A BI-TODIM Approach Used for Heterogeneous Information Fusion
-
摘要: 为了解决混合类型数据与专家知识等异质信息的融合决策问题,该文提出了基于信任区间的交互式多属性识别(BI-TODIM)方法。完善了混合类型数据的距离测度,根据信任区间的构建定理和灰关联方法构建了未知目标混合类型数据的信任区间,阐明了信任区间与直觉模糊数之间的等价关系,创建了混合类型数据和专家知识的识别决策模型,实现了特征层信息和决策层信息的统一表达;分析了基于信度函数的逼近理想解(BF-TOPSIS)方法的反转现象及算法的复杂度,定义了区间数的序关系,提出了BI-TODIM识别决策方法,及基于直觉模糊熵的未知权重计算方法。结合算例和目标识别案例,验证了该文方法在解决排序反转和异质信息融合方面的有效性,突出了该方法时间复杂度低、稳定性好、识别准确度高的优点。Abstract: A the Interative Multi-criteria Decision making based on Belief Interval (BI-TODIM) approach is proposed to solve the fusion decision problem of heterogeneous information with mixed type data and expert knowledge. According to the construction theorem of trust interval and grey relation method, the trust interval of mixed type data of unknown target is constructed. The equivalence relationship between trust interval and intuitionistic fuzzy number is clarified. The recognition decision model of mixed type data and expert knowledge is established. The unified expression of feature layer information and decision layer information is realized. The shortcomings of the Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution based on Belief Function (BF-TOPSIS) method are analyzed such as the inversion phenomenon and the complexity. To solve this problem, the order relation of interval numbers is defined, the BI-TODIM recognition decision method and the method of calculating unknown weight based on intuitionistic fuzzy entropy are proposed. The effectiveness of the proposed method in resolving ranking inversion and heterogeneous information fusion is verified by an example and a target identification case, which underlines low time complexity, good stability and high recognition accuracy.
-
表 1 本文方法及BF-TOPSIS1/2的计算结果
排序方法 备选方案集 排序结果 运行时间(s) 本文方法 {A1, A2, A3, A4} A1$ \succ $A2$ \succ $A4$ \succ $A3 0.003306 BF-TOPSIS1 A1$ \succ $A2$ \succ $A4$ \succ $A3 0.663752 BF-TOPSIS2 A1$ \succ $A2$ \succ $A4$ \succ $A3 0.789059 BF-TOPSIS3 A2$ \succ $A1$ \succ $A4$ \succ $A3 21.255864 表 2 分类结果比较(%)
分类方法 数据集 Iris Wine Glass KNN 95.33 72.47 74.29 LST-KSVC 99.27 94.27 65.76 FGGCA 97.22 97.10 93.65 WLTSVM 98.00 96.40 49.91 本文方案 97.10 96.20 94.70 表 3 工作模式的数据取值范围
类别 特征参数 RF(MHz) PRI(μs) PW(μs) Cr R1 [4940, 5160] [3680, 3750] [0.6, 1.2] [0.3800, 0.4041] R2 [5420, 5520] [3600, 3680] [0.2, 0.5] [0.6626, 0.6731] R3 [5100, 5420] [3580, 3650] [1.6, 2.0] [0.1622, 0.2294] R4 [5160, 5220] [3730, 3800] [0.9, 1.4] [0.6587, 0.6981] R5 [5520, 5620] [3450, 3550] [1.2, 1.5] [0.7776, 0.8098] 表 4 参数1下识别结果的正确率(%)
目标 本文方法 BF-TOPSIS1方法 本文权重 权重1 权重2 本文权重 权重1 权重2 1 97.3 91.8 60.6 87.2 86.0 33.6 2 94.4 86.8 38.0 79.6 79.6 27.9 3 97.1 92.3 52.4 88.7 87.8 33.2 -
[1] YING Chengshuo, LI Yanlai, CHIN K, et al. A new product development concept selection approach based on cumulative prospect theory and hybrid-information MADM[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2018, 122: 251–261. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2018.05.023 [2] 陈可嘉, 陈萍. 基于三参数区间灰数的TOPSIS决策方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(1): 124–130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.01.18CHEN Kejia and CHEN Ping. Decision making method of TOPSIS based on three-parameter interval grey numbers[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(1): 124–130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.01.18 [3] 关欣, 孙贵东, 衣晓, 等. 基于关联系数靶心距的混合多属性识别[J]. 航空学报, 2015, 36(7): 2431–2443. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2014.0299GUAN Xin, SUN Guidong, YI Xiao, et al. Hybrid multiple attribute recognition based on coefficient of incidence bull’s-eye-distance[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(7): 2431–2443. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2014.0299 [4] LOURENZUTTI R and KROHLING R A. TODIM based method to process heterogeneous information[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2015, 55: 318–327. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2015.07.056 [5] CHEN S, KUO Liwei, and ZOU Xinyao. Multiattribute decision making based on Shannon’s information entropy, non-linear programming methodology, and interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy values[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 465: 404–424. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.06.047 [6] CHENG Jin, FENG Yixiong, LIN Zhiqiang, et al. Anti-vibration optimization of the key components in a turbo-generator based on heterogeneous axiomatic design[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 141: 1467–1477. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.09.217 [7] 刁鹏飞, 王艳娇. 基于节点休眠的水下无线传感器网络覆盖保持分簇算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(5): 1101–1107. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170787DIAO Pengfei and WANG Yanjiao. Coverage-preserving clustering algorithm for underwater sensor networks based on the sleeping mechanism[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(5): 1101–1107. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170787 [8] PAVLICIC D. Normalization affects the results of MADM methods[J]. Yugoslav Journal of Operations Research, 2001, 11(2): 251–265. [9] DEZERT J, HAN Deqiang, and YIN Hanlin. A new belief function based approach for multi-criteria decision-making support[C]. The 19th International Conference on Information Fusion, Heidelberg, Germany, 2016: 782–789. [10] 李双明, 关欣, 赵静, 等. 一种参数区间交叉类型的目标识别方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(7): 1307–1316.LI Shuangming, GUAN Xin, ZHAO Jing, et al. A methodology for target recognition with parameters of interval cross type[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(7): 1307–1316. [11] IRPINO A and VERDE R. Dynamic clustering of interval data using a Wasserstein-based distance[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2008, 29(11): 1648–1658. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2008.04.008 [12] ACI M and AVCI M. K nearest neighbor reinforced expectation maximization method[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2011, 38(10): 12585–12591. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2011.04.046 [13] NIE Qingfeng, JIN Lizuo, FEI Shumin, et al. Neural network for multi-class classification by boosting composite stumps[J]. Neurocomputing, 2015, 149: 949–956. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.07.039 [14] SANCHEZ M A, CASTILLO O, CASTRO J R, et al. Fuzzy granular gravitational clustering algorithm for multivariate data[J]. Information Sciences, 2014, 279: 498–511. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2014.04.005 [15] SHAO Yuanhai, CHEN Weijie, WANG Zhen, et al. Weighted linear loss twin support vector machine for large-scale classification[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2015, 73: 276–288. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2014.10.011 [16] 黄颖坤, 金炜东, 葛鹏, 等. 基于多尺度信息熵的雷达辐射源信号识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1084–1091. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180535HUANG Yingkun, JIN Weidong, GE Peng, et al. Radar emitter signal identification based on multi-scale information entropy[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1084–1091. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180535 -





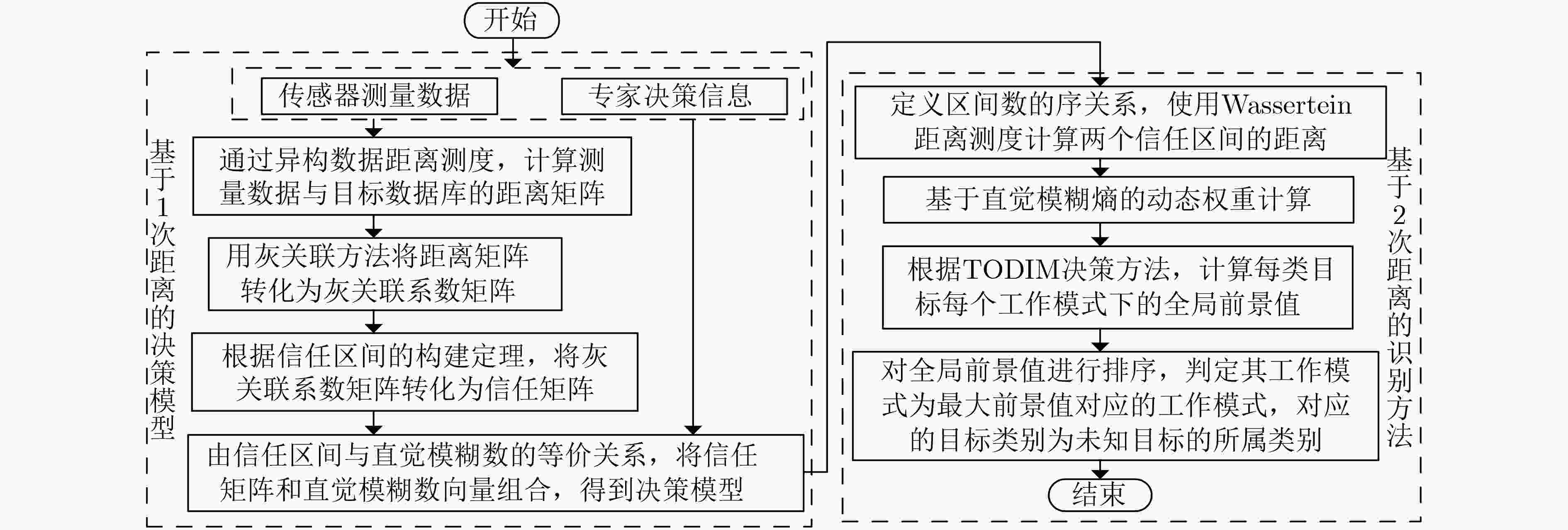
 下载:
下载:
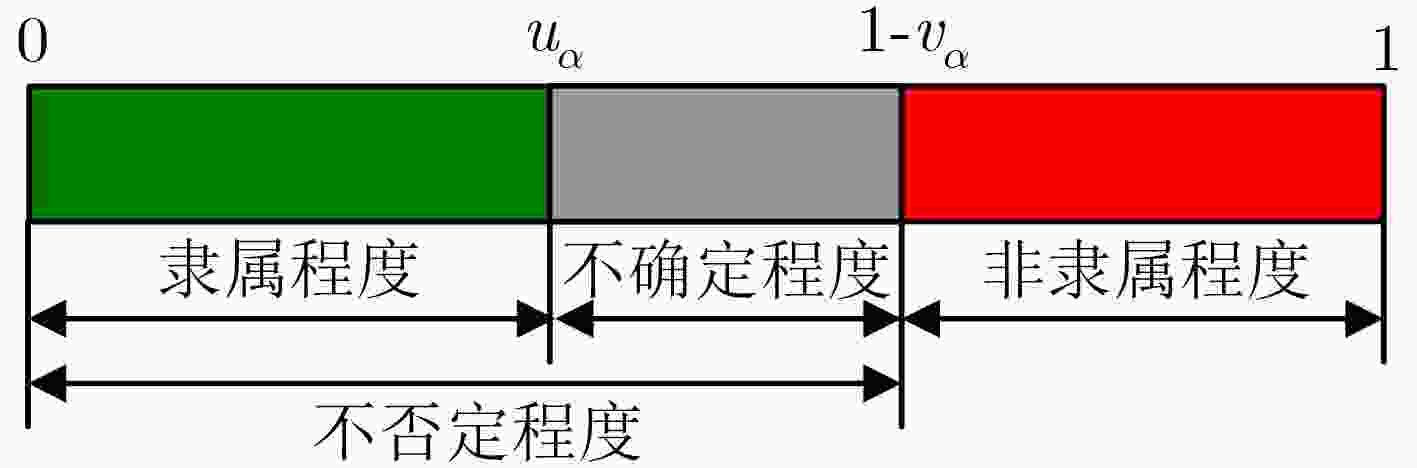
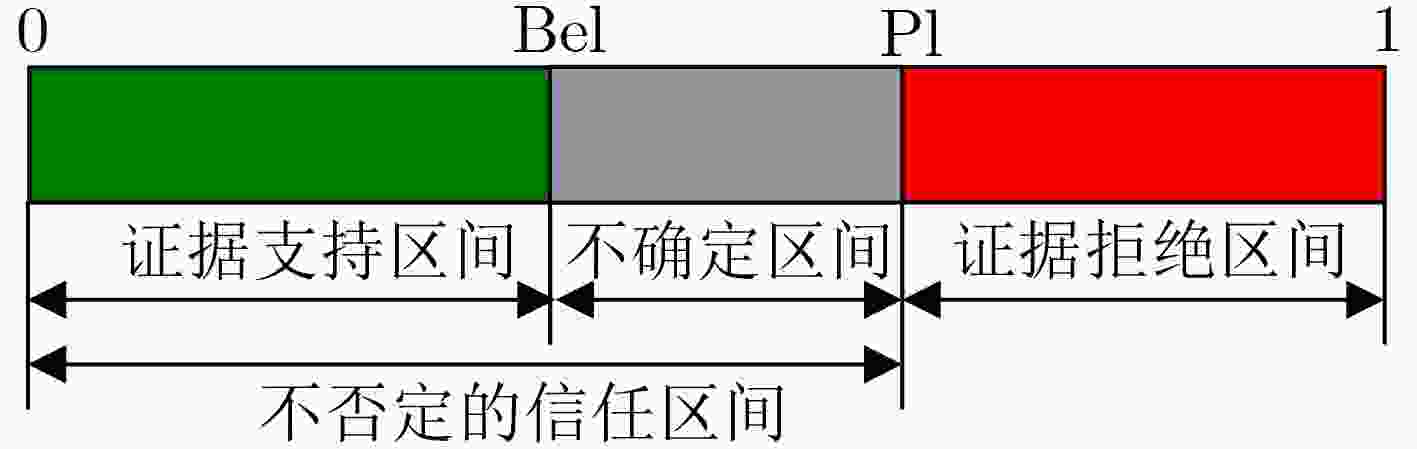
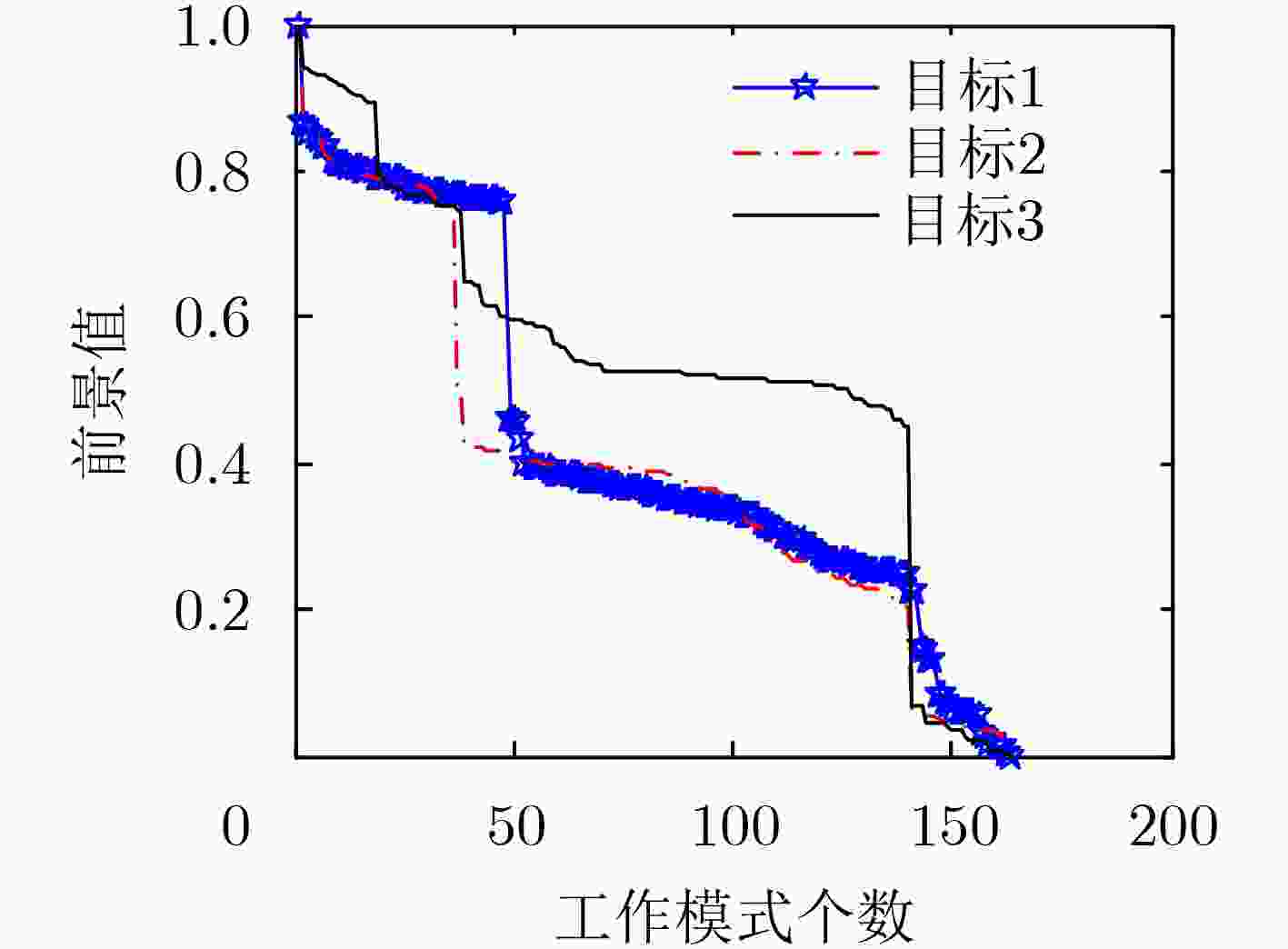


 下载:
下载:
