Optimization and Implementation of Number Theoretical Transform Multiplier Butterfly Operation for Fully Homomorphic Encryption
-
摘要: 全同态加密(FHE)可以真正从根本上解决云计算时将数据及其操作委托给第三方时的数据安全问题。针对全同态加密中占较大比例的大整数乘法运算优化需求,该文提出一种数论变换乘法蝶形运算的操作数合并算法,利用取模操作的快速算法,分别可将基16和基32运算单元的操作数减少到43.8%和39.1%。在此基础上,设计并实现了数论变换基32运算单元的硬件设计架构,在SMIC 90 nm工艺下的综合结果显示,电路的最高工作频率为600 MHz,面积1.714 mm2。实验结果表明,该优化算法提升了数论变换乘法蝶形运算的计算效率。Abstract: Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) allows data to be encrypted and out-sourced to commercial cloud environments for processing, while encrypted which diminishes privacy concerns. For the optimization requirements of large integer multiplication operations in fully homomorphic encryption, an operand merge algorithm of a Number Theory Transform (NTT) multiplier butterfly operation unit is proposed. By using a fast algorithm of modulo operation, the operands of the Radix-16 and Radix-32 units are reduced to 43.8% and 39.1%. The hardware architecture of the NTT Radix-32 unit is designed and implemented. The proposed design is synthesized using 90 nm process technology. The results show that the maximum frequency of the circuit is 600 MHz with die area 1.714 mm2. The results also show that the optimization algorithm improves the computational efficiency of NTT multiplier butterfly operation.
-
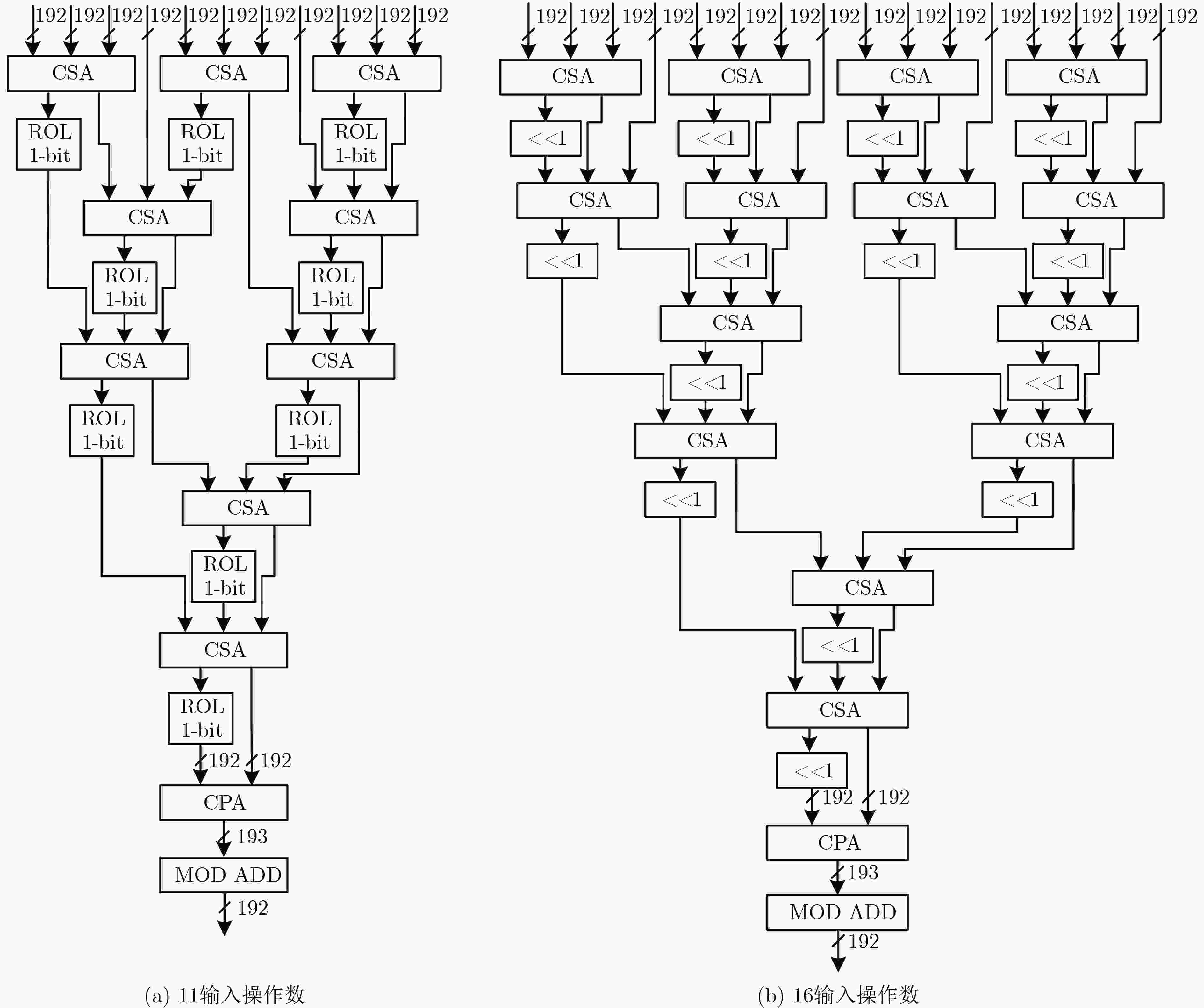
表 1 操作数合并算法
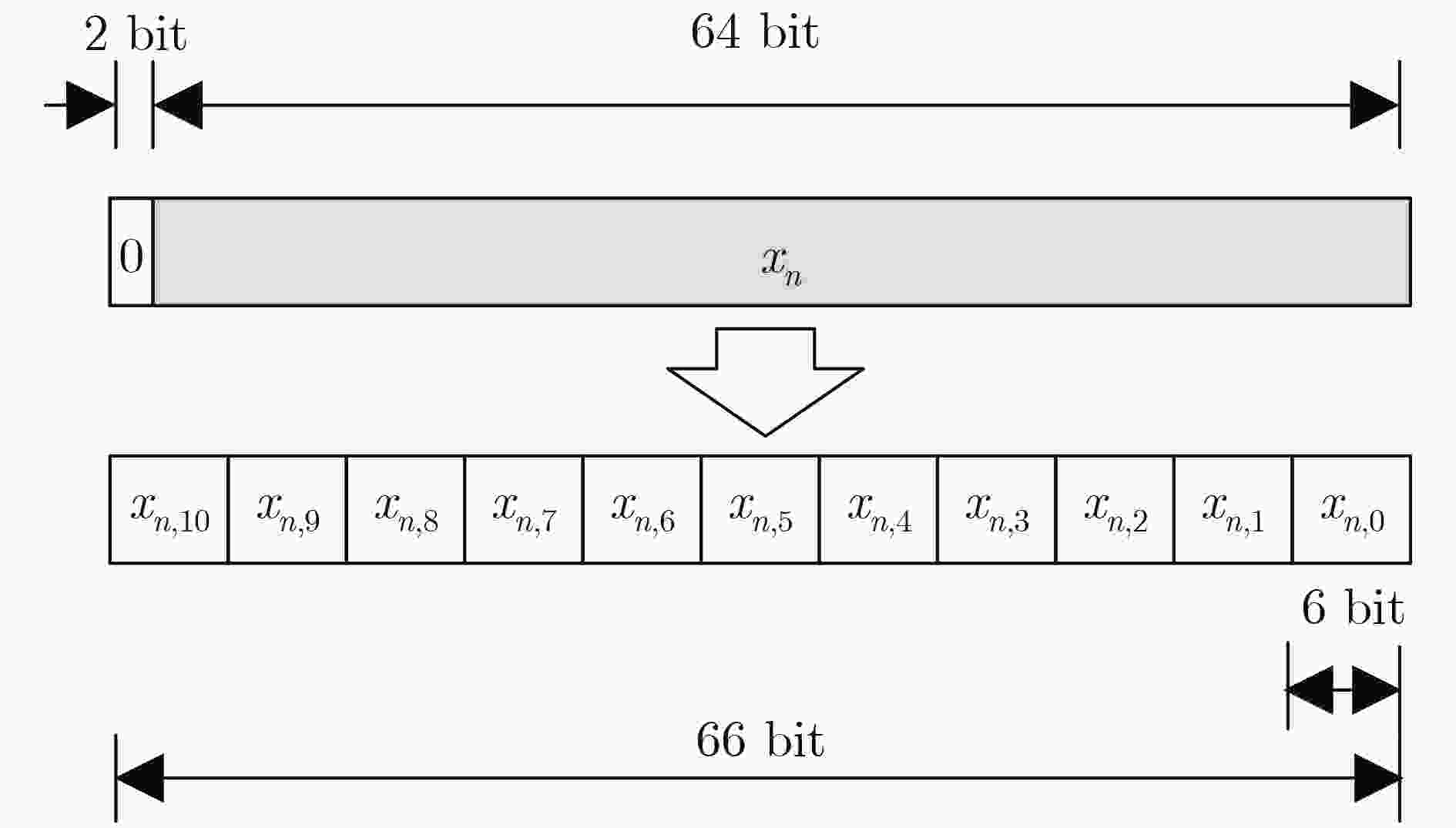
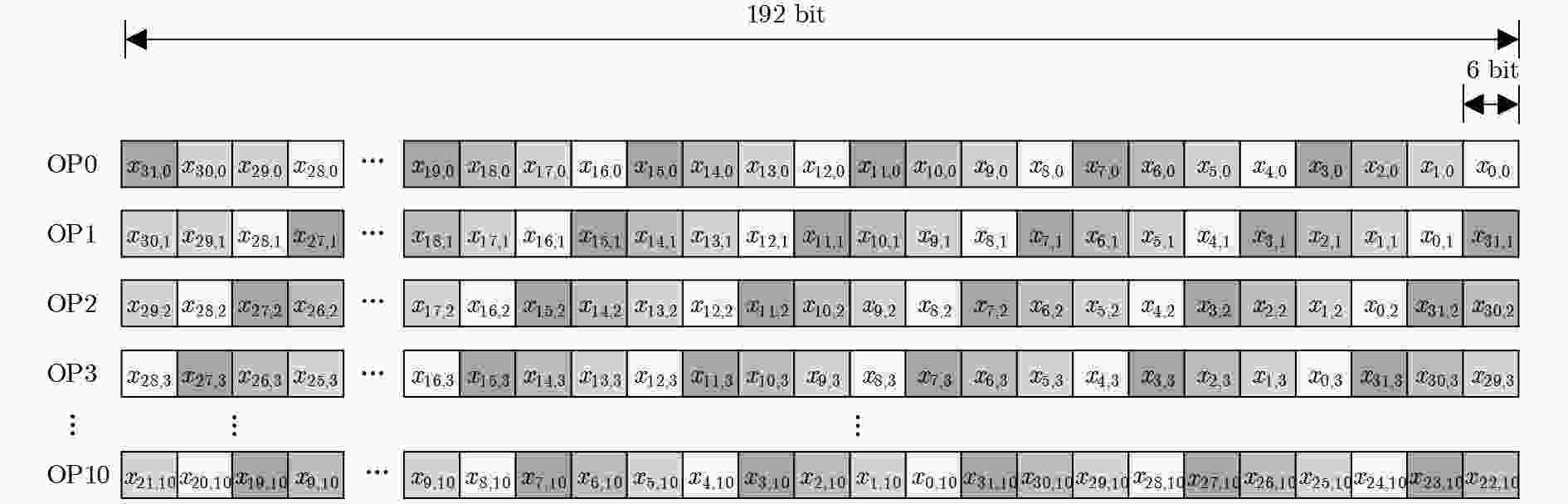
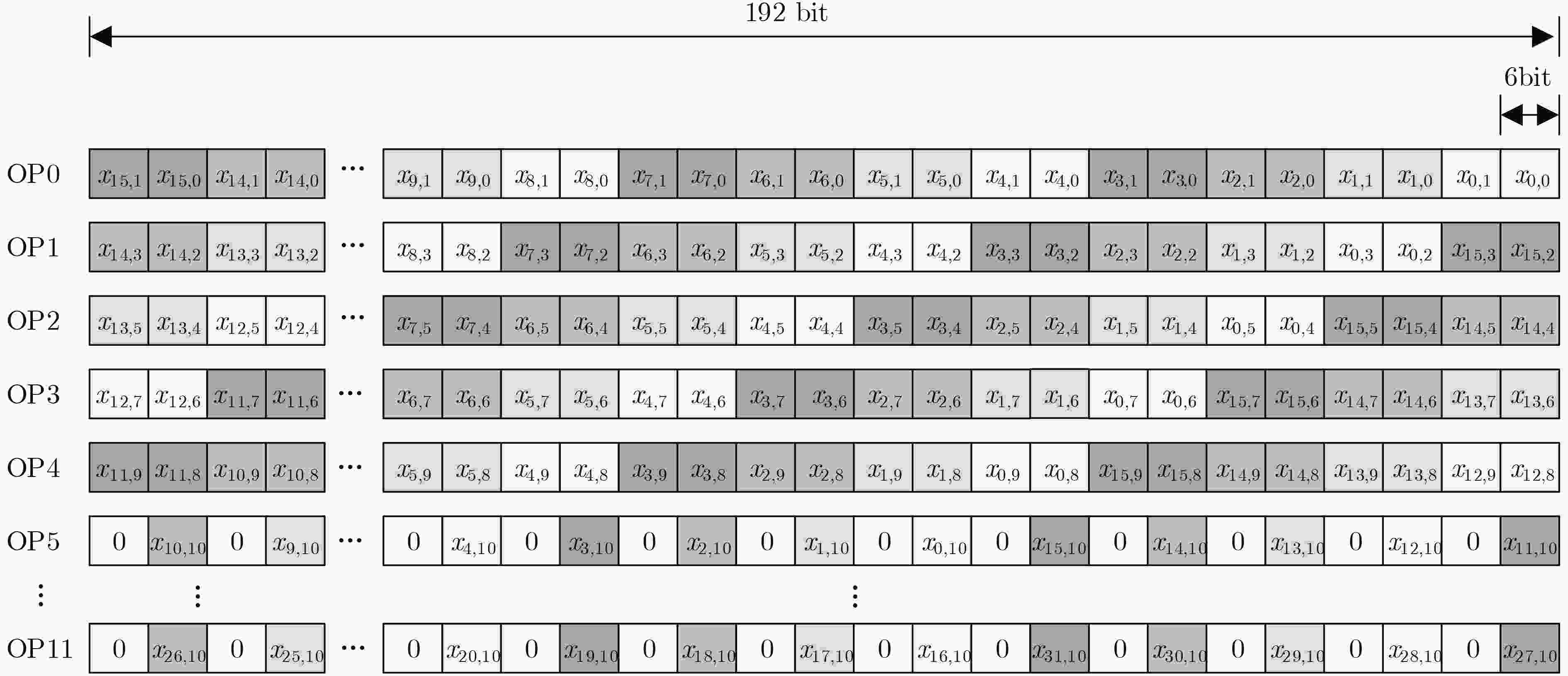
输入:原始输入数据$ x $ 输出:合并后的操作数$ {\rm{OP}} $ {//For $ {X}_{1} $ to $ {X}_{31} $ NTT output} for $ i=0 $ to 4 do for $ j=0 $ to $ 16/{2}^{i}-1 $ do $ k\leftarrow {2}^{i}\times \left(2j+1\right) $ {//For $ {\rm{OP}}\left[k\right] $ of $ k $-th NTT output} for $ \delta =0 $ to $ {2}^{i}-1 $ do for $ \beta =0 $ to CEILING($ 11/{2}^{i}-1 $) do $ n\leftarrow \delta \times $CEILING($ 11/{2}^{i}+\beta $) {//For $ {\rm{OP}}\left[k\right]\left[n\right] $} $ {\rm{OP}}\left[k\right]\left[n\right]\leftarrow {192'}{\rm{b}}0 $ for $ \gamma =0 $ to $ 32/{2}^{i}-1 $ do for $ \alpha =0 $ to $ {2}^{i}-1 $ do $ m\leftarrow {2}^{i}\times \beta +\alpha $ if $ m\ge 11 $ then PASS else
$ {\rm{OP}}\left[k\right]\left[n\right][6\left(m+\gamma k\right)+5\left({\rm{mod}}\;192\right):$
$6\left(m+\gamma k\right) \left({\rm{mod}}\;192\right)]\leftarrow x\left[6m+5:6m\right] $end if end for end for end for end for end for end for {//For $ {X}_{0} $ NTT output} for $ n=0 $ to 31 do $ {\rm{OP}}\left[0\right]\left[n\right]\leftarrow {96'}{\rm{b}}0 $ $ {\rm{OP}}\left[0\right]\left[n\right]\left[63:0\right]\leftarrow x\left[n\right] $ end for 表 2 基32运算单元的操作数
数论变换输出 个数 合并前操
作数数量合并后操
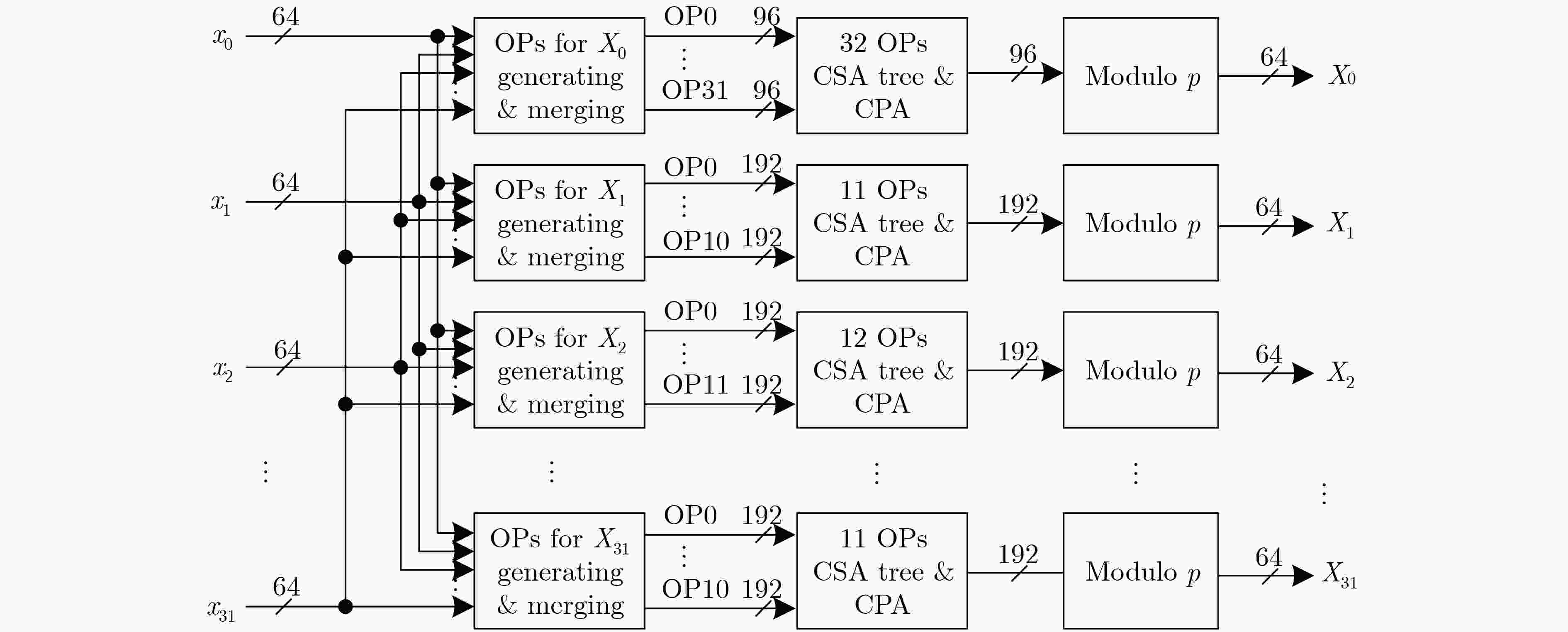
作数数量$ {X}_{0} $ 1 32 32 奇数输出 16 32 11 $ {X}_{8},{X}_{16},{X}_{24} $ 3 32 16 除$ {X}_{0},{X}_{8},{X}_{16},{X}_{24} $以外的偶数输出 12 32 12 合计 32 1024 400 -
[1] ALBRECHT M, CHASE M, CHEN Hao, et al. Homomorphic encryption standard[R/OL]. http://homomorphicencryption.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/HomomorphicEncryptionStandardv1.1.pdf, 2018. [2] 陈克非, 蒋林智. 同态加密专栏序言[J]. 密码学报, 2017, 4(6): 558–560. doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000207CHEN Kefei and JIANG Linzhi. Preface on homomorphic encrpytion[J]. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2017, 4(6): 558–560. doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000207 [3] 李增鹏, 马春光, 周红生. 全同态加密研究[J]. 密码学报, 2017, 4(6): 561–578. doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000208LI Zengpeng, MA Chunguang, and ZHOU Hongsheng. Overview on fully homomorphic encryption[J]. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2017, 4(6): 561–578. doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000208 [4] ARCHER D, CHEN L, CHEON J H, et al. Applications of homomorphic encryption[EB/OL]. http://homomorphicencryption.org/white_papers/applications_homomorphic_encryption_white_paper.pdf, 2017. [5] GENTRY C. Fully homomorphic encryption using ideal lattices[C]. The 41st Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Bethesda, USA, 2009: 169–178. doi: 10.1145/1536414.1536440. [6] ABOZAID G, EL-MAHDY A, and WADA Y. A Scalable multiplier for arbitrary large numbers supporting homomorphic encryption[C]. 2013 Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design, Los Alamitos, USA, 2013: 969–975. doi: 10.1109/DSD.2013.110. [7] RAFFERTY C, O’NEILL M, and HANLEY N. Evaluation of large integer multiplication methods on hardware[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2017, 66(8): 1369–1382. doi: 10.1109/TC.2017.2677426 [8] VAN METER R and ITOH K M. Fast quantum modular exponentiation[J]. Physical Review A, 2005, 71(5): 052320. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.71.052320 [9] GARCÍA L. Can Schönhage multiplication speed up the RSA encryption or decryption?[EB/OL]. https://www.informatik.tu-darmstadt.de/cdc/home_cdc/index.de.jsp, 2005. [10] FÜRER M. Faster integer multiplication[C]. The 39th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, San Diego, USA, 2007: 57–66. doi: 10.1145/1250790.1250800. [11] WANG Wei, HUANG Xinming, EMMART N, et al. VLSI design of a large-number multiplier for fully homomorphic encryption[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2014, 22(9): 1879–1887. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2013.2281786 [12] FENG Xiang and LI Shuguo. Design of an area-effcient million-bit integer multiplier using double modulus NTT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2017, 25(9): 2658–2662. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2017.2691727 [13] 施佺, 韩赛飞, 黄新明, 等. 面向全同态加密的有限域FFT算法FPGA设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(1): 57–62. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170312SHI Quan, HAN Saifei, HUANG Xinming, et al. Design of finite field FFT for fully homomorphic encryption based on FPGA[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(1): 57–62. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170312 [14] 谢星, 黄新明, 孙玲, 等. 大整数乘法器的FPGA设计与实现[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(8): 1855–1860. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180836XIE Xing, HUANG Xinming, SUN Ling, et al. FPGA design and implementation of large integer multiplier[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(8): 1855–1860. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180836 [15] Project Nayuki. Number-theoretic transform (integer DFT)[EB/OL]. https://www.nayuki.io/page/number-theoretic-transform-integer-dft, 2017. -






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
