Detection of ECG Signal P and T Wave Based on Stationary and Continuous Wavelet Transform Fusion
-
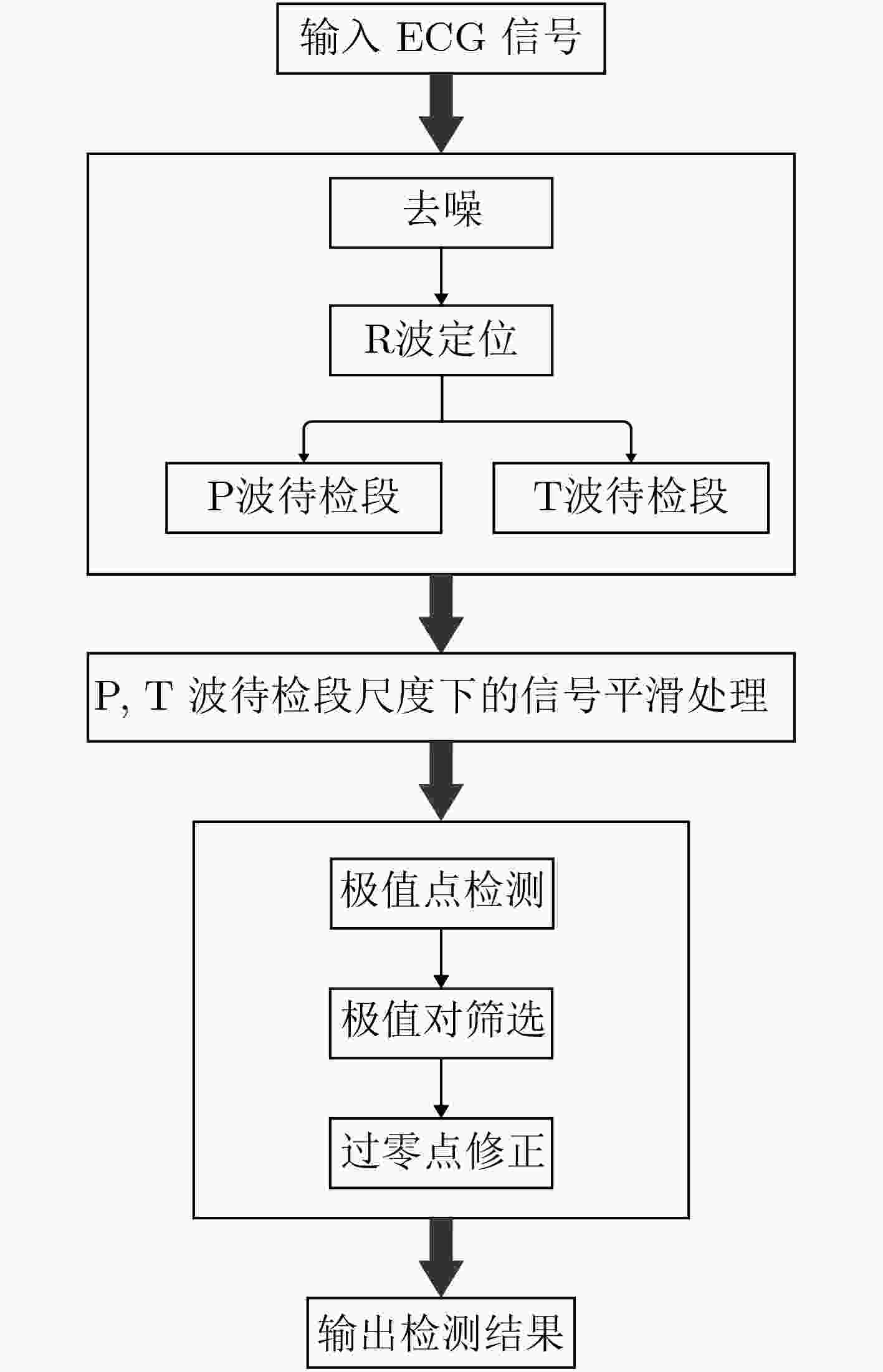
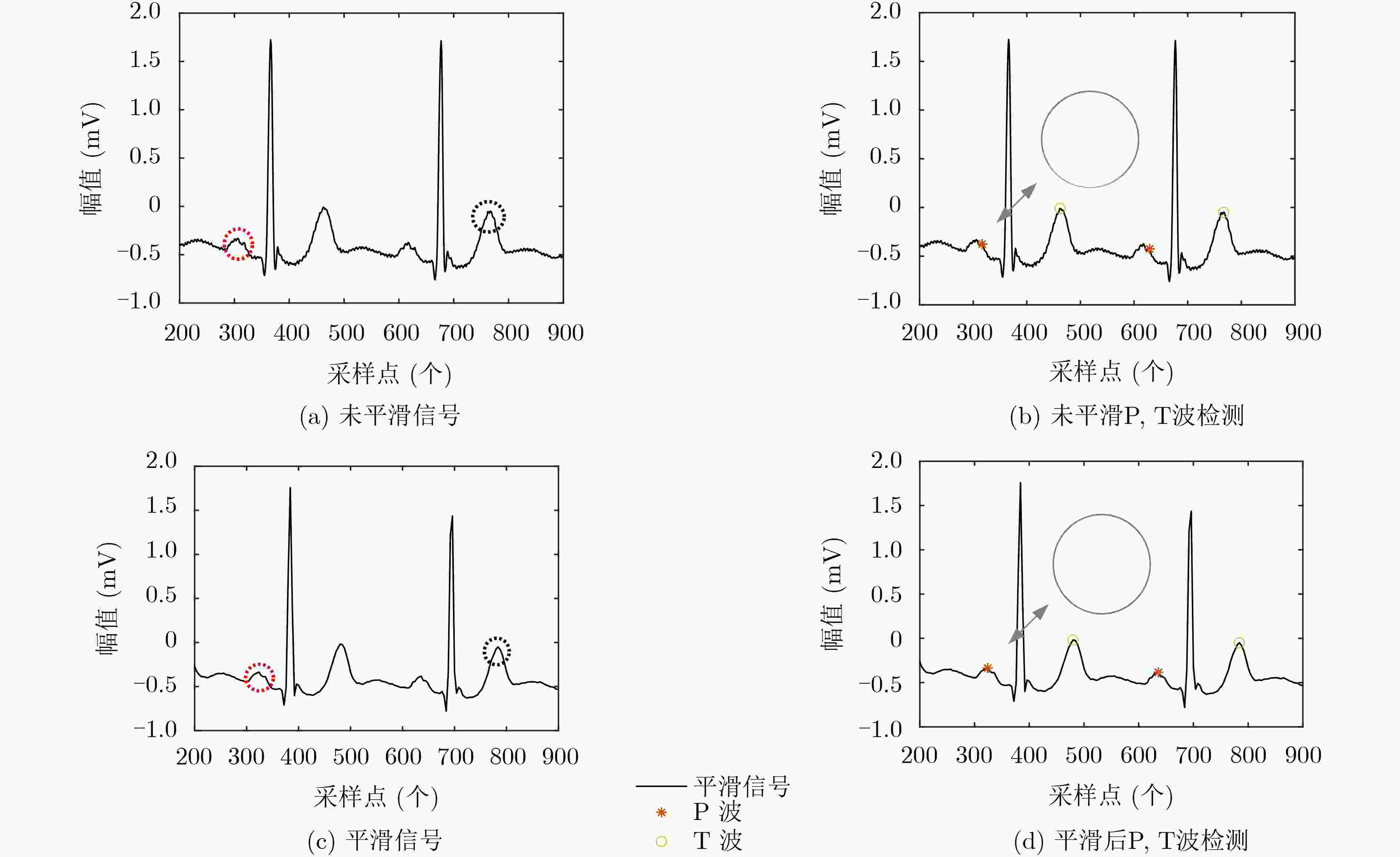
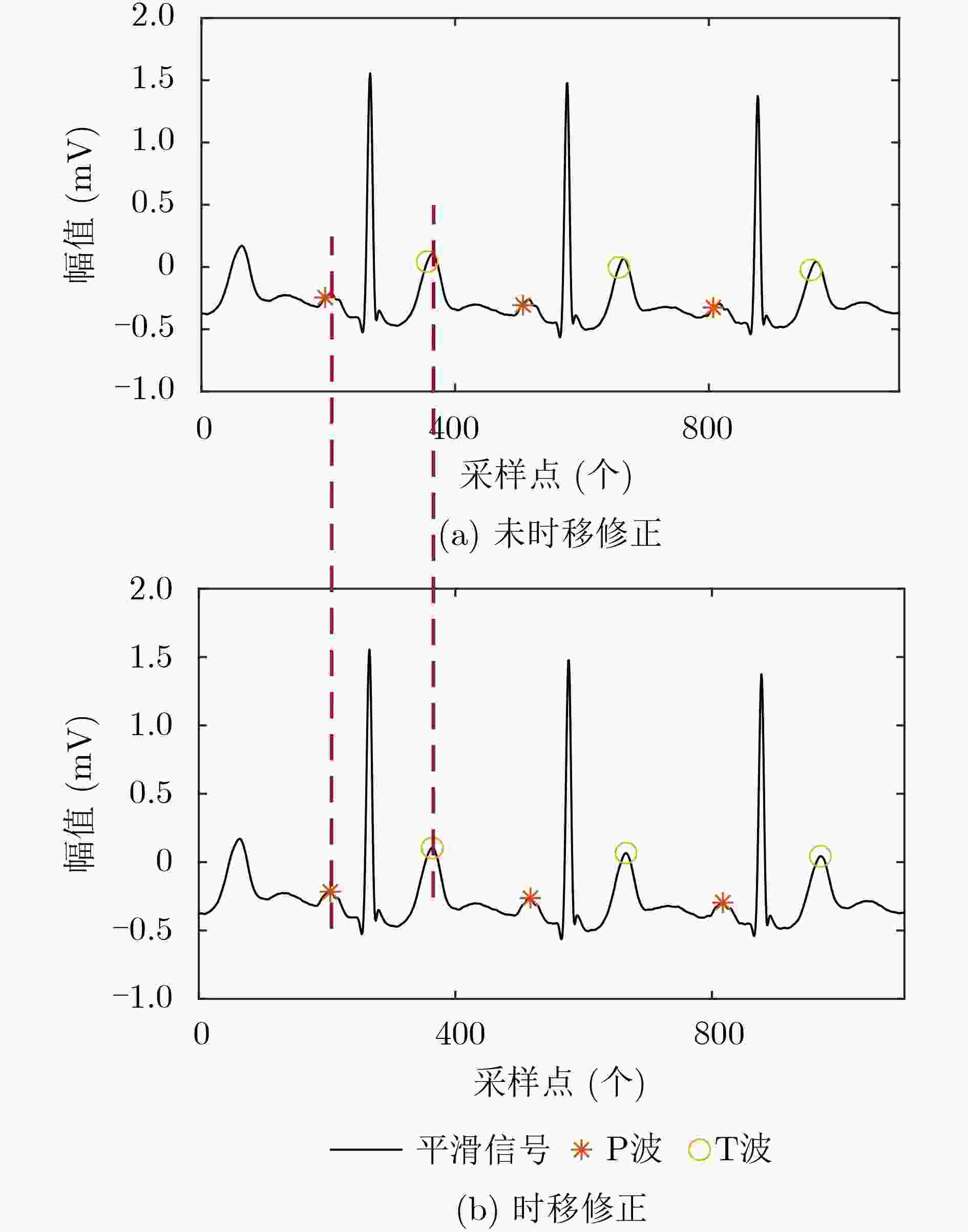
摘要: P, T波的检测在临床上是心血管疾病诊断的重要依据。由于其波形能量低、形态复杂,极易受到噪声干扰,导致现有检测算法精度仍有待提高。该文提出平稳和连续小波变换融合算法检测P, T波,利用连续小波变换的多尺度信息,获取心电图(ECG)信号中P, T波主要成分,融合其平稳小波对P, T波候选段进行平滑处理,消除波形中锯齿状毛刺对峰值点检测的影响,最后对P, T波过零点进行时移修正,保证过零点还原到原始信号过程中能够准确对应其峰值点,从而提高P, T波检测精度。该文算法在MIT-BIH arrhythmic数据库上进行验证,最终P波的误差率、敏感度、正确预测度达到:0.23%, 99.85%, 99.90%;T波的误差率、敏感度、正确预测度达到0.27%, 99.85%, 99.87%。Abstract: The detection of P and T waves is an important basis for the diagnosis of cardiovascular disease in the clinic. Because of its low waveform energy and complex shape, it is extremely susceptible to noise interference, which leads to the need to improve the accuracy of existing detection algorithms. In this paper, a P and T wave algorithm based on stable and continuous wavelet transform is proposed .First, the smooth wavelet transform is used to smooth the ElectroCardioGram (ECG) signal to eliminate the effect of jagged burrs on the peak point detection. Then, the multiscale information of continuous wavelet transform is used to obtain the main components of P and T waves in the ECG signal. According to the translation correction rule, the time shift of the zero crossings of P and T waves is corrected to improve the detection accuracy of P and T waves. The algorithm of this paper is verified on the MIT-BIH arrhythmic database, and the final P-wave error rate, sensitivity, and correct prediction reach 0.23%, 99.85%, 99.90%; the T-wave error rate, sensitivity, and correct prediction reach 0.27%, 99.85%, 99.87%.
-
表 1 频率分布(Hz)
尺度 频带(Hz) s=21 90~180 s=22 45~90 s=23 22.5~45 s=24 5.76~22.25 s=25 5.625~11.25 表 2 P, T波统计结果
$N$ ${F_{\rm{N}}}$ ${F_{\rm{P}}}$ ${R_{\rm{d}}}$ ${e_{\rm{r}}}(\% )$ ${S_{\rm{e}}}(\% )$ ${P_{\rm{p}}}(\% )$ P 69504 103 63 69388 0.23 99.85 99.90 T 69504 103 86 69315 0.27 99.85 99.87 -
[1] MAGNAN J W, GORODESKI E Z, JOHNSON V M, et al. P wave duration is associated with cardiovascular and all-cause mortality outcomes: The national health and nutrition examination survey[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2011, 8(1): 93–100. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2010.09.020 [2] AMORIM P, MORAES T, FAZANARO D, et al. Shearlet and contourlet transforms for analysis of electrocardiogram signals[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2018, 161: 125–132. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.04.021 [3] 季虎, 孙即祥, 王春光. 基于小波变换的自适应QRS-T对消P波检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(8): 1868–1871. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2006.00117JI Hu, SUN Jixiang, and WANG Chunguang. An adaptive QRS-T cancellation based on wavelet transform for P-wave detection[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2007, 29(8): 1868–1871. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2006.00117 [4] ELGENDI M, MEO M, and ABBOTT D. A proof-of-concept study: Simple and effective detection of P and T waves in arrhythmic ECG signals[J]. Bioengineering, 2016, 3(4): 26. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering3040026 [5] BECCHETTI C and NERI A. Medical Instrument Design and Development: From Requirements to Market Placements[M]. Hoboken: Wiley, 2013. [6] KORS J A and VAN HERPEN G. Computer analysis of the electrocardiogram[M]. MACFARLANE P W, VAN OOSTEROM A, PAHLM O, et al. Comprehensive Electrocardiology. London: Springer, 2010: 1721–1765. doi: 10.1007/978-1-84882-046-3_37. [7] PEIMANKAR A and PUTHUSSERYPADY S. DENS-ECG: A deep learning approach for ECG signal delineation[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2020, 165: 113911. [8] YANG Dandan, WANG Lixin, HU Wenbin, et al. Singularity detection in FOG-based pavement data by wavelet transform[C]. The 25th International Conference on Optical Fiber Sensors, Jeju, Korea, 2017. doi: 10.1117/12.2265514. [9] YOCHUM M, RENAUD C, and JACQUIR S. Automatic detection of P, QRS and T patterns in 12 leads ECG signal based on CWT[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2016, 25: 46–52. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2015.10.011 [10] DEV SHARMA L and SUNKARIA R K. Novel T-wave detection technique with minimal processing and RR-interval based enhanced efficiency[J]. Cardiovascular Engineering and Technology, 2019, 10(2): 367–379. doi: 10.1007/s13239-019-00415-4 [11] SAHOO S, KANUNGO B, BEHERA S, et al. Multiresolution wavelet transform based feature extraction and ECG classification to detect cardiac abnormalities[J]. Measurement, 2017, 108: 55–66. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2017.05.022 [12] KUMAR A, KOMARAGIRI R, and KUMAR M. Heart rate monitoring and therapeutic devices: A wavelet transform based approach for the modeling and classification of congestive heart failure[J]. ISA Transactions, 2018, 79: 239–250. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2018.05.003 [13] SAIVEENA K, GUPTA P, AMARNATH M, et al. Characterization of ECG signals using multiscale approach[C]. 2012 International Conference on Signal Processing and Communications (SPCOM), Bangalore, India, 2012. doi: 10.1109/SPCOM.2012.6289998. [14] MOODY G B and MARK R G. The MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database on CD-ROM and software for use with it[C]. 1990 Proceedings Computers in Cardiology, Chicago, USA, 1990. doi: 10.1109/CIC.1990.144205. [15] CLIFFORD G D, AZUAJE F, and MCSHARRY P. Advanced Methods and Tools for ECG Data Analysis[M]. 685 Canton St. Norwood, MA, USA: Artech House, Inc., 2006. [16] FAWCETT T. An introduction to ROC analysis[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2005, 27(8): 861–874. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
