Object Detection and Tracking of Unmanned Surface Vehicles Based on Spatial-temporal Information Fusion
-
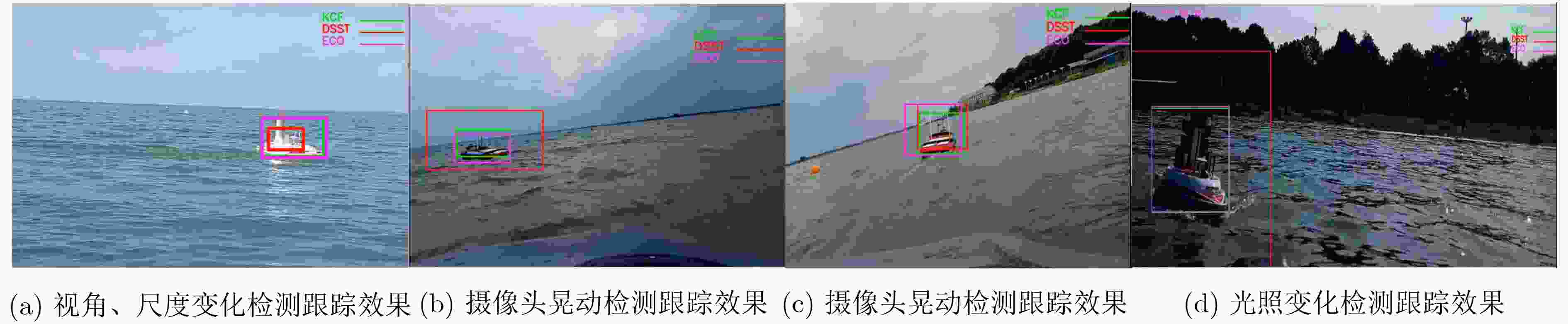
摘要: 在无人艇(USV)的导航、避障等多种任务中,目标检测与跟踪都十分重要,但水面环境复杂,存在目标尺度变化、遮挡、光照变化以及摄像头抖动等诸多问题。该文提出基于时空信息融合的无人艇水面视觉目标检测跟踪,在空间上利用深度学习检测,提取单帧深度语义特征,在时间上利用相关滤波跟踪,计算帧间方向梯度特征相关性,通过特征对比将时空信息进行融合,实现了持续稳定地对水面目标进行检测与跟踪,兼顾了实时性和鲁棒性。实验结果表明,该算法平均检测速度和精度相对较高,在检测跟踪速度为15 fps情况下,检测跟踪精确度为0.83。Abstract: Object detection and tracking is essential in the navigation, obstacle avoidance and other tasks of Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USV). However, the environment on the water is complex, and there are many problems such as object scale variation, occlusion, illumination variation and camera shaking, etc. This paper proposes the visual object detection and tracking of USV based on spatial-temporal information fusion. Deep learning detection in space is used to extract single-frame depth semantic features and correlation filter tracking in time is used to calculate the correlation of oriented gradient feature between frames. Temporal and spatial information through feature comparison are combined to achieve continuous and stable object detection and tracking with strong robustness at real-time. The experiments results demonstrate that the average detection and tracking accuracy is 0.83 with the average running speed of 15 fps, which illustrates the accuracy is improved and the speed is high.
-
表 1 测试数据集和检测跟踪结果(IOU@0.6)
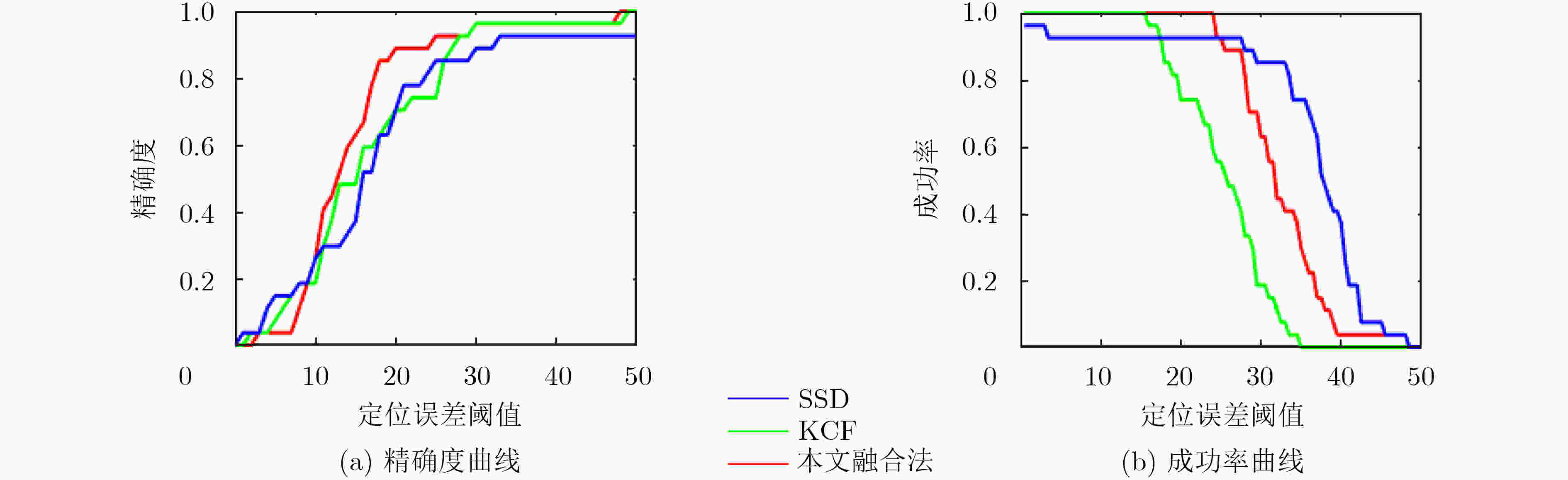
视频 主要环境影响 成功率 速度(FPS) 视频1 视角、尺度变化 0.88 18.52 视频2 遮挡、尺度变化 0.61 15.01 视频3 晃动 0.80 16.60 视频4 晃动 0.95 12.50 视频5 光照 0.63 13.19 表 2 分别使用KCF、SSD和融合算法的结果比较(视频2)
方法 KCF SSD 融合算法 精确度 0.30 0.49 0.69 成功率 0.29 0.45 0.61 速度 (fps) 19.60 0.74 15.01 表 3 分别使用KCF, SSD和融合算法的结果比较(视频5)
方法 KCF SSD 融合算法 精确度 0.97 0.69 0.94 成功率 0.25 0.72 0.95 速度 (FPS) 15.34 0.77 13.19 表 4 单一SSD, YOLOv3, KCF, DSST和ECO的算法成功率对比(IOU@0.6)
类别 检测算法 跟踪算法 融合算法 方法 SSD YOLOv3 KCF DSST ECO SSD+KCF 成功率 0.56 0.30 0.29 0.19 0.29 0.77 速度 (fps) 0.77 0.90 15.60 11.60 4.01 15.00 表 5 SSD与KCF, DSST和ECO融合算法的成功率对比
方法 SSD+DSST SSD+ECO SSD+KCF 精确度 0.46 0.71 0.77 速度 (FPS) 11.00 3.90 15.00 -
[1] 李寰宇, 毕笃彦, 杨源, 等. 基于深度特征表达与学习的视觉跟踪算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(9): 2033–2039. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150031LI Huanyu, BI Duyan, YANG Yuan, et al. Research on visual tracking algorithm based on deep feature expression and learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(9): 2033–2039. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150031 [2] WANG Bo, SU Yumin, and WAN Lei. A sea-sky line detection method for unmanned surface vehicles based on gradient saliency[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(4): 543. doi: 10.3390/s16040543 [3] KRISTAN M, KENK V S, KOVAČIČ S, et al. Fast image-based obstacle detection from unmanned surface vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(3): 641–654. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2412251 [4] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]. International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Istanbul, Turkey, 2015: 91–99. [5] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. doi: 10.1109/Cvpr.2016.91. [6] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[C]. 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2. [7] QIN Yueming and ZHANG Xiuzhi. Robust obstacle detection for unmanned surface vehicles[C]. MIPPR 2017: Remote Sensing Image Processing, Geographic Information Systems, and Other Applications, Xiangyang, China, 2018: 10611E1–10611E6. doi: 10.1117/12.2285607. [8] YANG Jian, XIAO Yang, FANG Zhiwen, et al. An object detection and tracking system for unmanned surface vehicles[C]. Target and Background Signatures III, Warsaw, Poland, 2017: 104320R1–104320R8. doi: 10.1117/12.2278220. [9] COMANICIU D, RAMESH V, and MEER P. Real-time tracking of non-rigid objects using mean shift[C]. The 2000 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Hilton Head, USA, 2000: 142–149. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2000.854761. [10] LI Yongmin. On incremental and robust subspace learning[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2004, 37(7): 1509–1518. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2003.11.010 [11] XUE Mei and LING Haibin. Robust visual tracking using ℓ1 minimization[C]. The 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 2009: 1436–1443. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2009.5459292. [12] OZA N C. Online bagging and boosting[C]. The 2005 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Waikoloa, USA, 2005: 2340–2345. doi: 10.1109/ICSMC.2005.1571498. [13] HARE S, SAFFARI A, and TORR P H S. Struck: Structured output tracking with kernels[C]. The 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 263–270. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126251. [14] BREIMAN L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5–32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 [15] 侯志强, 王帅, 廖秀峰, 等. 基于样本质量估计的空间正则化自适应相关滤波视觉跟踪[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(8): 1983–1991. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180921HOU Zhiqiang, WANG Shuai, LIAO Xiufeng, et al. Adaptive regularized correlation filters for visual tracking based on sample quality estimation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(8): 1983–1991. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180921 [16] BOLME D S, BEVERIDGE J R, DRAPER B A, et al. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters[C]. 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 2544–2550. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2010.5539960. [17] HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels[C]. Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012: 702–715. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-33765-9_50. [18] LI Yang and ZHU Jianke. A scale adaptive kernel correlation filter tracker with feature integration[C]. 2014 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops, Zurich, 2014: 254–265. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-16181-5_18. [19] DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, KHAN F S, et al. Accurate scale estimation for robust visual tracking[C]. British Machine Vision Conference, Nottingham, UK, 2014: 65.1–65.11. doi: 10.5244/C.28.65. [20] 王鹏, 孙梦宇, 王海燕, 等. 一种目标响应自适应的通道可靠性跟踪算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(8): 1950–1958. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190569WANG Peng, SUN Mengyu, WANG Haiyan, et al. An object tracking algorithm with channel reliability and target response adaptation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(8): 1950–1958. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190569 [21] HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 583–596. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2014.2345390 -





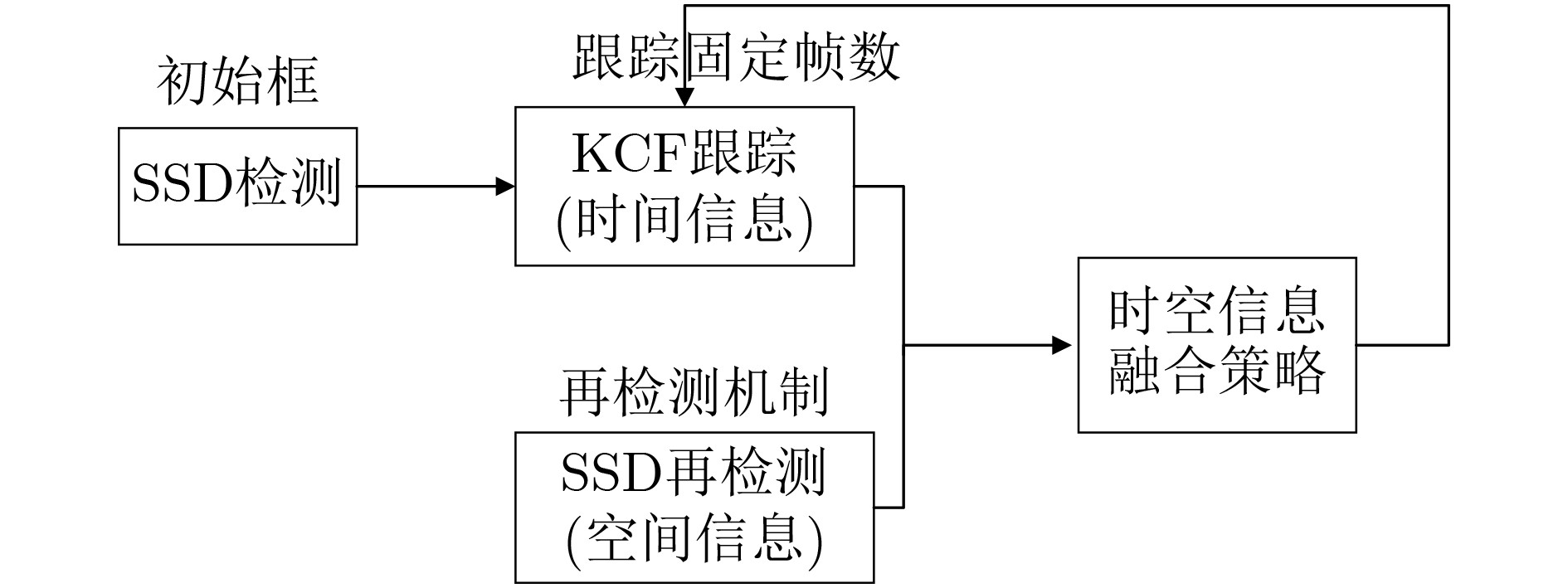
 下载:
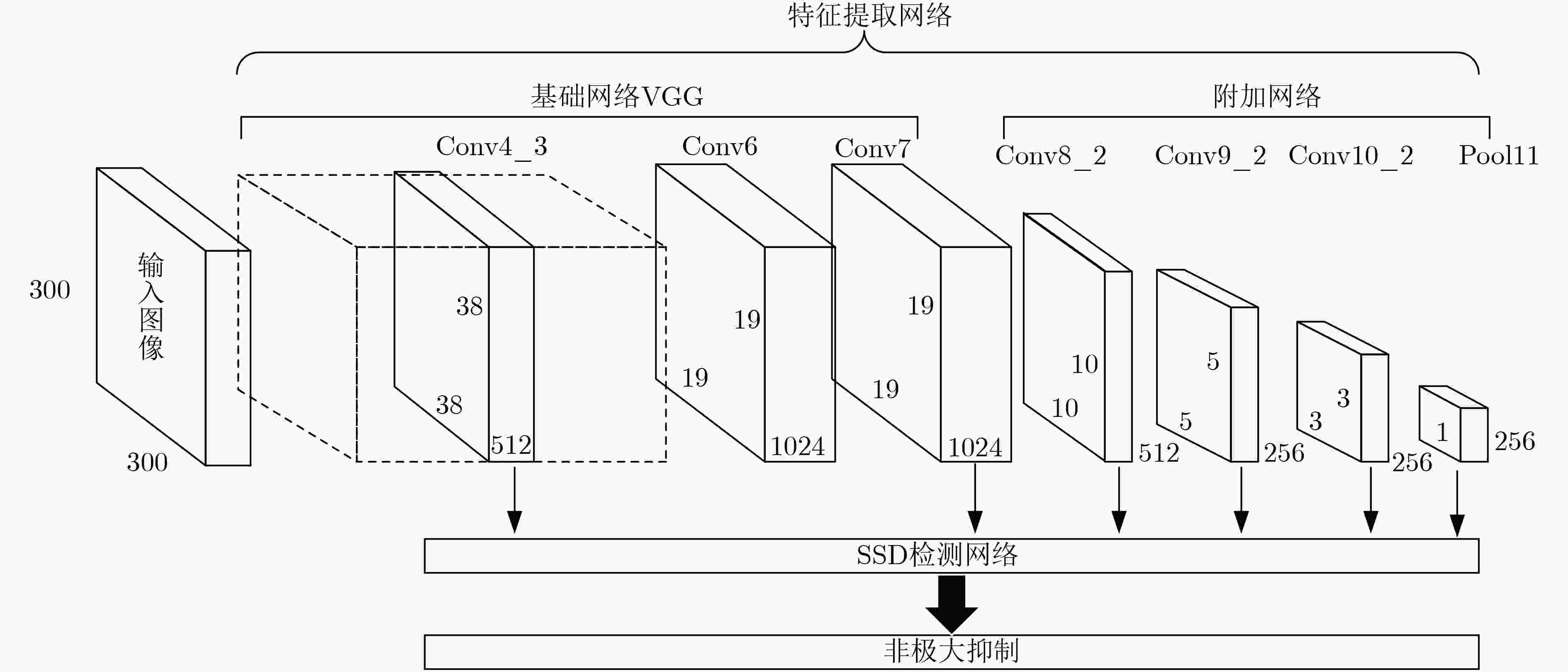
下载:
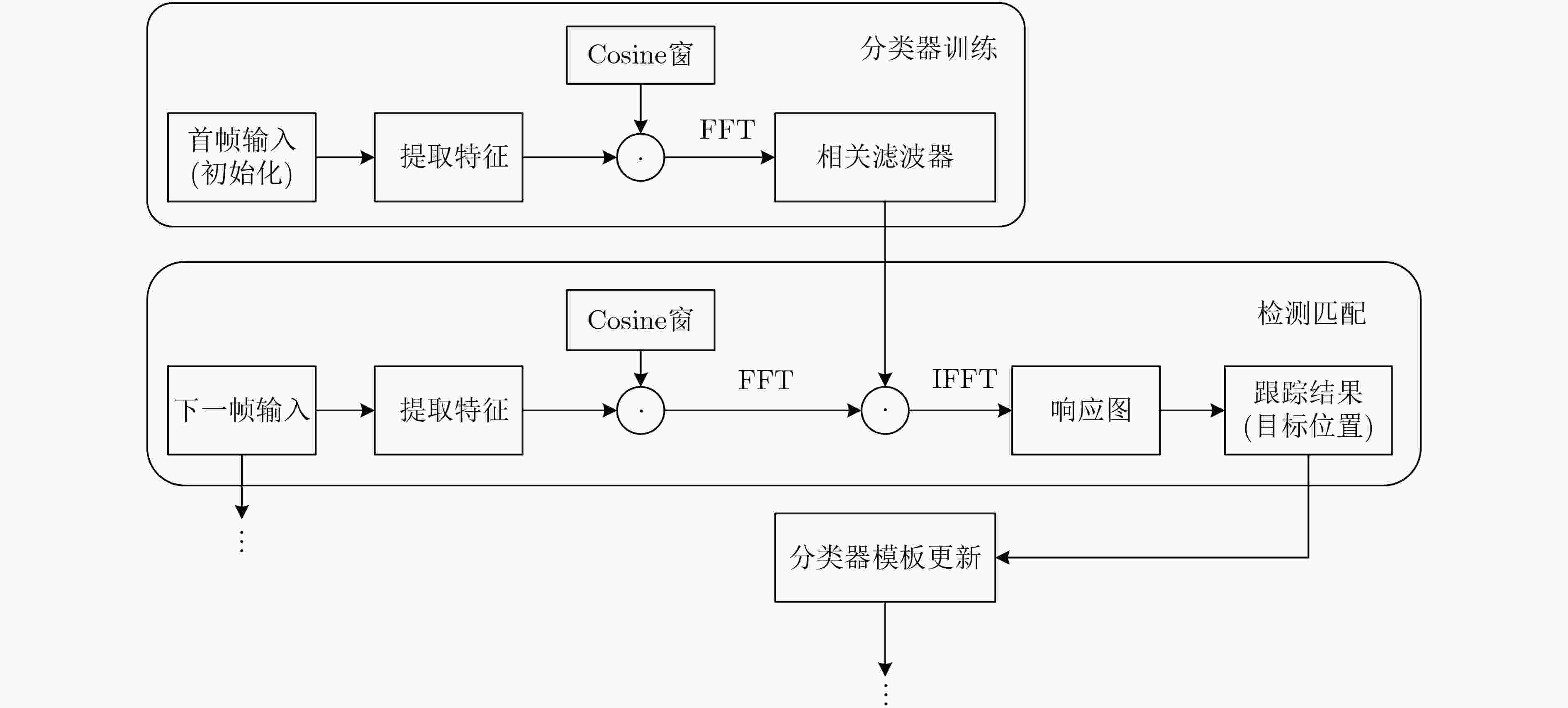




 下载:
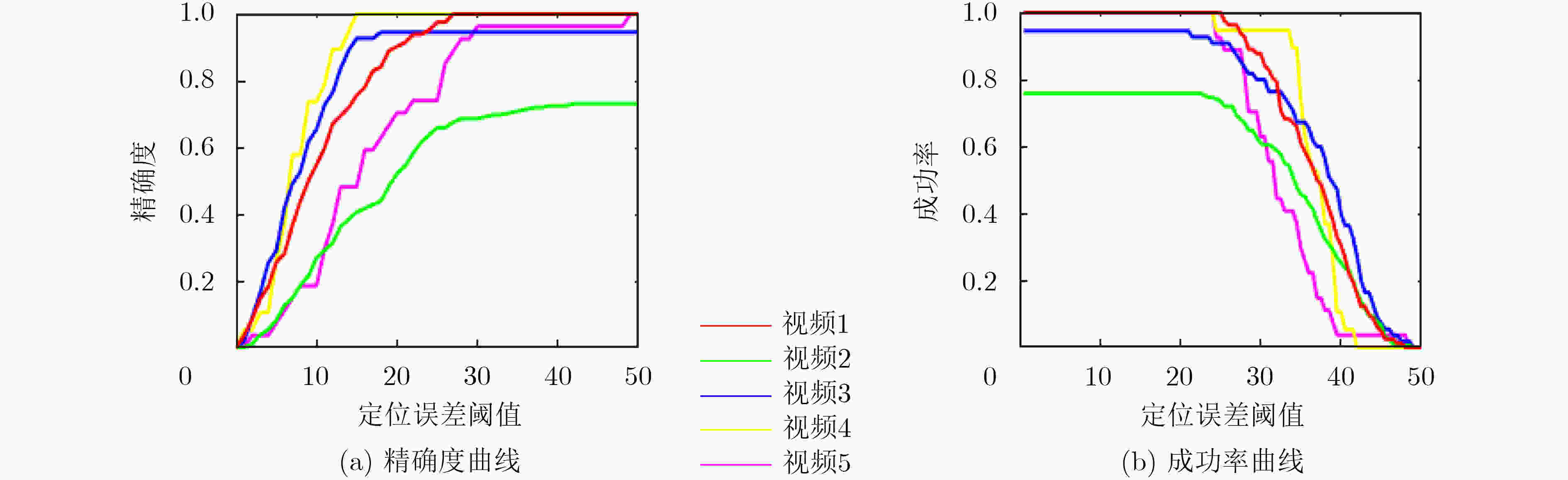
下载:
