A Glioma Detection and Segmentation Method in MR Imaging
-
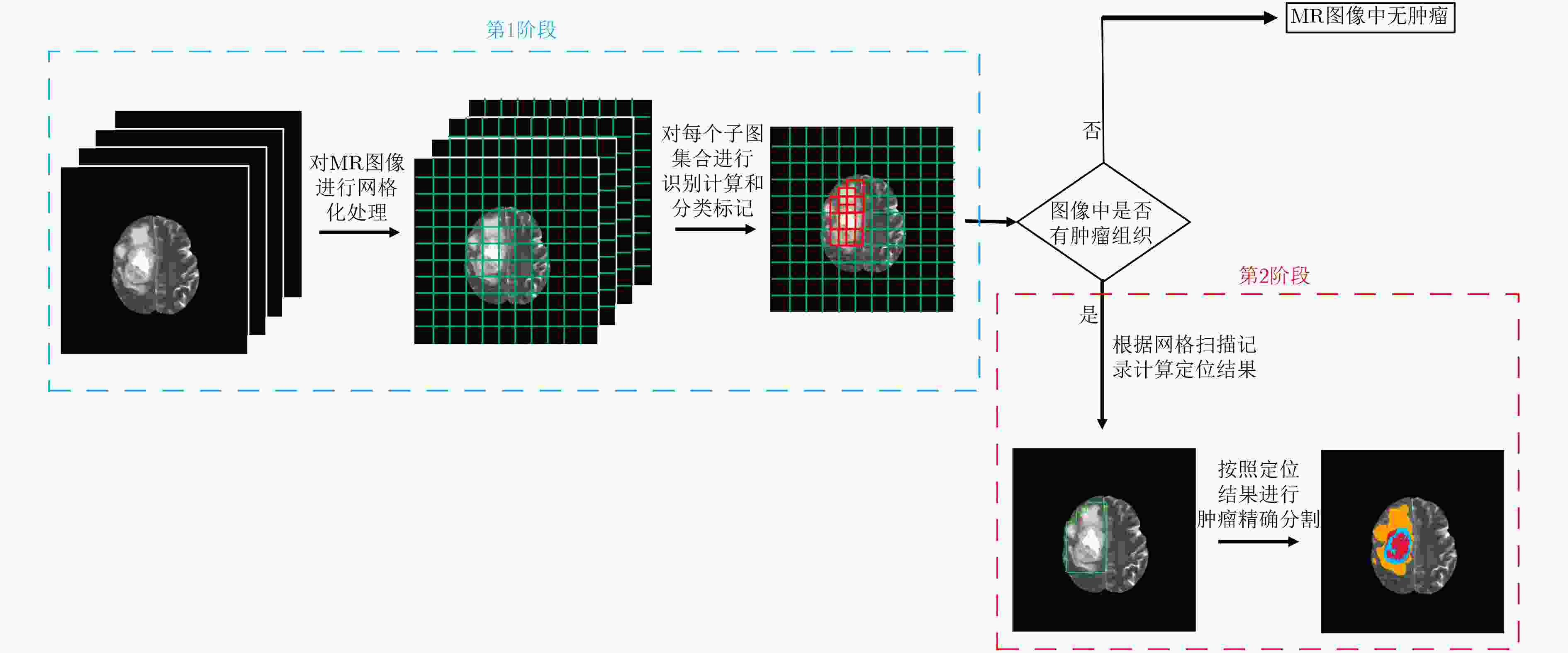
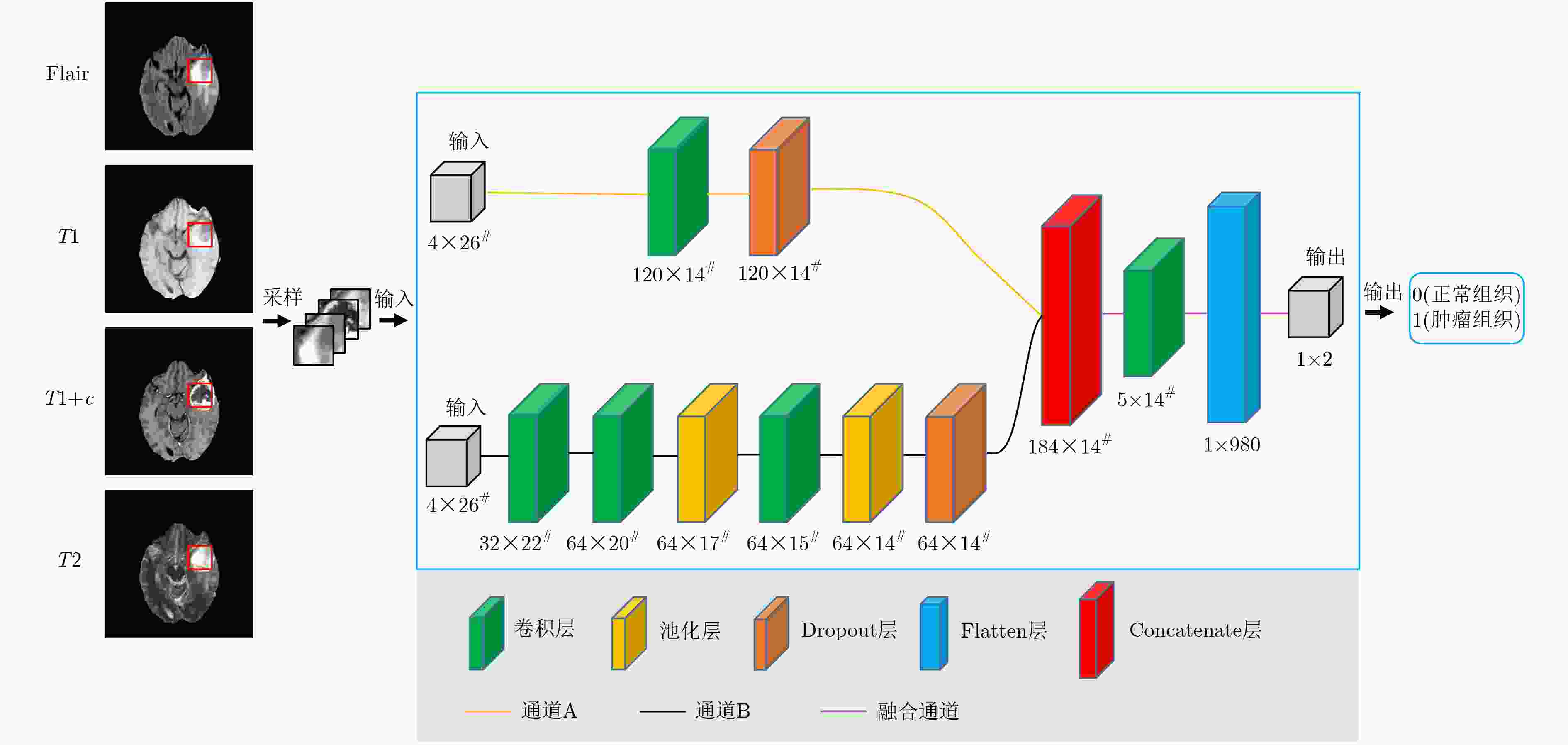
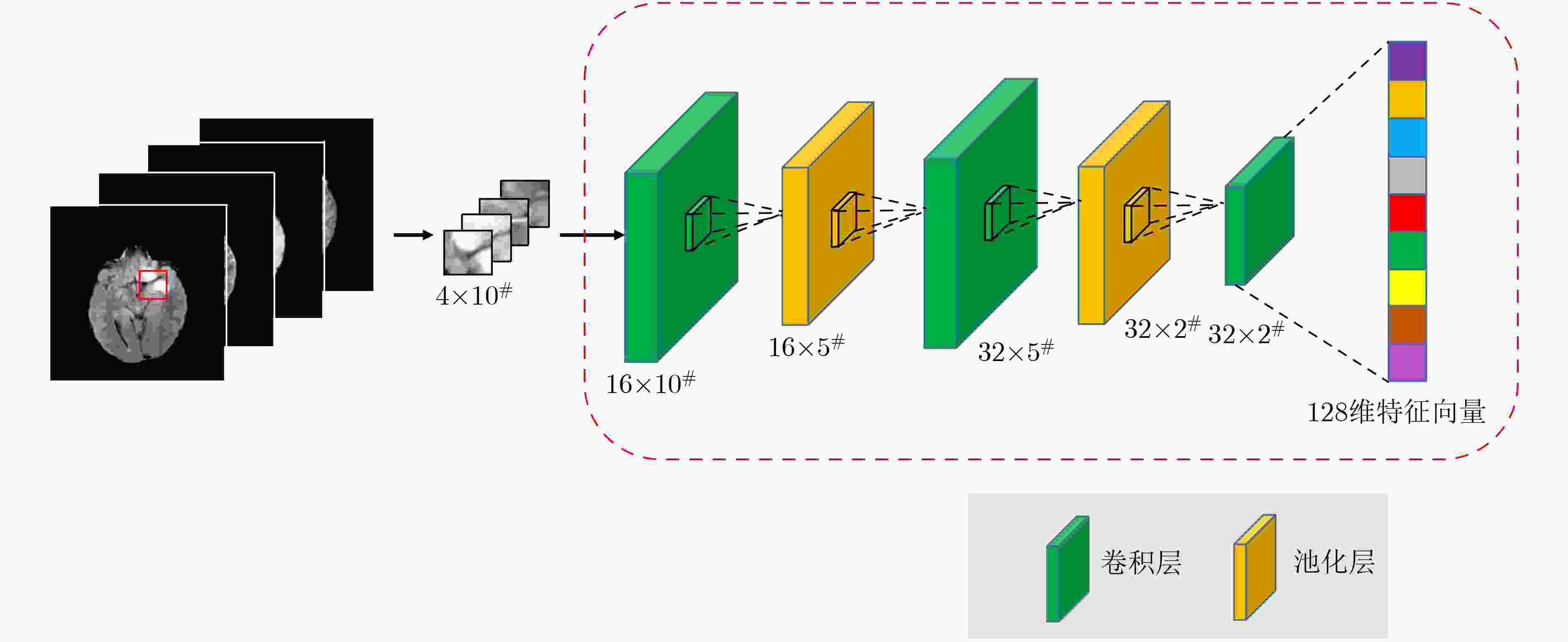
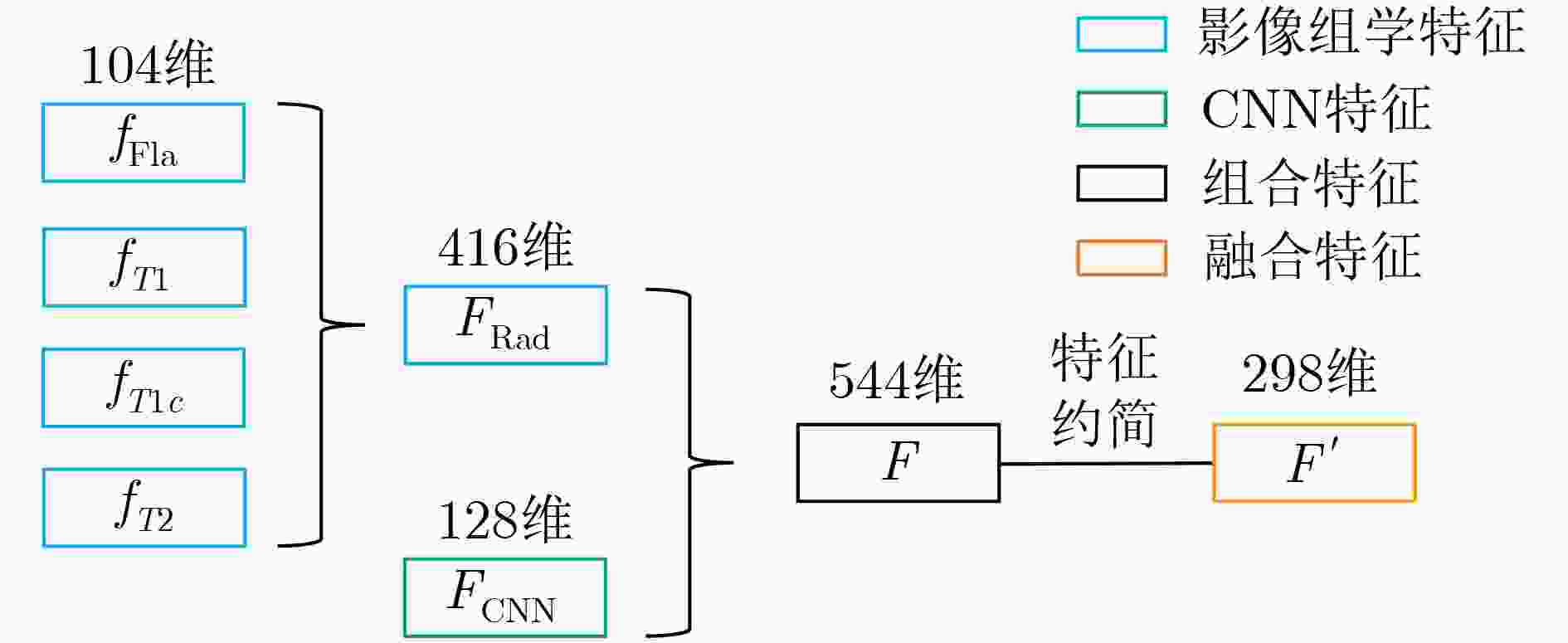
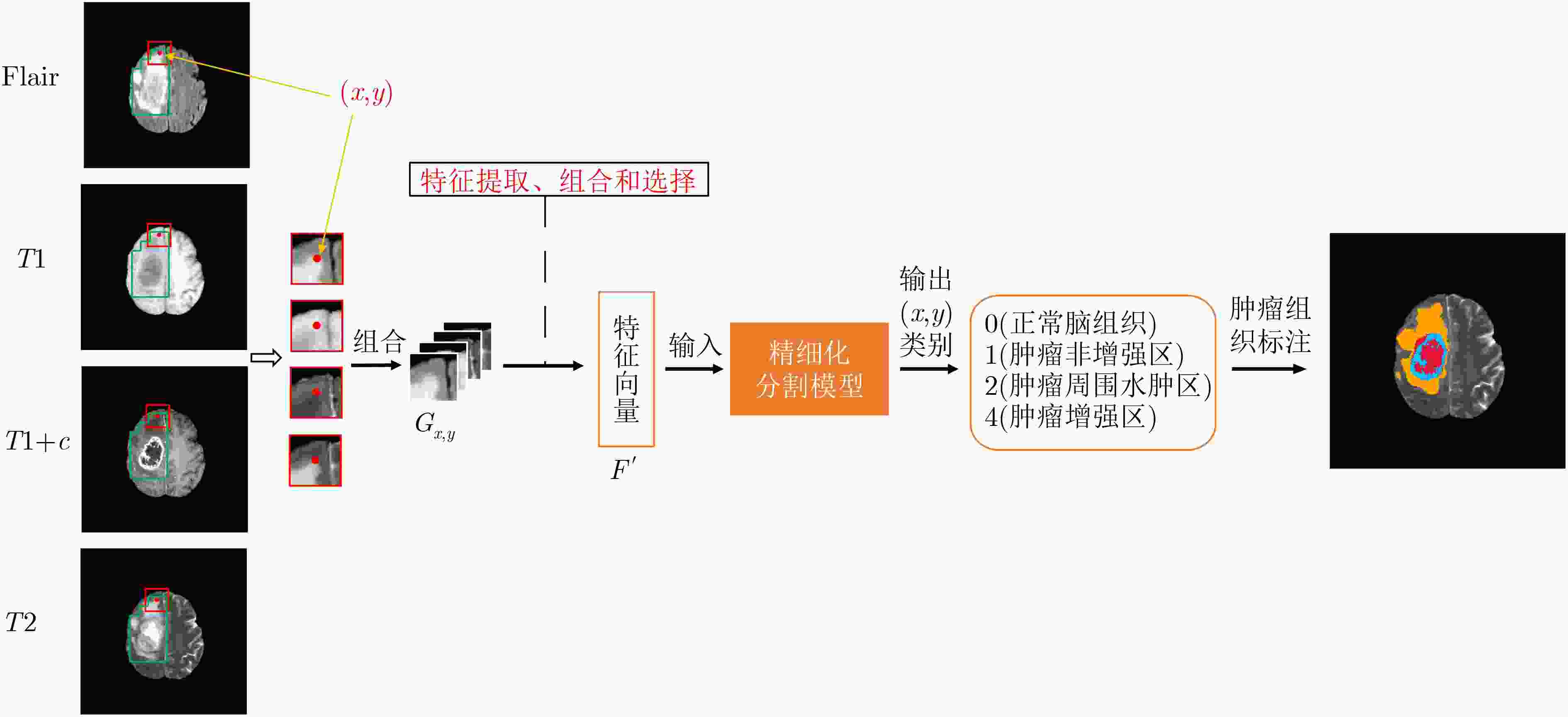
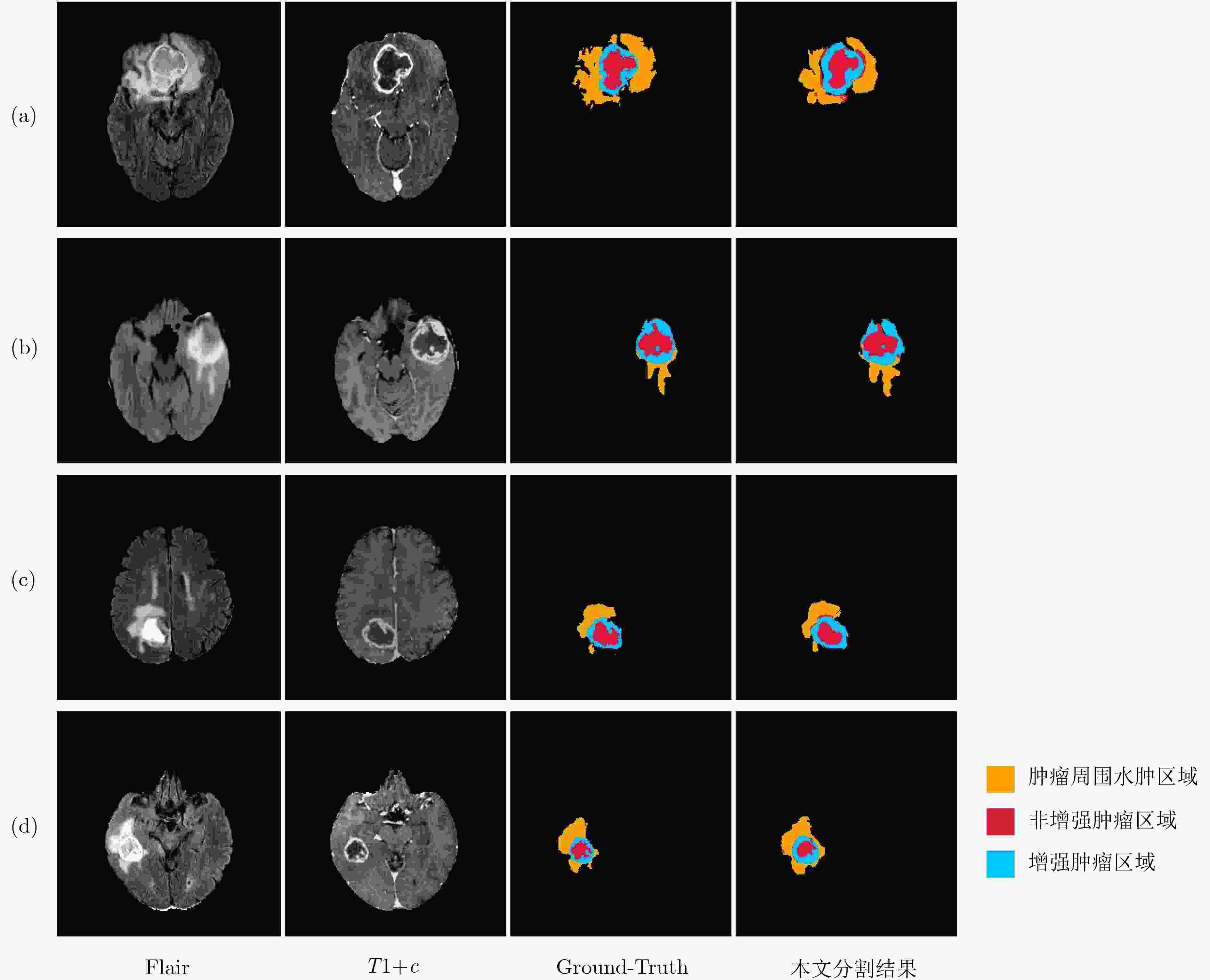
摘要: 针对磁共振图像(MRI)进行脑胶质瘤检测及病灶分割对临床治疗方案的选择和手术实施过程的引导都有着重要的价值。为了提高脑胶质瘤的检测效率和分割准确率,该文提出了一种两阶段计算方法。首先,设计了一个轻量级的卷积神经网络,并通过该网络完成MR图像中肿瘤的快速检测及大致定位;接着,通过集成学习过程对肿瘤周围水肿、肿瘤非增强区、肿瘤增强区和正常脑组织等4种不同区域进行分类与彼此边界的精细分割。为提高分割的准确率,在MR图像中提取了416维影像组学特征并与128维通过卷积神经网络提取的高阶特征进行组合和特征约简,将特征约简后产生的298维特征向量用于分类学习。为对算法的性能进行验证,在BraTS2017数据集上进行了实验,实验结果显示该文提出的方法能够快速检测并定位肿瘤,同时相比其它方法,整体分割精度也有明显提升。Abstract: The glioma detection and focus segmentation in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has important value for the therapeutic schedule selection and the surgical operations. In order to improve the detection efficiency and segmentation accuracy for glioma, this paper proposes a two-stage calculating method. First, a light convolutional neural network is designed to implement rapidly detection and localization for the glioma in MR images. Then, the peritumoral edema, non-enhancing tumor, enhancing tumor, and normal are classified and segmented from each other through an Ensemble Learning (EL) process. In order to improve the accuracy of segmentation, 416 radiomics features extracted from multi-modal MR images and 128 CNN features extracted by a convolutional neural network are mixed. The feature vector consisting of 298 features for classification learning are formed after a feature reduction process. In order to verify the performance of the proposed algorithm, experiments are carried out on the BraTS2017 dataset. The experimental results show that the proposed method can quickly detect and locate the tumor. The overall segmentation accuracy is improved distinctly with respect to 4 state-of-the-art approaches.
-
Key words:
- Tumor detection /
- Focus segmentation /
- Features selection /
- Ensemble Learning (EL)
-
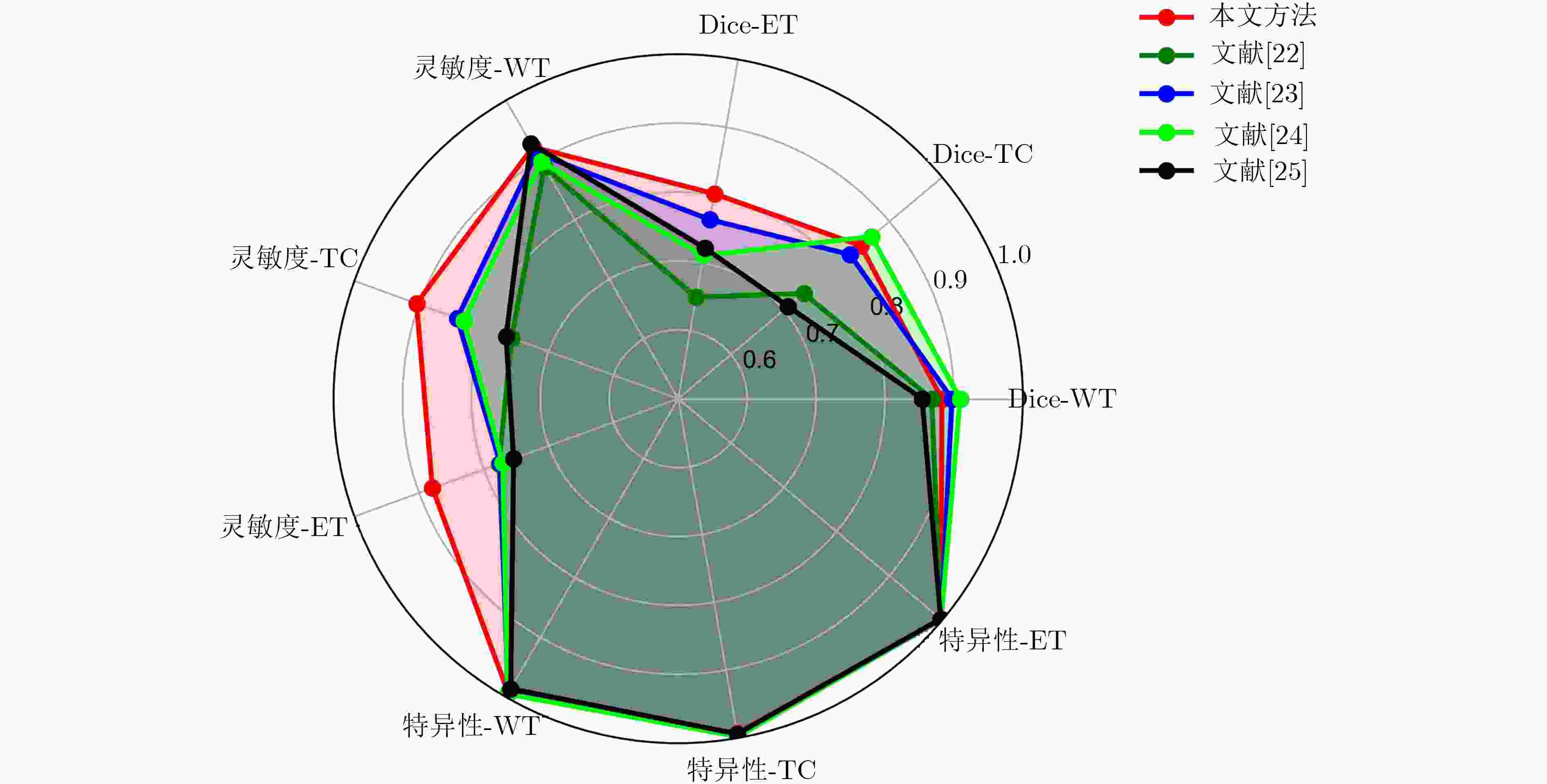
表 1 实验统计结果
方法 Dice系数 灵敏度 特异性 WT TC ET WT TC ET WT TC ET 均值 0.882 0.846 0.802 0.922 0.904 0.879 0.993 0.993 0.998 标准差 0.055 0.084 0.121 0.069 0.073 0.063 0.010 0.006 0.002 中值 0.904 0.845 0.795 0.938 0.932 0.875 0.996 0.994 0.999 第1四分位数 0.863 0.799 0.765 0.885 0.841 0.829 0.993 0.991 0.997 第3四分位数 0.938 0.896 0.865 0.981 0.967 0.919 0.998 0.997 0.999 表 2 实验结果对比
表 3 实验效率对比
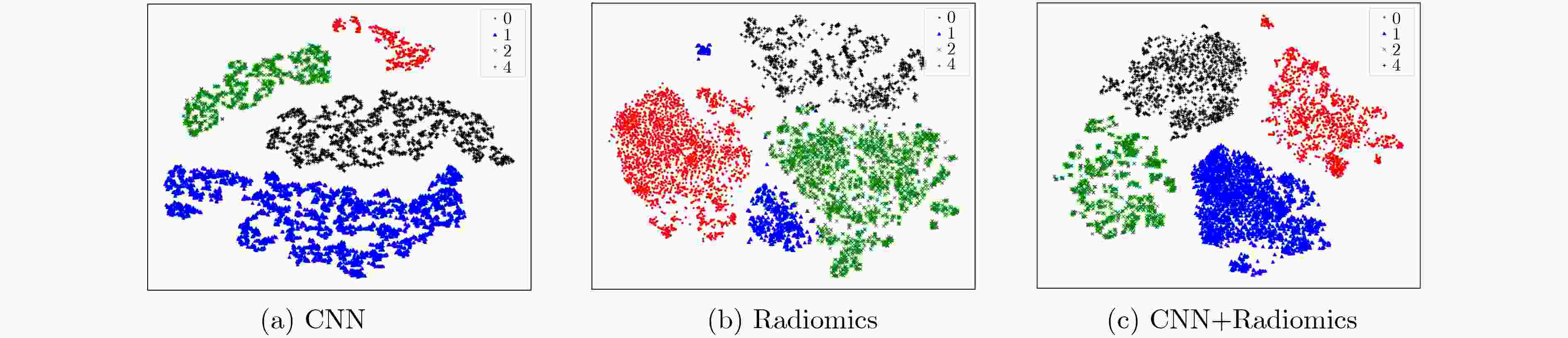
Dice-WT Dice-TC Dice-ET 时间(s) 本文方法 0.882 0.846 0.802 258.3 RF 0.854 0.802 0.770 796.5 XGBoost 0.882 0.845 0.802 814.6 U-Net 0.796 0.769 0.681 4.2 表 4 3组特征聚类结果的评价结果
方法 AMI 均一性 V-Measure CNN 0.4361 0.4363 0.4657 Radiomics 0.2972 0.2974 0.3105 CNN + Radiomics 0.4796 0.4798 0.4816 -
FURNARI F B, FENTON T, BACHOO R M, et al. Malignant astrocytic glioma: Genetics, biology, and paths to treatment[J]. Genes & Development, 2007, 21(21): 2683–2710. doi: 10.1101/gad.1596707 OHGAKI H and KLEIHUES P. Population-based studies on incidence, survival rates, and genetic alterations in astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas[J]. Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology, 2005, 64(6): 479–489. SACHDEVA J, KUMAR V, GUPTA I, et al. Segmentation, feature extraction, and multiclass brain tumor classification[J]. Journal of Digital Imaging, 2013, 26(6): 1141–1150. doi: 10.1007/s10278-013-9600-0 SOLTANINEJAD M, YANG Guang, LAMBROU T, et al. Automated brain tumour detection and segmentation using superpixel-based extremely randomized trees in FLAIR MRI[J]. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2017, 12(2): 183–203. doi: 10.1007/s11548-016-1483-3 SONG Guoli, HUANG Zheng, ZHAO Yiwen, et al. A Noninvasive system for the automatic detection of gliomas based on hybrid features and PSO-KSVM[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 13842–13855. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2894435 CAO Zhantao, DUAN Lixin, YANG Guowu, et al. Breast tumor detection in ultrasound images using deep learning[C]. The 3rd International Workshop on Patch-based Techniques in Medical Imaging, Quebec City, Canada, 2017: 121–128. SHKOLYAR E, JIA Xiao, CHANG T C, et al. Augmented bladder tumor detection using deep learning[J]. European Urology, 2019, 76(6): 714–718. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.08.032 ÖZYURT F, SERT E, and AVCI D. An expert system for brain tumor detection: Fuzzy c-means with super resolution and convolutional neural network with extreme learning machine[J]. Medical Hypotheses, 2019, 134: 109433. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2019.109433 KUMAR S, NEGI A, SINGH J H, et al. Brain tumor segmentation and classification using MRI images via fully convolution neural networks[C]. 2018 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication Control and Networking, Greater Noida, India, 2018: 1178–1181. ZHAO Xiaomei, WU Yihong, SONG Guidong, et al. A deep learning model integrating FCNNs and CRFs for brain tumor segmentation[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2018, 43: 98–111. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2017.10.002 YANG Tiejun and SONG Jikun. An automatic brain tumor image segmentation method based on the U-Net[C]. The 2018 4th International Conference on Computer and Communications, Chengdu, China, 2018: 1600–1604. AMIRI A, MAHJOUB M A, and REKIK I. Tree-based ensemble classifier learning for automatic brain glioma segmentation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 313: 135–142. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.05.112 MUDGAL T K, GUPTA A, JAIN S, et al. Automated system for brain tumour detection and classification using eXtreme gradient boosted decision trees[C]. 2017 International Conference on Soft Computing and its Engineering Applications, Changa, India, 2017: 1–6. 陈忠辉, 凌献尧, 冯心欣, 等. 基于模糊c均值聚类和随机森林的短时交通状态预测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(8): 1879–1886. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171090CHEN Zhonghui, LING Xianyao, FENG Xinxin, et al. Short-term traffic state prediction approach based on FCM and random forest[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(8): 1879–1886. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171090 RAJAGOPAL R. Glioma brain tumor detection and segmentation using weighting random forest classifier with optimized ant colony features[J]. International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, 2019, 29(3): 353–359. doi: 10.1002/ima.22331 CHO H H and PARK H. Classification of low-grade and high-grade glioma using multi-modal image radiomics features[C]. The 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Seogwipo, South Korea, 2017: 3081–3084. CHADDAD A, DANIEL P, DESROSIERS C, et al. Novel radiomic features based on joint intensity matrices for predicting glioblastoma patient survival time[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2019, 23(2): 795–804. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2018.2825027 罗会兰, 卢飞, 孔繁胜. 基于区域与深度残差网络的图像语义分割[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(11): 2777–2786. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190056LUO Huilan, LU Fei, and KONG Fansheng. Image semantic segmentation based on region and deep residual network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(11): 2777–2786. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190056 KIDO S, HIRANO Y and HASHIMOTO N. Detection and classification of lung abnormalities by use of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and regions with cnn features (R-CNN)[C]. 2018 International Workshop on Advanced Image Technology, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2018: 1–4. SHEN Wei, ZHOU Mu, YANG Feng, et al. Multi-scale convolutional neural networks for lung nodule classification[C]. The 24th International Conference on Information Processing in medical Imaging, Sabhal Mor Ostaig, Isle of Skye, UK, 2015: 588–599. MENZE B H, JAKAB A, BAUER S, et al. The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2015, 34(10): 1993–2014. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2014.2377694 CHEN Shengcong, DING Changxing, and ZHOU Chenhong. Brain tumor segmentation with label distribution learning and multi-level feature representation[C]. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Interventions, Quebec, Canada, 2017: 50–53. WANG Guotai, LI Wenqi, OURSELIN S, et al. Automatic brain tumor segmentation using cascaded anisotropic convolutional neural networks[C]. The 3rd International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop, Quebec City, Canada, 2018: 178–190. ISLAM M and REN Hongliang. Fully convolutional network with hypercolumn features for brain tumor segmentation[C]. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Interventions, Quebec, Canada, 2017: 108–115. ZHOU Fan, LI Tengfei, LI Heng, et al. TP-CNN: A two-phase convolution neural network based model to do automatic brain tumor segmentation by using BRATS 2017 data[C]. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Interventions, Quebec, Canada, 2017: 334–341. -





 下载:
下载:
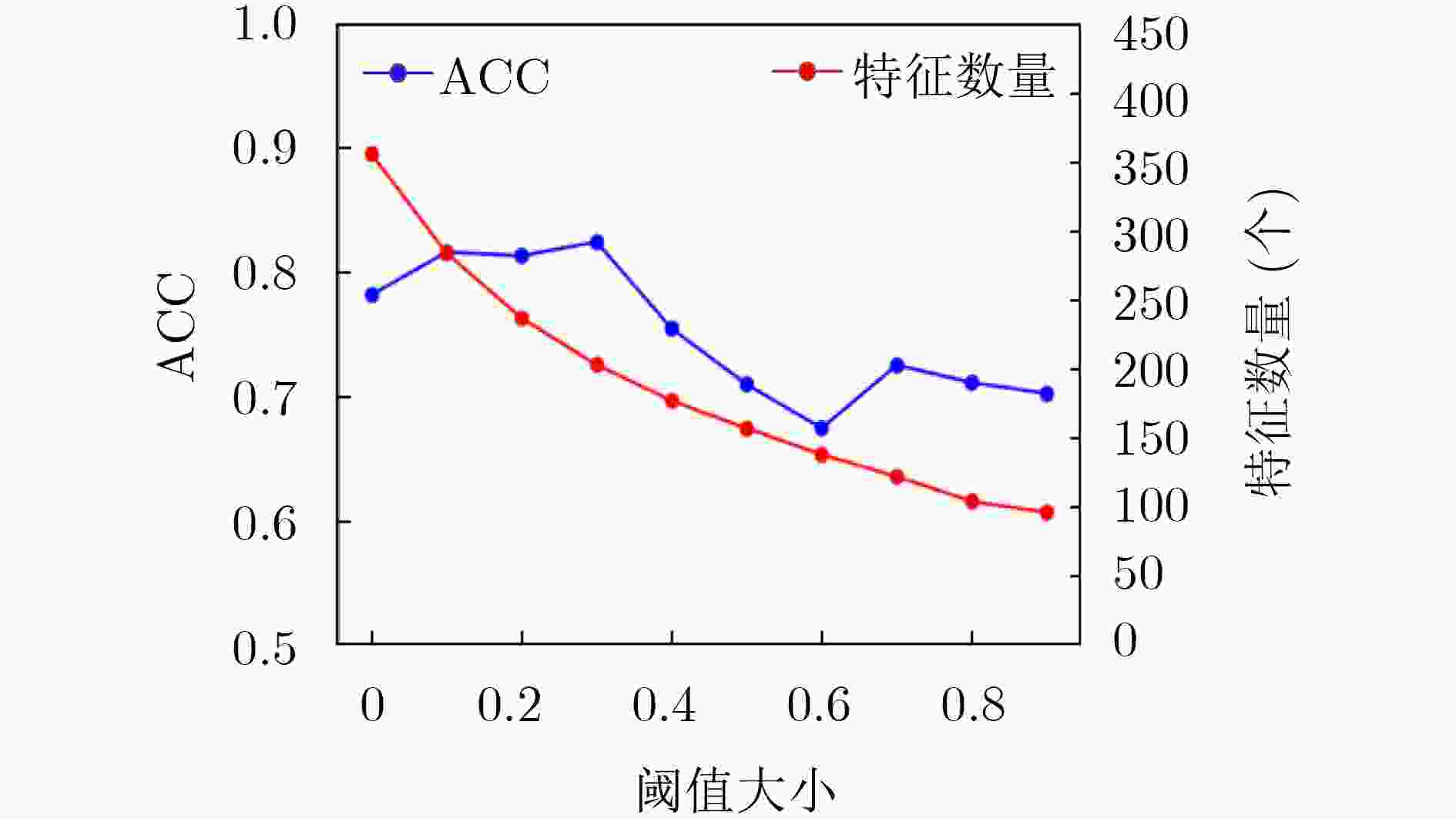
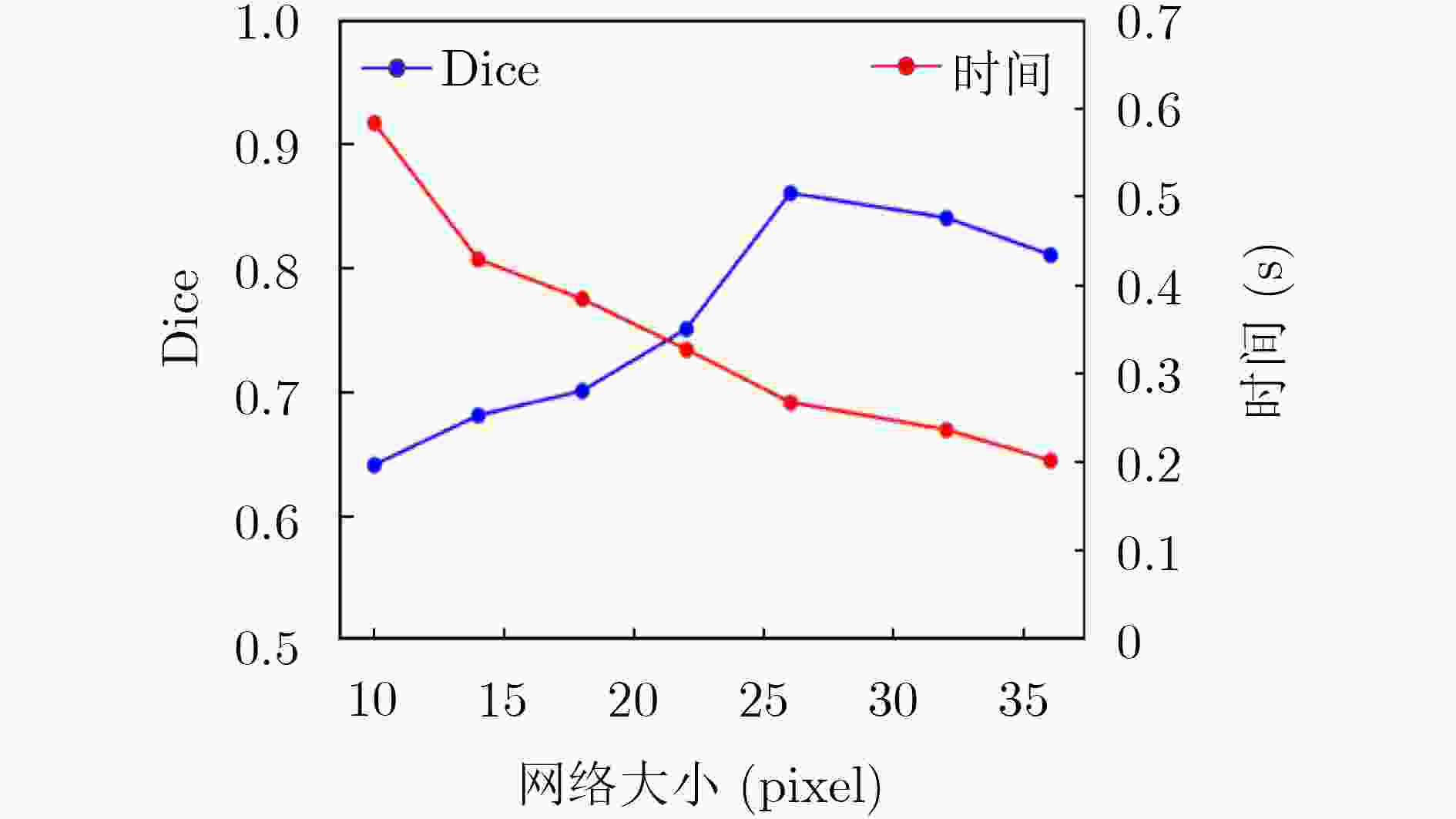
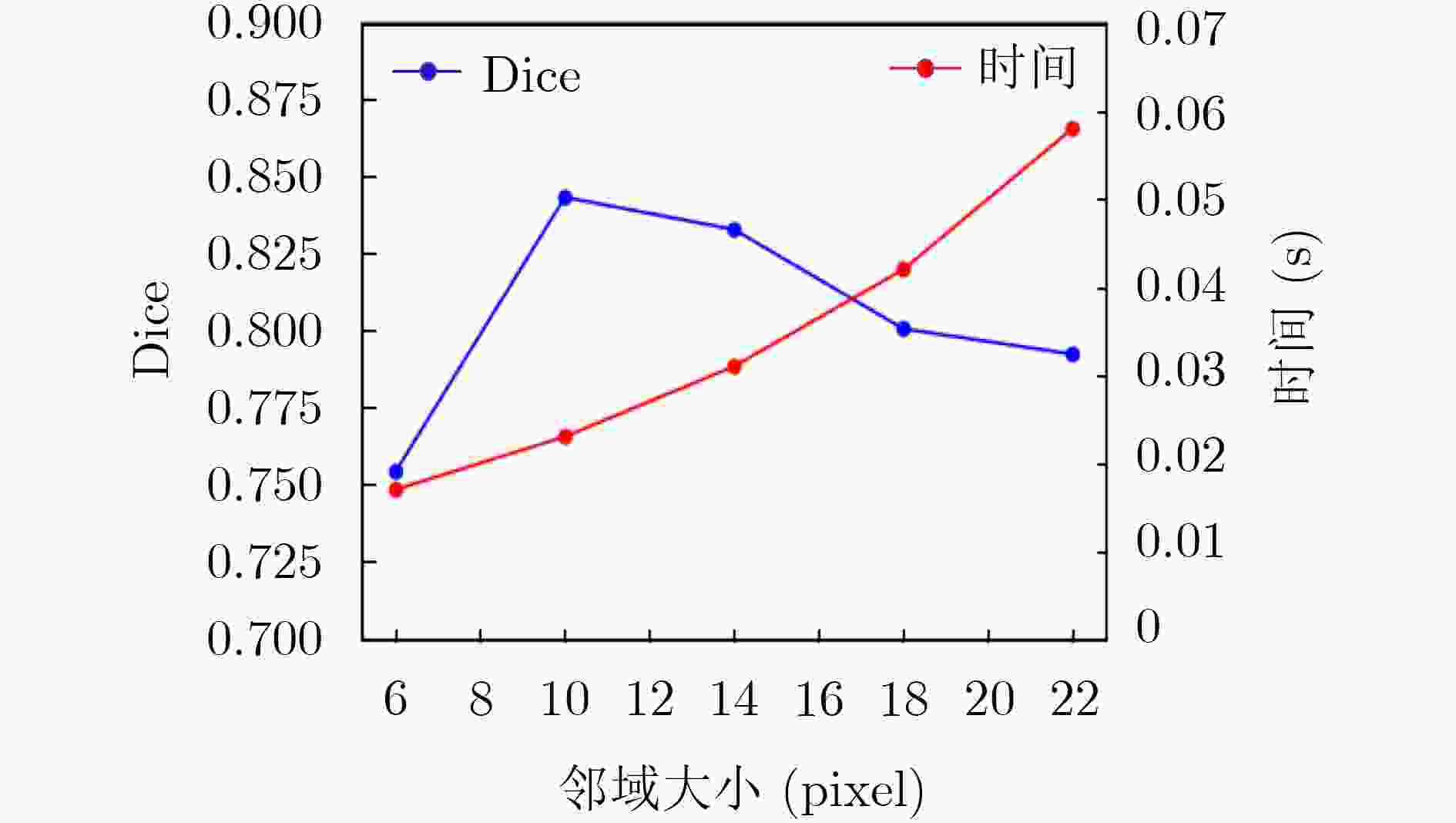


 下载:
下载:
