Structural Refinement of Neural Style Transfer
-
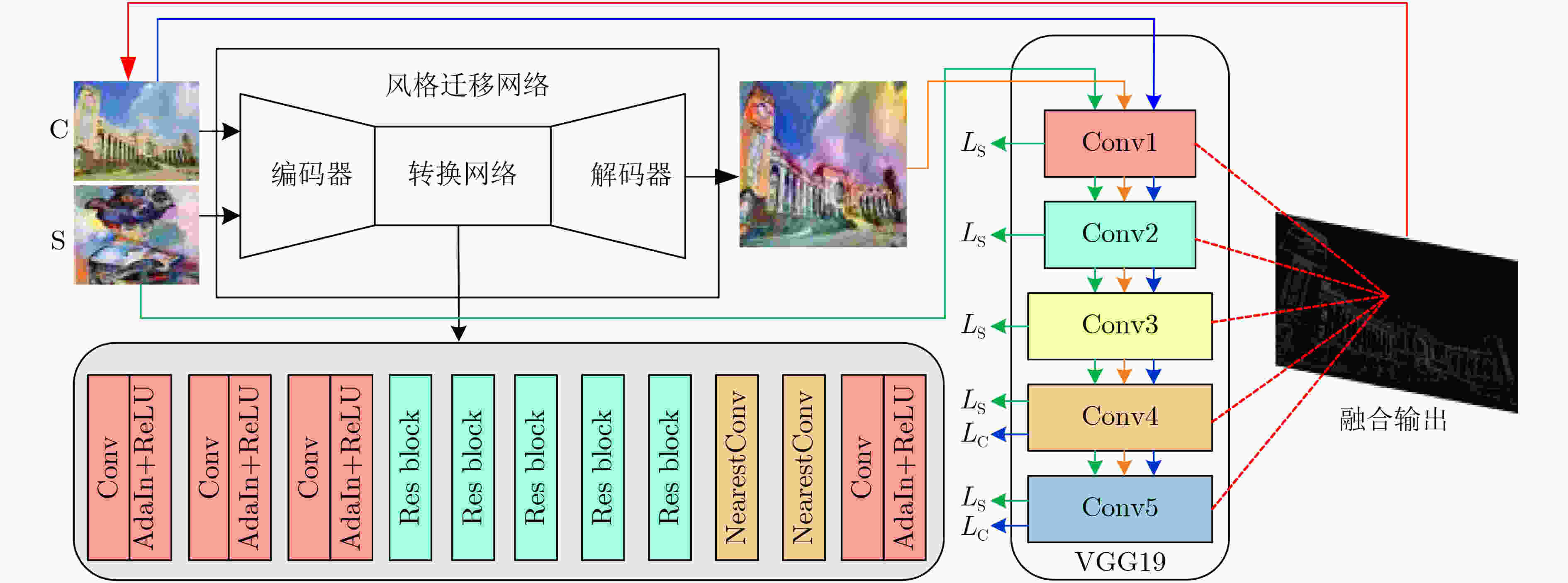
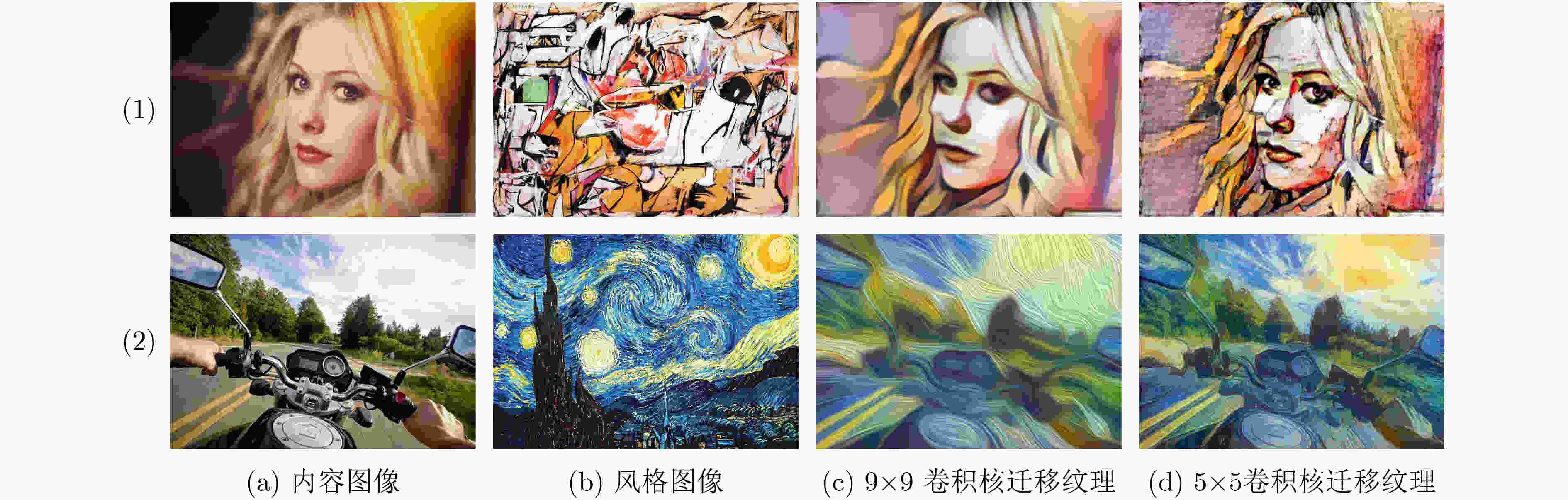
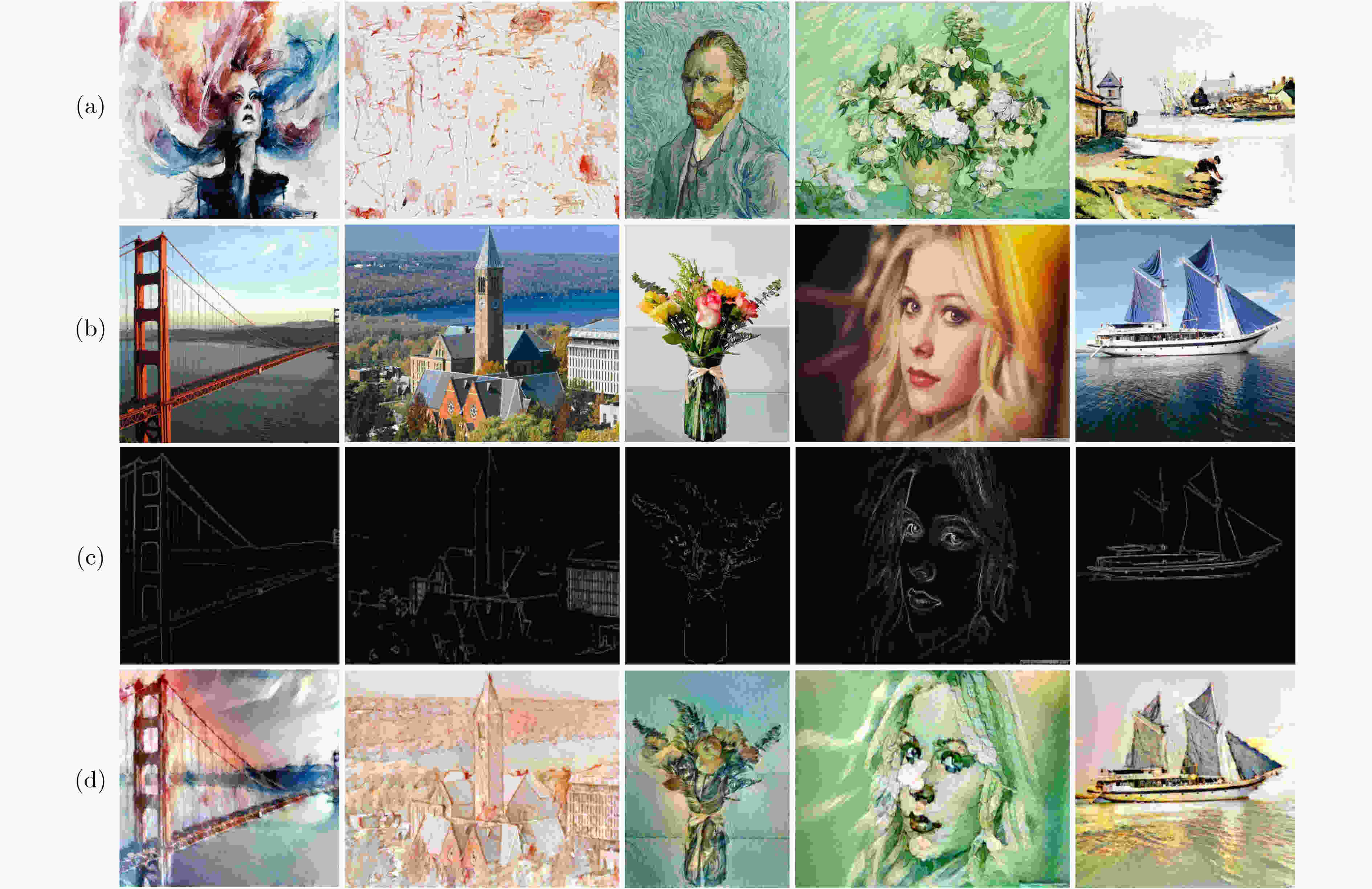
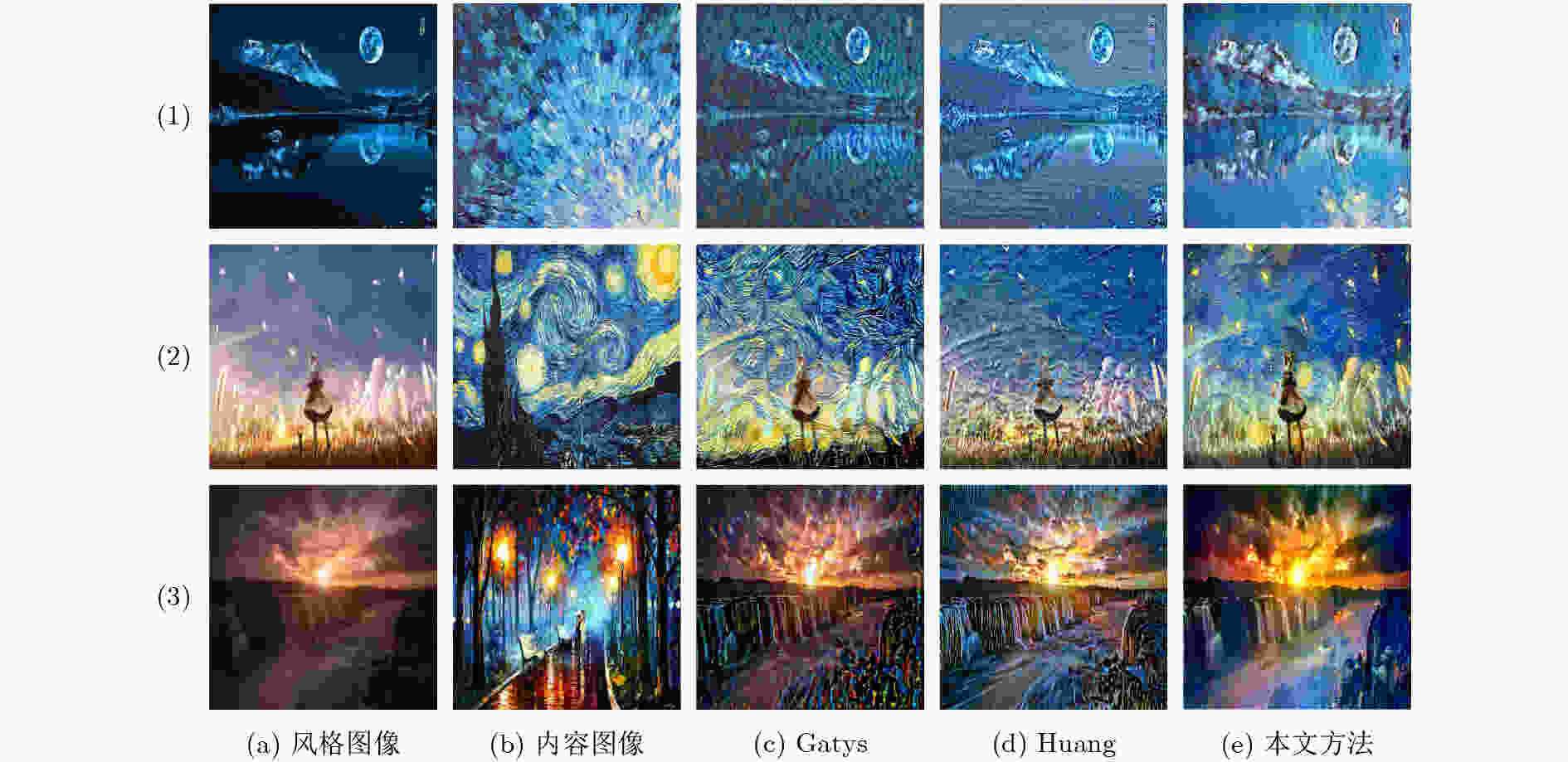
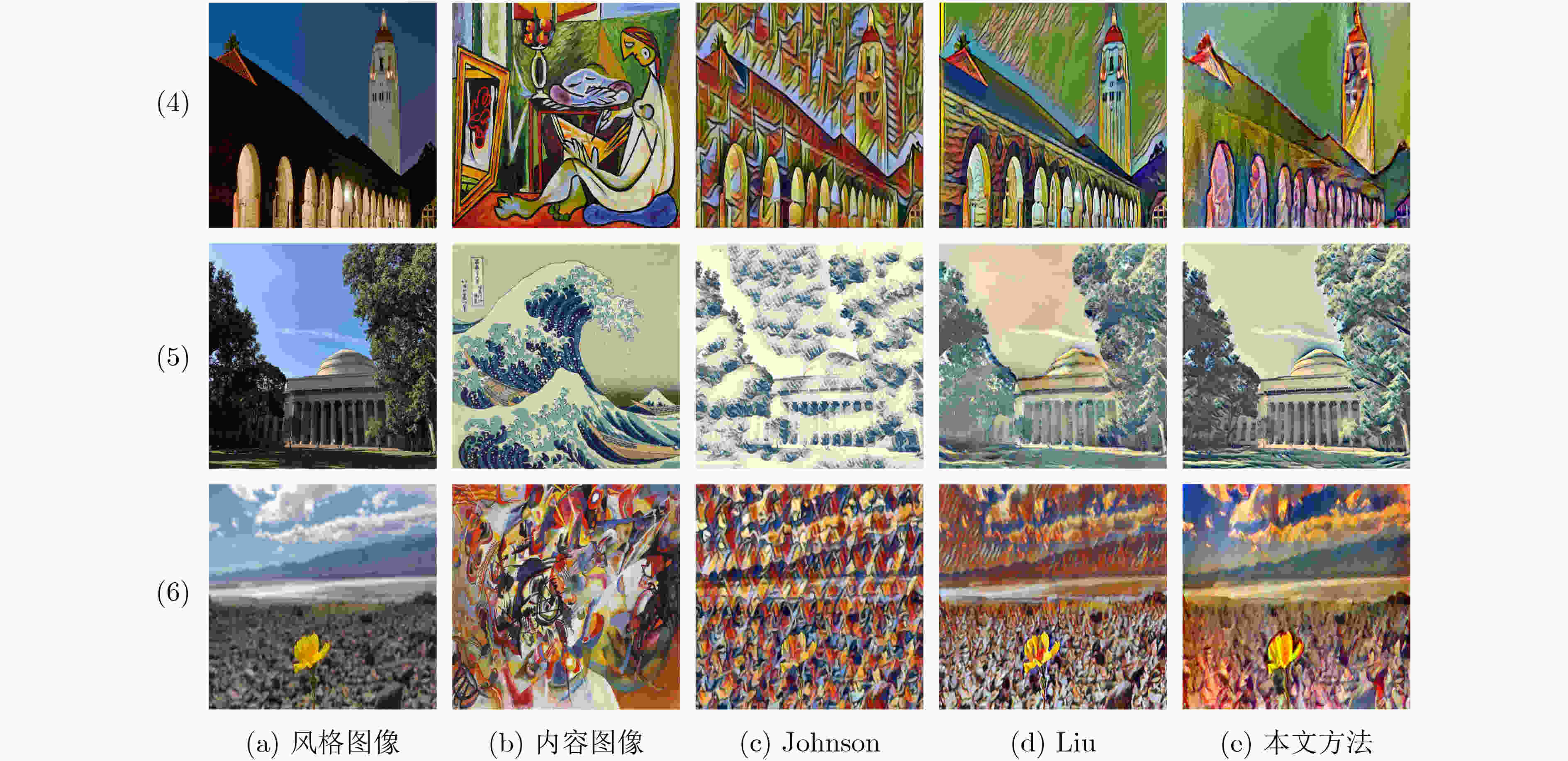
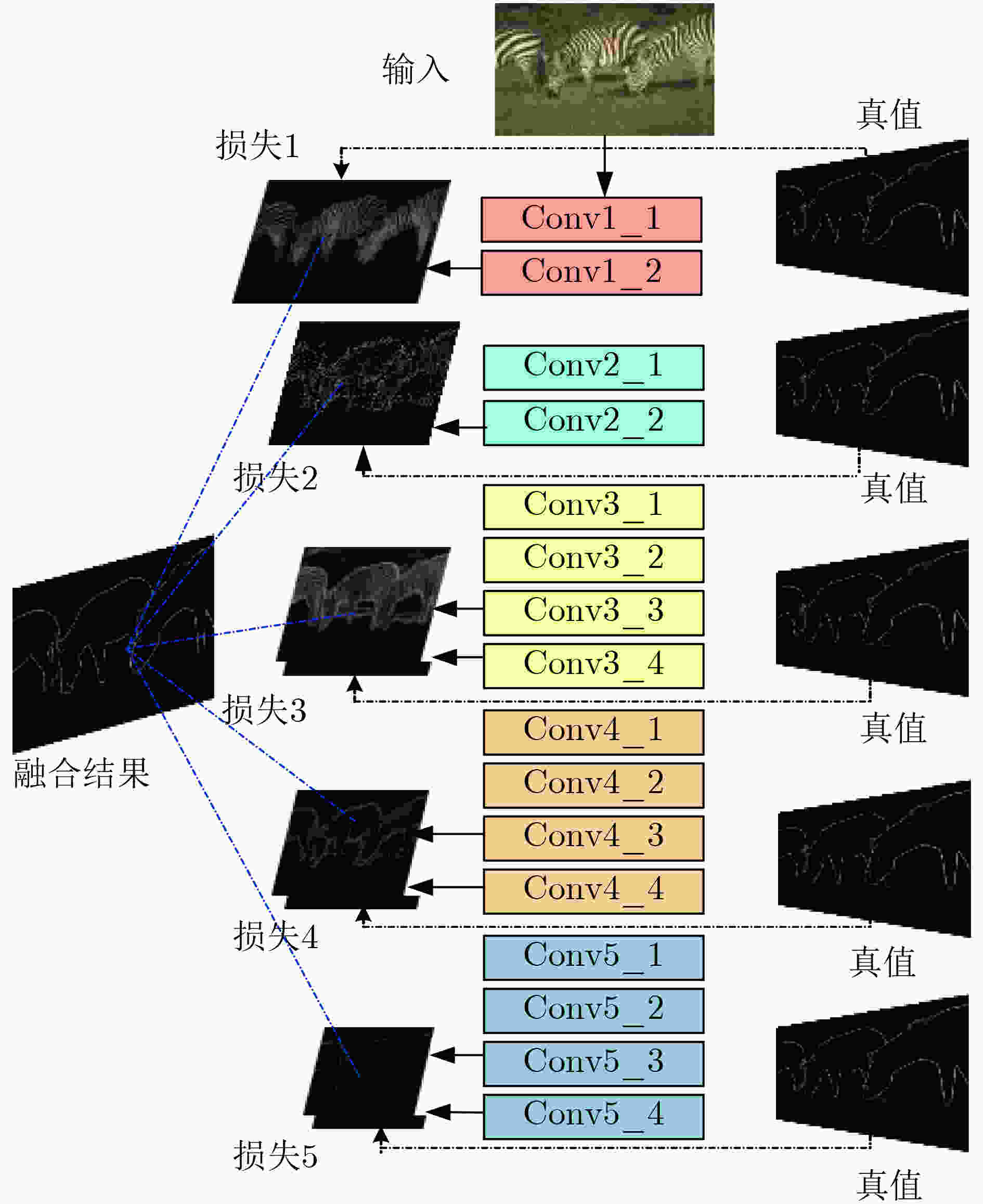
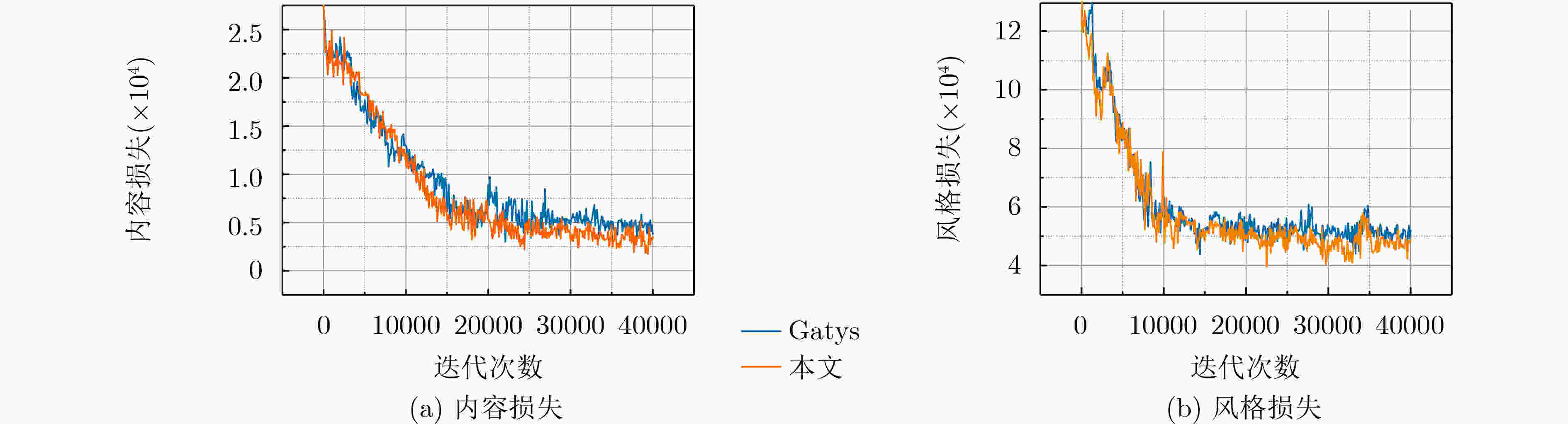
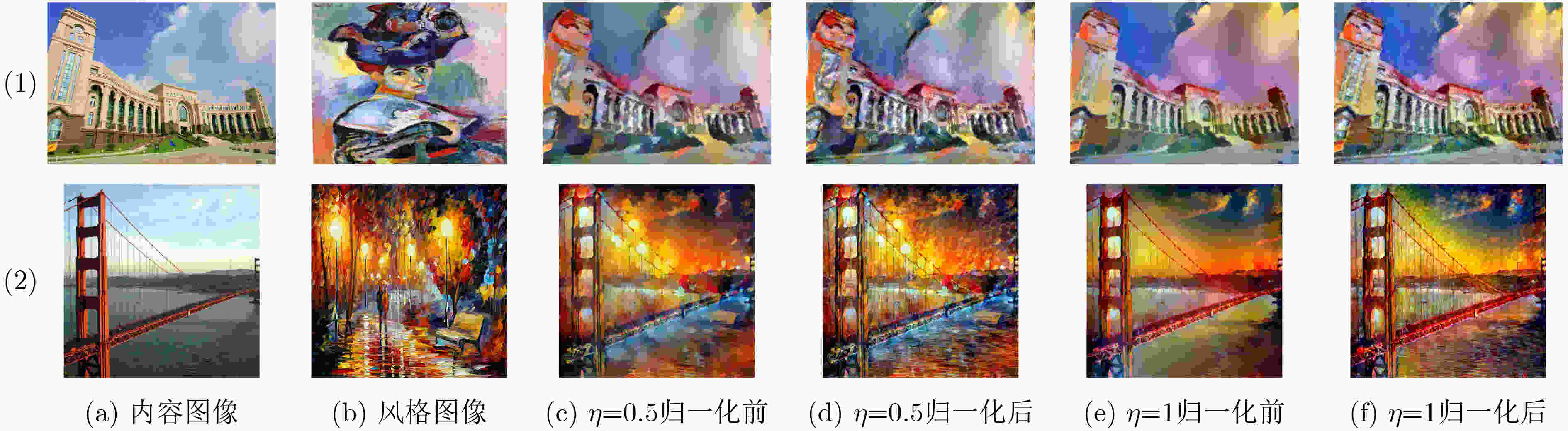
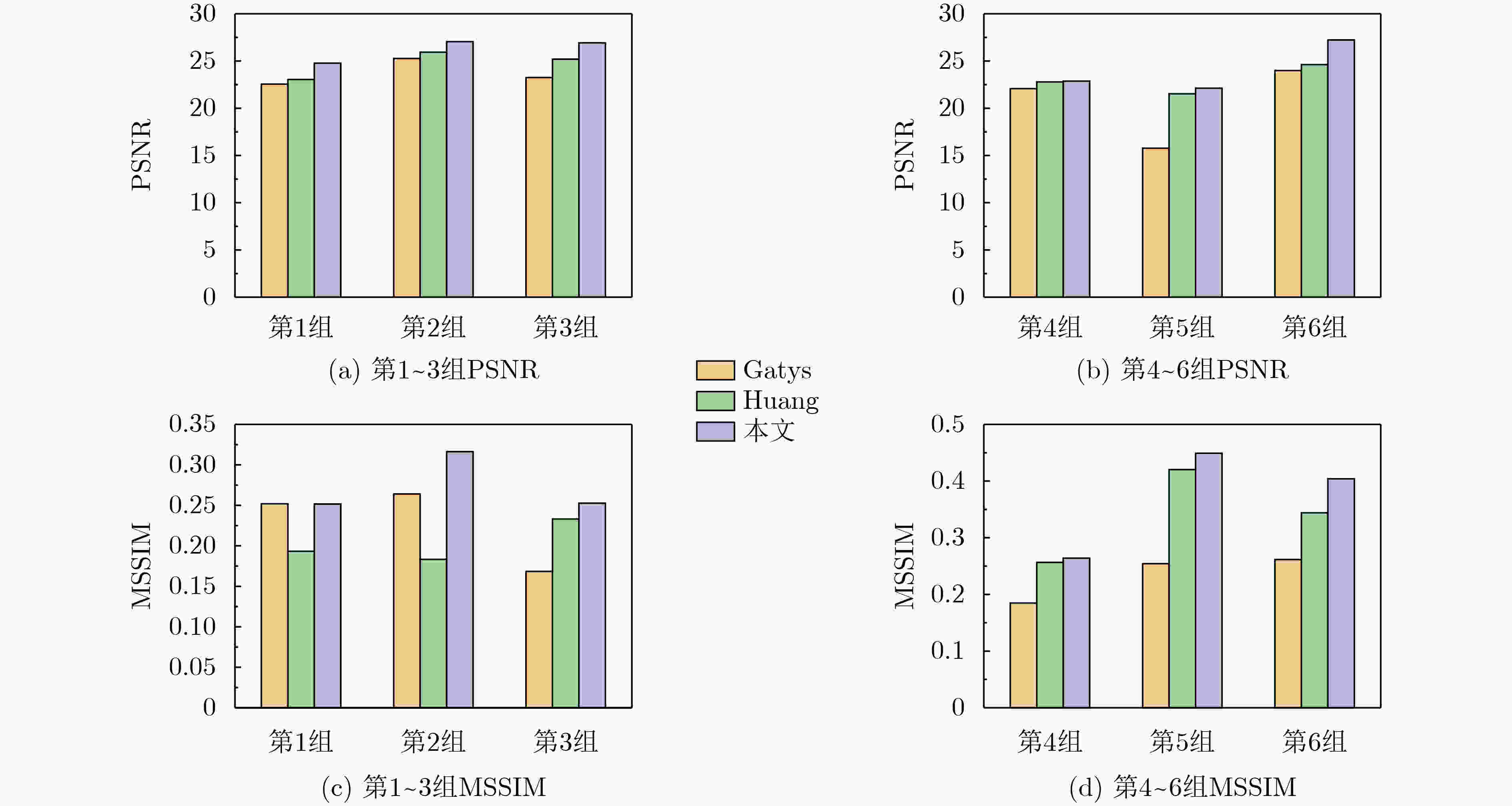
摘要: 风格迁移过程中风格元素均匀分布在整个图像中会使风格化图像细节模糊,现有的迁移方法主要关注迁移风格的多样性,忽略了风格化图像的内容结构和细节信息。因此,该文提出结构细化的神经风格迁移方法,通过增加边缘检测网络对内容图像的轮廓边缘进行提取实现风格化图像内容结构的细化,凸显内容图像中的主要目标;通过对转换网络中的常规卷积层的较大卷积核进行替换,在具有相同的感受野的条件下,使网络模型参数更少,提升了迁移速度;通过对转换网络中的常规卷积层添加自适应归一化层,利用自适应归一化在特征通道中检测特定样式笔触产生较高的非线性同时保留内容图像的空间结构特性来细化生成图像的结构。该方法能够细化风格化图像的整体结构,使得风格化图像连贯性更好,解决了风格纹理均匀分布使得风格化图像细节模糊的问题,提高了图像风格迁移的质量。Abstract: In the process of style transfer, stylized image details are blurred when style elements are evenly distributed in the whole image. Besides, the existing style transfer methods mainly focus on the diversity of transferred styles, ignoring the content structure and details of the stylized images. To this end, a neural style transfer method of structure refinement is proposed, which refines the content structure of stylized image by adding edge detection network to extract the contour edge of the content image to highlight the main objectives in the content image. By replacing the larger convolution kernel of the conventional convolution layer in the transfer network, the model parameters of the transfer network are reduced, and the transfer speed is improved, while ensuring that the original receptive field is unchanged. Through the adaptive normalization of the conventional convolution layer, the structure of the generated image is refined by using the adaptive normalization to detect certain style of stroke in the feature channel to produce high nonlinearity while preserving the spatial structure of the content image. The method can refine the overall structure of the stylized image, make the stylized image more coherent, that the stylized image details are blurred due to the uniform distribution of style texture, and improve the quality of image style transfer.
-
Key words:
- Image processing /
- Deep learning /
- Neural network /
- Style transfer /
- Edge detection /
- Normalization
-
表 1 步长和感受野参数设置
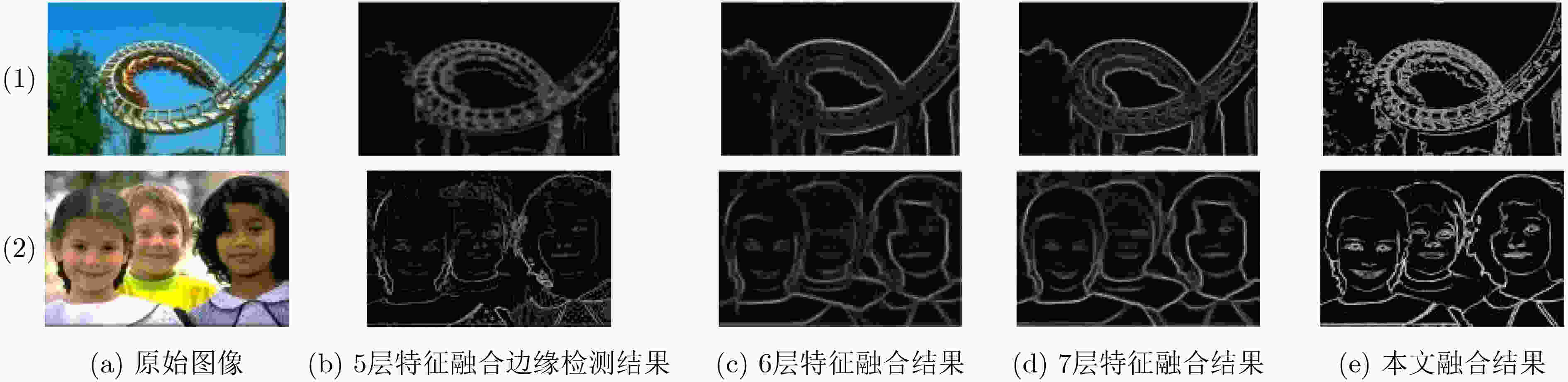
Layer Conv1_2 Conv2_2 Conv3_3 Conv3_4 Conv4_3 Conv4_4 Conv5_3 Conv5_4 步长 1 2 4 4 8 8 16 16 接受域 5 14 40 44 92 100 196 212 表 2 在BSDS500数据集上的客观评价指标
指标 ODS OIS AP 5层融合边缘检测图 0.760 0.784 0.800 6层融合边缘检测图 0.774 0.797 0.798 7层融合边缘检测图 0.777 0.788 0.814 8层融合边缘检测图 0.786 0.802 0.822 表 3 迁移网络改进前后参数量对比
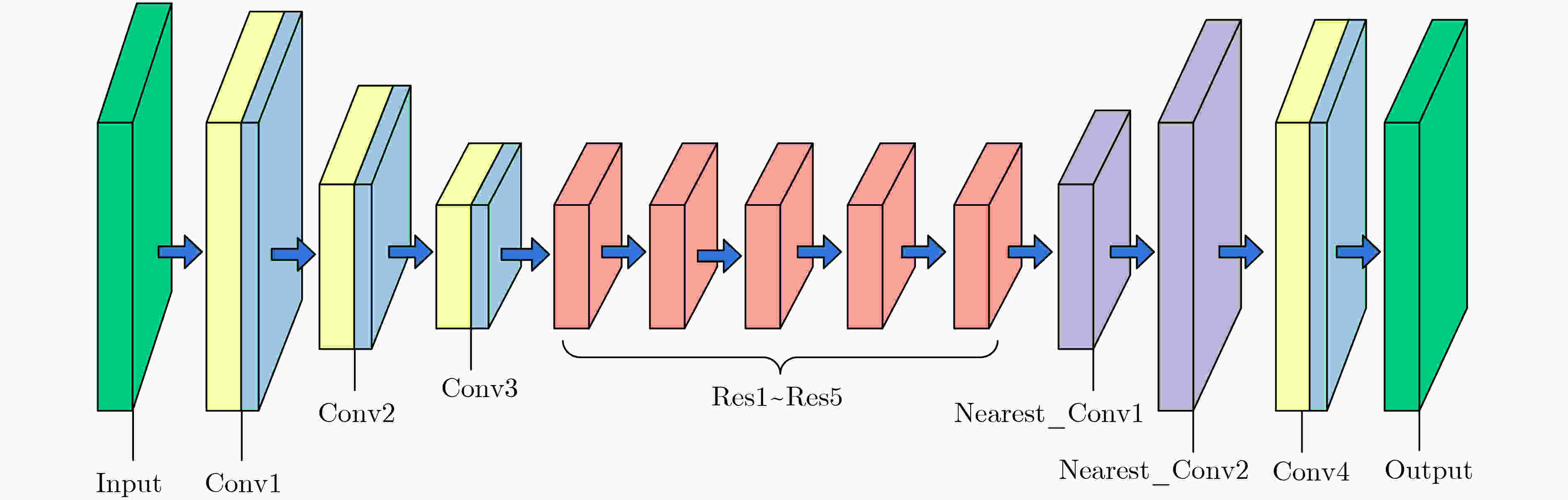
对应卷积层参数量 特征图通道数 步长 卷积核尺寸,参数量 卷积核尺寸,参数量 Conv1 32 1 9×9, 159418368 2×5×5, 98406400 Conv2 64 2 3×3, 8856576 3×3, 8856576 Conv3 128 2 3×3, 4428288 3×3, 4428288 Resblock1-Resblock5 128 23454552 23454552 Nearest_Conv1 64 1/2 3×3, 57600 3×3, 57600 Nearest_Conv2 32 1/2 3×3, 73728 3×3, 73728 Conv4 3 1 9×9, 15552 2×5×5, 9600 总参数量 196.30×106 135.29×106 -
[1] KYPRIANIDIS J E, COLLOMOSSE J, WANG Tinghuai, et al. State of the “Art”: a taxonomy of artistic stylization techniques for images and video[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2013, 19(5): 866–885. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2012.160 [2] 袁野, 贾克斌, 刘鹏宇. 基于深度卷积神经网络的多元医学信号多级上下文自编码器[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(2): 371–378. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190135YUAN Ye, JIA Kebin, and LIU Pengyu. Multi-context autoencoders for multivariate medical signals based on deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(2): 371–378. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190135 [3] GATYS L A, ECKER A S, and BETHGE M. A neural algorithm of artistic style[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1508.06576, 2015. [4] GATYS L A, ECKER A S, and BETHGE M. Image style transfer using convolutional neural networks[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2414–2423. doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2016.265. [5] LUAN Fujun, PARIS S, SHECHTMAN E, et al. Deep photo style transfer[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6997–7005. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.740. [6] HUANG Xun and BELONGIE S. Arbitrary style transfer in real-time with adaptive instance normalization[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 1510–1519. doi: 10.1109/iccv.2017.167. [7] LI Chuan and WAND M. Combining Markov random fields and convolutional neural networks for image synthesis[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2479–2486. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.272. [8] DUMOULIN V, SHLENS J, and KUDLUR M. A learned representation for artistic style[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1610.07629, 2016. [9] CHEN Yang, LAI Yukun, and LIU Yongjing. CartoonGAN: generative adversarial networks for photo cartoonization[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 9465–9474. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00986. [10] JOHNSON J, ALEXANDRE A, and LI Feifei. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 694–711. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_43. [11] 王鑫, 李可, 宁晨, 等. 基于深度卷积神经网络和多核学习的遥感图像分类方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1098–1105. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180628WANG Xin, LI Ke, NING Chen, et al. Remote sensing image classification method based on deep convolution neural network and multi-kernel learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1098–1105. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180628 [12] CHEN Chunfu, FAN Quanfu, MALLINAR N, et al. Big-little net: an efficient multi-scale feature representation for visual and speech recognition[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1807.03848, 2018. [13] WANG Xin, YU F, DOU Ziyi, et al. SkipNet: Learning dynamic routing in convolutional networks[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 420–436. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01261-8_25. [14] LIU Yun, CHENG Mingming, HU Xiaowei, et al. Richer convolutional features for edge detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(8): 1939–1946. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2878849 [15] XIE Saining and TU Zhuowen. Holistically-nested edge detection[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2017, 125(1): 3–18. doi: 10.1007/s11263-017-1004-z [16] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: common objects in context[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 740–755. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_48. [17] SAIF M M and SVETLANA K. WikiArt emotions: an annotated dataset of emotions evoked by art[C]. The 11th International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, Miyazaki, Japan, 2018: 1225–1238. [18] LIU Xiaochang, CHENG Mingming, LAI Yukun, et al. Depth-aware neural style transfer[C]. The Symposium on Non-Photorealistic Animation and Rendering, California, USA, 2017: 4. doi: 10.1145/3092919.3092924. -





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:
