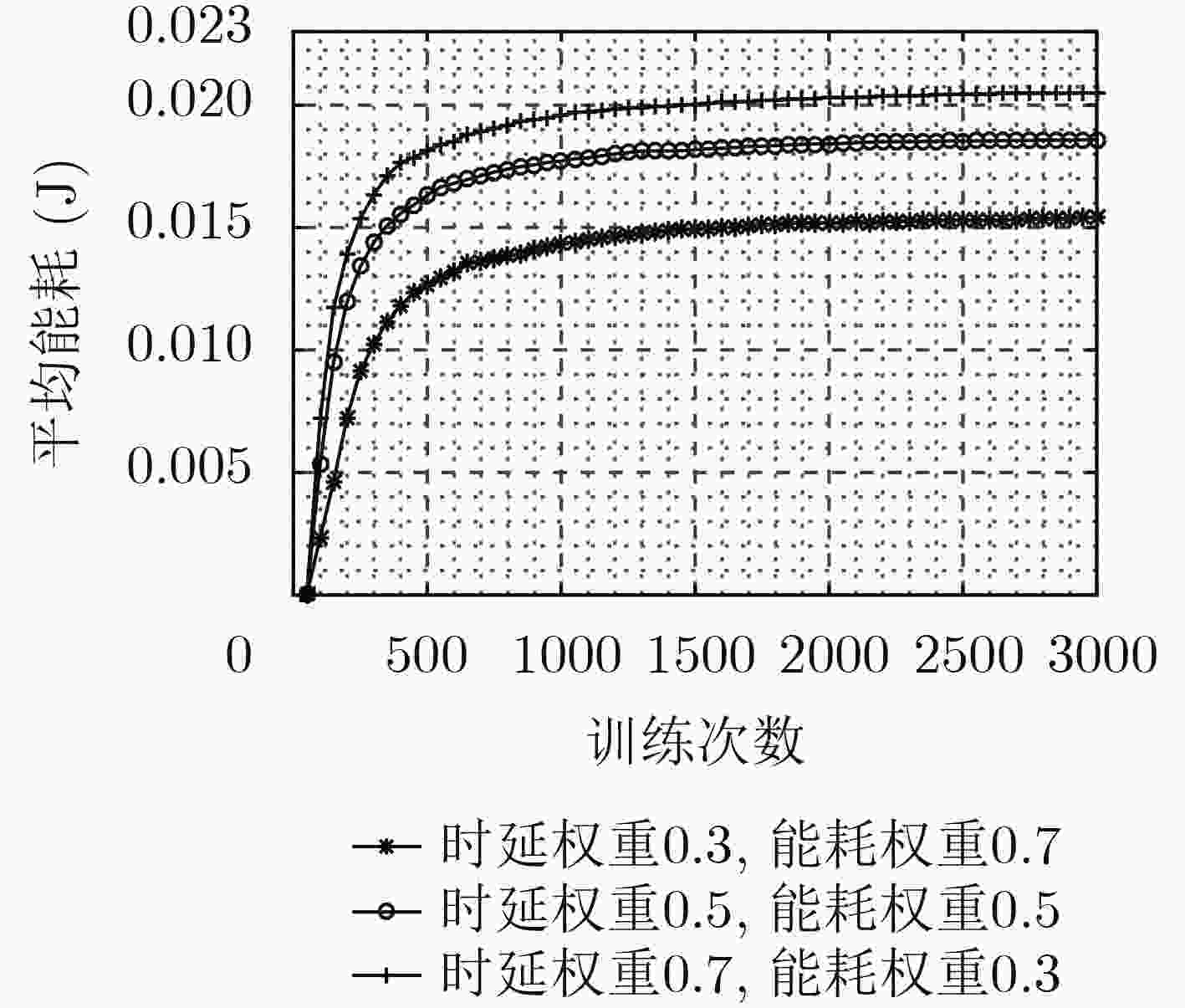


 下载:
下载:
