A Fast Ambiguity Solution Method for Network RTK Reference Station
-
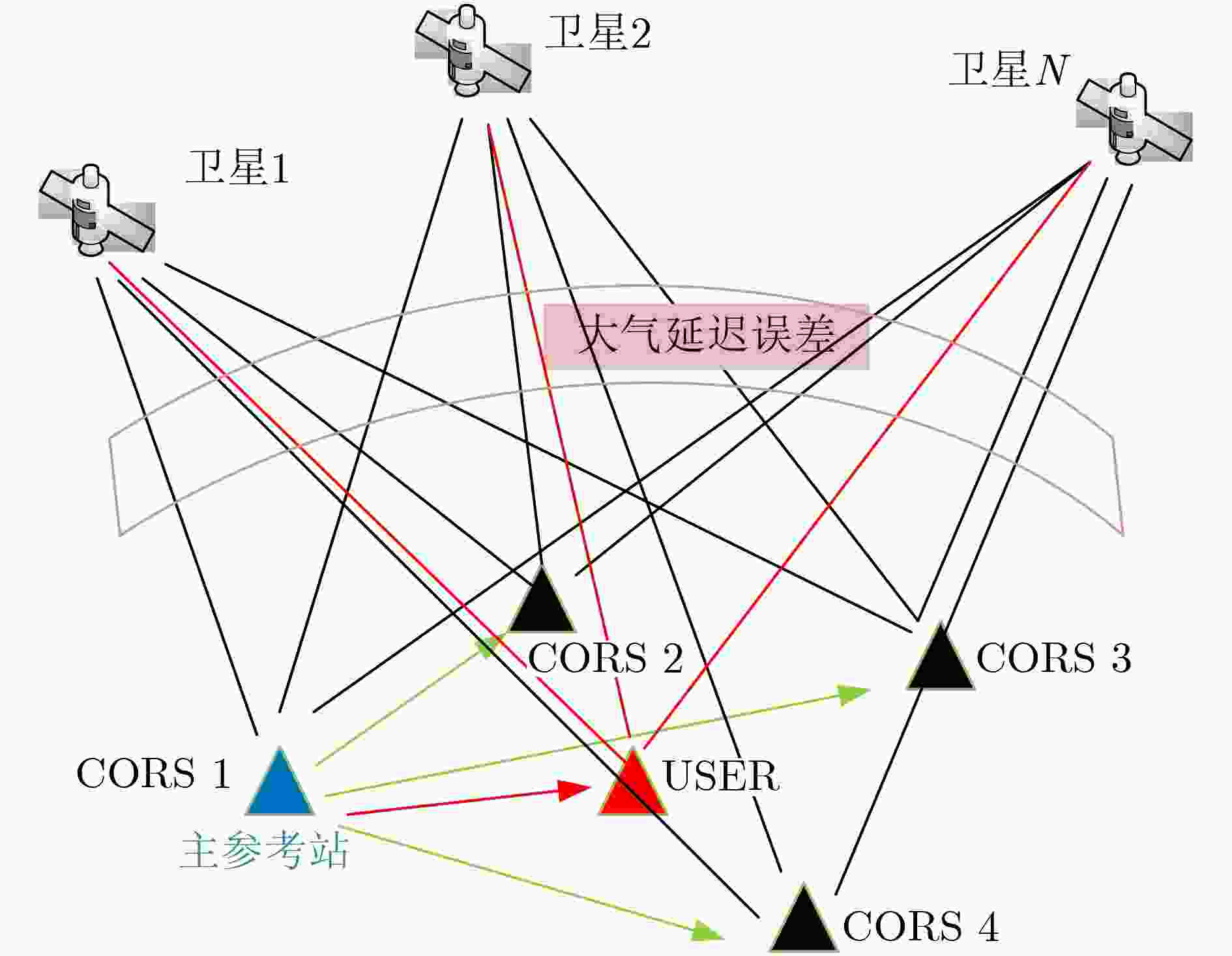
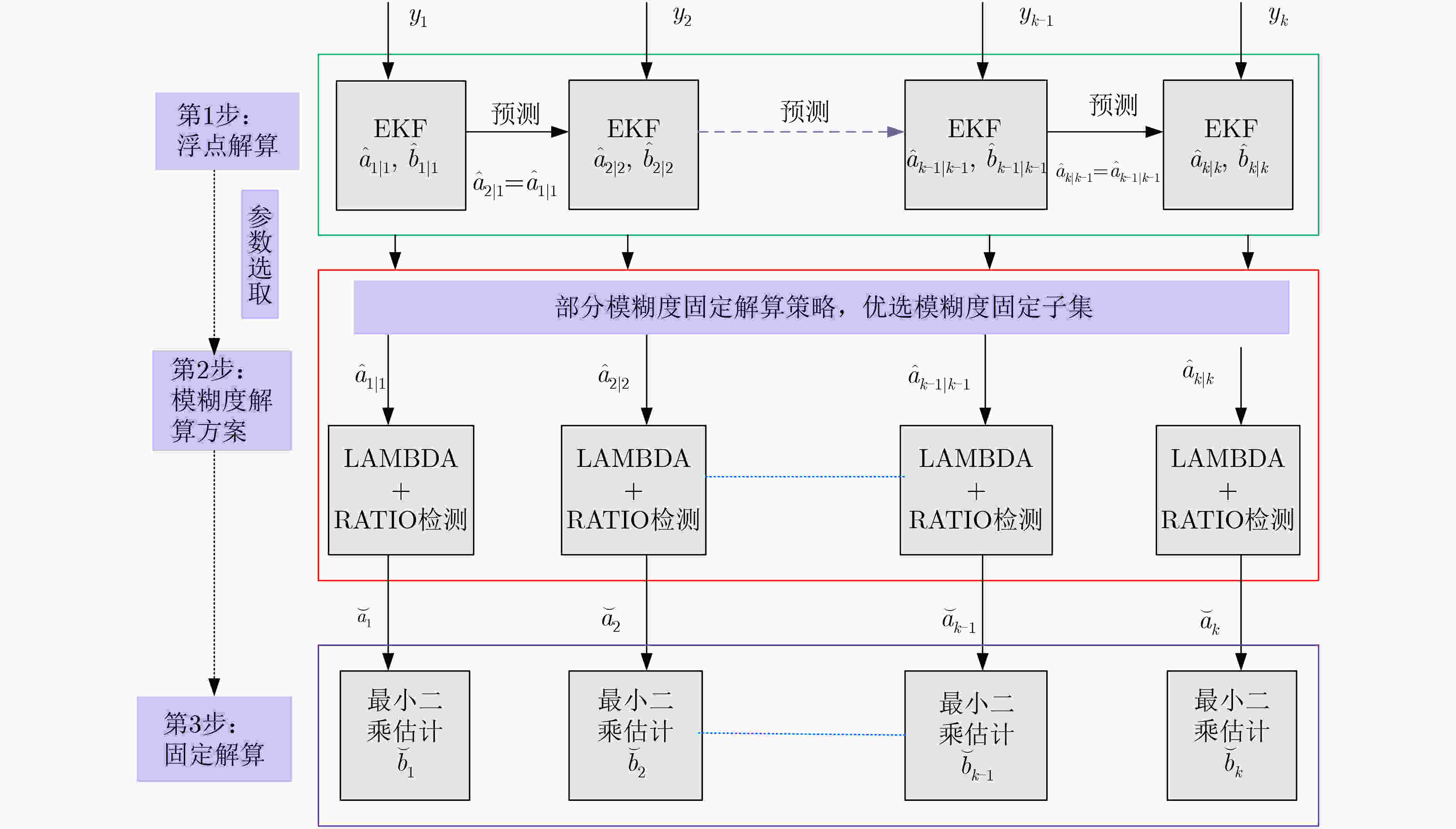
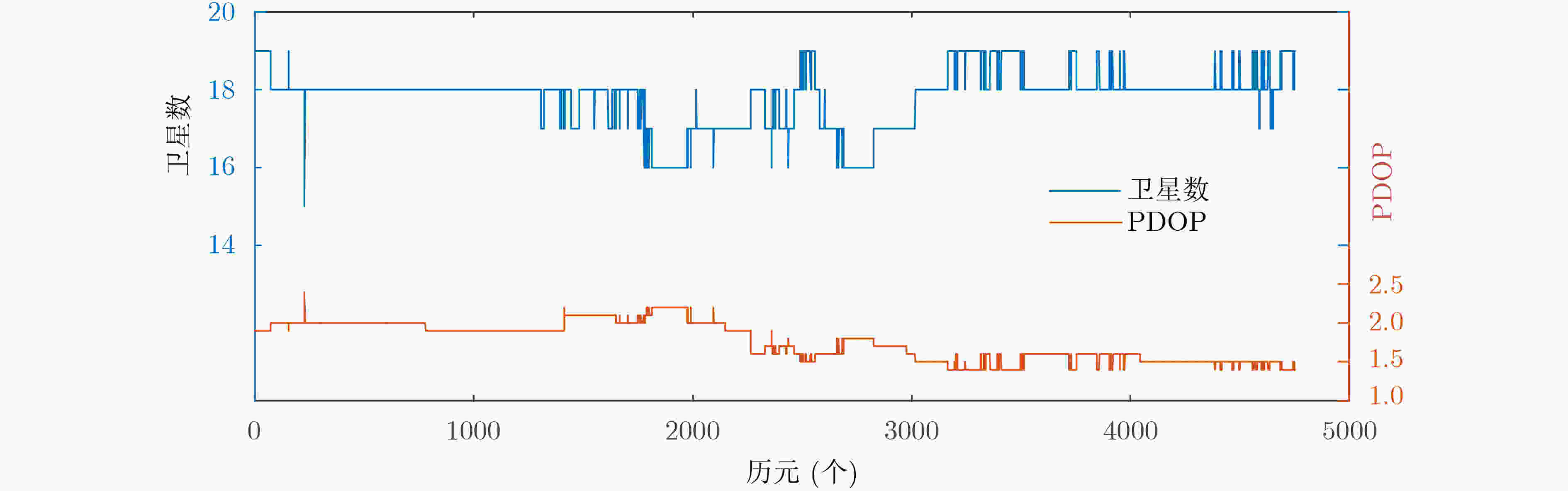
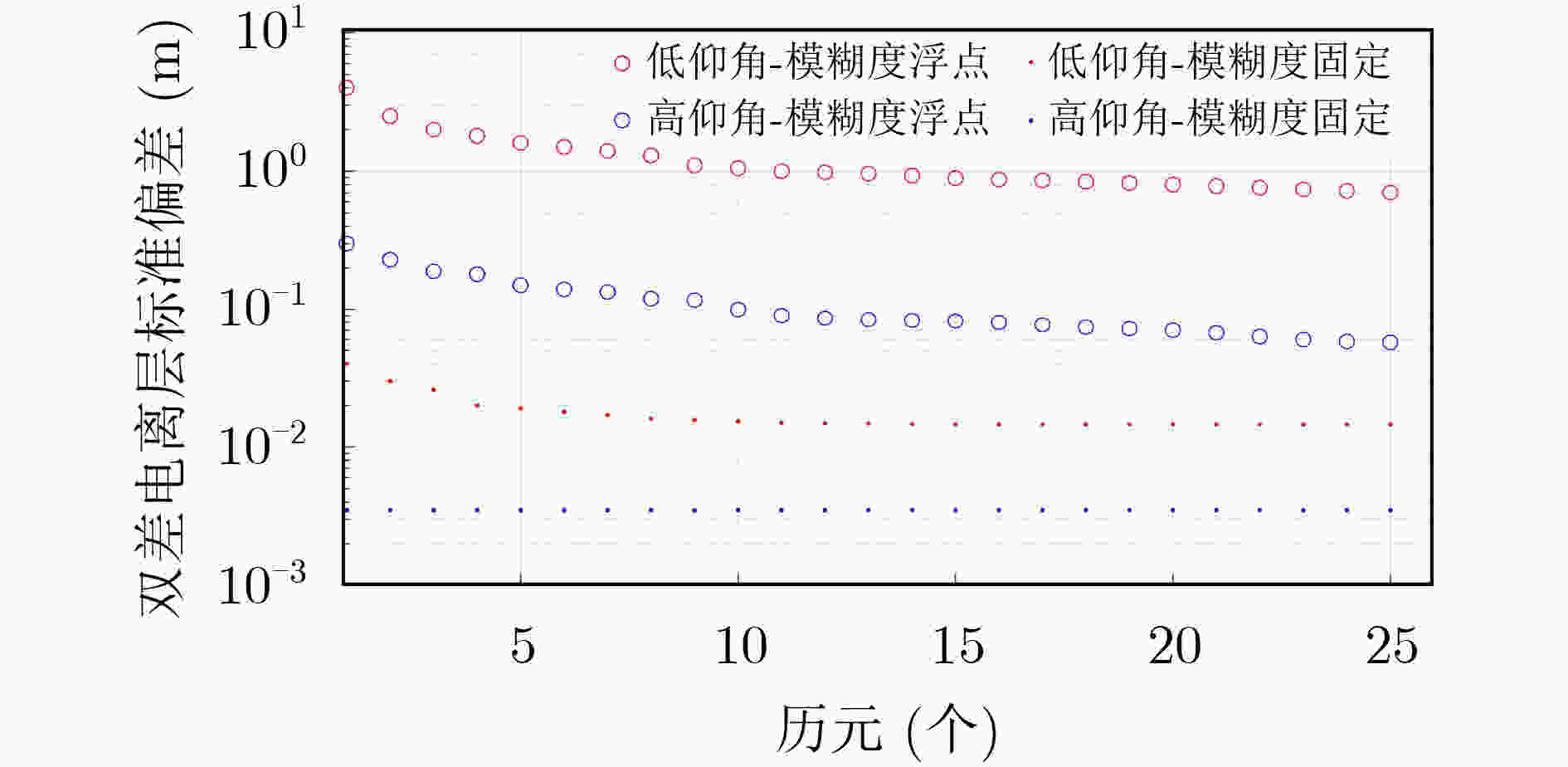
摘要: 针对由于存在大气因素的干扰,网络载波相位差分技术(RTK)参考站模糊度解算会受到影响,同时当新卫星升至预先设置的截止高度角以上时,需要较长的初始化收敛时间,该文提出一种网络RTK参考站模糊度快速解算方法。该方法先利用电离层加权策略,辅助基线模糊度的快速解算,再采用扩展卡尔曼滤波(EKF)技术估计浮点模糊度,利用部分模糊度解算方法,最后通过最小二乘模糊度降相关(LAMBDA)算法和比率(RATIO)检测对模糊度进行固定解算。实验结果表明,该方法可以显著提高网络RTK参考站模糊度的固定率和缩短初始化收敛时间。Abstract: Due to the interference of atmospheric factors, the ambiguity resolution of network Real Time kinematic (RTK) reference stations is affected, and when new satellites rise above the preset cutoff height, a longer initialization convergence time is required. A fast ambiguity solution method for Network RTK reference stations is proposed. Firstly, the ionosphere weighting strategy is used to assist the fast resolution of baseline ambiguity. Then, Extended Kalman Filter(EKF)is used to estimate ambiguity floating solution; The partial ambiguity solution method is adopted. Finally, the ambiguities are fixed in combination with Least squares AMBiguity Decorrelation Adjustment(LAMBDA) and RATIO detection. Experiments results show that this method can significantly improve the ambiguity fixation rate of network RTK reference stations and shorten the initialization convergence time.
-
Key words:
- Network RTK /
- Ambiguity resolution /
- Partial ambiguity fixed /
- Ionosphere weighted method
-
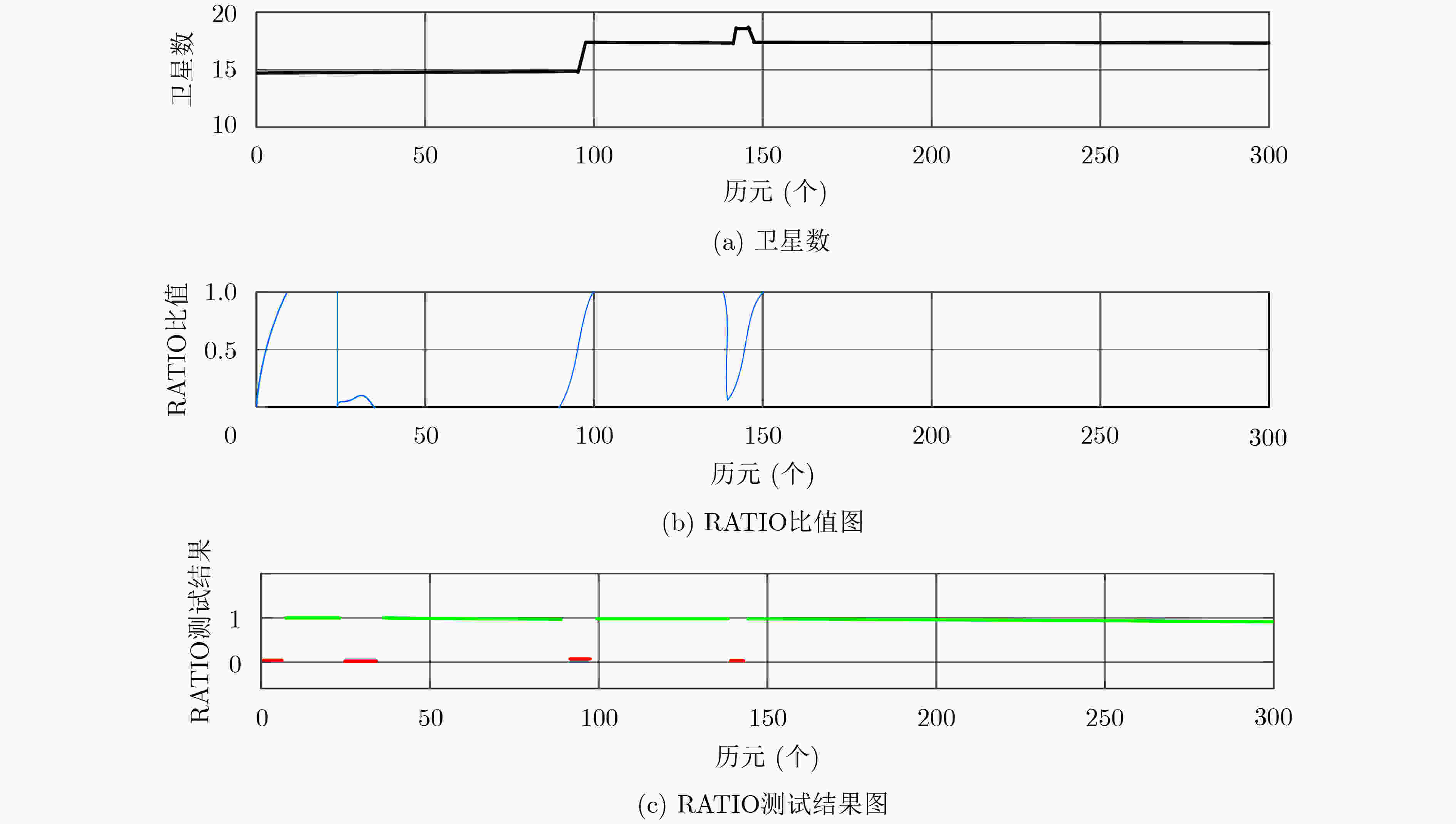
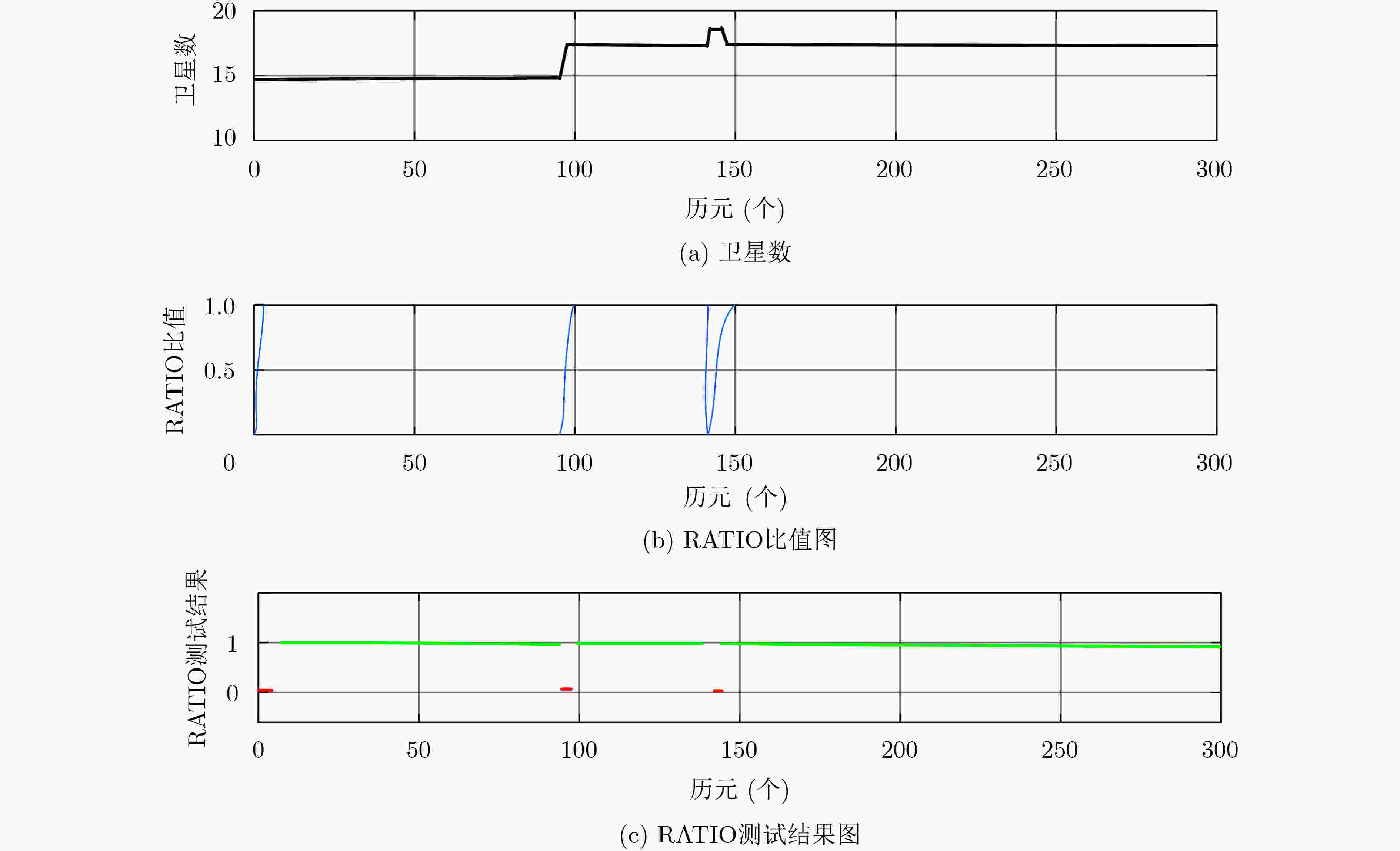
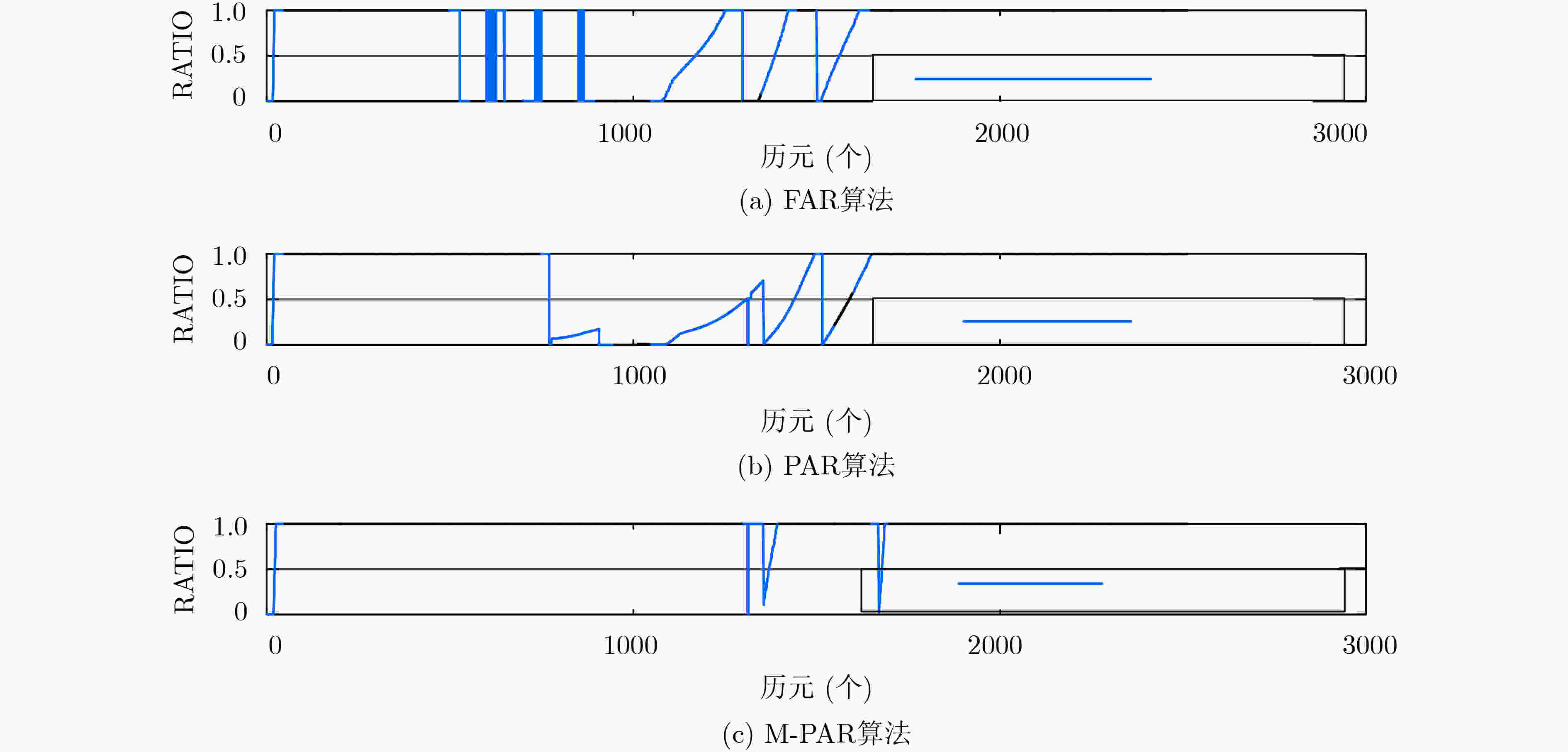
表 1 不同解算方法的固定率和初始化时间对比
模糊度解算方法 模糊度固定率(%) 初始化时间(s) LAMBDA(全) 18.6 3680 FAR 82.3 270 PAR 92.6 20 M-PAR 97.6 20 表 2 不同解算方法的定位结果绝对误差(m)
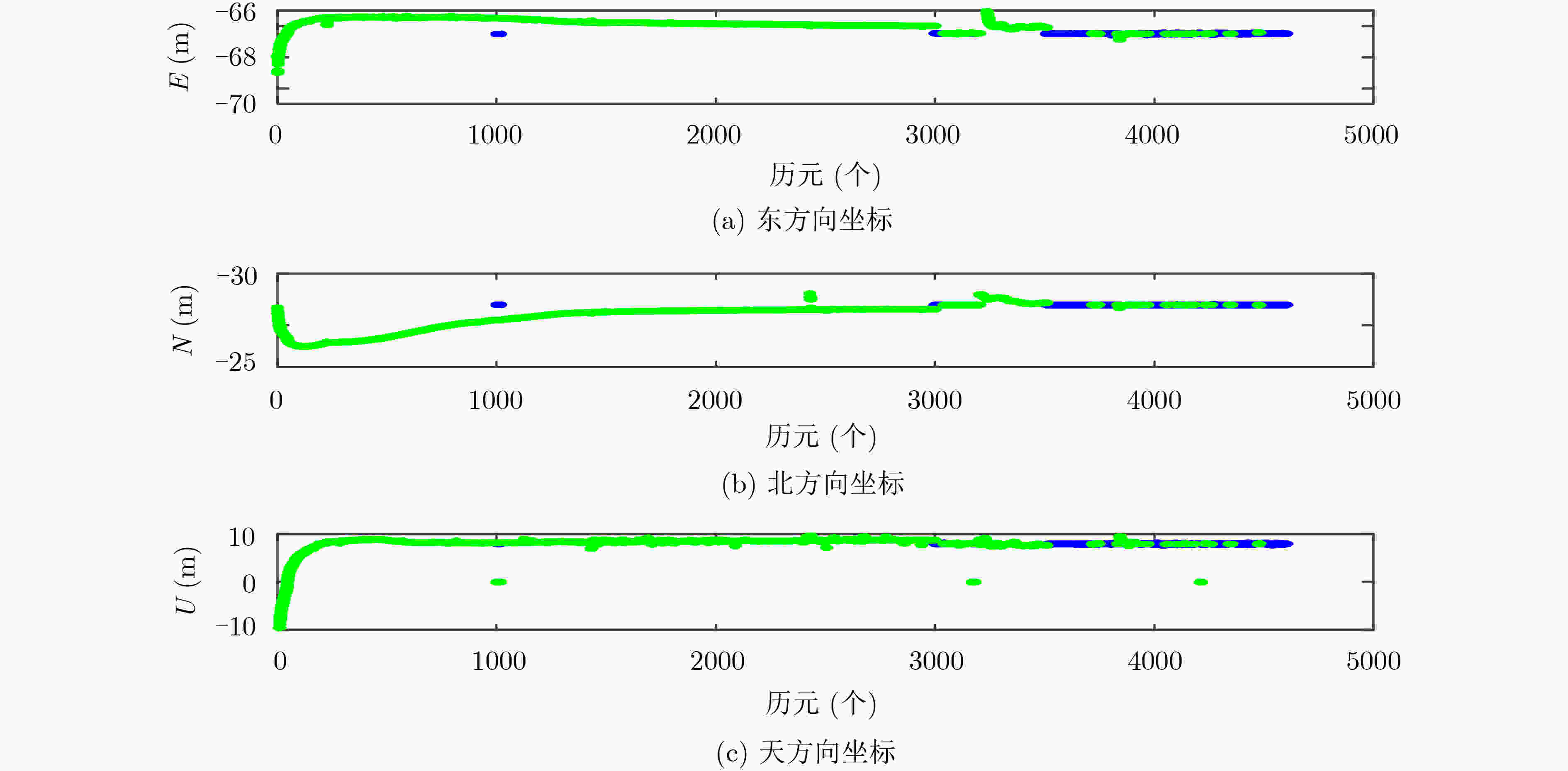
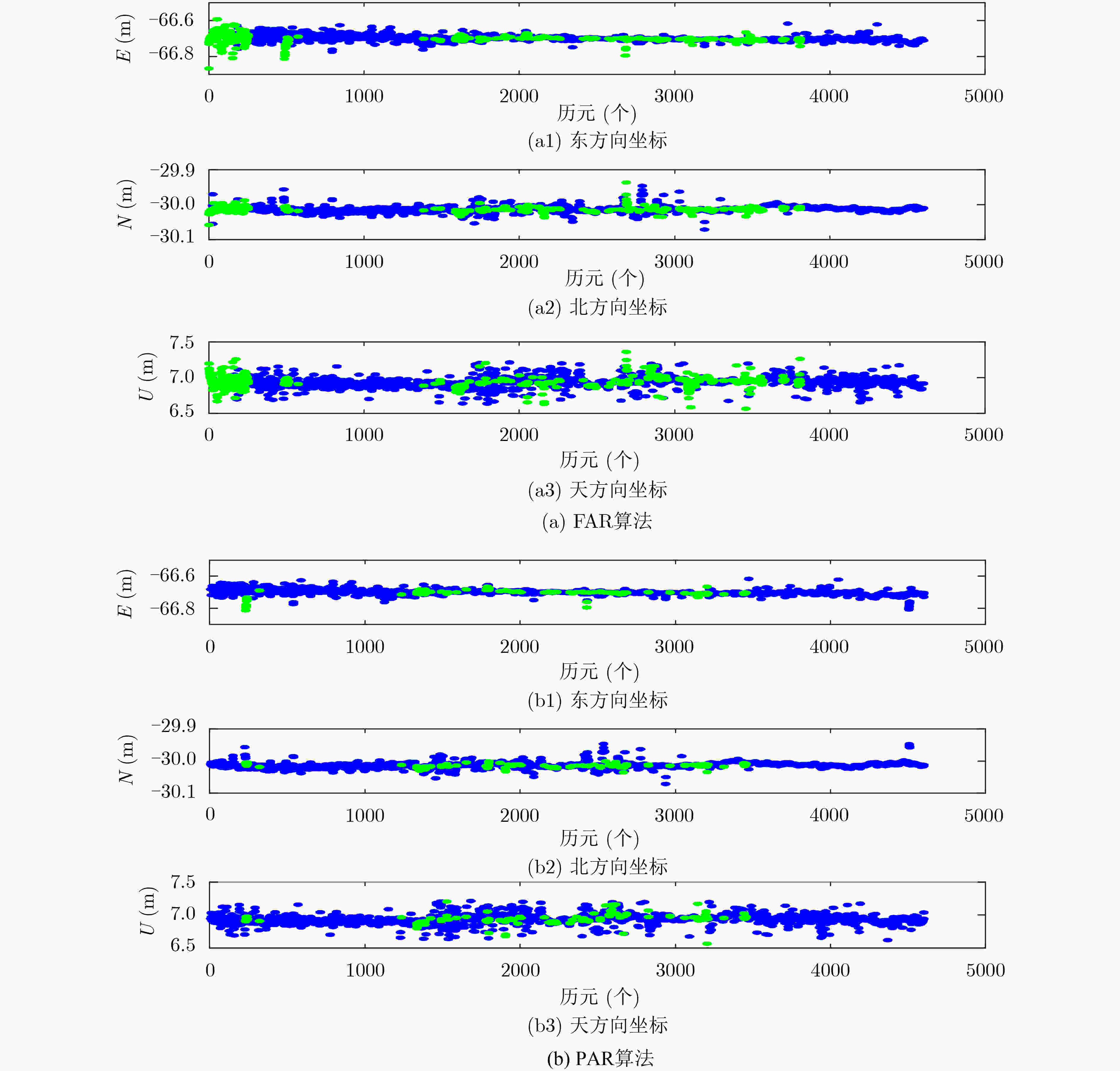
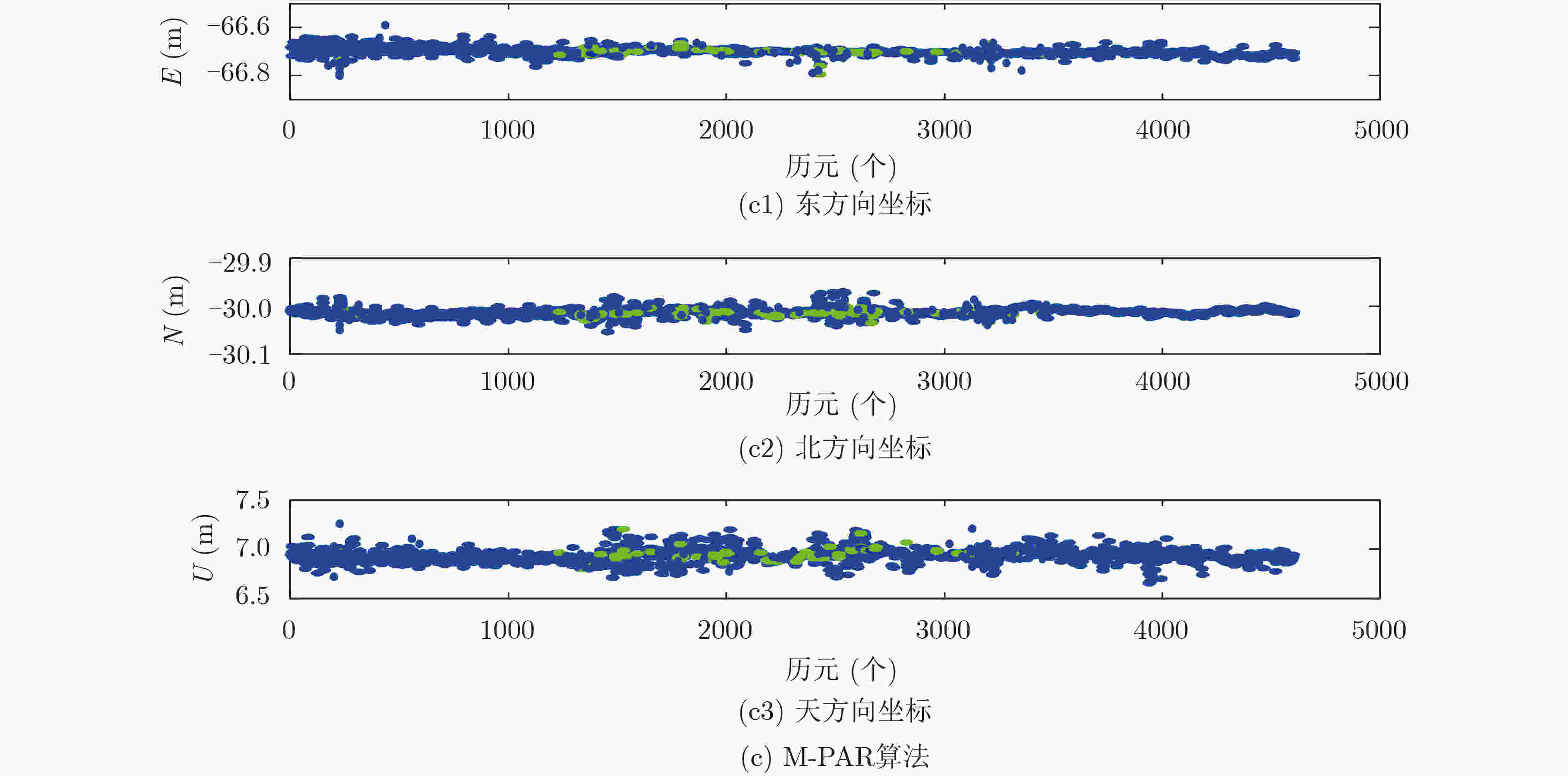
模糊度解算方法 ΔE ΔN ΔU FAR(Float/fix) 0.375 0.224 0.544 PAR(Float/Fix) 0.162 0.112 0.205 M-PAR(Float/Fix) 0.045 0.068 0.104 FAR(Fix) 0.113 0.141 0.231 PAR(Fix) 0.013 0.012 0.063 M-PAR(Fix) 0.008 0.010 0.032 注:ΔE表示东向误差;ΔN表示北向误差;ΔU表示天向误差 -
[1] TEUNISSEN P J G. Success probability of integer GPS ambiguity rounding and bootstrapping[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 1998, 72(10): 606–612. doi: 10.1007/s001900050199 [2] 范建军, 雍少为, 王飞雪. 基于卡尔曼滤波的多径误差消除及双频模糊度快速估计方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2008, 30(5): 1075–1079.FAN Jianjun, YONG Shaowei, and WANG Feixue. Study on multipath mitigation and dual-frequency fast ambiguity estimation based on Kalman filter[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2008, 30(5): 1075–1079. [3] ODIJK D, ARORA B S, and TEUNISSEN P J G. Predicting the success rate of long-baseline GPS+Galileo (Partial) ambiguity resolution[J]. The Journal of Navigation, 2014, 67(3): 385–401. doi: 10.1017/S037346331400006X [4] 周乐韬, 黄丁发, 袁林果, 等. 网络RTK参考站间模糊度动态解算的卡尔曼滤波算法研究[J]. 测绘学报, 2007, 36(1): 37–42. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1595.2007.01.007ZHOU Letao, HUANG Dingfa, YUAN Linguo, et al. A Kalman filtering algorithm for online integer ambiguity resolution in reference station network[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2007, 36(1): 37–42. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1595.2007.01.007 [5] 丁乐乐, 张小红, 于兴旺, 等. 网络RTK双差模糊度解算成功率的提高[C]. 第二届中国卫星导航学术年会电子文集, 上海, 2011.DING Lele, ZHANG Xiaohong, YU Xingwang, et al. Network RTK double difference ambiguity resolution success rate of increase[C]. Electronic Collection of the 2nd China Satellite Navigation Annual Conference, Shanghai, China, 2011. [6] 高旺, 高成发, 潘树国, 等. 基于部分固定策略的多系统长距离基准站间模糊度快速解算[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2017, 42(4): 558–562.GAO Wang, GAO Chengfa, PAN Shuguo, et al. Fast ambiguity resolution between GPS/GLONASS/BDS combined long-range base stations based on partial-fixing strategy[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2017, 42(4): 558–562. [7] BOCK Y, GOUREVITCH S A, COUNSELMAN III C C, et al. Interferometric analysis of GPS phase observations[J]. Manuscripta Geodaetica, 1986, 11(4): 282–288. [8] WANG Shengli, DENG Jian, OU Jikun, et al. Three-step algorithm for rapid ambiguity resolution between reference stations within network RTK[J]. The Journal of Navigation, 2016, 69(6): 1310–1324. doi: 10.1017/S037346331600031X [9] 祝会忠, 徐爱功, 高猛, 等. BDS网络RTK中距离参考站整周模糊度单历元解算方法[J]. 测绘学报, 2016, 45(1): 50–57.ZHU Huizhong, XU Aigong, GAO Meng, et al. The algorithm of single-epoch integer ambiguity resolution between middle-range BDS network RTK reference stations[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2016, 45(1): 50–57. [10] 吴康良, 罗晨曦, 杨菂. 随机模型对BDS/GPS长基线解算精度的影响[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2018, 38(4): 386–389, 406.WU Kangliang, LUO Chenxi, and YANG Di. The effect of stochastic model on the accuracy of BDS/GPS long baseline solution[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2018, 38(4): 386–389, 406. [11] ODIJK D, VERHAGEN S, and TEUNISSEN P J G. Medium-distance GPS Ambiguity Resolution with Controlled Failure Rate[M]. KENYON S, PACINO M C, and Marti U. Geodesy for Planet Earth. Berlin, Germany, Springer, 2012. [12] SASI G and RAO B. Ionospheric delay estimation for improving the global positioning system position accuracy[J]. IETE Journal of Research, 2008, 54(1): 23–29. doi: 10.1080/03772063.2008.10876178 [13] 刘鸣, 柴洪洲, 董冰全. 北斗网络RTK基准站间整周模糊度快速确定方法[J]. 信息工程大学学报, 2016, 17(6): 760–763. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0673.2016.06.023LIU Ming, CHAI Hongzhou, and DONG Bingquan. Algorithm of instantaneous integer ambiguity resolution for reference stations of BDS network RTK[J]. Journal of Information Engineering University, 2016, 17(6): 760–763. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0673.2016.06.023 [14] SUN R, HAN K, HU J, et al. Integrated solution for anomalous driving detection based on BeiDou/GPS/IMU measurementss[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2016, 69: 193–207. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2016.06.006 [15] 张晋升, 李成钢, 何冰, 等. 区域电离层估计方法在网络RTK中的应用[J]. 导航定位学报, 2018, 6(3): 107–112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2018.03.020ZHANG Jinsheng, LI Chenggang, HE Bing, et al. Application of regional ionospheric parameter estimation in network RTK[J]. Journal of Navigation and Positioning, 2018, 6(3): 107–112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2018.03.020 [16] SCHAFFRIN B and BOCK Y. A unified scheme for processing GPS dual-band phase observations[J]. Bulletin Géodésique, 1988, 62(2): 142–160. [17] 陈凯, 孙希延, 纪元法, 等. 基于载波相位差分的形变监测高精度定位算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2019, 39(4): 1234–1239. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2018071454CHEN Kai, SUN Xiyan, JI Yuanfa, et al. High-precision positioning algorithm for deformation monitoring based on carrier phase difference[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2019, 39(4): 1234–1239. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2018071454 [18] 王守华, 陆明炽, 孙希延, 等. 基于无迹卡尔曼滤波的iBeacon/INS数据融合定位算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(9): 2209–2216. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180748WANG Shouhua, LU Mingchi, SUN Xiyan, et al. IBeacon/INS data fusion location algorithm based on unscented Kalman filter[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(9): 2209–2216. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180748 [19] 王守华, 李云柯, 孙希延, 等. 基于低成本接收机的双天线测姿算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2019, 39(8): 2381–2385. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2018122554WANG Shouhua, LI Yunke, SUN Xiyan, et al. Dual-antenna attitude determination algorithm based on low-cost receiver[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2019, 39(8): 2381–2385. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2018122554 [20] TEUNISSEN P J G, JOOSTEN P, and TIBERIUS C. Geometry-free ambiguity success rates in case of partial fixing[C]. Proceedings of 1999 National Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation, San Diego, 1999. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
