Recognition Method of Radar Signal Based on the Energy Cumulant of Choi-Williams Distribution and Improved Semi-supervised Naïve Bayes
-
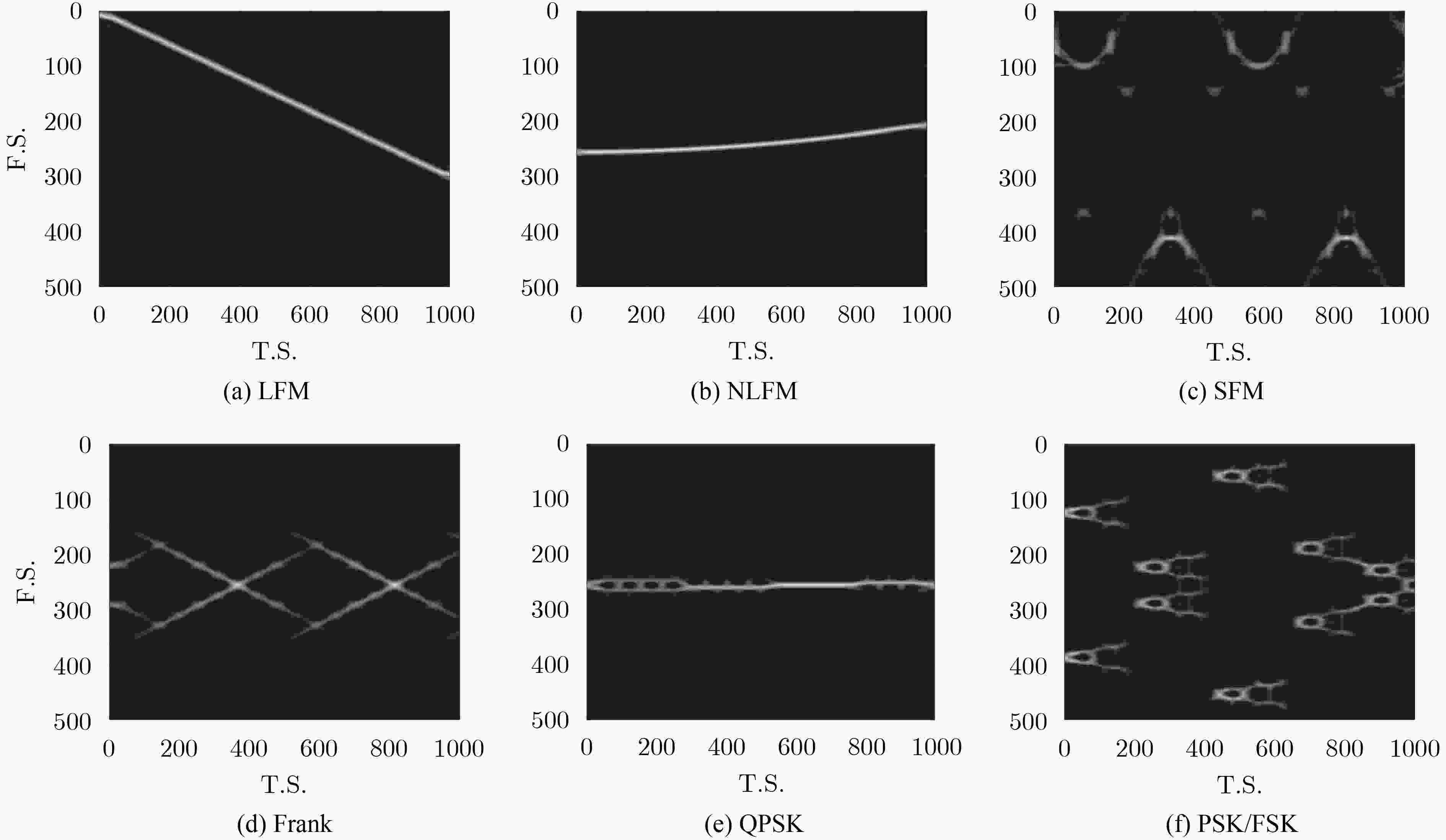
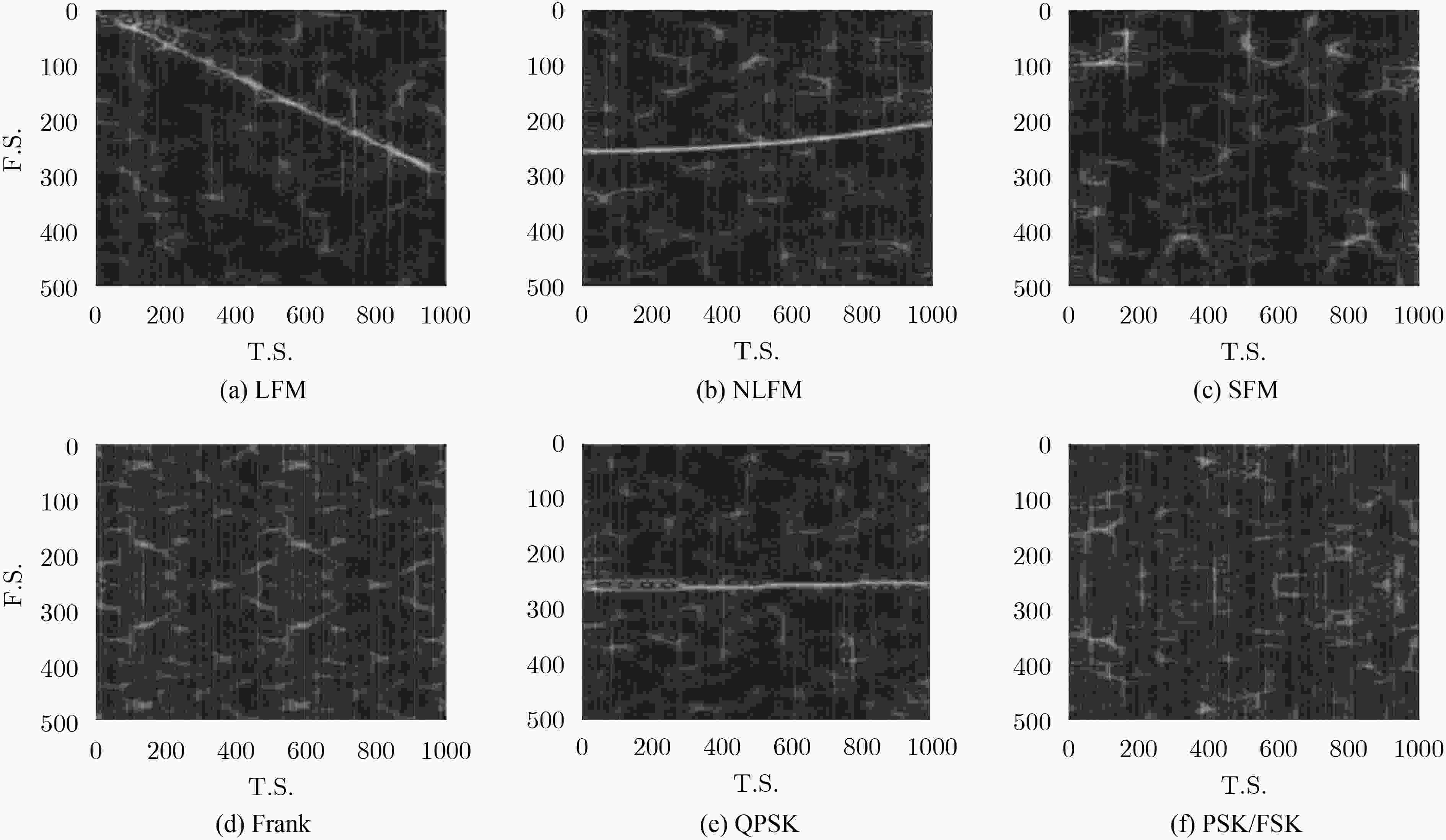
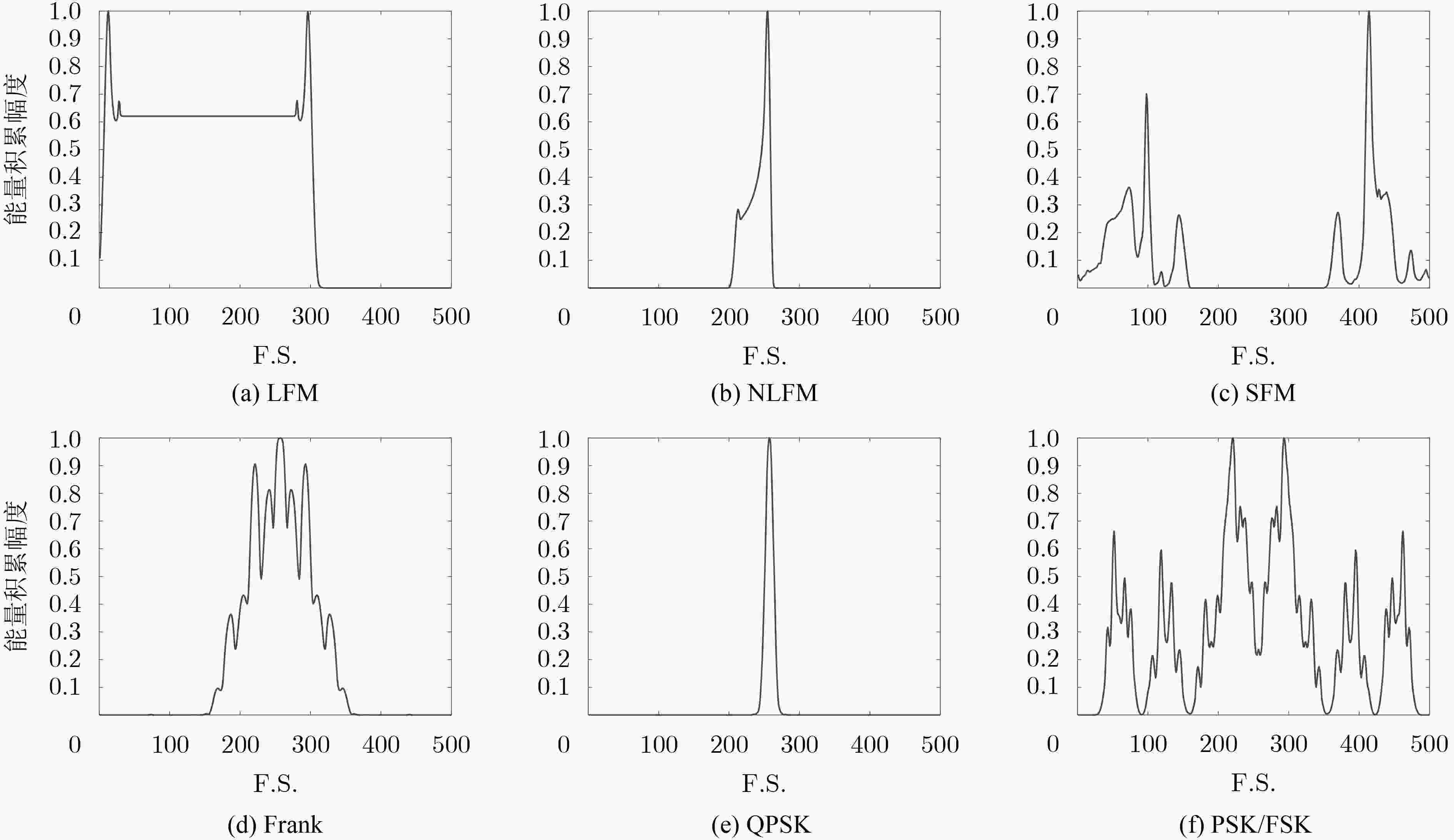
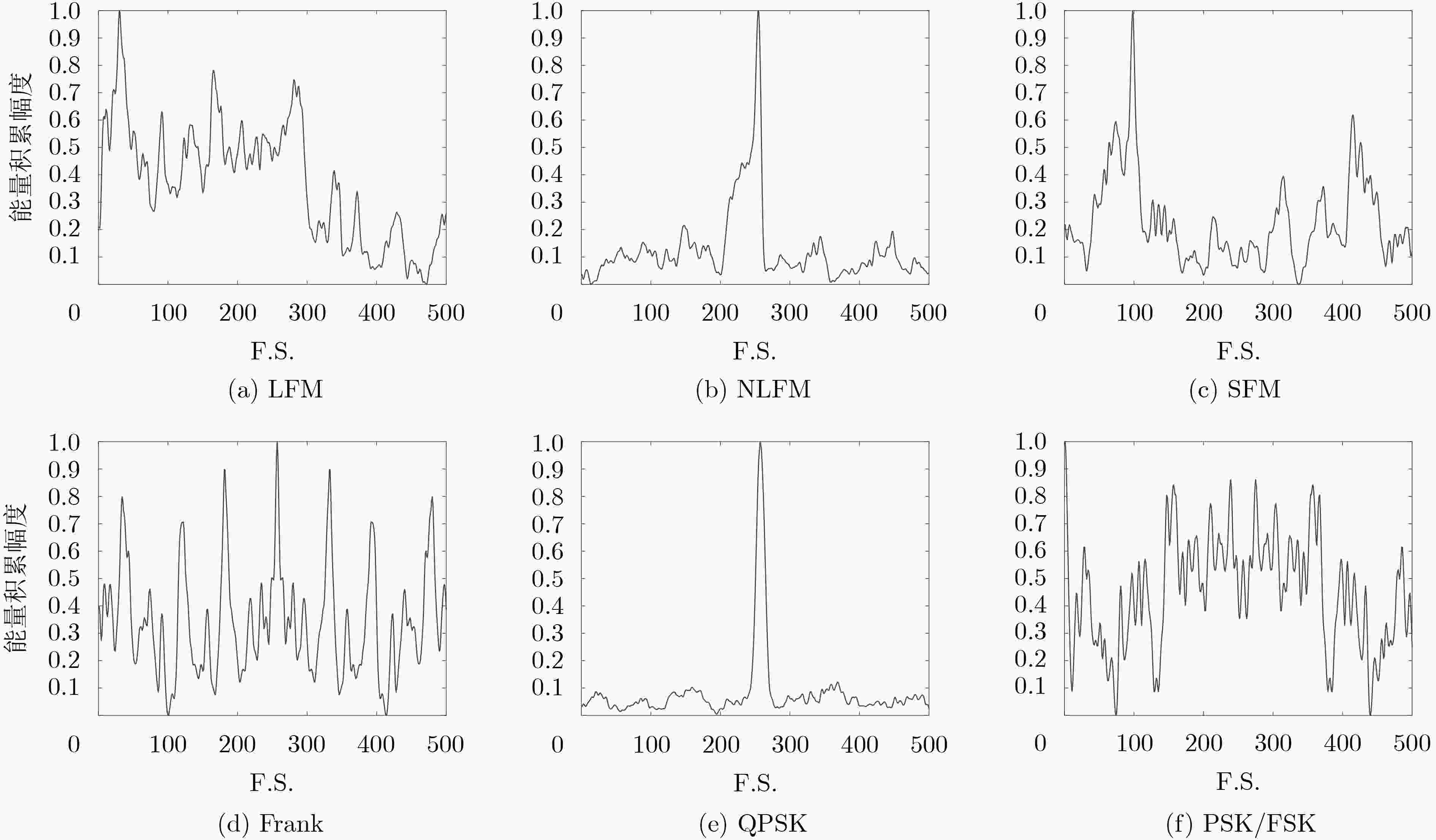
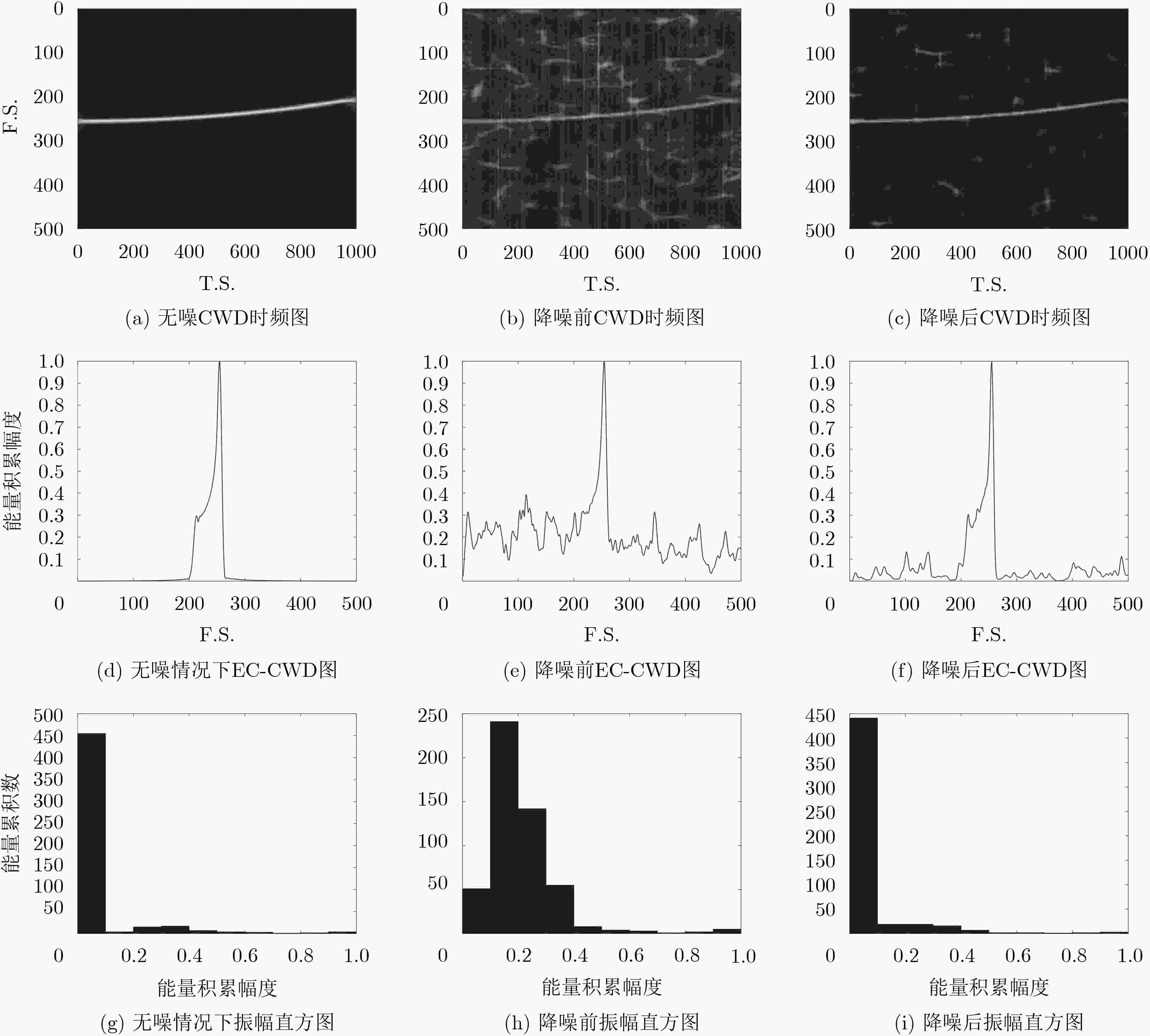
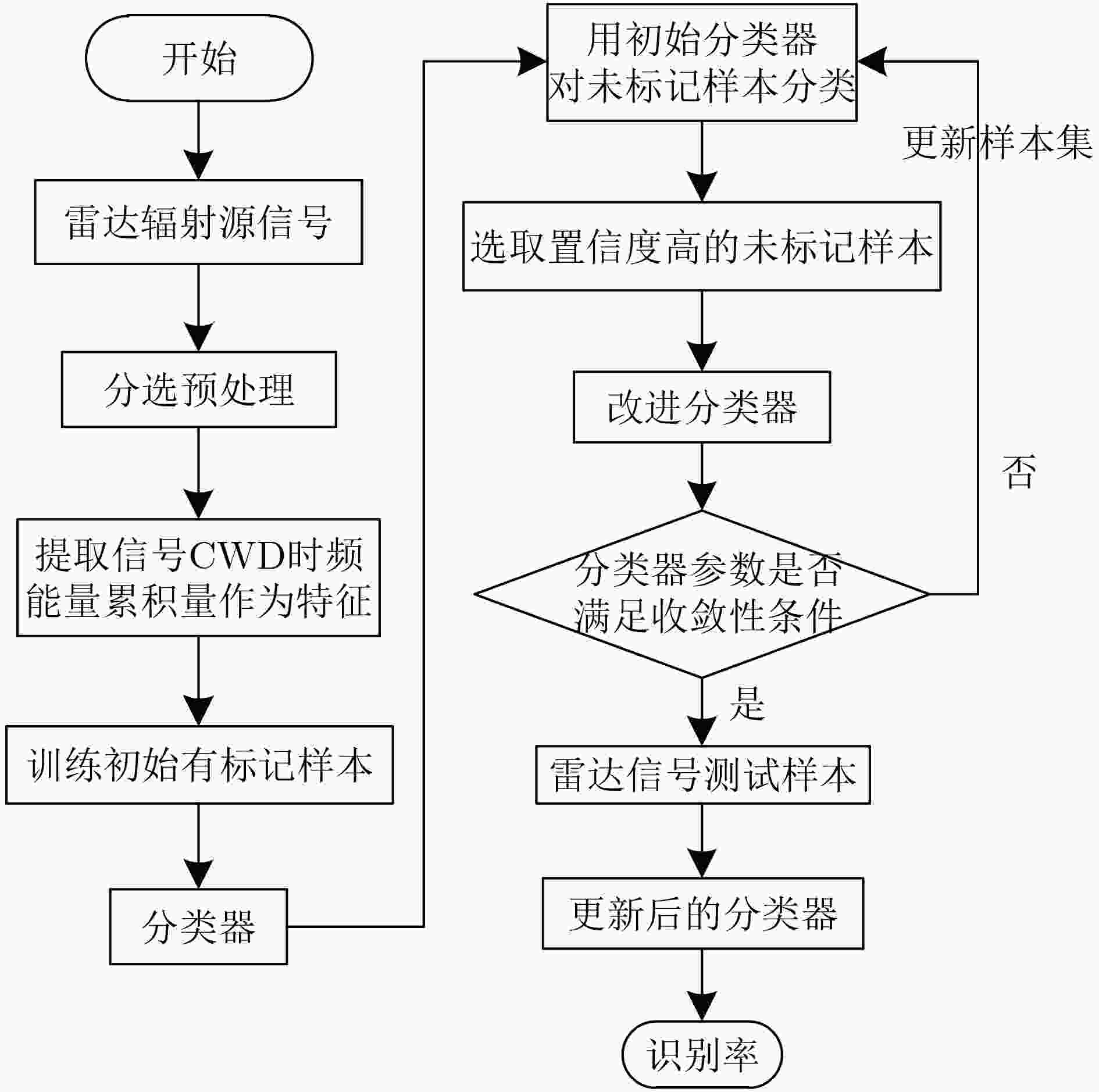
摘要: 针对非合作电子侦察雷达信号识别中先验信息残缺的问题,该文提出一种基于Choi-Williams时频分布(CWD)的改进半监督朴素贝叶斯的识别算法(ISNB)。首先对CWD进行降噪预处理,然后通过计算降噪后CWD不同时间下各频率采样值的积累量,从而得到CWD的能量积累量这一新特征;针对传统的半监督朴素贝叶斯(SNB)在更新训练样本集过程中会产生迭代错误的不足,通过在无标签样本集生成的置信度列表中选取置信度高的样本添加到有标签样本集中,再利用预测后的分类结果对分类器参数进行改进,进而构建改进的SNB分类器,有效解决了传统SNB算法分类精度低且分类性能不稳定的缺点。理论分析和仿真结果表明,所提方法相比于传统SNB算法均提高了3%左右;在相同信噪比下,相比于传统的主成分分析加支持向量机法,该算法具有更高的分类识别率和更好的分类性能。
-
关键词:
- 雷达信号识别 /
- Choi-Williams时频分布 /
- 能量累积量 /
- 朴素贝叶斯 /
- 半监督学习
Abstract: In order to solve incomplete prior information of radar in non-cooperative electronic countermeasure environment, a novel recognition algorithm named ISNB (Improved Semi-supervised Naïve Bayes) based on the energy cumulant of Choi-Williams Distribution(CWD) is put forward. This algorithm extracts the energy cumulant of Choi-Williams distribution of radar signals as the recognition feature. The energy cumulant of CWD is attained by calculating the accumulations of each frequency sample value with the different time samples. Before this procedure, CWD is processed by base noise reduction. Considering disadvantages of traditional Semi-supervised Naïve Bayes(SNB) which comes from repeated errors in updating sample sets, it uses ISNB to construct classifier, and then completes the recognition of tested sample sets. ISNB selects those samples with high degree of confidence which comes from generated confidence. Theoretical analysis and simulation results show that the proposed method is about 3% higher than the traditional SNB algorithm. Under the same signal-to-noise ratio, this algorithm has higher classification recognition rate and better classification performance than the traditional principal component analysis plus support vector machine. -
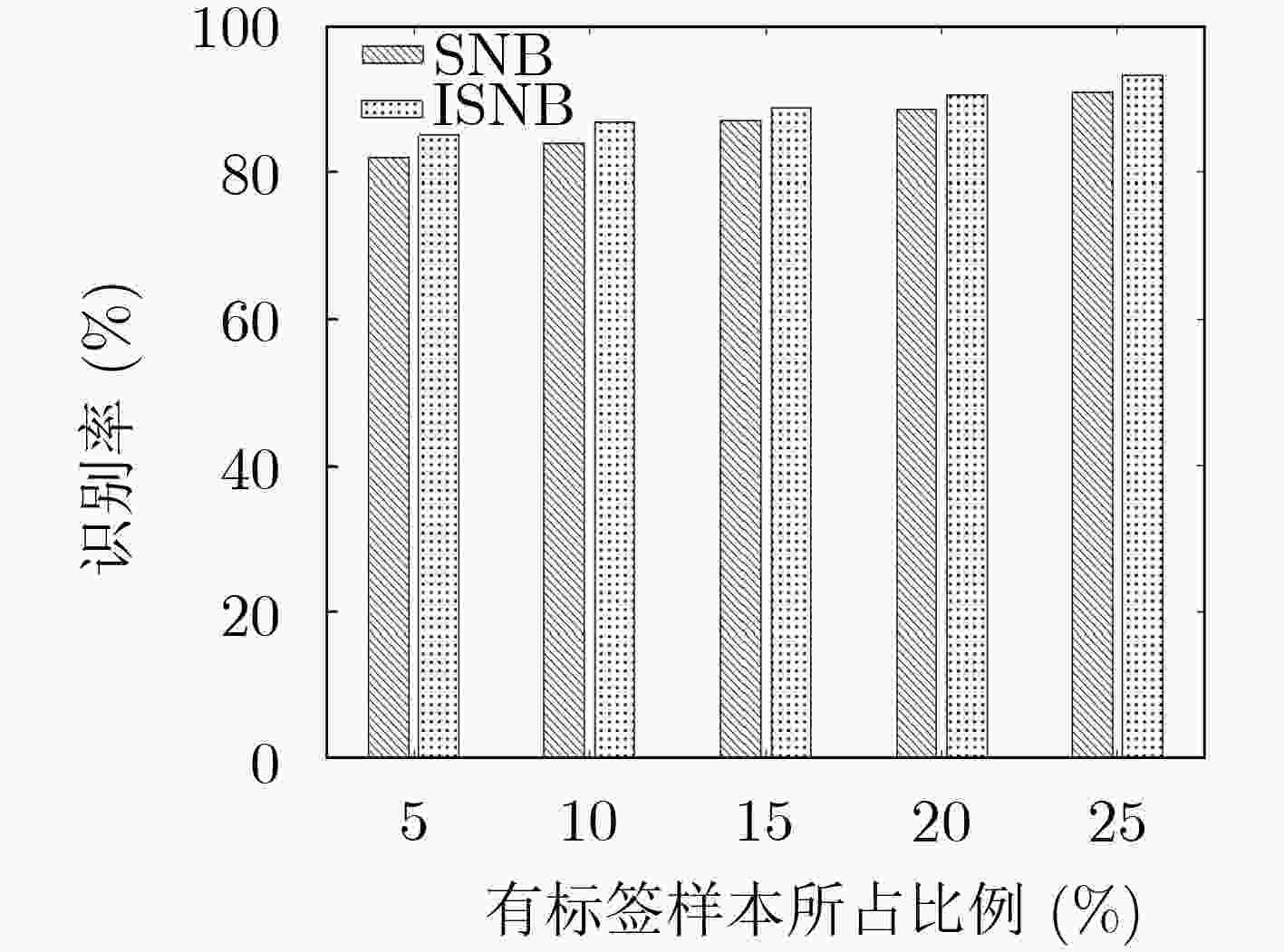
表 1 两种方法在不同标记样本下的识别效果比较
有标签样本比例(%) 5 10 15 20 25 不同算法 SNB ISNB SNB ISNB SNB ISNB SNB ISNB SNB ISNB LFM 86.25 89.00 89.50 93.75 92.25 96.25 95.75 98.50 99.00 99.75 NLFM 87.75 89.50 88.50 90.25 91.25 91.00 90.50 92.50 90.50 92.50 SFM 79.25 81.75 82.50 85.00 85.25 87.00 86.75 89.50 91.00 93.75 Frank 76.00 80.25 78.25 83.00 81.75 83.25 85.50 85.25 87.25 89.50 QPSK 85.75 88.25 86.25 89.75 88.00 90.50 88.75 91.25 89.75 92.00 PSK/FSK 77.50 81.50 79.00 83.25 83.75 85.25 84.50 86.75 88.25 92.50 平均识别率(%) 82.08 85.04 84.00 86.83 87.04 88.88 88.63 90.64 90.96 93.33 表 2 不同信噪比下的识别正确率
信噪比(dB) –2 0 2 4 6 8 文献[19]+SNB 51.35 58.26 65.33 73.79 77.55 81.86 PCA-SVM 38.67 45.33 58.91 67.68 75.72 81.93 SNB 55.28 61.28 68.74 76.56 84.57 90.96 ISNB 58.37 67.37 72.58 77.42 87.44 93.33 -
ZHOU Zhiwen, HUANG Gaoming, CHEN Haiyang, et al. Automatic radar waveform recognition based on deep convolutional denoising auto-encoders[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2018, 37(9): 4034–4048. doi: 10.1007/s00034-018-0757-0 黄颖坤, 金炜东, 葛鹏, 等. 基于多尺度信息熵的雷达辐射源信号识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1084–1091. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180535HUANG Yingkun, JIN Weidong, GE Peng, et al. Radar emitter signal identification based on multi-scale information entropy[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1084–1091. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180535 YANG Zhutian, WU Zhilu, YIN Zhendong, et al. Hybrid radar emitter recognition based on rough k-means classifier and relevance vector machine[J]. Sensors, 2013, 13(1): 848–864. doi: 10.3390/s130100848 RU Xiaohu, LIU Zheng, JIANG Wenli, et al. Recognition performance analysis of instantaneous phase and its transformed features for radar emitter identification[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(5): 945–952. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0512 陈锡明, 祝正威, 卢显良. 新型雷达辐射源识别专家系统的研究与实现[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2000, 22(8): 58–62. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2000.08.017CHEN Ximing, ZHU Zhengwei, and LU Xianliang. Research and implementation on a new radar radiating-source recognizing expert system[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2000, 22(8): 58–62. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2000.08.017 张葛祥, 胡来招, 金炜东. 基于熵特征的雷达辐射源信号识别[J]. 电波科学学报, 2005, 20(4): 440–445. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2005.04.006ZHANG Gexiang, HU Laizhao, and JIN Weidong. Radar emitter signal recognition based on entropy features[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2005, 20(4): 440–445. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2005.04.006 王彩云, 黄盼盼, 李晓飞, 等. 基于AEPSO-SVM算法的雷达HRRP目标识别[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(9): 1984–1989. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.09.10WANG Caiyun, HUANG Panpan, LI Xiaofei, et al. Radar HRRP target recognition based on AEPSO-SVM algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(9): 1984–1989. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.09.10 胡国兵, 徐立中, 徐淑芳, 等. 基于能量聚焦效率检验的信号脉内调制识别[J]. 通信学报, 2013, 34(6): 136–145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436x.2013.06.017HU Guobing, XU Lizhong, XU Shufang, et al. Intrapulse modulation recognition of signals based on statistical test of energy focusing efficiency[J]. Journal on Communications, 2013, 34(6): 136–145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436x.2013.06.017 王磊, 史亚, 姬红兵. 基于多集典型相关分析的雷达辐射源指纹识别[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 40(2): 164–171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2013.02.027WANG Lei, SHI Ya, JI Hongbing. Specific radar emitter identification using multiset canonical correlation analysis[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2013, 40(2): 164–171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2013.02.027 白航, 赵拥军, 胡德秀. 时频图像局部二值模式特征在雷达信号分类识别中的应用[J]. 宇航学报, 2013, 34(1): 139–146. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2013.01.020BAI Hang, ZHAO Yongjun, and HU Dexiu. Radar signal recognition based on the local binary pattern feature of time-frequency image[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2013, 34(1): 139–146. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2013.01.020 孟凡杰, 唐宏, 王义哲. 基于多特征融合的雷达辐射源信号识别[J]. 计算机仿真, 2016, 33(3): 18–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2016.03.005MENG Fanjie, TANG Hong, and WANG Yizhe. Radar emitter signal recognition based on fusion of features[J]. Computer Simulation, 2016, 33(3): 18–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2016.03.005 LI Rong, WANG Huaning, CUI Yanmei, et al. Solar flare forecasting using learning vector quantity and unsupervised clustering techniques[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics and Astronomy, 2011, 54(8): 1546–1552. doi: 10.1007/s11433-011-4391-0 李序, 张葛祥, 荣海娜. 基于加权K-近邻法和SVC的雷达辐射源信号识别[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2010, 32(6): 1215–1219. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2010.06.023LI Xu, ZHANG Gexiang, and RONG Haina. Radar emitter signal recognition based on weighted K-nearest neighbor and SVC[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2010, 32(6): 1215–1219. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2010.06.023 REN Minglun, DUAN Juanjuan, and YANG Shanlin. Decision models evaluation using fuzzy pattern recognition[C]. 2007 IEEE International Conference on Grey Systems and Intelligent Services, Nanjing, China, 2007: 1035–1039. doi: 10.1109/GSIS.2007.4443430. LIN Yun, XU Xiaochun, and WANG Zicheng. New individual identification method of radiation source signal based on entropy feature and SVM[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014, 21(1): 98–101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9113.2014.01.014 刘明骞, 孟燕, 张卫东. 雷达辐射源信号识别的效能综合评估方法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2019, 46(6): 1–8. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2019.06.001LIU Mingqian, MENG Yan, and ZHANG Weidong. Method for comprehensive evaluation of effectiveness of radar emitter signals recognition[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2019, 46(6): 1–8. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2019.06.001 杜兰, 魏迪, 李璐, 等. 基于半监督学习的SAR目标检测网络[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 154–163. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190783DU Lan, WEI Di, LI Lu, et al. SAR target detection network via semi-supervised learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 154–163. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190783 FENG Zhipeng, LIANG Ming, and CHU Fulei. Recent advances in time-frequency analysis methods for machinery fault diagnosis: A review with application examples[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2013, 38(1): 165–205. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2013.01.017 WANG Chao, WANG Jian, and ZHANG Xudong. Automatic radar waveform recognition based on time-frequency analysis and convolutional neural network[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, New Orleans, USA, 2017. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2017.7952594. WANG Xuebao, HUANG Gaoming, ZHOU Zhiwen, et al. Radar emitter recognition based on the short time Fourier transform and convolutional neural networks[C]. The 10th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics, Shanghai, China, 2017. doi: 10.1109/CISP-BMEI.2017.8302111. 曾谁飞, 张笑燕, 杜晓峰, 等. 改进的朴素贝叶斯增量算法研究[J]. 通信学报, 2016, 37(10): 81–91.ZENG Shuifei, ZHANG Xiaoyan, DU Xiaofeng, et al. Improved incremental algorithm of Naive Bayes[J]. Journal on Communications, 2016, 37(10): 81–91. MANN G S and MCCALLUM A. Generalized expectation criteria for semi-supervised learning with weakly labeled data[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2010, 11(2): 955–984. HALL M, FRANK E, HOLMES G, et al. The WEKA data mining software: An update[J]. ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter, 2009, 11(1): 10–18. doi: 10.1145/1656274.1656278 MODHA D S and SPANGLER W S. Feature weighting in k-means clustering[J]. Machine Learning, 2003, 52(3): 217–237. doi: 10.1023/A:1024016609528 张锐戈, 谭永红. 双谱主成分分析的滚动轴承智能故障诊断[J]. 振动工程学报, 2014, 27(5): 763–769. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4523.2014.05.017ZHANG Ruige and TAN Yonghong. Intelligent fault diagnosis of rolling element bearings based on bispectrum principal components analysis[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2014, 27(5): 763–769. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4523.2014.05.017 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
