Vehicle Trajectory Prediction Method Based on Intersection Context and Deep Belief Network
-
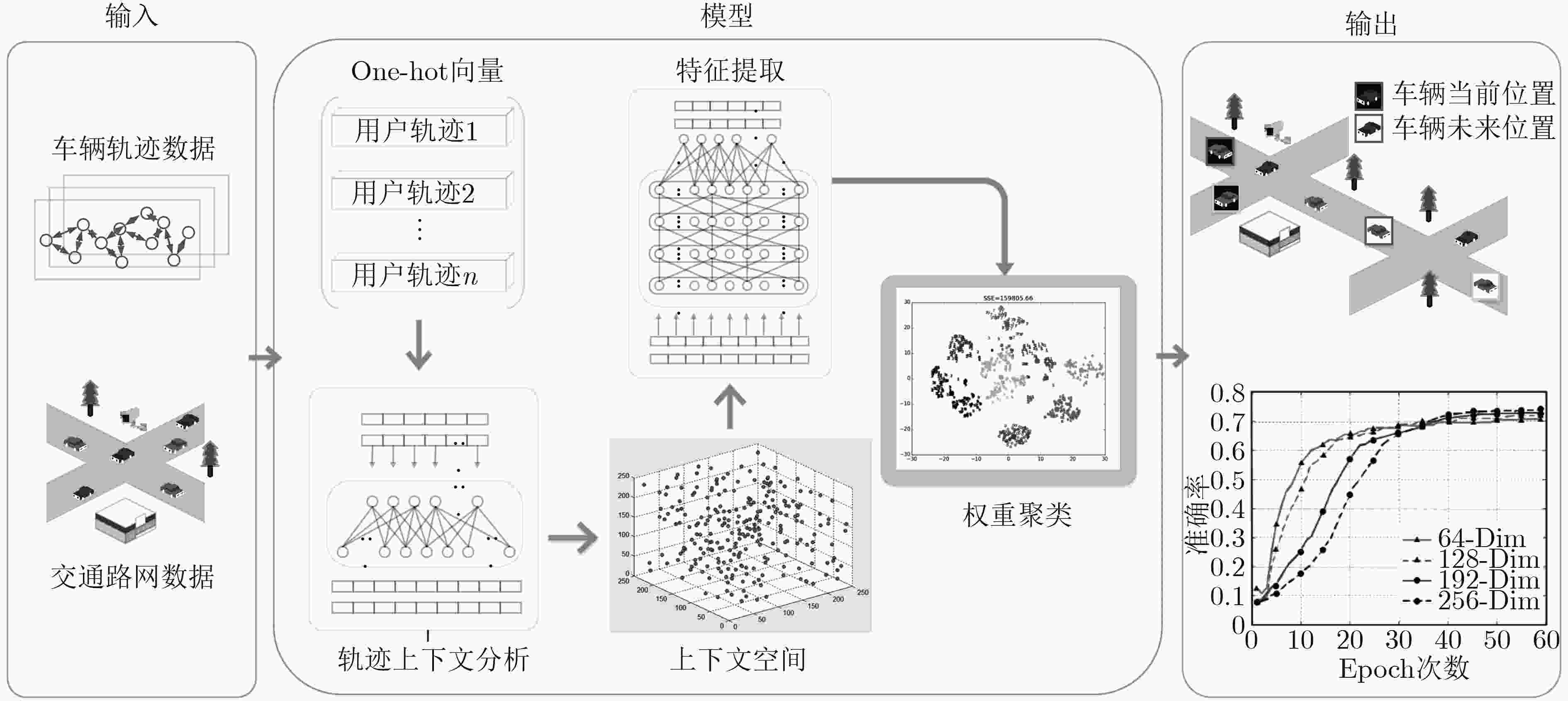
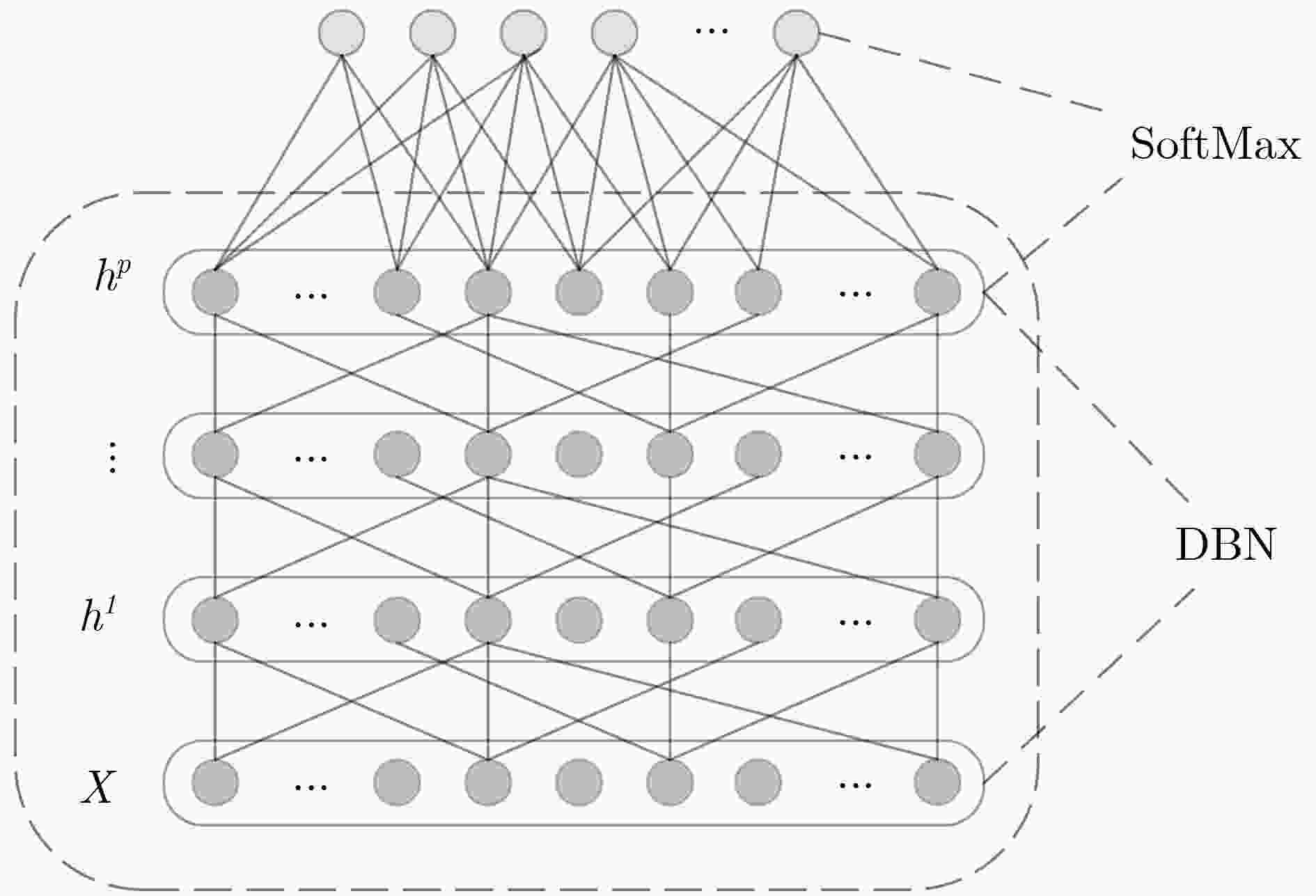
摘要: 针对车辆轨迹预测中节点序列的时序特性和实际路网中的空间关联性,该文提出一种基于深度置信网络和SoftMax (DBN-SoftMax)轨迹预测方法。首先,考虑到轨迹在节点集合中的强稀疏性和一般特征学习方法对新特征的泛化能力不足,该文利用深度置信网络(DBN)较强的无监督特征学习能力,达到提取轨迹局部空间特性的目的;然后,针对轨迹的时序特性,该文采用逻辑回归的预测思路,用当前轨迹集在路网特征空间中的线性组合来预测轨迹;最后,结合自然语言处理领域中的词嵌入的思想,基于实际轨迹中节点存在的上下文关系,运用节点的向量集表征了节点间的交通时空关系。实验结果表明该模型不仅能够有效地提取轨迹特征,并且在拓扑结构复杂的路网中也能得到较好的预测结果。Abstract: For the temporal features of trajectory intersection sequence and spatial correlation of the actual road network, a trajectory prediction method based on the Deep Belief Networks and SoftMax (DBN-SoftMax) is proposed. At first, considering the sparsity of trajectory in an intersection set and the insufficiency of generalization ability in general feature learning methods for new features, the strong unsupervised feature learning ability of Deep Belief Network (DBN) is used to extract the local spatial features of trajectory. Secondly, considering the temporal features of the trajectory, the logistic regression method and the linear combination of the current trajectory set in the road network features space are used to predict the trajectory. Finally, Based on the idea of word embedding in the field of natural language processing and the contextual relationship of intersections in the actual trajectory, the vector set of intersections is used to represent the spatiotemporal relationship of traffic between intersections. The experimental results show that the model can not only extract the trajectory features effectively, but also obtain better prediction performance in a road network with complex topology.
-
表 1 DBN-SoftMax算法
输入: 交通卡口集${{C}} = \{ {{c}}_1,{{c}}_2, ··· ,{{c}}_m\} $; 交通轨迹${{T} } = \{ {{t} }_1,{{t} }_2, ··· ,{{t} }_m\} ,{{t} }_i = {[{{c} }_1,{{c} }_2, ··· ,{{c} }_n]^{\rm{T}}}$; 输出: 预测卡口编号; 初始化$\theta = [\theta_{c1},\theta_{c2}, ··· ,\theta_{cm}],{ x} = [x_{c1},x_{c2}, ··· ,x_{cm}]$ 采样neg个负样本$({\rm{Context}}(c_0),c_0)$对每一个采样
($({\rm{Context}}(c_0),c_i),i = 0,1,2, ··· ,{\rm{neg}}$对每一个采样($({\rm{Context}}(c_0),c_i),i = 0,1,2, ··· ,{\rm{neg}}$ do: for $i = 1$ to $2c$: $\det {\rm{a}}X = 0$ for $j = 0$ to net: 计算$f = \sigma ({{x} }_{c0}^{\rm{T} }\theta_{c_j})$ 计算$g = (y_i - f)\eta $ 更新${\rm{deta}}X = {\rm{deta}}X + g\theta_{cj}$ 更新$\theta_{cj} = \theta_{cj} + gx_{c0}$ end for 更新$x_{c0} = x_{c0} + {\rm{deta}}X$ end for 获取参数$ {\theta ,x}$ 嵌入化轨迹集t ${ {{T} }^{'} } = \{ t_1^{'},t_2^{'}, ··· ,t_m^{'}\} ,{{t} }_i^{'} = {[x_{c1},x_{c2}, ··· ,x_{cn}]^{\rm{T}}}$ 嵌入化向量${{{t}}}_{i}^{'}$首尾拼接得到$ {v}_{i} $ 使用CD-k算法实现RBM DBN深度为DEPTH, RBM隐藏层的大小为RBM-SIZE 初始化$\theta = \{ \theta_1,\theta_2, ··· ,\theta_{{\rm{DEPTH}}}\}$ 初始迭代 for i in DEPTH, do for 在范围ITERATION内迭代, do: 使用CD-k算法: 通过式(16)计算概率分布$p(h_i|v_i;\theta_i)$ 通过式(17)计算概率分布$p(v_i|h_i;\theta_i)$ 采样获取$h_i$和$\theta_i$ 产生$\Delta w_i,\Delta b_i$ 更新$w_i = w_i + \Delta w_i,b_i = b_i + \Delta b_i$ End for End for 权重矩阵${{w}} = \{ w_1,w_2, ··· ,w_m\}$聚类得到${{{w}}^{'} } = \{ w_1^{'},w_2^{'}, ··· ,w_m^{'}\}$ 使用式(20)预测下一个卡口编号 表 2 数据样例
车牌号 通过时间 卡口号 纬度 经度 *A***14B 2017/09/09 09:09 1534****798 Lat1 Lng1 *D***153 2017/09/14 14:49 JF4****798 Lat2 Lng2 *B***433 2017/10/02 09:35 1534****342 Lat3 Lng3 *C***545 2017/10/24 09:51 JF4****798 Lat4 Lng4 *A***90O 2017/11/09 13:54 SH****798 Lat5 Lng5 *E***M78 2017/11/27 18:06 1534****092 Lat6 Lng6 表 3 实验结果指标对比
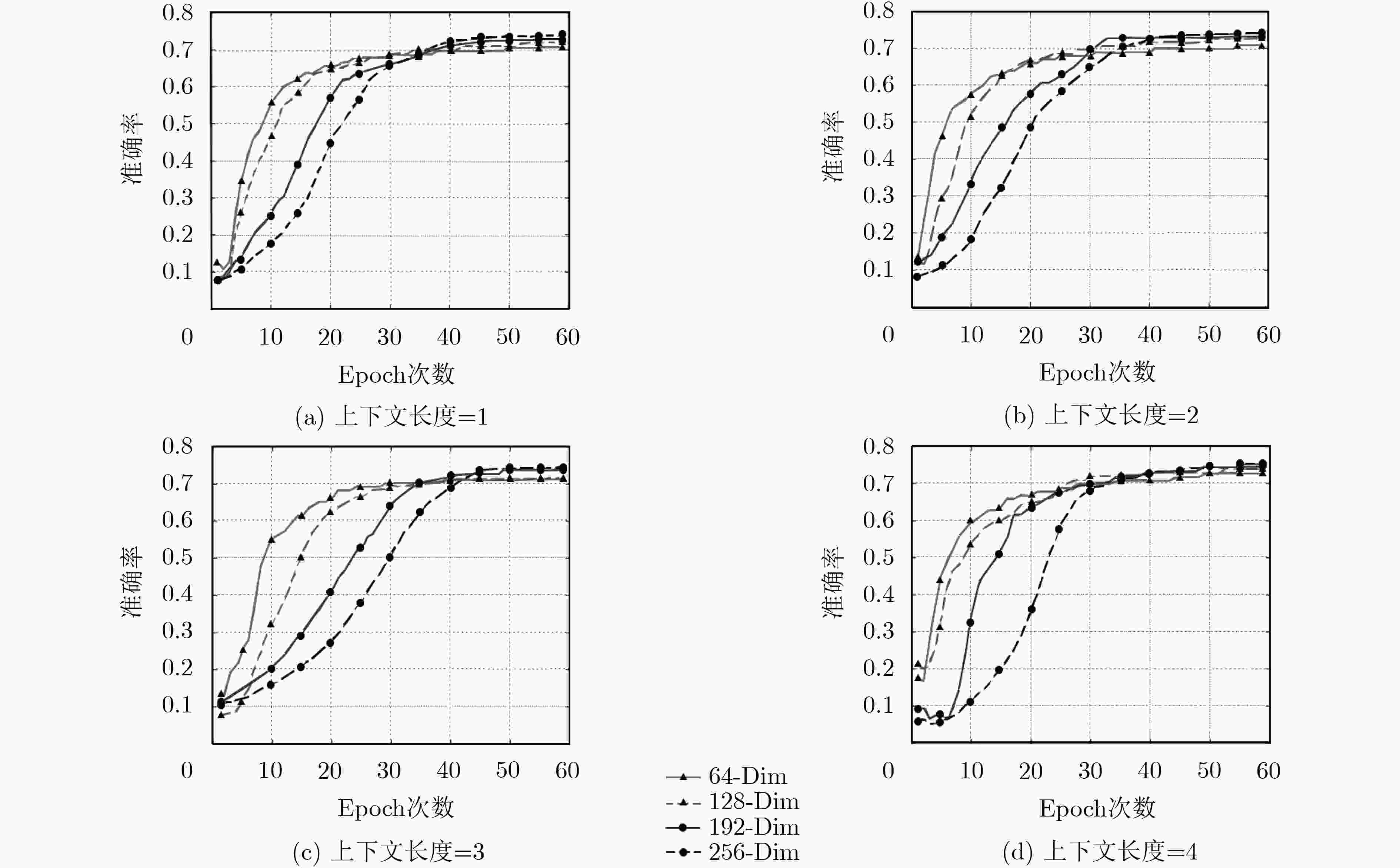
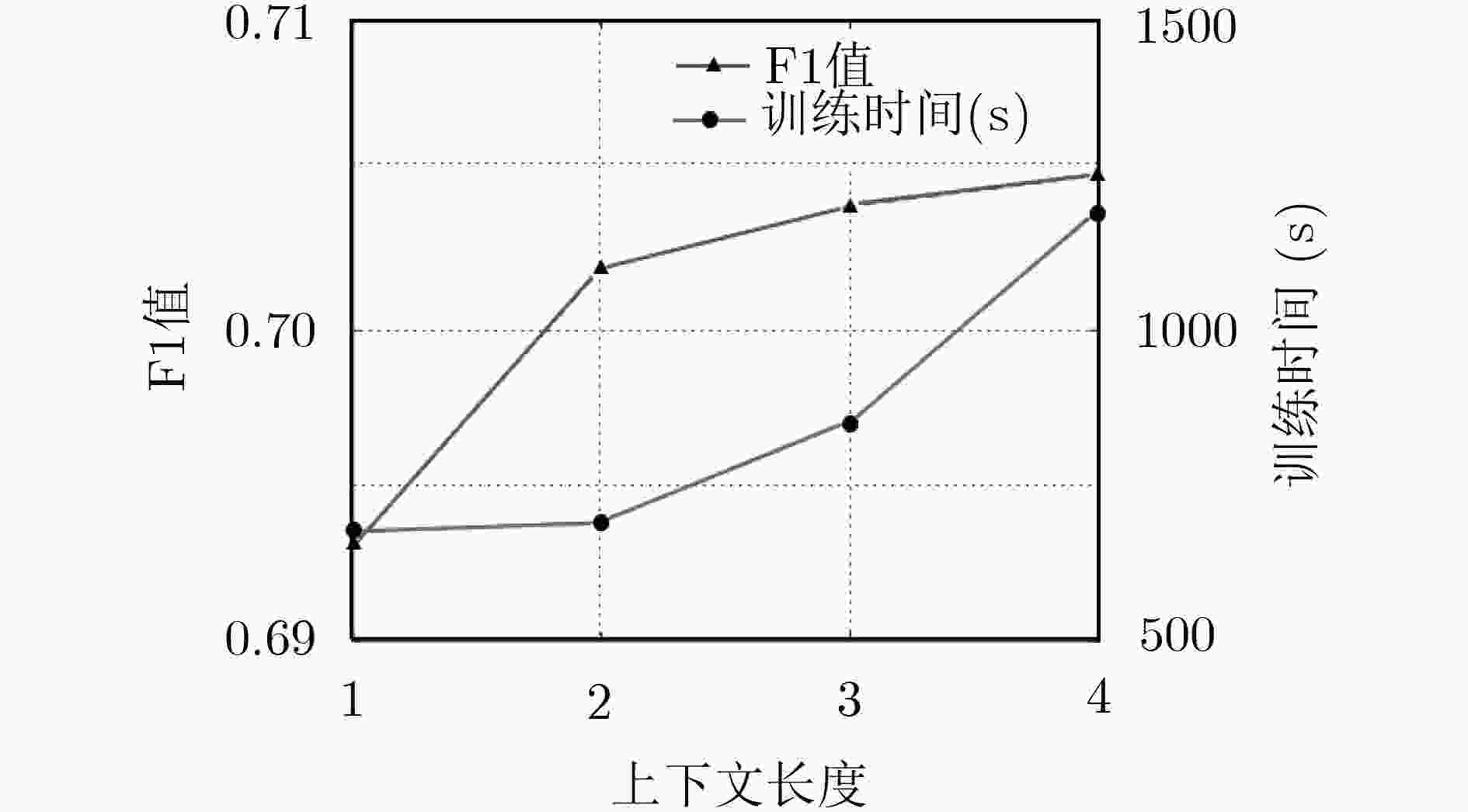
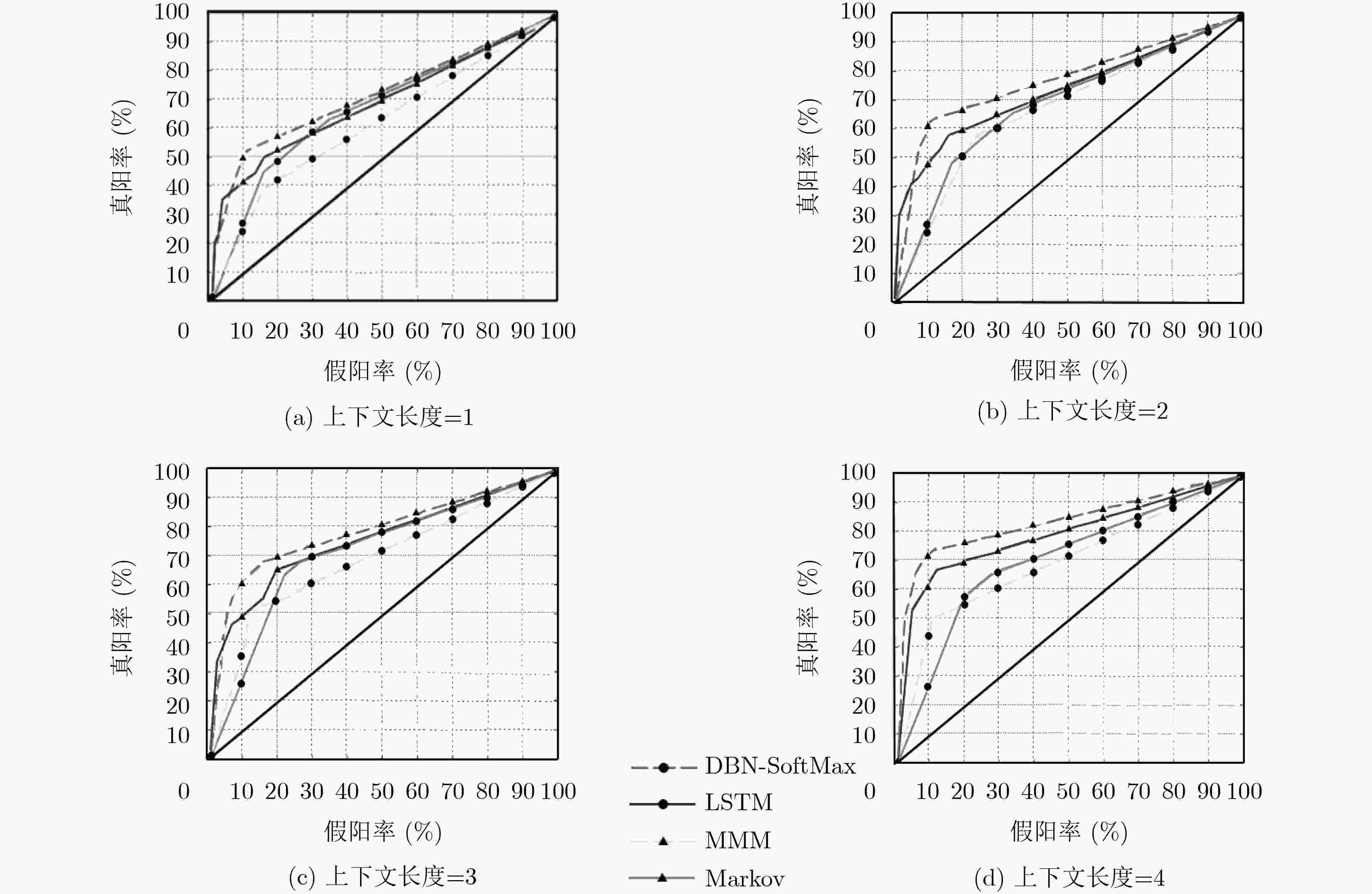
分类器 深度 精准率 召回率 F1值 训练时间(s) 测试时间(s) DBN-SoftMax 1 0.693 0.672 0.6823 675.178 0.001 2 0.704 0.686 0.6948 792.213 0.014 3 0.709 0.693 0.7009 903.291 0.016 4 0.715 0.702 0.7084 1093.629 0.020 5 0.710 0.701 0.7055 1309.841 0.023 NN-SoftMax 0.691 0.684 0.6875 939.620 0.031 RBF SVM 0.681 0.665 0.6729 103.897 98.460 -
[1] 芮兰兰, 李钦铭. 基于组合模型的短时交通流量预测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(5): 1227–1233. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150846RUI Lanlan and LI Qinming. Short-term traffic flow prediction algorithm based on combined model[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(5): 1227–1233. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150846 [2] YUAN Guan, SUN Penghui, ZHAO Jie, et al. A review of moving object trajectory clustering algorithms[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2017, 47(1): 123–144. doi: 10.1007/s10462-016-9477-7 [3] ENDO Y, TODA H, NISHIDA K, et al. Deep feature extraction from trajectories for transportation mode estimation[C]. The 20th Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Auckland, New Zealand, 2016: 54–66. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-31750-2_5. [4] PORIKLI F. Clustering variable length sequences by eigenvector decomposition using HMM[C]. The Joint IAPR International Workshops on Statistical Techniques in Pattern Recognition (SPR) and Structural and Syntactic Pattern Recognition (SSPR), Lisbon, Portugal, 2004: 352–360. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-27868-9_37. [5] WU Bin and QIN Lei. Design and implementation of business-driven bi platform based on cloud computing[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing and Intelligence Systems, Beijing, China, 2011: 118–122. doi: 10.1109/CCIS.2011.6045044. [6] WANG Yuqi, CAO Jiannong, LI Wengen, et al. Exploring traffic congestion correlation from multiple data sources[J]. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 2017, 41: 470–483. doi: 10.1016/j.pmcj.2017.03.015 [7] ANAGNOSTOPOULOS C and HADJIEFTHYMIADES S. Intelligent trajectory classification for improved movement prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2014, 44(10): 1301–1314. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2014.2316742 [8] ZHANG Fusang, JIN Beihong, WANG Zhaoyang, et al. On geocasting over urban bus-based networks by mining trajectories[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 17(6): 1734–1747. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2015.2504513 [9] 陈忠辉, 凌献尧, 冯心欣, 等. 基于模糊C均值聚类和随机森林的短时交通状态预测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(8): 1879–1886. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171090CHEN Zhonghui, LING Xianyao, FENG Xinxin, et al. Short-term traffic state prediction approach based on FCM and random forest[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(8): 1879–1886. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171090 [10] PIRES T J P and FIGUEIREDO M A T. Shape-based trajectory clustering[C]. The 6th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods, Porto, Portugal, 2017: 71–81. doi: 10.5220/0006117400710081. [11] ZHAO Pengxiang, QIN Kun, YE Xinyue, et al. A trajectory clustering approach based on decision graph and data field for detecting hotspots[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2017, 31(6): 1101–1127. doi: 10.1080/13658816.2016.1213845 [12] MIRGE V, VERMA K, and GUPTA S. Dense traffic flow patterns mining in bi-directional road networks using density based trajectory clustering[J]. Advances in Data Analysis and Classification, 2017, 11(3): 547–561. doi: 10.1007/s11634-016-0256-8 [13] BROWN P F, DESOUZA P V, MERCER R L, et al. Class-based n-gram models of natural language[J]. Computational Linguistics, 1992, 18(4): 467–479. [14] MIKOLOV T, SUTSKEVER I, CHEN Kai, et al. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality[C]. The 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, United States, 2013: 3111–3119. [15] HINTON G E, OSINDERO S, and TEH Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets[J]. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(7): 1527–1554. doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527 [16] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. [17] LAROCHELLE H, BENGIO Y, LOURADOUR J, et al. Exploring strategies for training deep neural networks[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2009, 10(1): 1–40. [18] MENZ L, HERBERTH R, LUO Chunbo, et al. An improved method for mobility prediction using a Markov model and density estimation[C]. 2018 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 2018: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/WCNC.2018.8377086. [19] XUE Hao, HUYNH D Q, and REYNOLDS M. SS-LSTM: A hierarchical LSTM model for pedestrian trajectory prediction[C]. 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2018: 1186–1194. doi: 10.1109/WACV.2018.00135. [20] GIACOMETTI A and SOULET A. Frequent pattern outlier detection without exhaustive mining[C]. The 20th Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Auckland, New Zealand, 2016: 196–207. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-31750-2_16. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
