Siamese Network Combined Learning Saliency and Online Leaning Interference for Aerial Object Tracking Algorithm
-
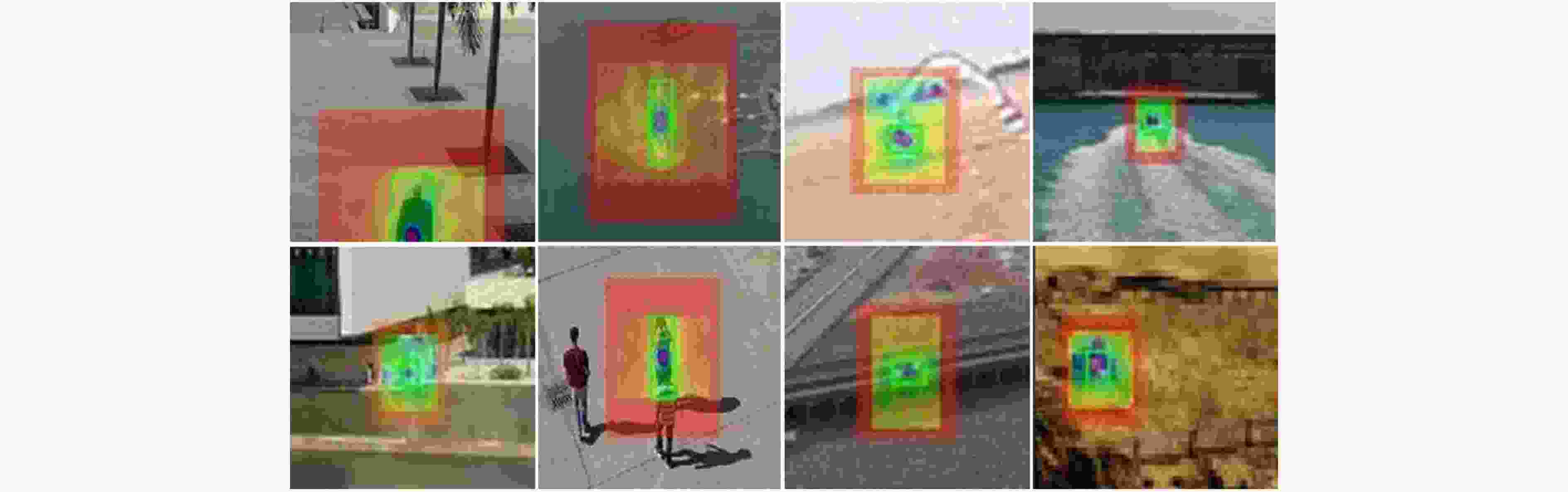
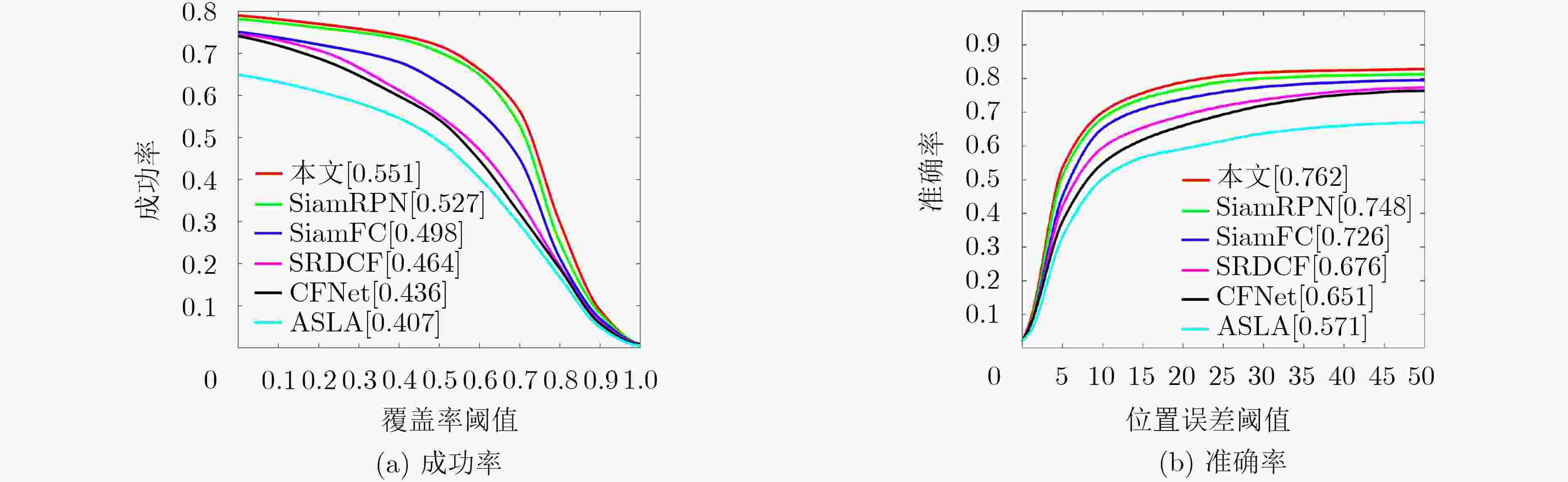
摘要: 针对一般跟踪算法不能很好地解决航拍视频下目标分辨率低、视场大、视角变化多等特殊难点,该文提出一种融合目标显著性和在线学习干扰因子的无人机(UAV)跟踪算法。通用模型预训练的深层特征无法有效地识别航拍目标,该文跟踪算法能根据反向传播梯度识别每个卷积滤波器的重要性来更好地选择目标显著性特征,以此凸显航拍目标特性。另外充分利用连续视频丰富的上下文信息,通过引导目标外观模型与当前帧尽可能相似地来在线学习动态目标的干扰因子,从而实现可靠的自适应匹配跟踪。实验证明:该算法在跟踪难点更多的UAV123数据集上跟踪成功率和准确率分别比孪生网络基准算法高5.3%和3.6%,同时速度达到平均28.7帧/s,基本满足航拍目标跟踪准确性和实时性需求。Abstract: In view of the fact that the general tracking algorithm can not solve the special problems such as low resolution, large field of view and many changes of view angle, a Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) tracking algorithm combining target saliency and online learning interference factor is proposed. The deep feature that the general model pre-trained can not effectively identify the aerial target, the tracking algorithm can better select the salient feature of each convolution filter according to the importance of the back propagation gradient, so as to highlight the aerial target feature. In addition, it makes full use of the rich context information of the continuous video, and learn the interference factor of the dynamic target online by guiding the target appearance model as similar as possible to the current frame, so as to achieve reliable adaptive matching tracking. It is proved that the tracking success rate and accuracy rate of the algorithm are 5.3% and 3.6% higher than that of the siamese network benchmark algorithm on the more difficult UAV123 dataset, respectively, and the speed reaches an average of 28.7 frames per second, which basically meet the aerial target tracking accuracy and real-time requirements.
-
表 1 本文跟踪算法流程
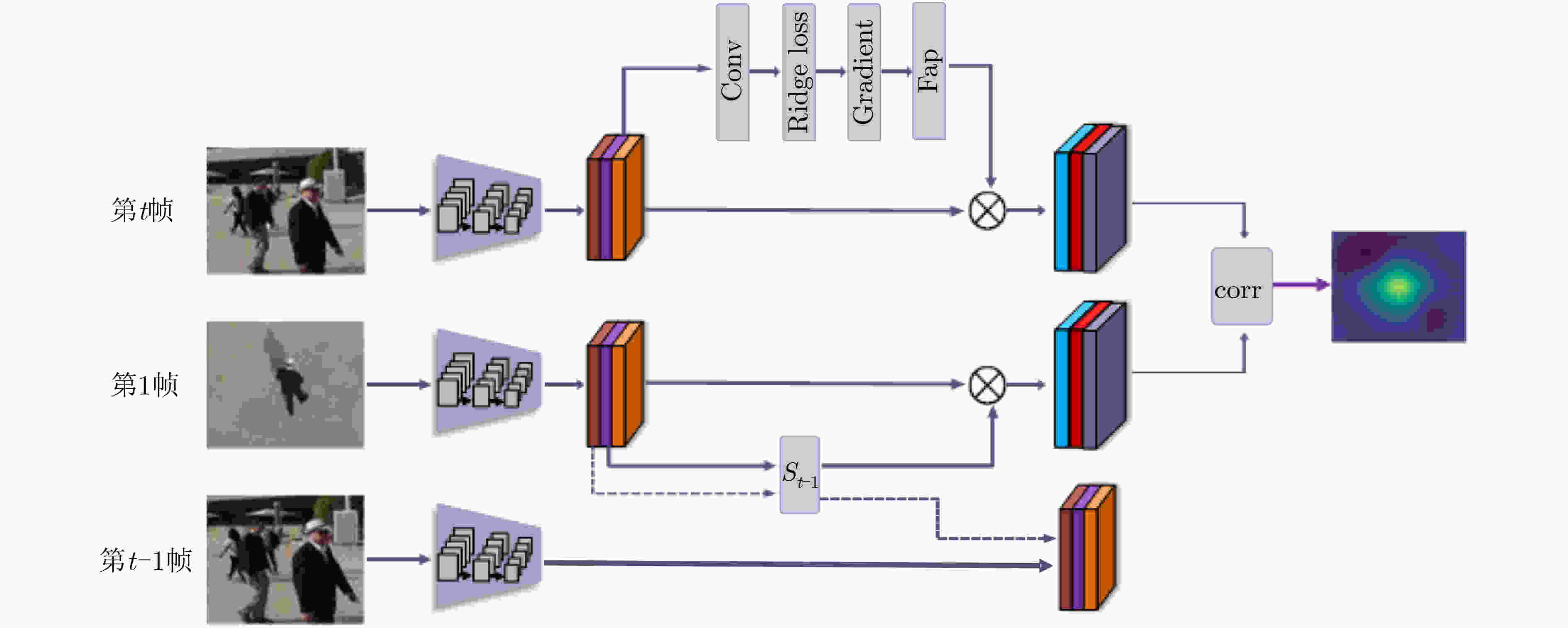
输入: (1) 第1帧$ {{Z}}_{1} $:目标位置坐标$ {{L}}_{1} $和包围框${{{b}}_{1}}$ (2) 第$t - {1}$帧${{{X}}_{t{ - 1}}}$:目标位置坐标${{{L}}_{t - {1}}}$和包围框${{{b}}_{t - {1}}}$ (3) 第$t$帧${{{X}}_t}$(当前帧) 输出; ${\rm{res}}$;当前帧每个位置的相似度值 Function $\left( {{{{O}}_t}:{{{O}}_1}:{{{O}}_{t - 1}}} \right)$= pretrain_feature
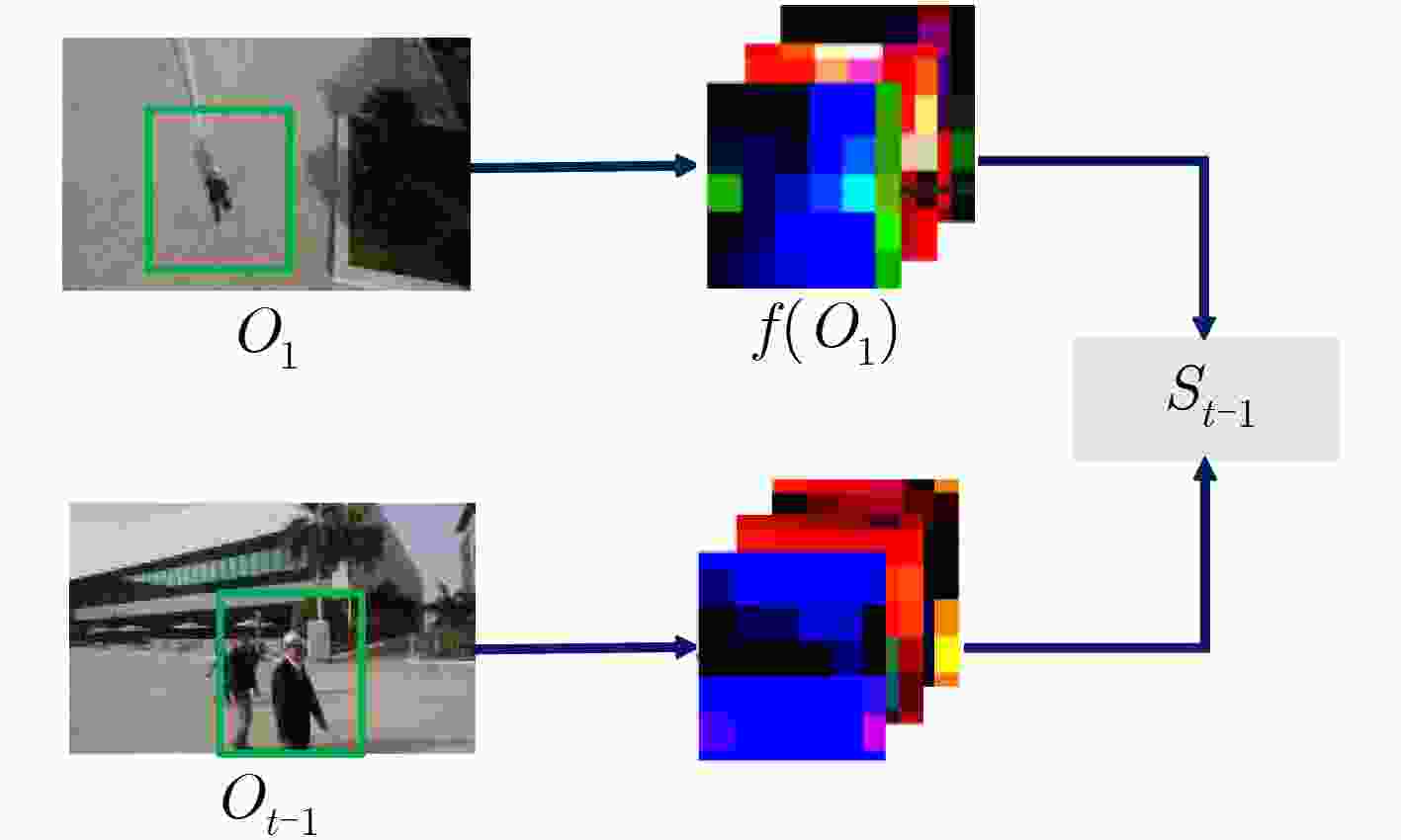
$\left( {{{{X}}_t}:{{{Z}}_1}:{{{X}}_{t - 1}}} \right)$$\left( {{{{O}}_t}:{{{O}}_1}:{{{O}}_{t - 1}}} \right) = \varphi \left( {{{{X}}_t}:{{{Z}}_1}:{{{X}}_{t - 1}}} \right)$ end Function ${ {{O} }_t}^{'}$= Target_saliency_feature(${{{O}}_t}$) ${M_i} = {F_{ {\rm{ap} } } }\left(\dfrac{ {\partial J} }{ {\partial {F_i} } }\right)$ ${{{O}}_t}^{'} = {{f}}({{{O}}_t};{{M}_i})$ end Function ${{{S}}_{t - {1}}}$= get_disturbance_factor $\left( {{{{O}}_1}:{{{O}}_{t - 1}}:{\lambda _s}} \right)$
${ {{S} }_{t - {1} } } = { {\cal F}^{ - 1} }\left(\dfrac{ { { {\cal F}^ * }({ {{O} }_1}) \odot {\cal F}({ {{O} }_{t - 1} })} }{ { { {\cal F}^ * }({ {{O} }_1}) \odot {\cal F}({ {{O} }_1}) + {\lambda _s} } }\right)$end Function ${\rm{res}}$= detection $ \left({{S}}_{{t}-1};{{O}}_{1};{{O}}_{t}\right) $ ${\rm{res}} = {\rm{corr} }({ {{S} }_{t - {1} } } * { {{O} }_{1} },{ {{O} }_t}^\prime )$ end 表 2 部分视频的跟踪成功率和跟踪准确率比较(%)
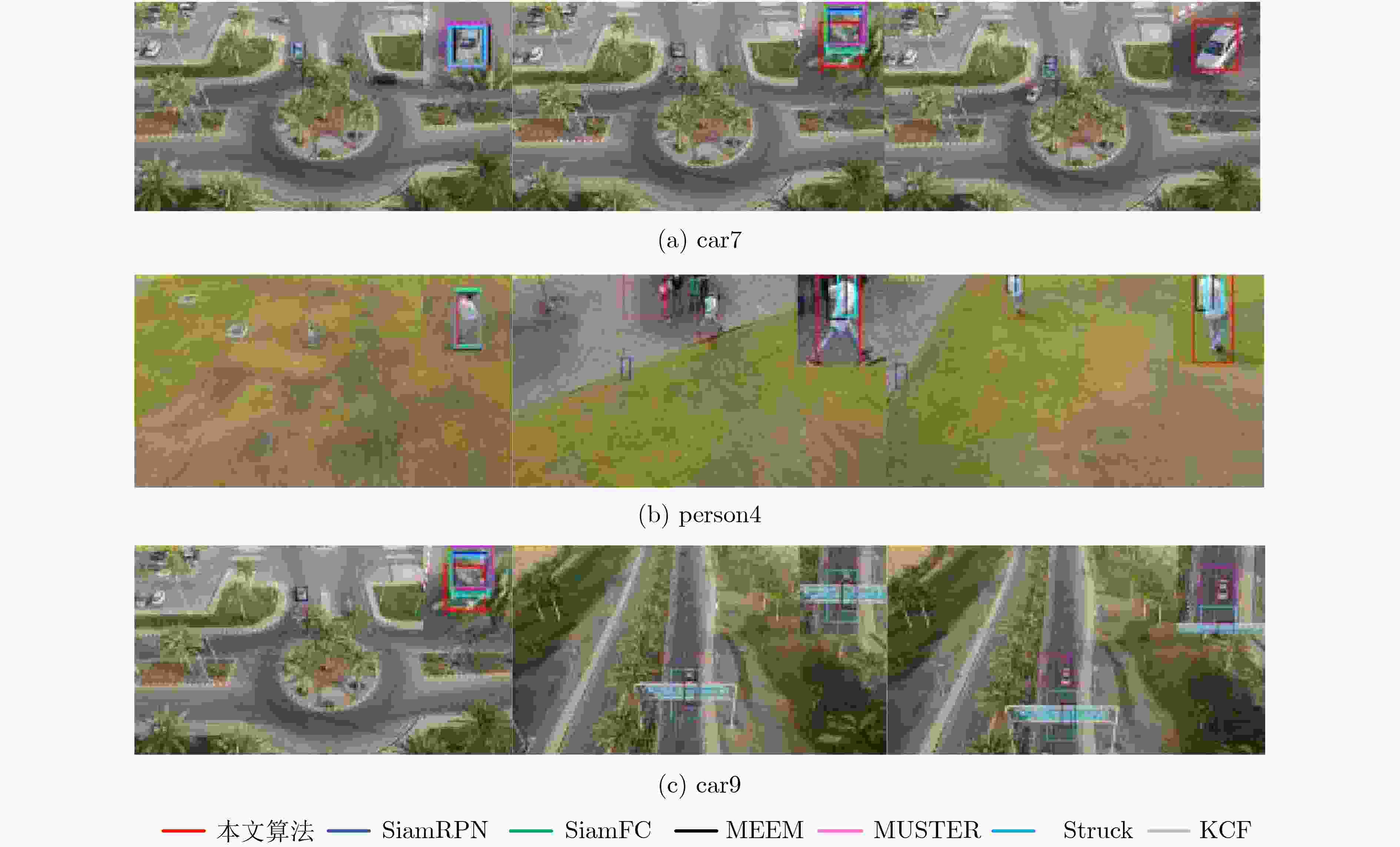
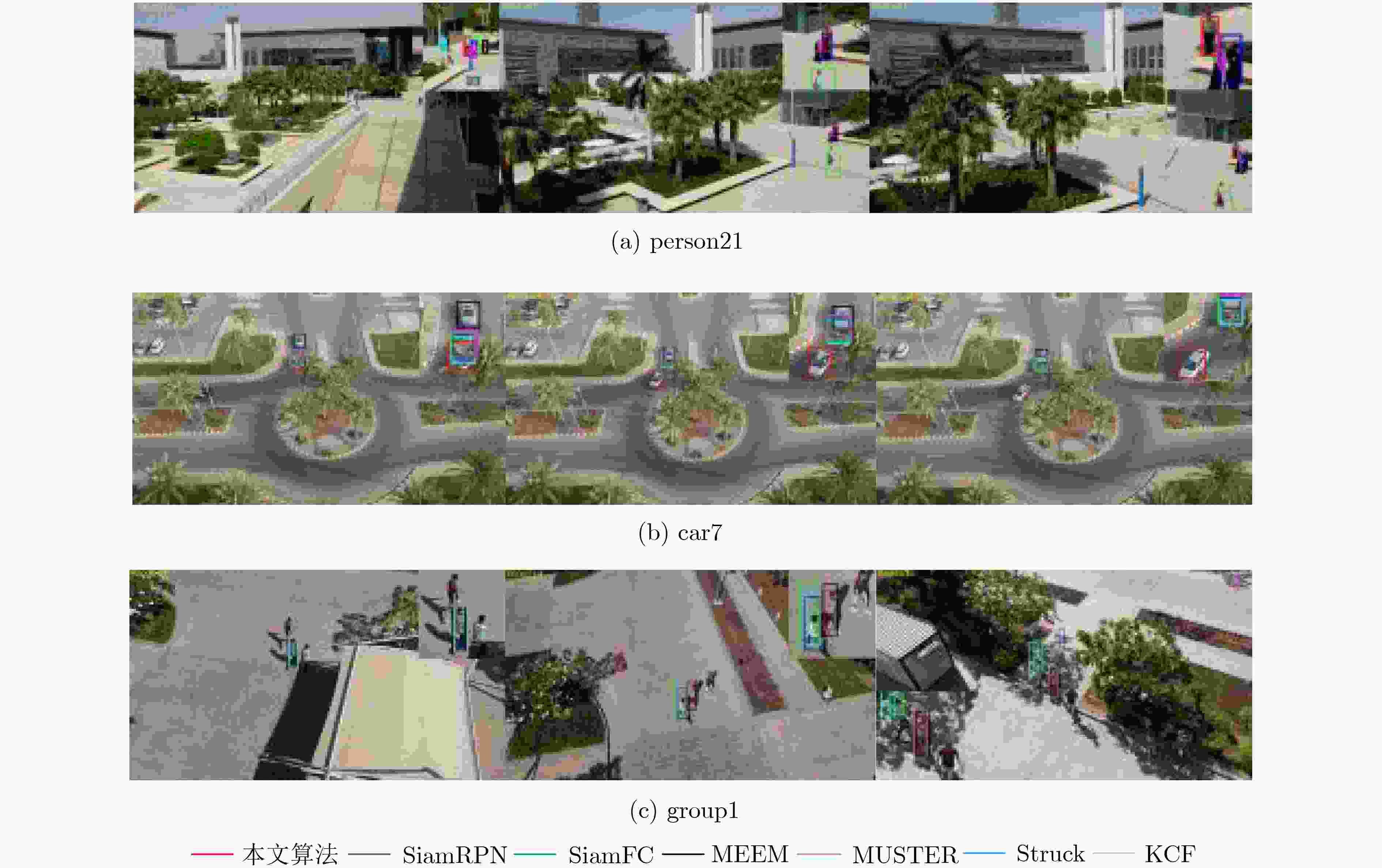
序列 Attibutes Struck SAMF MUSTER KCF SRDCF CFNet 本文 bike3 LR POC 6.9/30.0 15.7/22.8 19.4/27.7 12.2/20.5 13.9/35.4 14.1/45.2 17.8/65.5 boat5 VC 16.6/10.6 74.7/61.8 85.1/67.7 23.2/9.5 48.6/89.7 36.0/17.2 38.7/37.6 building5 CM 99.3/99.3 96.9/98.6 97.3/98.9 89.0/99.7 97.5/98.9 21.6/61.6 99.8/99.8 car15 LR POC SOB 42.4/96 3.0/8.5 8.5/11.7 2.3/8.5 44.4/100.0 45.8/82.4 49.1/99.7 person21 LR POC VC SOB 31.2/43.9 0.6/9.4 51.3/79 0.6/5.7 30.8/82.9 18.6/47.2 28.7/73.9 truck2 LR POC 42.9/44.4 86.1/100 48.9/48.8 39.2/44.4 70.5/100.0 88.2/62.3 88.5/99.7 uav4 LR SOB 6.3/14.4 1.9/14.0 3.8/13.3 1.3/14.0 7.6/15.3 2.8/5.7 8.9/19.8 wakeboard2 VC CM 3.1/48.2 3.3/16.0 5.3/21.4 4.9/22.0 4.5/13.1 6.4/12.2 26.1/64.6 car1_s POC OV VC CM 18.4/18.4 18.4/18.4 18.4/18.4 18.4/18.7 23.2/22.1 10.6/10.3 23.1/21.0 person3_s POC OV CM 30.2/20.7 46.5/35 46.1/41.7 30.0/31.2 69.5/46.5 25.1/16.8 48.3/55.8 表 3 算法的速度(fps)比较
算法 Struck SAMF MUSTER KCF DCF SRDCF CFNet 本文 FPS 15.4 6.4 1.0 526.5 470.2 8.4 31.4 28.7 -
[1] TRILAKSONO B R, TRIADHITAMA R, ADIPRAWITA W, et al. Hardware-in-the-loop simulation for visual target tracking of octorotor UAV[J]. Aircraft Engineering and Aerospace Technology, 2011, 83(6): 407–419. doi: 10.1108/00022661111173289 [2] 黄静琪, 胡琛, 孙山鹏, 等. 一种基于异步传感器网络的空间目标分布式跟踪方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1132–1139. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190460HUANG Jingqi, HU Chen, SUN Shanpeng, et al. A distributed space target tracking algorithm based on asynchronous multi-sensor networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1132–1139. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190460 [3] KRISTAN M, MATAS J, LEONARDIS A, et al. A novel performance evaluation methodology for single-target trackers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(11): 2137–2155. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2516982 [4] HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 583–596. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345390 [5] SUN Chong, WANG Dong, LU Huchuan, et al. Correlation tracking via joint discrimination and reliability learning[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 489–497. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00058. [6] SUN Chong, WANG Dong, LU Huchuan, et al. Learning spatial-aware regressions for visual tracking[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8962–8970. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00934. [7] QI Yuankai, ZHANG Shengping, QIN Lei, et al. Hedging deep features for visual tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(5): 1116–1130. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2828817 [8] SONG Yibing, MA Chao, WU Xiaohe, et al. VITAL: Visual tracking via adversarial learning[C]. The 31st IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8990–8999. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00937. [9] BERTINETTO L, VALMADRE J, HENRIQUES J F, et al. Fully-convolutional Siamese networks for object tracking[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 850–865. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-48881-3_56. [10] KRISTAN M, LEONARDIS A, MATAS J, et al. The sixth visual object tracking vot2018 challenge results[C]. Computer Vision ECCV 2018 Workshops, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–53. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-11009-3_1. [11] CHEN Kai and TAO Wenbing. Once for all: A two-flow convolutional neural network for visual tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2018, 28(12): 3377–3386. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2017.2757061 [12] HELD D, THRUN S, SAVARESE S, et al. Learning to track at 100 fps with deep regression networks [C] The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) , Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016, 9905: 749–765. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_45. [13] 侯志强, 陈立琳, 余旺盛, 等. 基于双模板Siamese网络的鲁棒视觉跟踪算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(9): 2247–2255. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181018HOU Zhiqiang, CHEN Lilin, YU Wangsheng, et al. Robust visual tracking algorithm based on Siamese network with dual templates[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(9): 2247–2255. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181018 [14] HUANG Chen, LUCEY S, RAMANAN D, et al. Learning policies for adaptive tracking with deep feature cascades[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 105–114. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.21. [15] SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 618–626. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.74. [16] MUELLER M, SMITH N, and GHANEM B. A benchmark and simulator for UAV tracking[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 445–461. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_27. [17] HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels[C]. The 12th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Florence, Italy, 2012: 702–715. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-33765-9_50. [18] DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, SHAHBAZ K, et al. Accurate scale estimation for robust visual tracking[C]. The British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Nottingham, UK, 2014: 65.1–65.11. doi: 10.5244/C.28.65. [19] HARE S, GOLODETZ S, and SAFFARI A. Struck: Structured output tracking with kernels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(10): 2096–2109. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2509974 [20] ZHANG Jianming, MA Shugao, and SCLAROFF S. MEEM: Robust tracking via multiple experts using entropy minimization[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 188–203. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10599-4_13. [21] HONG Zhibin, CHEN Zhe, WANG Chaohui, et al. Multi-store tracker (MUSTer): A cognitive psychology inspired approach to object tracking[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, USA, 2015: 749–758. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298675. [22] KRISTAN M, PFLUGFELDER R, LEONARDIS A, et al. The visual object tracking VOT2014 challenge results[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 191–217. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-16181-5_14. [23] JIA Xu, LU Huchuan, and YANG M H. Visual tracking via adaptive structural local sparse appearance model[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Providence, USA, 2012: 1822–1829. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2012.6247880. [24] VALMADRE J, BERTINETTO L, HENRIQUES J, et al. End-to-end representation learning for correlation filter based tracking[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5000–5008. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.531. [25] DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, KHAN F S, et al. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4310–4318. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.490. [26] LI Bo, YAN Junjie, WU Wei, et al. High performance visual tracking with Siamese region proposal network[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8971–8980. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00935. -





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:
