Research on Mobile Robot Bionic Location Algorithm Based on Growing Self-Organizing Map
-
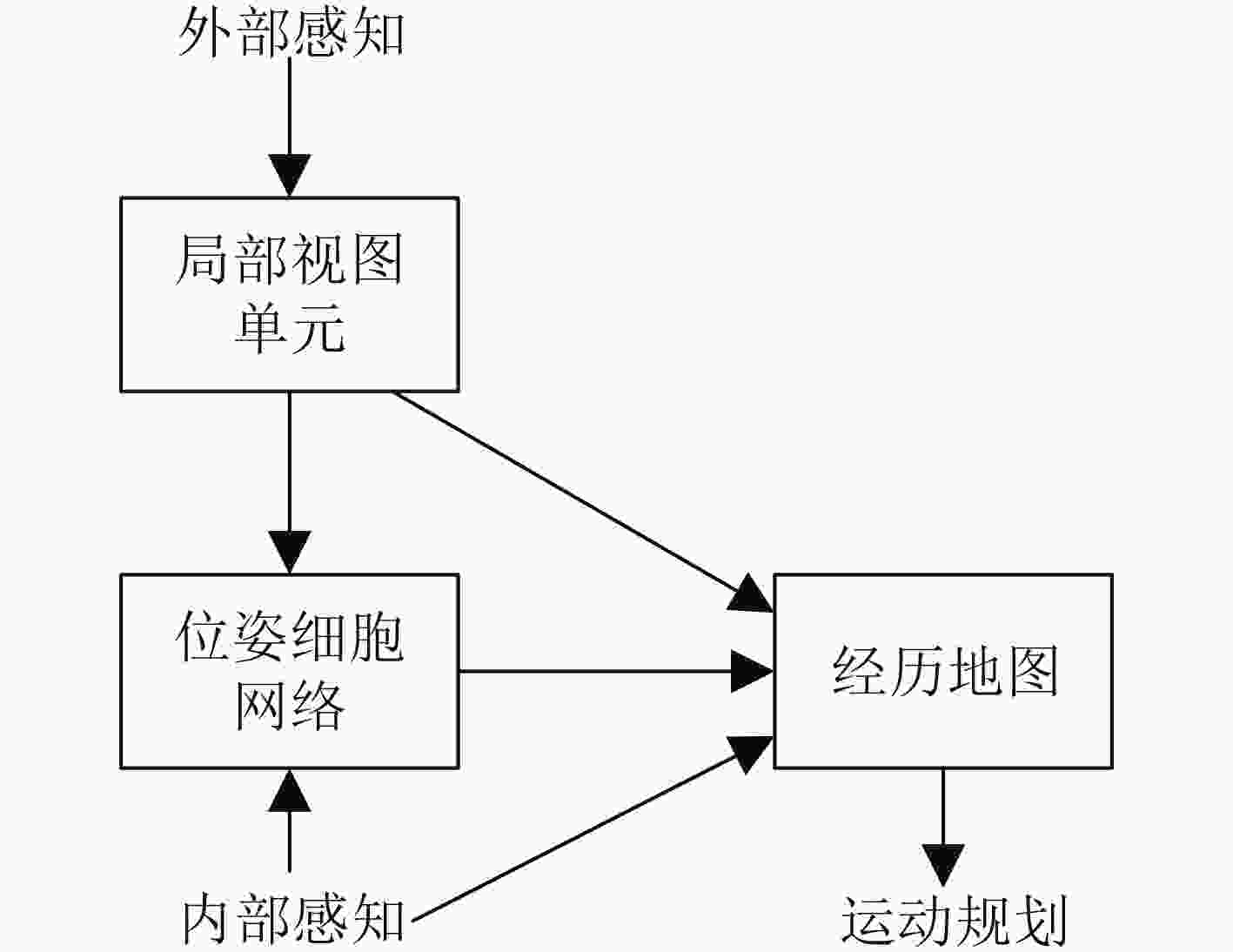
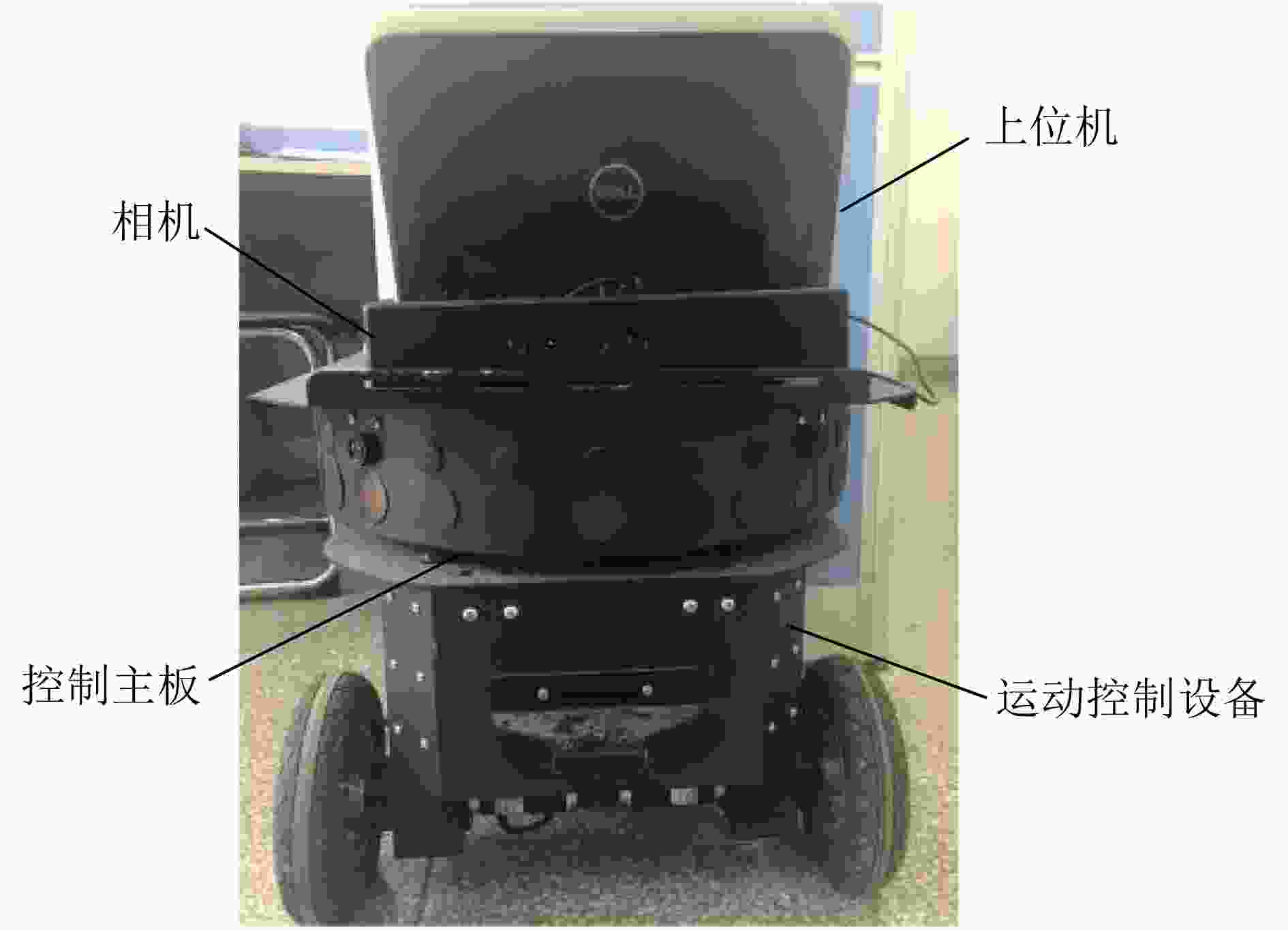
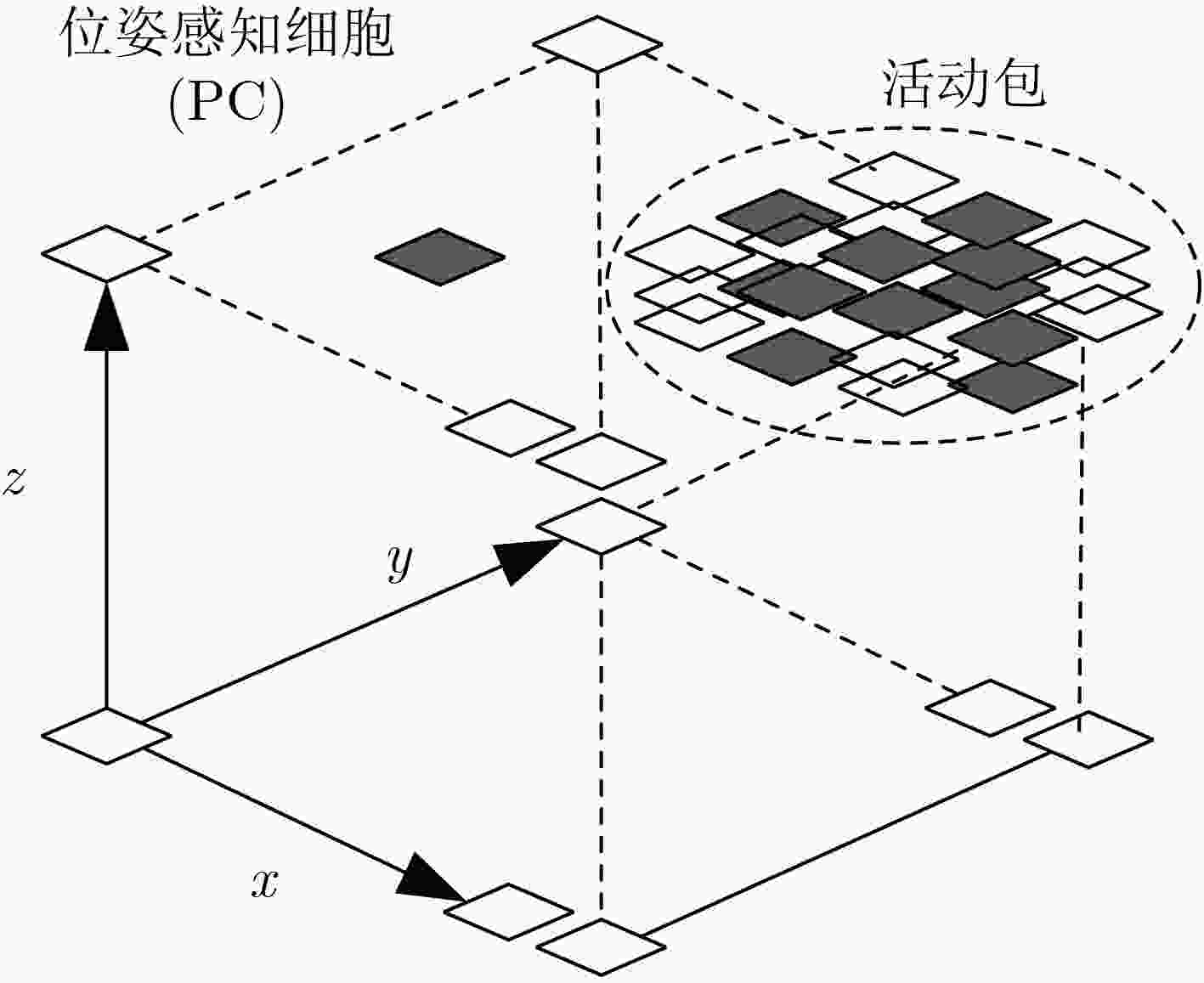
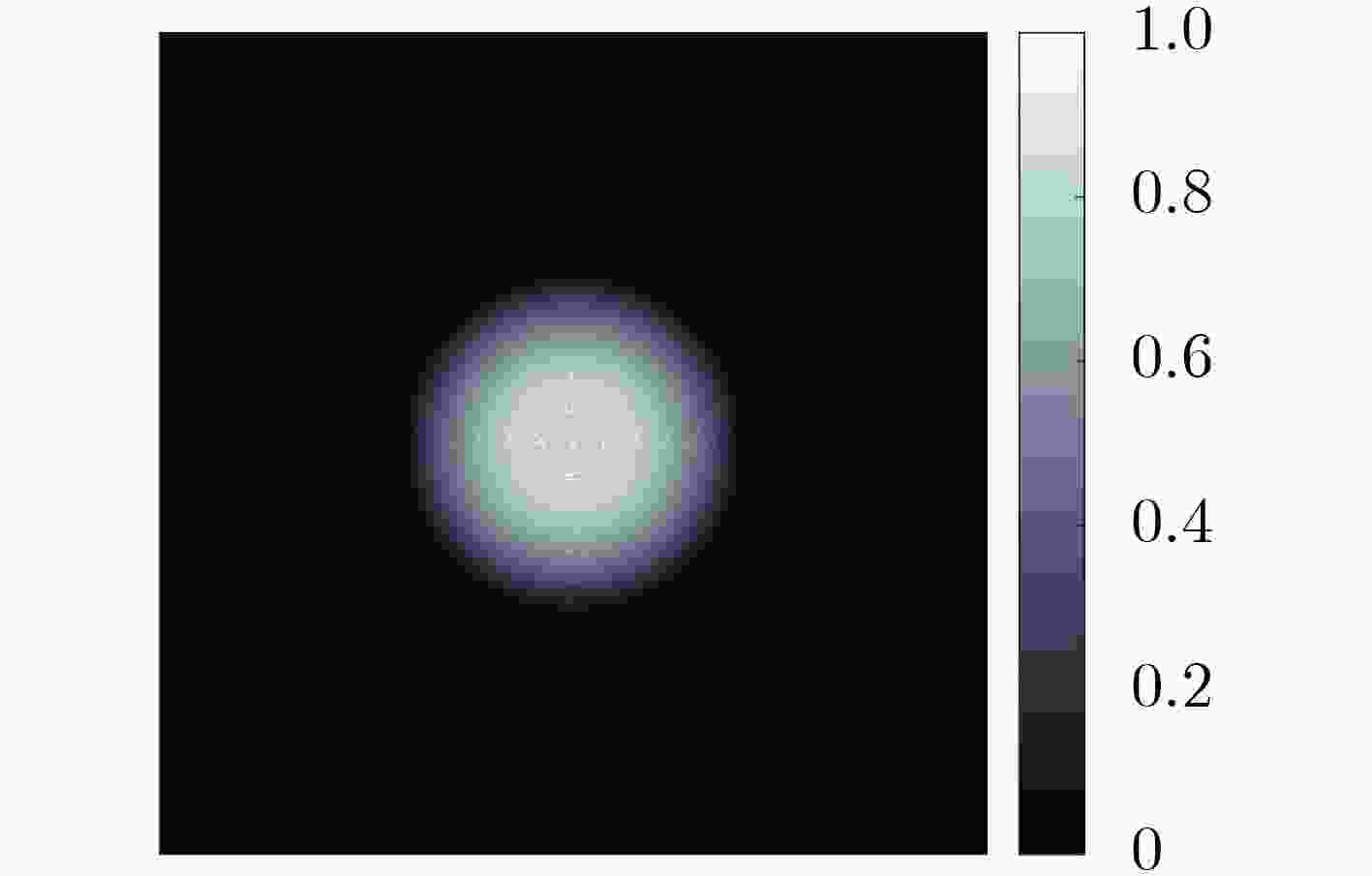
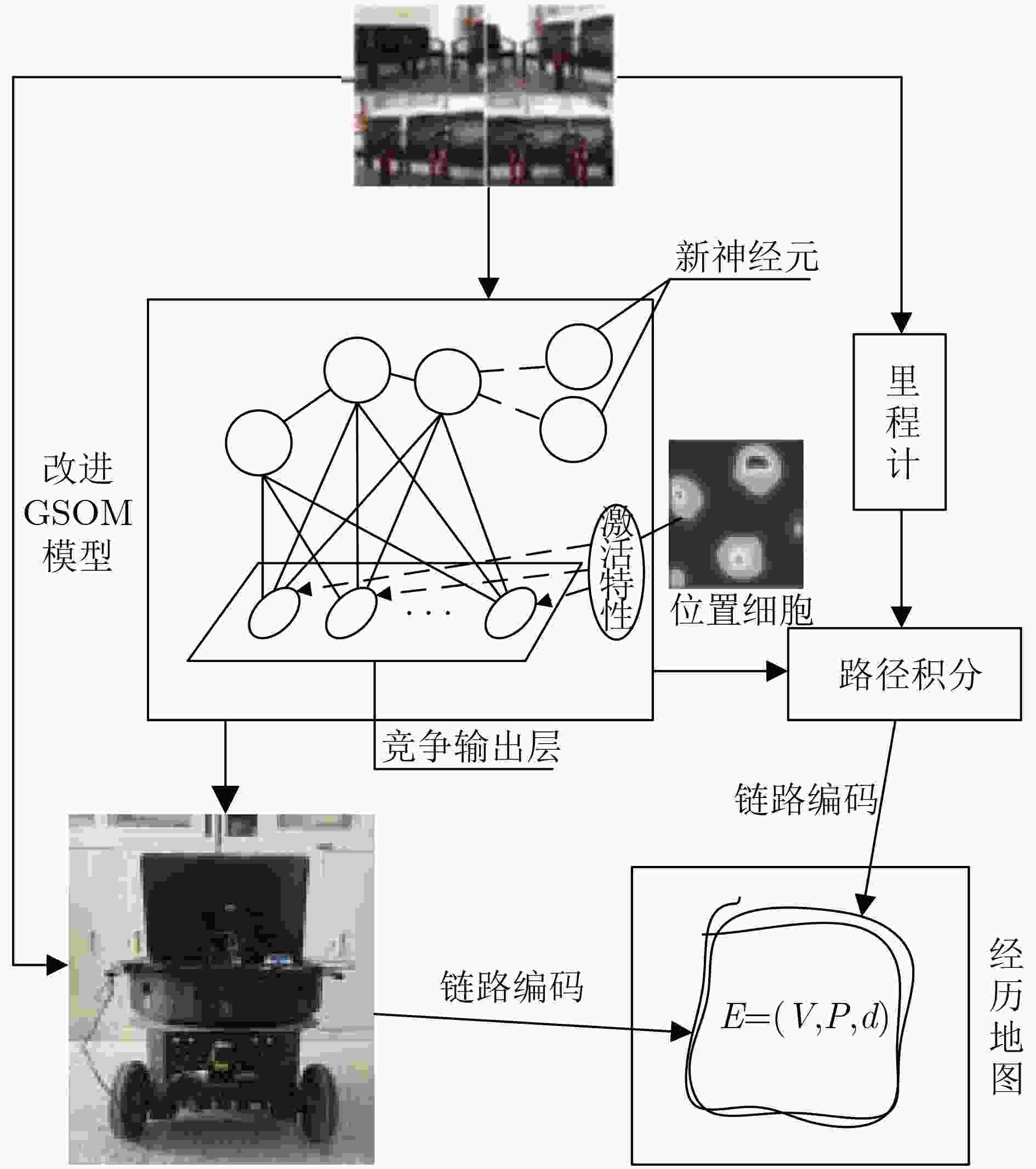
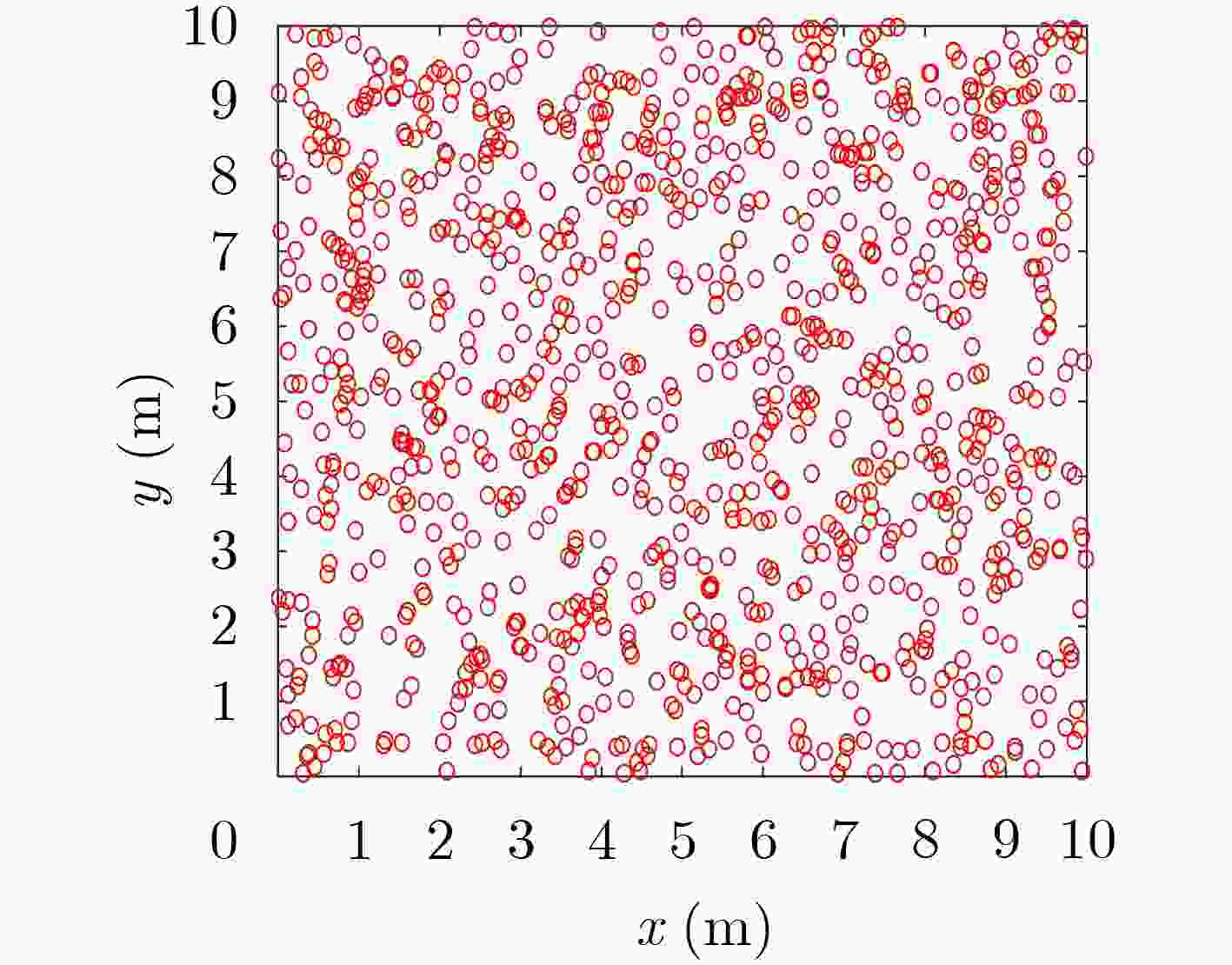
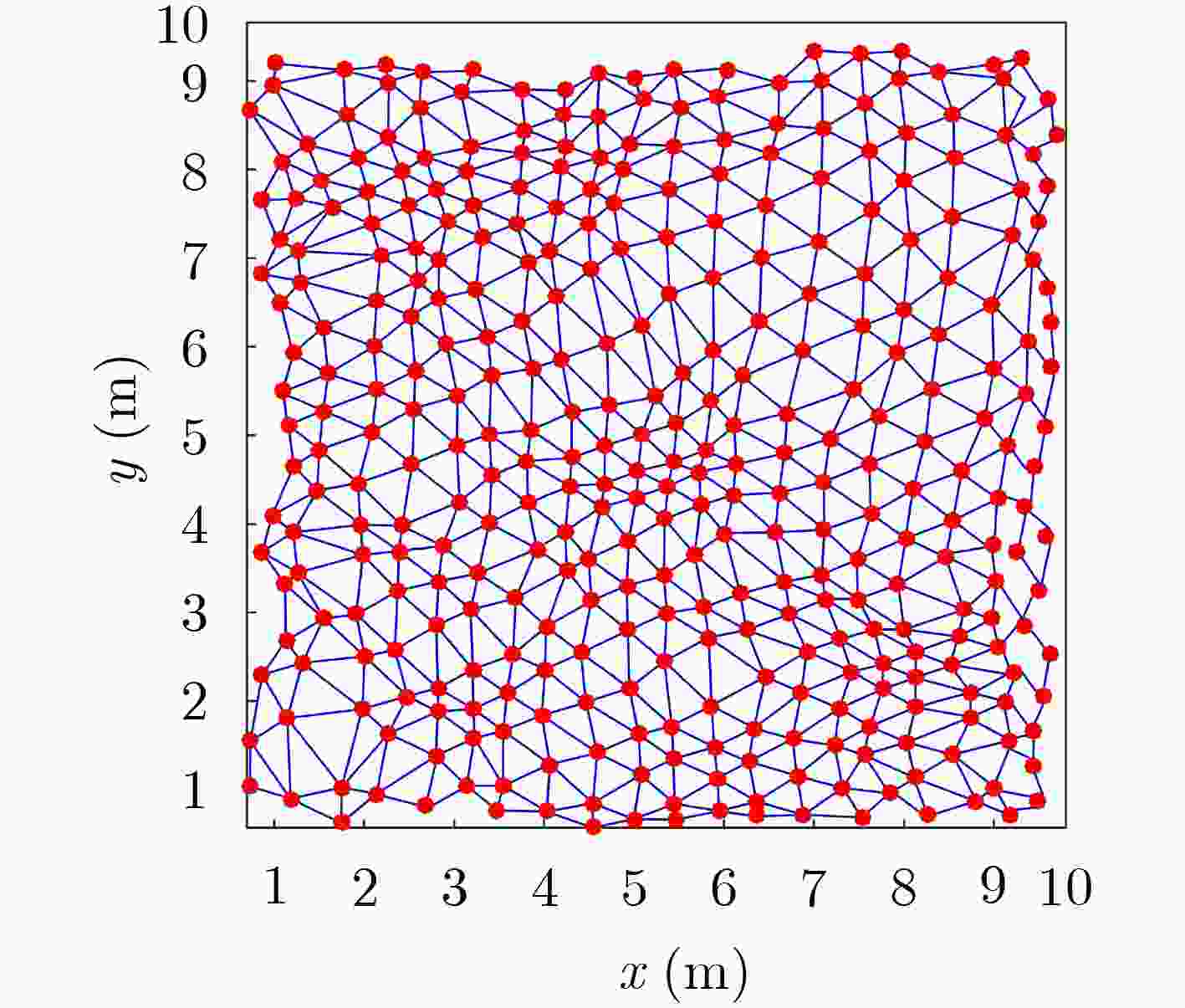
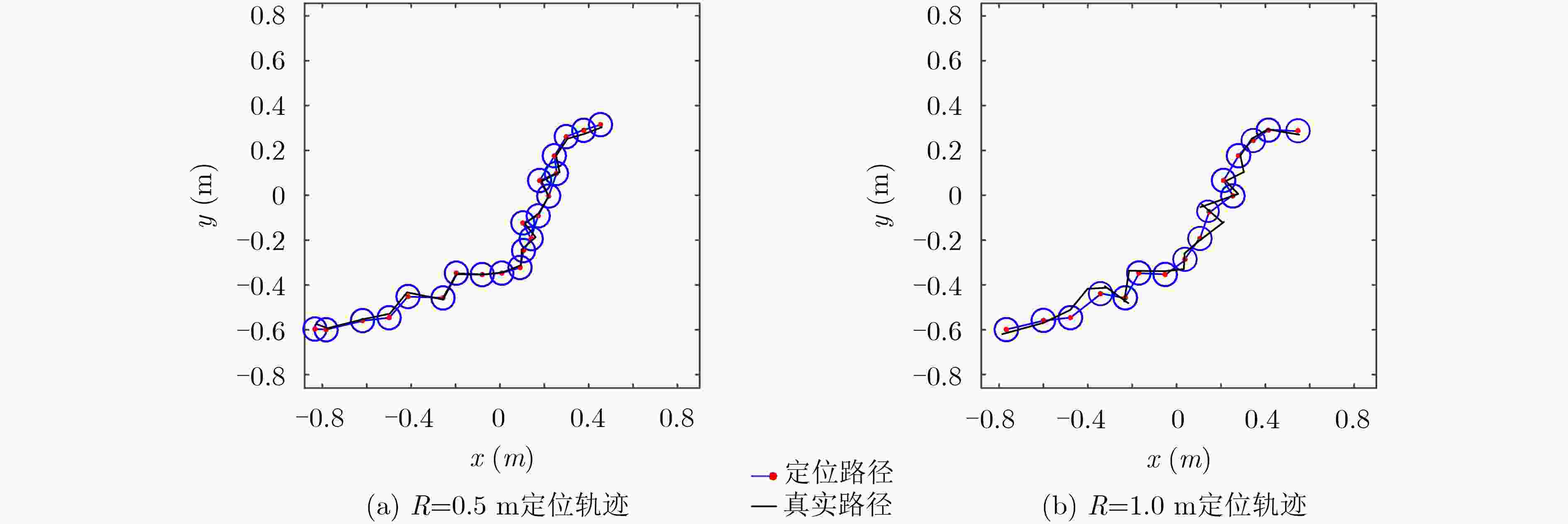
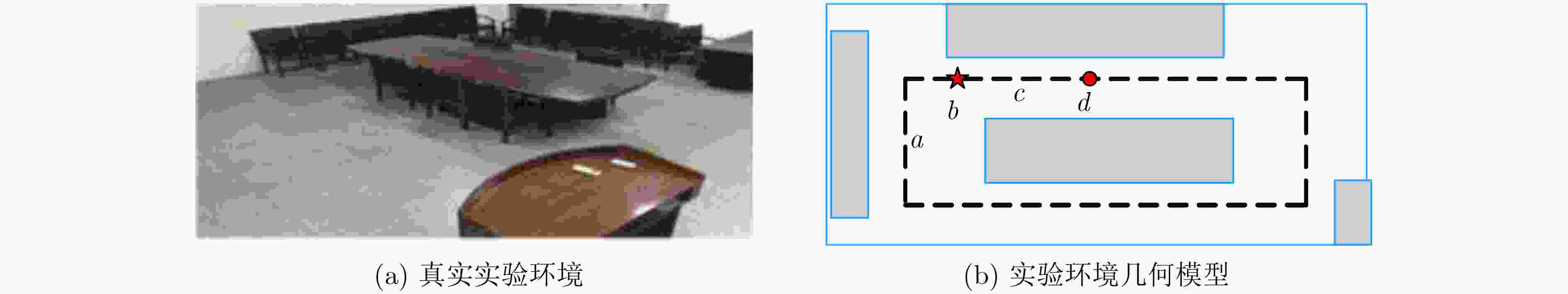
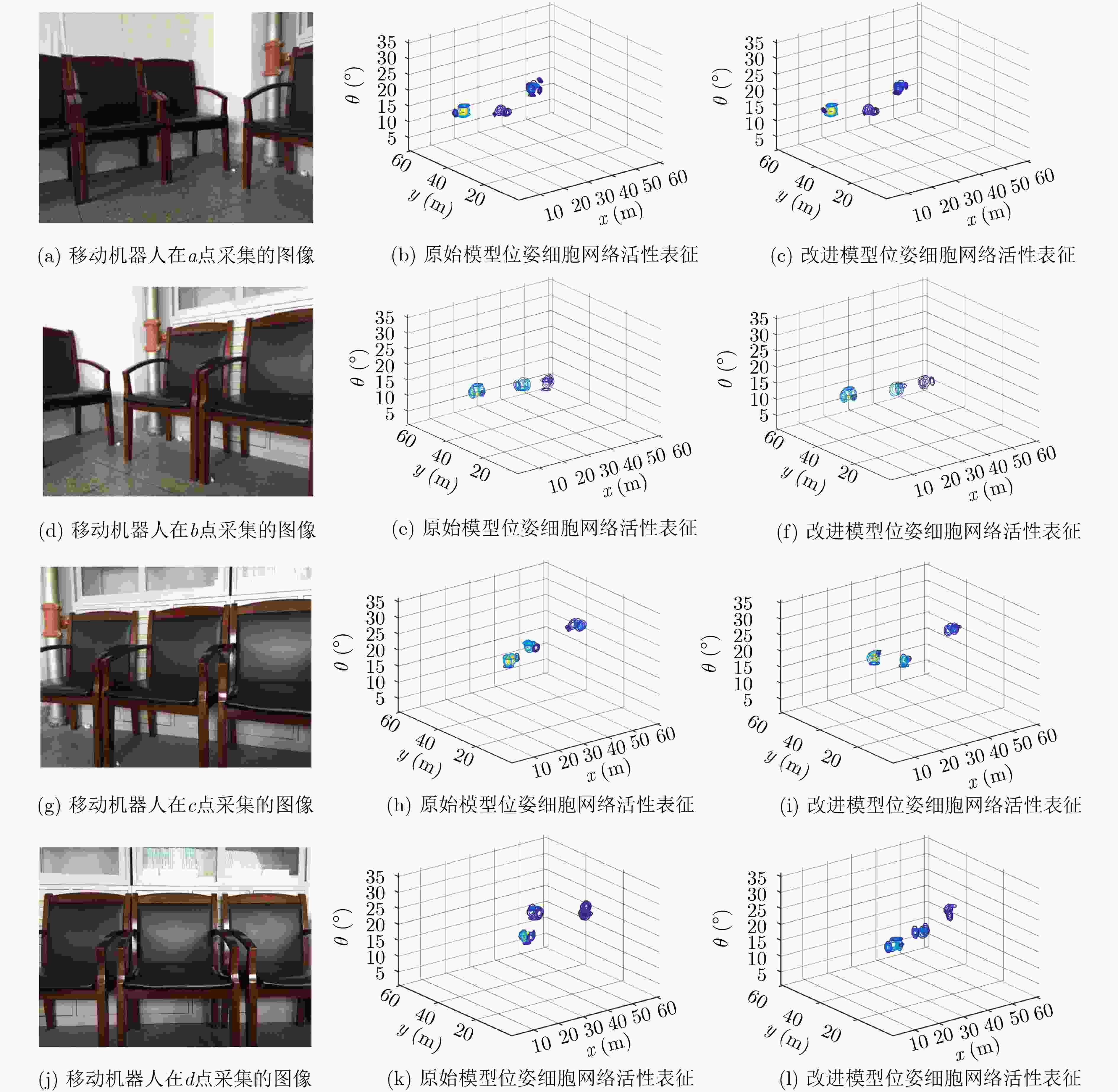
摘要: 为提高移动机器人在同步定位和地图构建(SLAM)中的定位精度,该文提出一种基于自组织可增长映射 (GSOM)的仿生定位算法。该方法将位置细胞的激活特性和神经网络输出层神经元建立响应连接,通过GSOM神经网络构建空间的拓扑地图,利用感知距离信息实现位置细胞的激活响应从而估计机器人位置,以此还原机器人的运行路径。实验结果表明细胞间隔R对定位精度有较大影响,选取合适的细胞间隔能有效地减少神经网络的学习时间,提高定位精度,该文算法平均误差在0.153 m以内,定位精度达到90.243%,均优于原有算法。经验证该文算法建立的模型能够实现机器人的空间位置表征,提高了机器人在实验场景下的定位精度,表现出良好的位置估计性能。Abstract: In order to improve the positioning accuracy of mobile robots in Simultaneous Localization And Mapping (SLAM), a bionic localization algorithm based on Growing Self-Organizing Map(GSOM) neural network is proposed. The method connects the activation characteristics of the place cells with the neural network output layer neurons to establish a response, and constructs a spatial topology map through the GSOM neural network, and uses the perceived distance information to realize the activation response of the place cells to estimate the position of the robot. The running path of the robot is restored in this way. The experimental results show that the cell spacing R has a great influence on the positioning accuracy. Choosing the appropriate cell spacing can effectively reduce the learning time of the neural network and improve the positioning accuracy. The average error of the algorithm is less than 0.153 m, and the positioning accuracy is 90.243%, which is better than the original algorithm. It is verified that the model established by the algorithm can realize the spatial position representation of the robot, improves the positioning accuracy of the object under the experimental scene, and shows good position estimation performance.
-
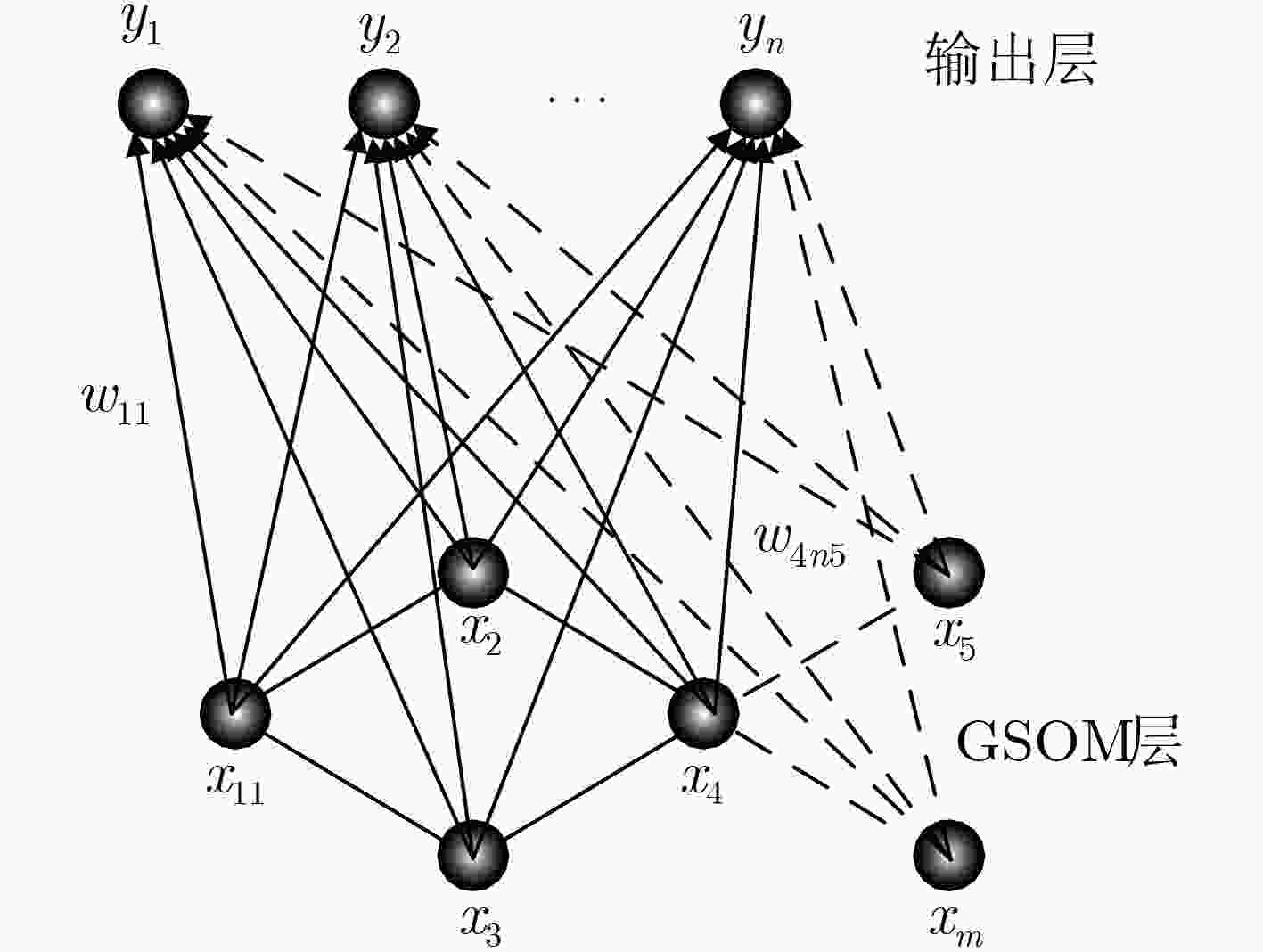
表 1 GSOM学习算法
输入:环境样本${{{x}}_k} = \left[ {{x_1},{x_2}, ··· ,{x_m}} \right]$ 输出:映射2维结构${{{y}}_k} = \left[ {{y_1},{y_2}, ··· ,{y_n}} \right]$ for输出单元$j$, do 计算输入到输出的欧氏距离${d_j}$; 计算最小相似度量$\min {d_j}$; if ${j^*} = \min {d_j}$; 即选定单元为最佳匹配单元; else 更新胜出单元${j^*}$的邻域内所有单元的连接权重为式(14) end if if误差${\left[ {{x_i}(t) - {w_{ij}}(t)} \right]^2} > \delta $; 调整学习因子,缩小胜出单元${j^*}$的邻域范围,为式(12); else ${y_k} = {j^*}$ end if end for 表 2 两种模型的定位误差
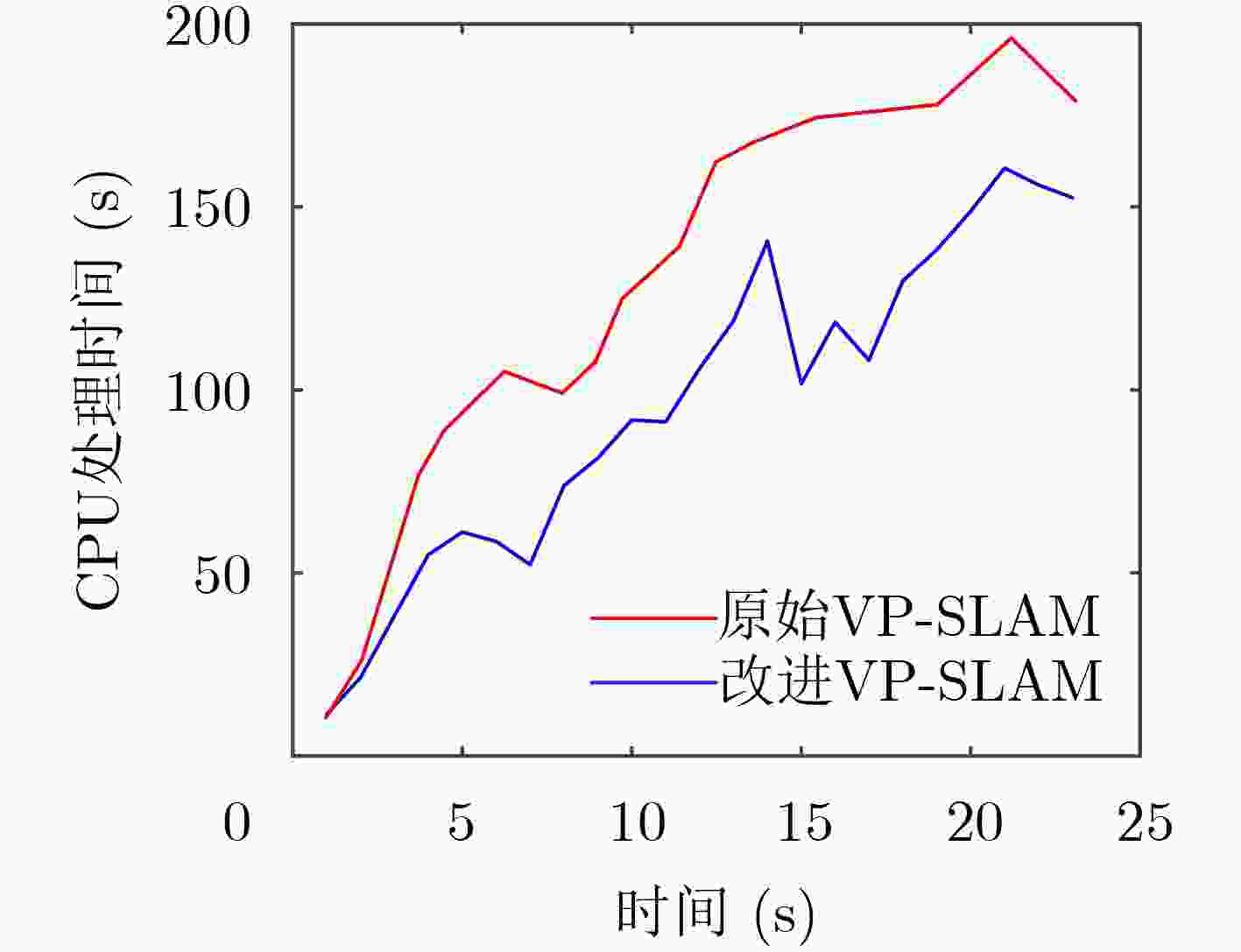
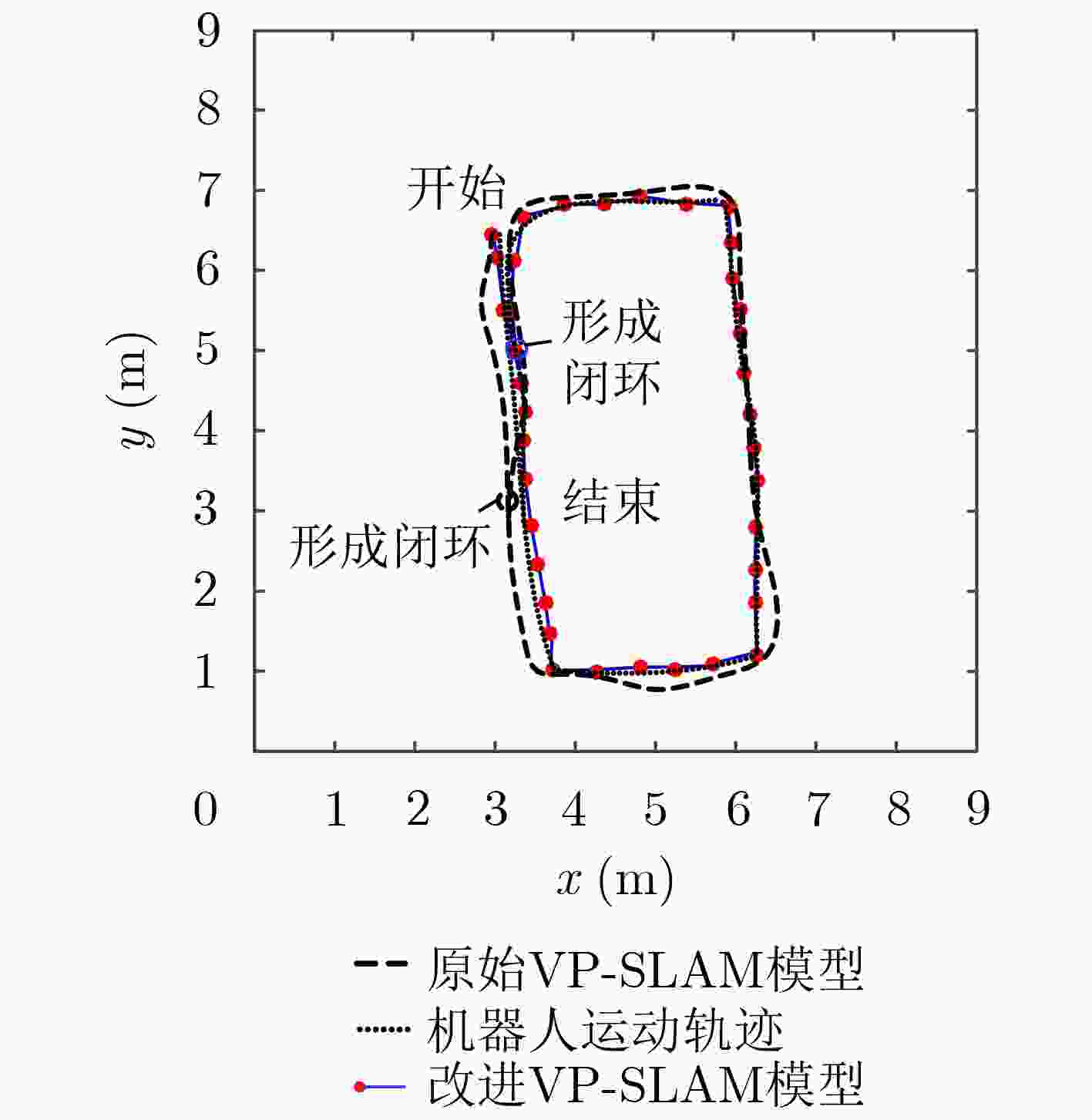
定位方法 最大绝对误差MAE(m) 平均误差(m) 准确率(%) 改进VP-SLAM 0.3018 0.1525 90.2436 原始VP-SLAM 0.4237 0.3116 87.7264 -
邹强, 丛明, 刘冬, 等. 基于生物认知的移动机器人路径规划方法[J]. 机器人, 2018, 40(6): 894–902.ZOU Qiang, CONG Ming, LIU Dong, et al. Path planning of mobile robots based on biological cognition[J]. Robot, 2018, 40(6): 894–902. 董星亮, 苑晶, 张雪波, 等. 室内环境下基于图像序列拓扑关系的移动机器人全局定位[J]. 机器人, 2019, 41(1): 83–94, 103.DONG Xingliang, YUAN Jing, ZHANG Xuebo, et al. Mobile robot global localization based on topological relationship between image sequences in indoor environments[J]. Robot, 2019, 41(1): 83–94, 103. O’KEEFE J and DOSTROVSKY J. The hippocampus as a spatial map. Preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely-moving rat[J]. Brain Research, 1971, 34(1): 171–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90358-1 HAFTING T, FYHN M, MOLDEN S, et al. Microstructure of a spatial map in the entorhinal cortex[J]. Nature, 2005, 436(7052): 801–806. doi: 10.1038/nature03721 MOSER E I, KROPFF E, and MOSER M B. Place cells, grid cells, and the brain’s spatial representation system[J]. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 2008, 31: 69–89. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.061307.090723 DERDIKMAN D and MOSER E I. A manifold of spatial maps in the brain[J]. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2010, 14(12): 561–569. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2010.09.004 BURGESS N. The 2014 Nobel prize in physiology or medicine: A spatial model for cognitive neuroscience[J]. Neuron, 2014, 84(6): 1120–1125. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.12.009 KESNER R P and ROLLS E T. A computational theory of hippocampal function, and tests of the theory: New developments[J]. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 2015, 48: 92–147. DALLEMOLE V L and ARAÚJO A R F. A novel topological map of place cells for autonomous robots[C]. The 20th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2010: 296–306. JAUFFRET A, CUPERLIER N, and GAUSSIER P. From grid cells and visual place cells to multimodal place cell: A new robotic architecture[J]. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2015, 9: 1. 李伟龙, 吴德伟, 周阳, 等. 基于生物位置细胞放电机理的空间位置表征方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(8): 2040–2046. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151331LI Weilong, WU Dewei, ZHOU Yang, et al. A method of spatial place representation based on biological place cells firing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(8): 2040–2046. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151331 周牧, 王烟濛, 袁慧, 等. 基于Mann-Whitney秩和检验的无线局域网室内映射与定位方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1555–1564. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180392ZHOU Mu, WANG Yanmeng, YUAN Hui, et al. Mann-Whitney rank sum test based wireless local area network indoor mapping and localization approach[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1555–1564. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180392 李世宝, 王升志, 刘建航, 等. 基于接收信号强度非齐性分布特征的半监督学习室内定位指纹库构建[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(10): 2302–2309. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180599LI Shibao, WANG Shengzhi, LIU Jianhang, et al. Semi-supervised indoor fingerprint database construction method based on the nonhomogeneous distribution characteristic of received signal strength[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(10): 2302–2309. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180599 ARONOV D, NEVERS R, and TANK D W. Mapping of a non-spatial dimension by the hippocampal–entorhinal circuit[J]. Nature, 2017, 543(7647): 719–722. doi: 10.1038/nature21692 MILFORD M, JACOBSON A, CHEN Zetao, et al. RatSLAM: Using models of rodent hippocampus for robot navigation and beyond[M]. INABA M and CORKE P. Robotics Research. Cham: Springer, 2016: 467–485. MILFORD M J, WYETH G F, and PRASSER D. RatSLAM: A hippocampal model for simultaneous localization and mapping[C]. 2004 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, New Orleans, USA, 2004: 403–408. MILFORD M and WYETH G. Persistent navigation and mapping using a biologically inspired SLAM system[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2010, 29(9): 1131–1153. doi: 10.1177/0278364909340592 KOHONEN T. The self-organizing map[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1990, 78(9): 1464–1480. doi: 10.1109/5.58325 KOHONEN T. Self-organized formation of topologically correct feature maps[J]. Biological Cybernetics, 1982, 43: 59–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00337288 MONTAZERI H, MORADI S, and SAFABAKHSH R. Continuous state/action reinforcement learning: A growing self-organizing map approach[J]. Neurocomputing, 2011, 74(7): 1069–1082. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2010.11.012 于乃功, 王丽. 双目立体视觉和GSOM相结合的机器人自主地图构建方法[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2011, 19(11): 2810–2813.YU Naigong and WANG Li. Autonomous mapping for robot using a combination of binocular stereo vision and GSOM algorithm[J]. Computer Measurement &Control, 2011, 19(11): 2810–2813. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
