An Efficient and Robust Algorithm to Generate Initial Center of Bisecting K-means for High-dimensional Big Data Based on Random Integer Triangular Matrix Mappings
-
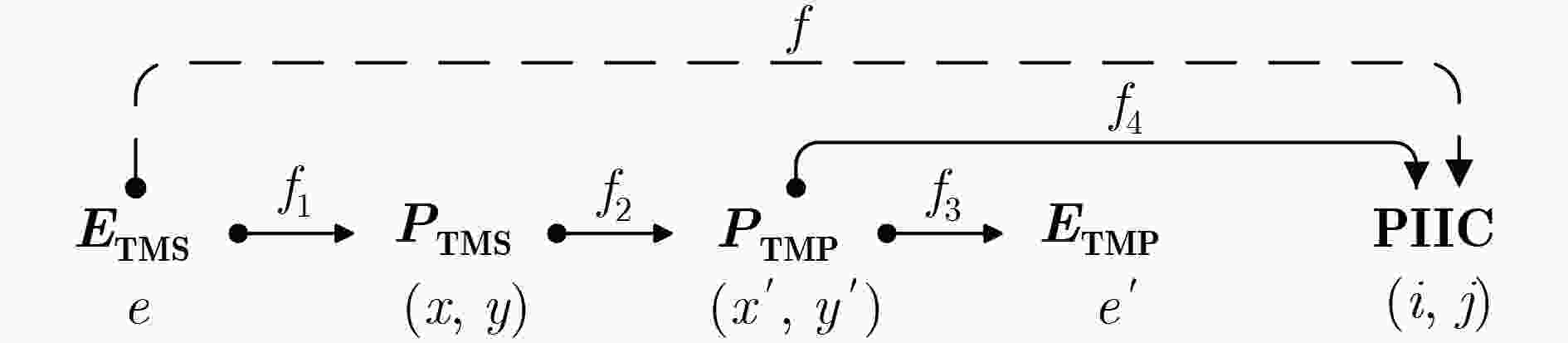
摘要: Bisecting K-means算法通过使用一组初始中心对分割簇,得到多个二分聚类结果,然后从中选优以减轻局部最优收敛问题对算法性能的不良影响。然而,现有的随机采样初始中心对生成方法存在效率低、稳定性差、缺失值等不同问题,难以胜任大数据聚类场景。针对这些问题,该文首先创建出了初始中心对组合三角阵和初始中心对编号三角阵,然后通过建立两矩阵中元素及元素位置间的若干映射,从而实现了一种从随机整数集合中生成二分聚类初始中心对的线性复杂度算法。理论分析与实验结果均表明,该方法的时间效率及效率稳定性均明显优于常用的随机采样方法,特别适用于高维大数据聚类场景。Abstract: The algorithm of Bisecting K-means obtains multiple clustering results by using a set of initial center pairs to segment a cluster, and then selects the best from them to mitigate the adverse effect of the local optimal convergence on the performance of the algorithm. However, the current methods of random sampling to generate initial center pairs for Bisecting K-means have some problems, such as low efficiency, poor stability, missing values and so on, which are not competent for big data clustering. In order to solve these problems, firstly the lower triangular matrix composed by the pairs of initial centers and the lower triangular matrix composed by serial numbers of the pairs of initial centers are created. Then, by establishing several mappings between the elements and their positions in the two matrices, a linear complexity algorithm is proposed to generate initial center pairs from the set of random integers. Both theoretical analysis and experimental results show that the time efficiency and efficiency stability of this method are significantly better than the current methods of random sampling, so it is particularly suitable for these scenarios of high-dimensional big data clustering.
-
表 1 算法复杂度对比
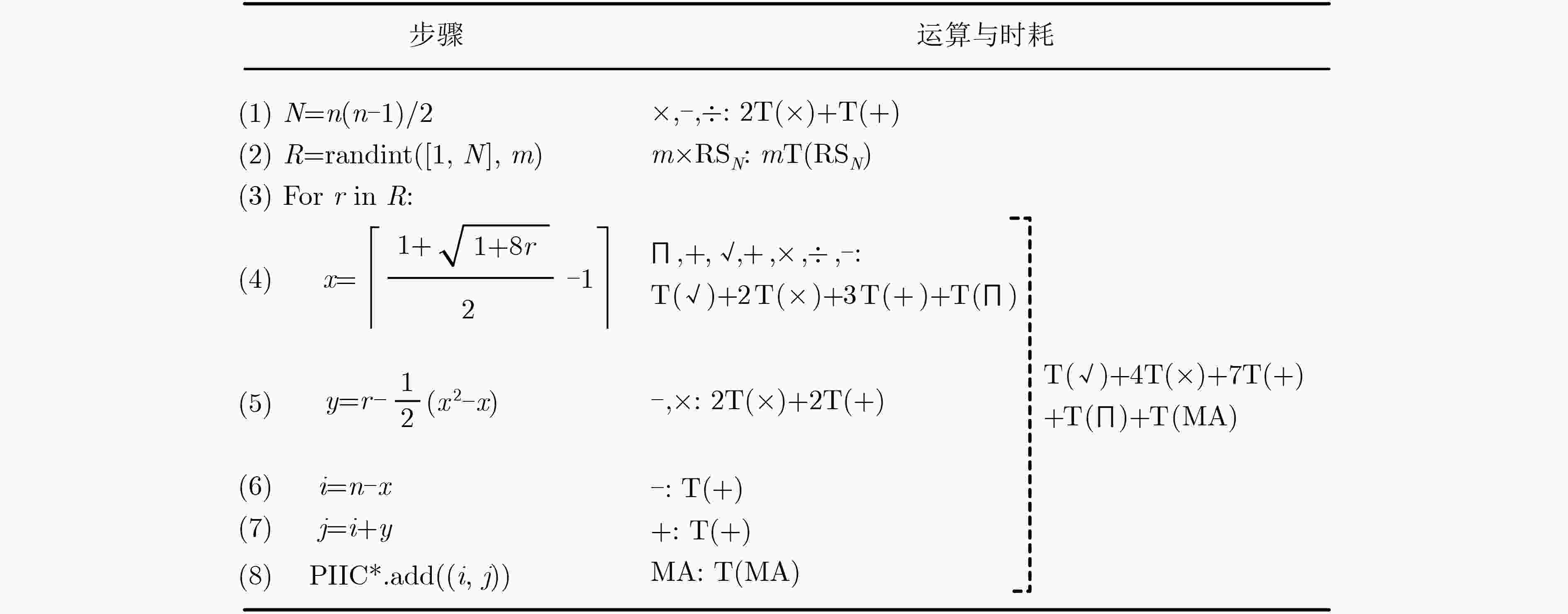
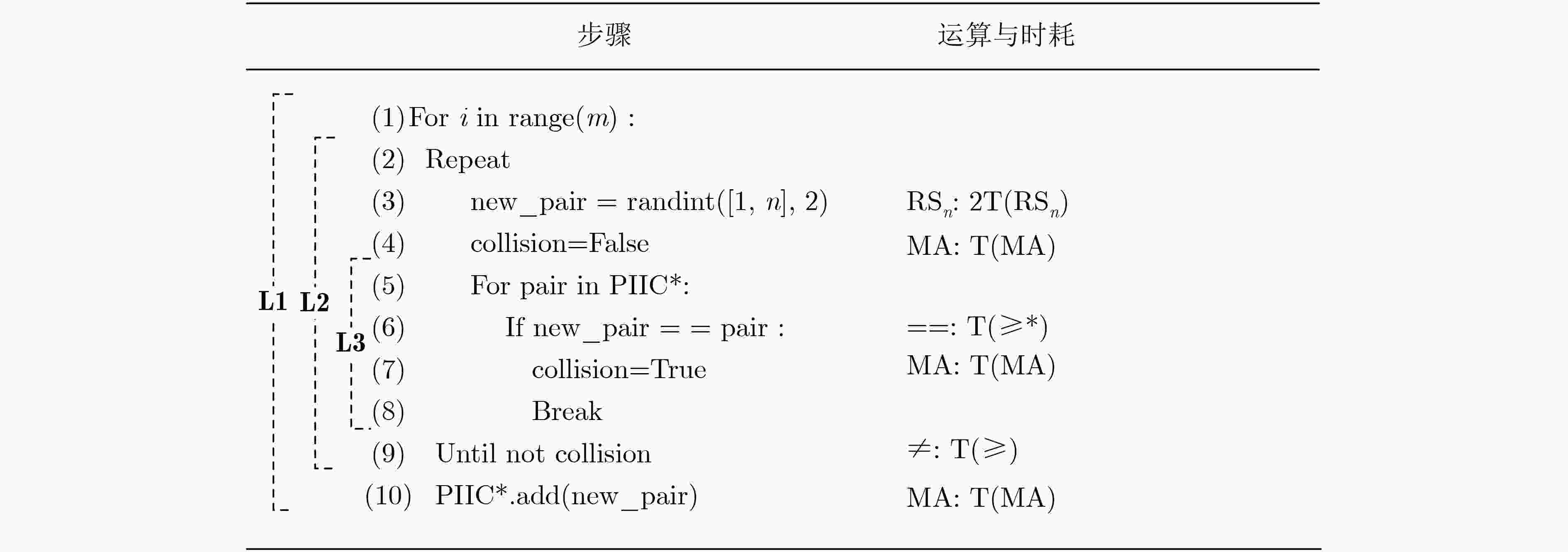
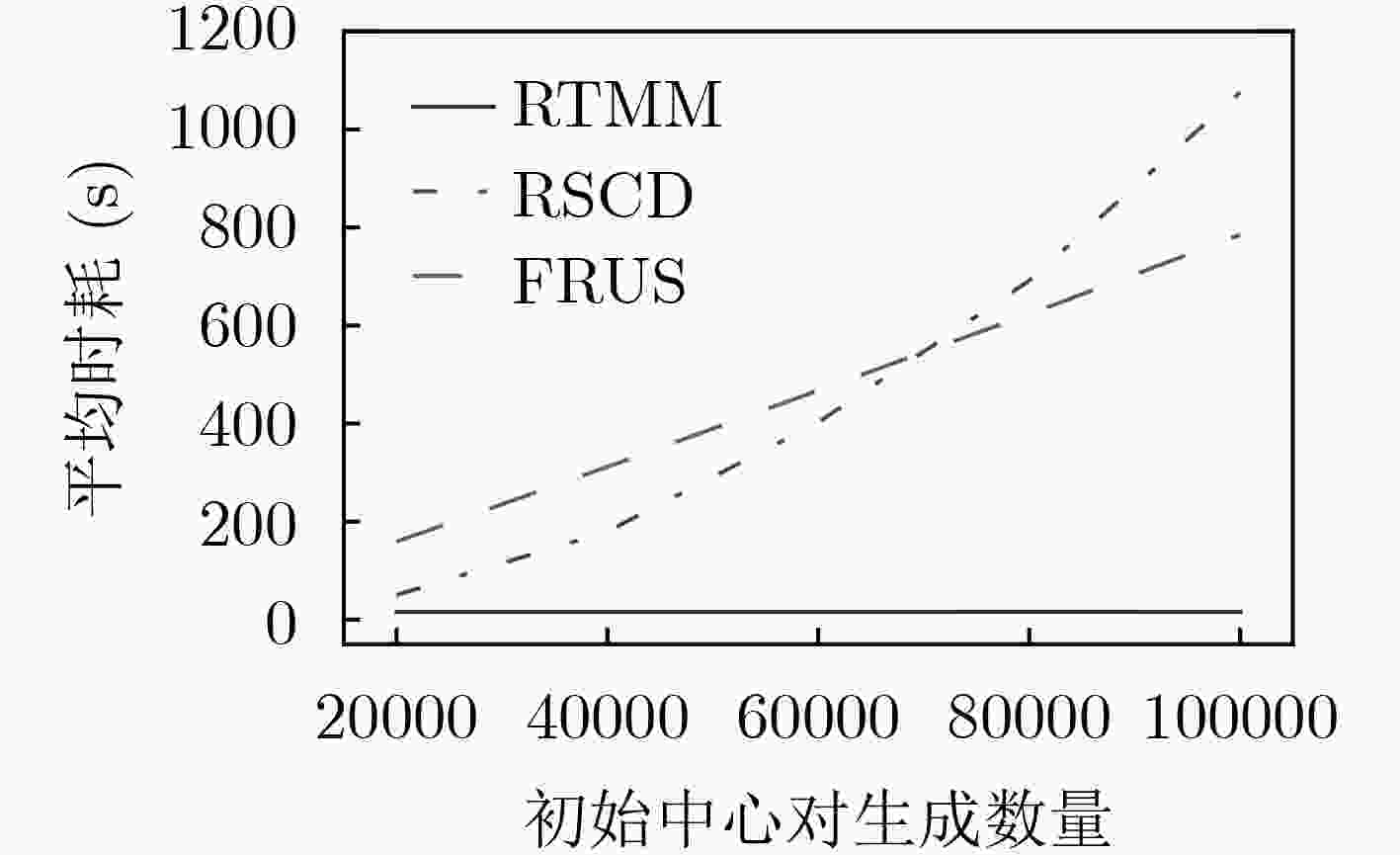
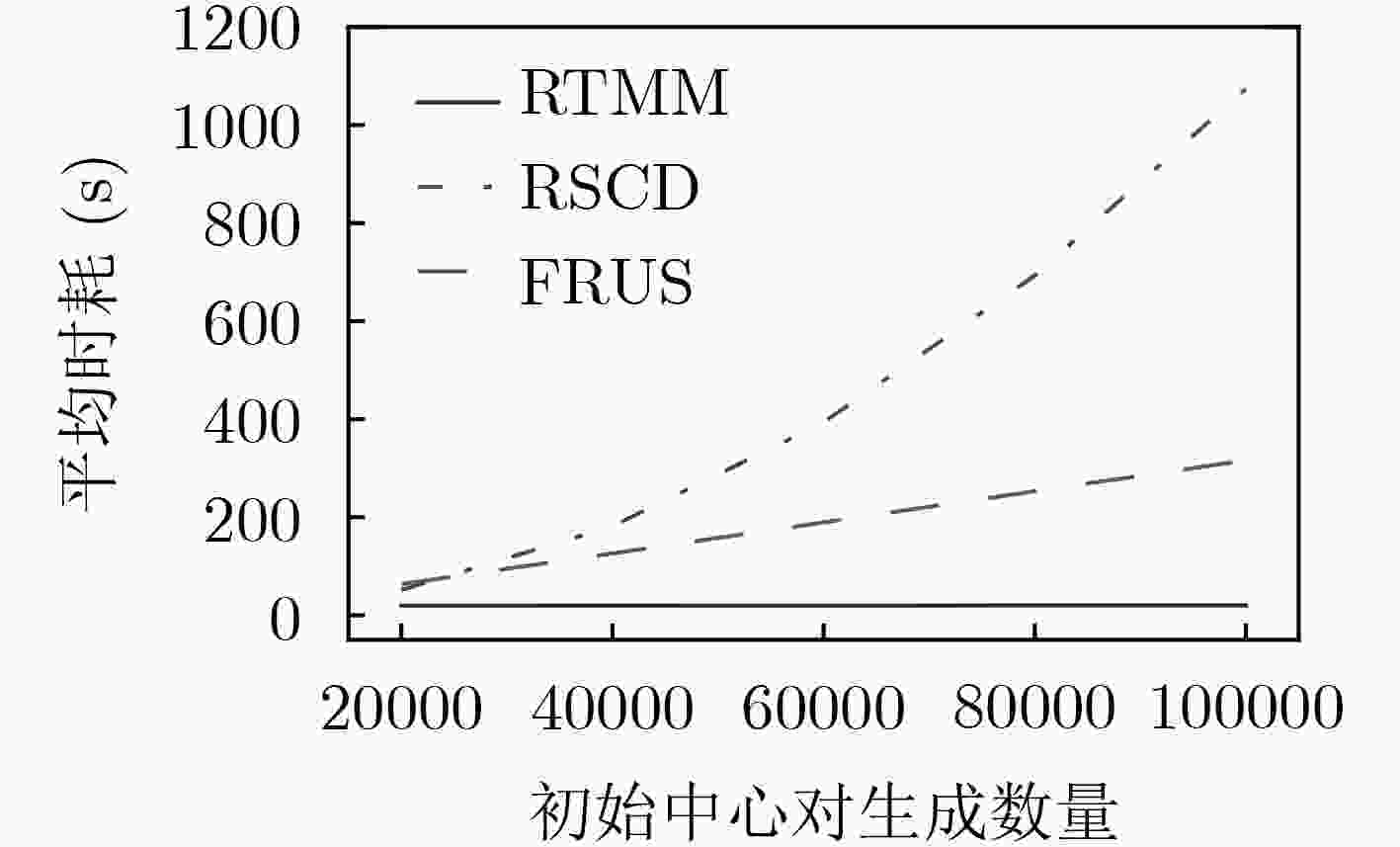
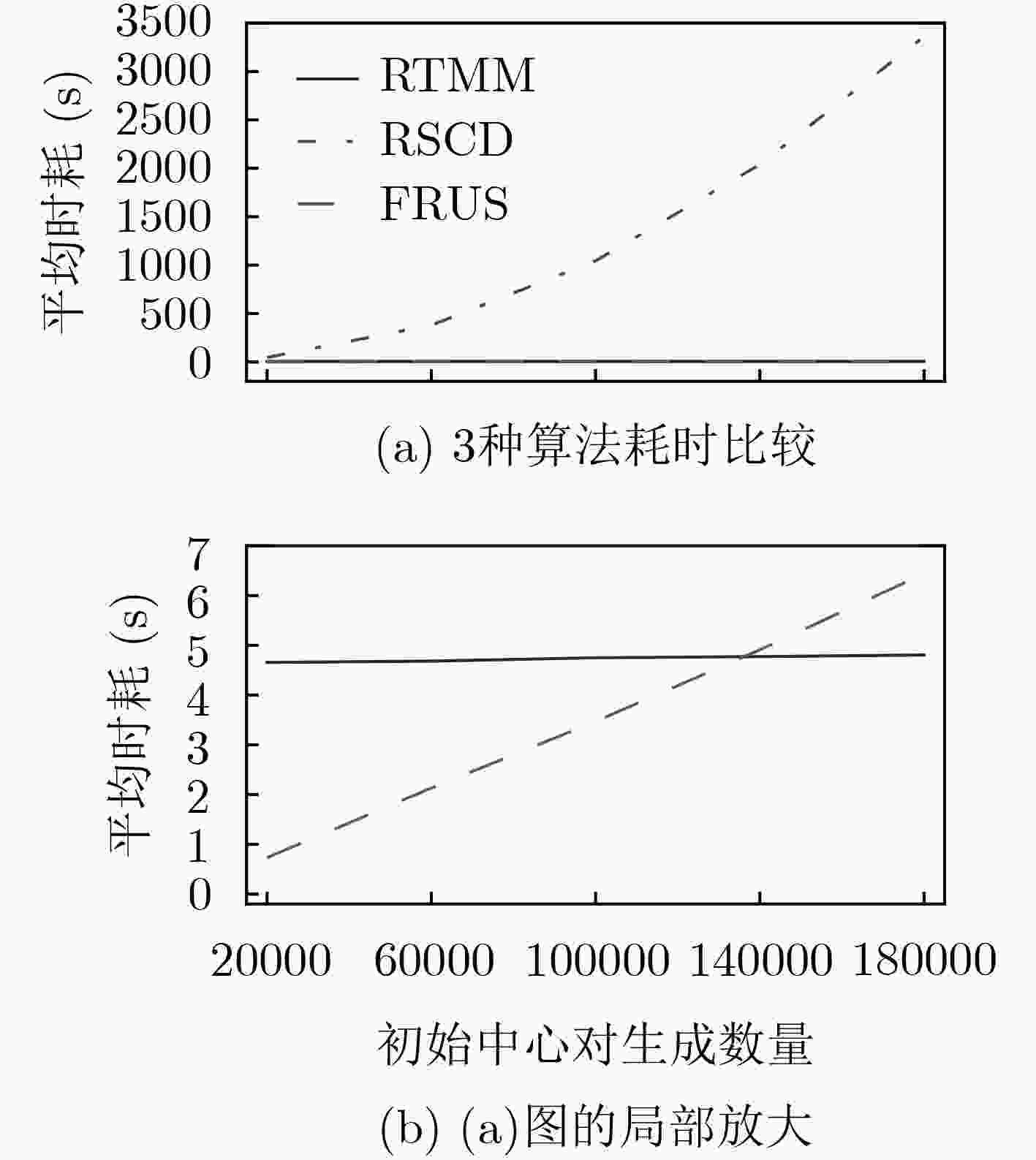
算法 时间复杂度 空间复杂度 随机数三角阵映射算法 O(m) O(m) 随机样本碰撞检测算法 O(m2+mK) Ob(m2); Ow(∞); Oa(mN·lnN) O(m) 表 2 大规模初始中心生成任务下的算法时耗对比
DataSet 平均时耗(s) RTMM RSCD FRUS 20NEWS 15.988381 3304.241926 1398.781894 IMDB 20.109095 3349.822651 567.211075 MNIST 4.805166 3360.242473 6.441524 -
JAIN A K. Data clustering: 50 years beyond K-means[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2010, 31(8): 651–666. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2009.09.011 YANG Qiang and WU Xindong. 10 challenging problems in data mining research[J]. International Journal of Information Technology & Decision Making, 2006, 5(4): 597–604. doi: 10.1142/s0219622006002258 ZHAO Wanlei, DENG Chenghao, and NGO C W. K-means: A revisit[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 291: 195–206. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.02.072 KADAM P and MATE G S. Improving efficiency of similarity of document network using bisect K-means[C]. 2017 International Conference on Computing, Communication, Control and Automation, Pune, India, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/iccubea.2017.8463865. WEI Zhaolan and XIA Jing. Optimal sensor placement based on bisect k-means clustering algorithm[C]. 2018 3rd International Conference on Materials Science, Machinery and Energy Engineering (MSMEE 2018), Taiyuan, China, 2018: 228–232. doi: 10.23977/msmee.2018.72138. ABUAIADAH D. Using bisect K-Means clustering technique in the analysis of Arabic documents[J]. ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing, 2016, 15(3): 17. doi: 10.1145/2812809 王燕, 李晴, 张光普. 长基线/超短基线组合系统抗异常值定位技术研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(11): 2578–2583. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180056WANG Yan, LI Qing, and ZHANG Guangpu. On anti-outlier localization for integrated long baseline/ultra-short baseline systems[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(11): 2578–2583. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180056 STEINBACH M, KARYPIS G, and KUMAR V. A comparison of document clustering techniques[C]. KDD Workshop on Text Mining, Boston, USA, 2000: 1–20. WANG Yong and HODGES J E. A comparison of document clustering algorithms[C]. The 5th International Workshop on Pattern Recognition in Information Systems, Miami, USA, 2005: 186–191. doi: 10.5220/0002557501860191. BAGIROV A M, UGON J, and WEBB D. Fast modified global k-means algorithm for incremental cluster construction[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2011, 4: 866–876. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2010.10.018 JAIN A K, MURTY M N, and FLYNN P J. Data clustering: A review[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 1999, 31(3): 264–323. doi: 10.1145/331499.331504 赵凤, 孙文静, 刘汉强, 等. 基于近邻搜索花授粉优化的直觉模糊聚类图像分割[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 1005–1012. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190428ZHAO Feng, SUN Wenjing, LIU Hanqiang, et al. Intuitionistic fuzzy clustering image segmentation based on flower pollination optimization with nearest neighbor searching[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 1005–1012. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190428 WU Xindong, KUMAR V, QUINLAN J R, et al. Top 10 algorithms in data mining[J]. Knowledge and Information Systems, 2008, 14(1): 1–37. doi: 10.1007/s10115-007-0114-2. WITTEN I H, FRANK E, HALL M A, et al. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques[M]. 4th ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2017: 97–98. MARSLAND S. Machine Learning: An Algorithmic Perspective[M]. 2nd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2015: 197–200. HAN Jiawei and KAMBER M. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques[M]. 2nd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2006: 402–404. ELKAN C. Clustering with k-means: Faster, smarter, cheaper[EB/OL]. http://www.doc88.com/p-347627347988.html, 2004. KOPEC D. Classic Computer Science Problems in Python[M]. Shelter Island: Manning Publications, 2019: 117–118. JREN N. The 20 newsgroups data set[EB/OL]. http://qwone.com/~jason/20Newsgroups, 2008. BO P and LILLIAN L. Movie review data[EB/OL]. http://www.cs.cornell.edu/people/pabo/movie-review-data, 2020. LECUN Y, CORTES C, and BURGES C J C. The MNIST database of handwritten digits[EB/OL]. http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist, 2020. -






 下载:
下载:
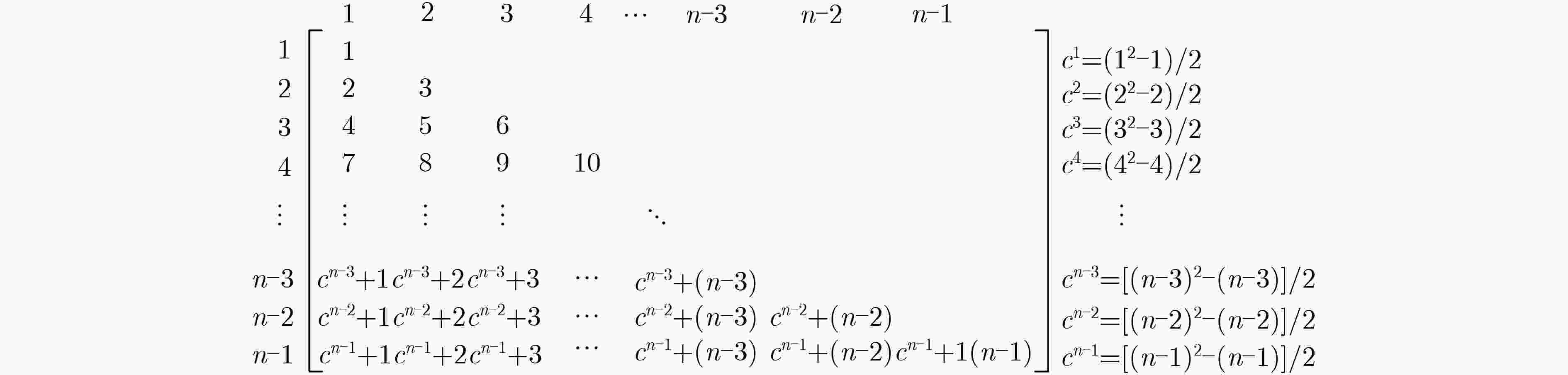
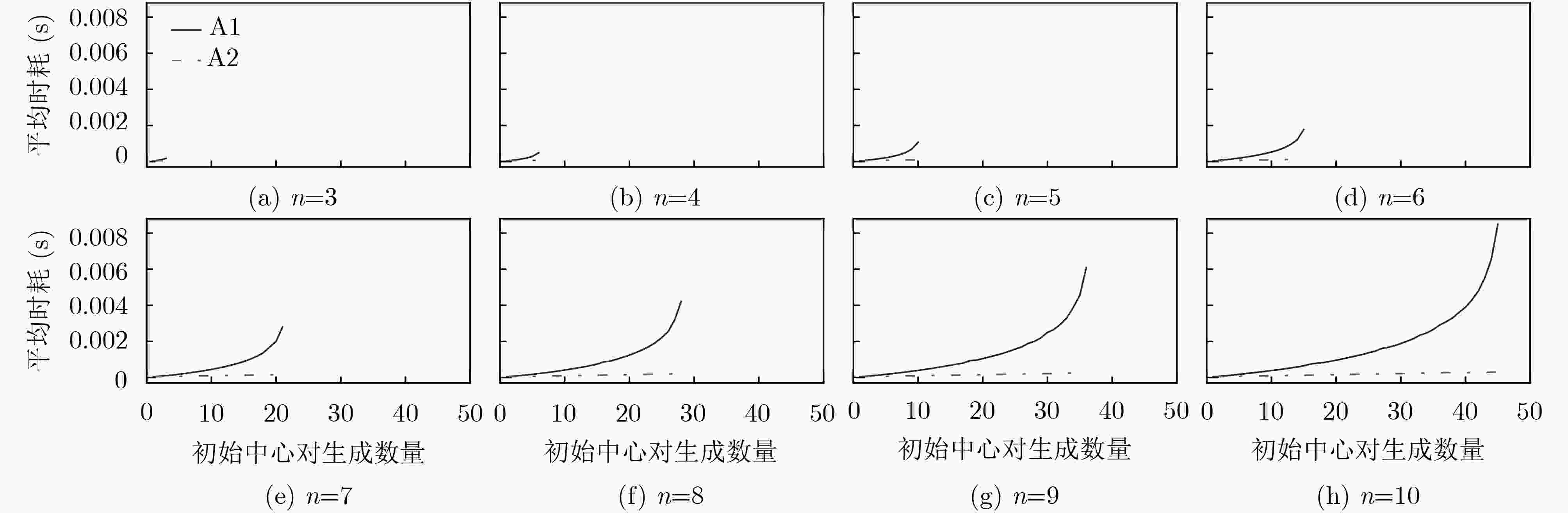
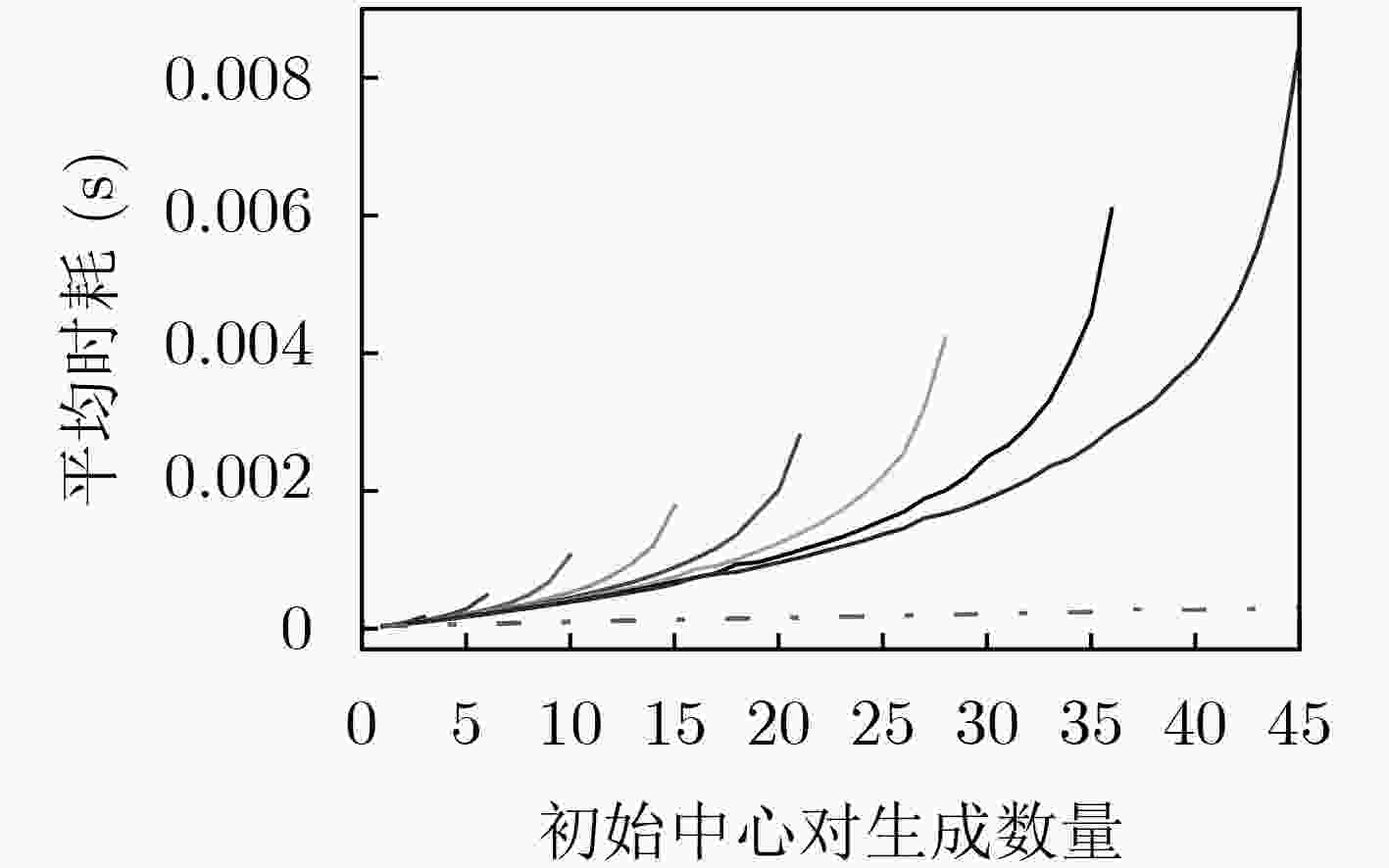
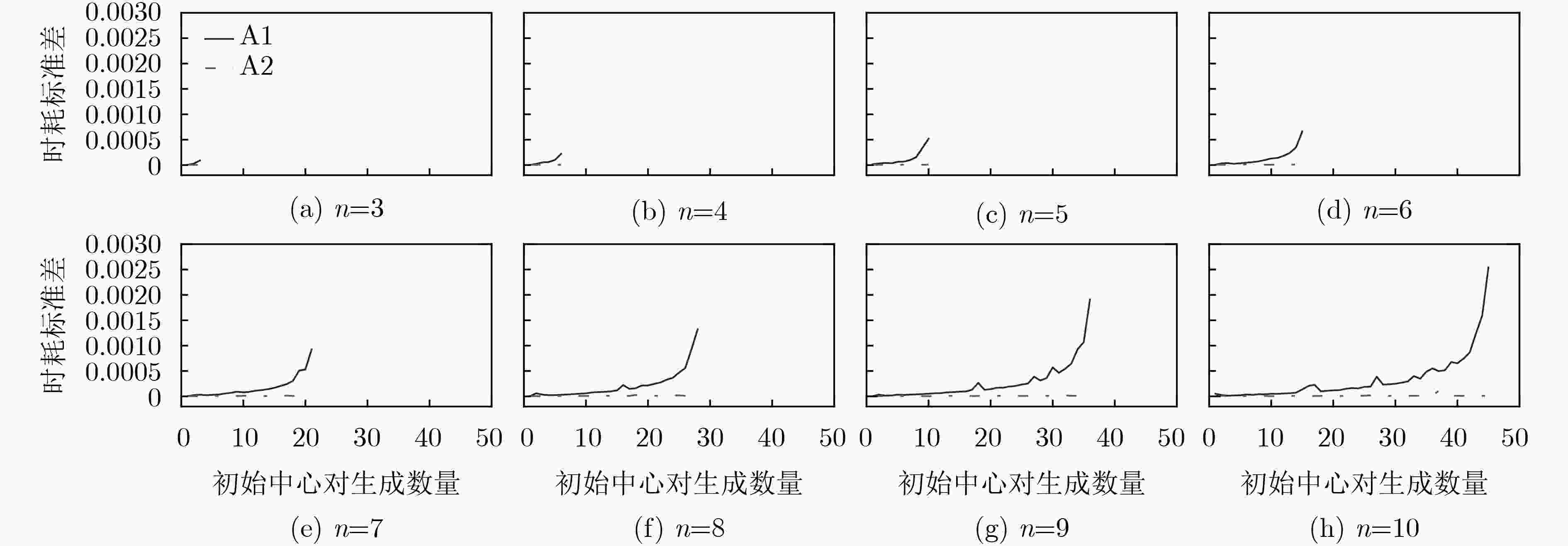
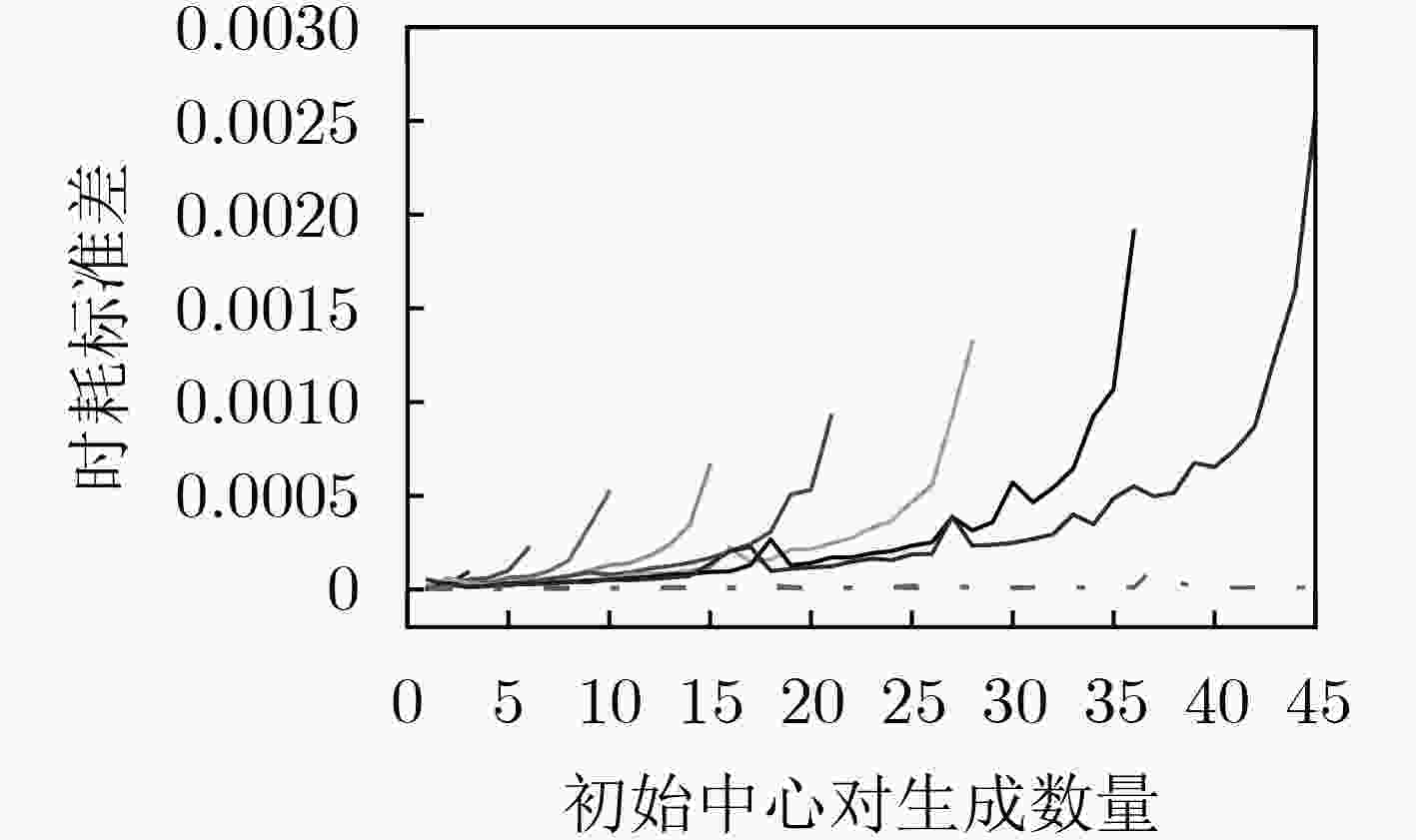


 下载:
下载:
