Method for Generating Malicious Code Adversarial Samples Based on Genetic Algorithm
-
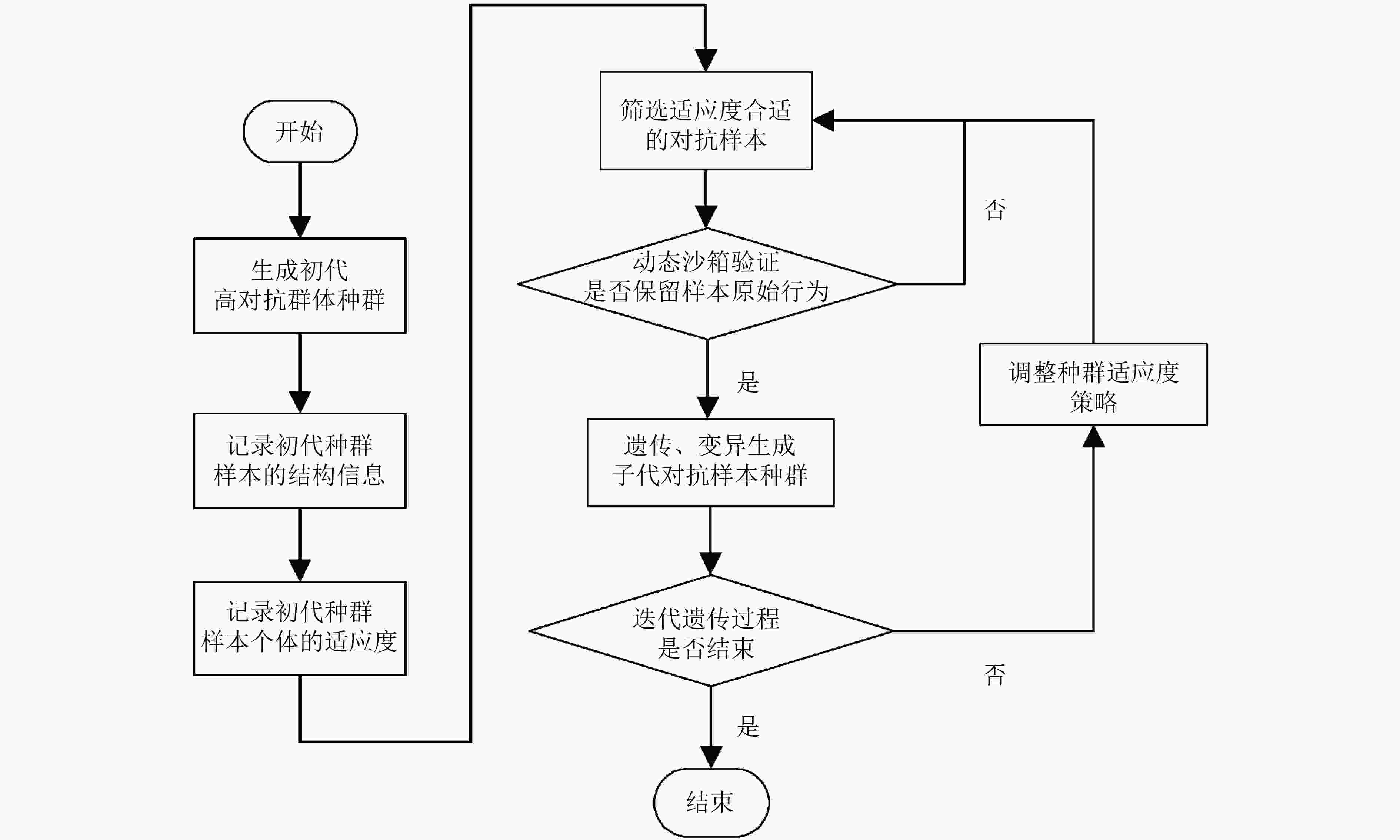
摘要: 机器学习已经广泛应用于恶意代码检测中,并在恶意代码检测产品中发挥重要作用。构建针对恶意代码检测机器学习模型的对抗样本,是发掘恶意代码检测模型缺陷,评估和完善恶意代码检测系统的关键。该文提出一种基于遗传算法的恶意代码对抗样本生成方法,生成的样本在有效对抗基于机器学习的恶意代码检测模型的同时,确保了恶意代码样本的可执行和恶意行为的一致性,有效提升了生成对抗样本的真实性和模型对抗评估的准确性。实验表明,该文提出的对抗样本生成方法使MalConv恶意代码检测模型的检测准确率下降了14.65%;并可直接对VirusTotal中4款基于机器学习的恶意代码检测商用引擎形成有效的干扰,其中,Cylance的检测准确率只有53.55%。Abstract: Machine learning is widely used in malicious code detection and plays an important role in malicious code detection products. Constructing adversarial samples for malicious code detection machine learning models is the key to discovering defects in malicious code detection models, evaluating and improving malicious code detection systems. This paper proposes a method for generating malicious code adversarial samples based on genetic algorithms. The generated samples combat effectively the malicious code detection model based on machine learning, while ensuring the consistency of the executable and malicious behavior of malicious code samples, and improving effectively the authenticity of the generated adversarial samples and the accuracy of the model adversarial evaluation are presented. The experiments show that the proposed method of generating adversarial samples reduces the detection accuracy of the MalConv malicious code detection model by 14.65%, and can directly interfere with four commercial machine-based malicious code detection engines in VirusTotal. Among them, the accuracy rate of Cylance detection is only 53.55%.
-
Key words:
- Malware detection /
- Machine learning /
- Adversarial sample
-
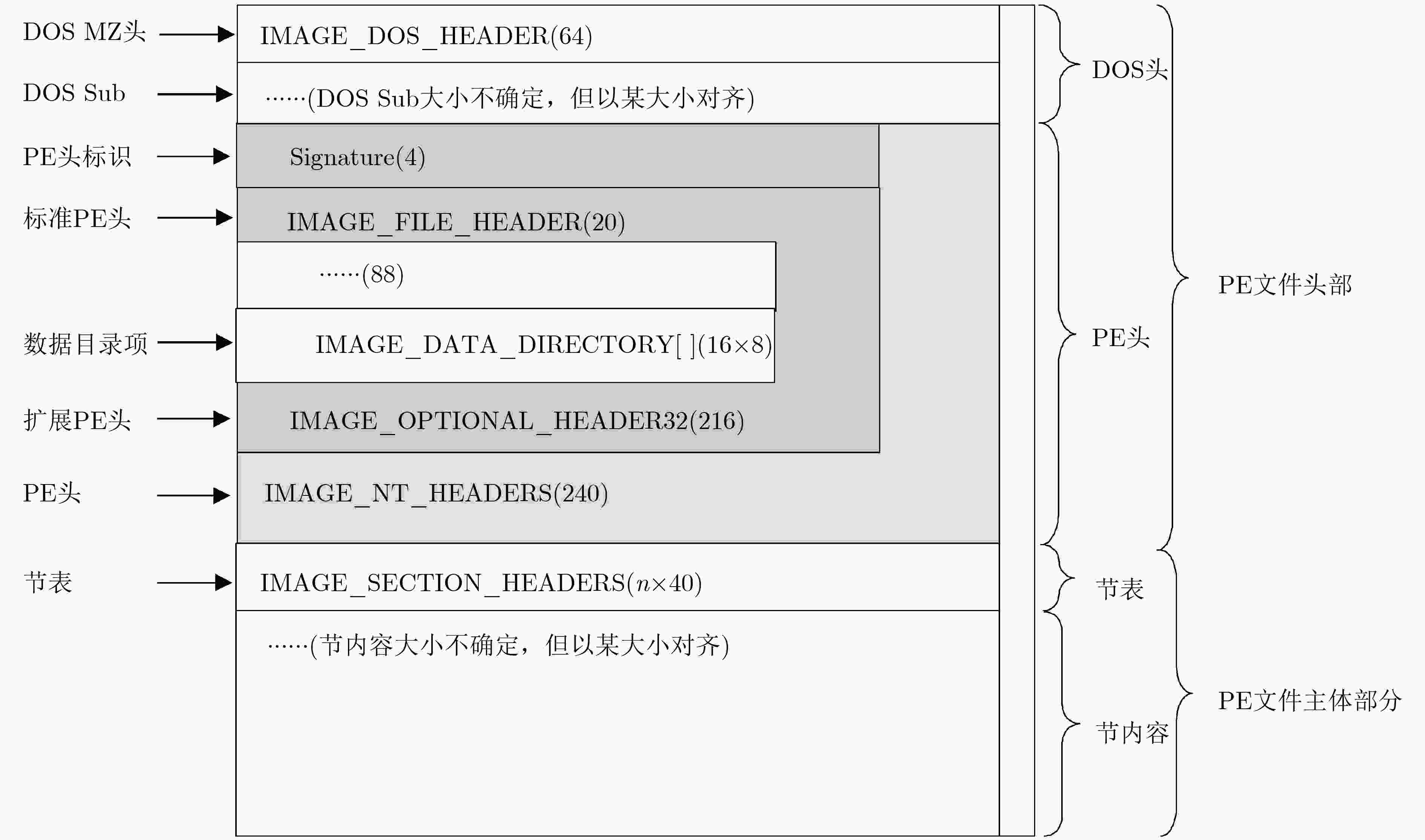
表 1 PE文件改写原子操作
改写模块 改写内容 PE头文件 PE标志位修改 PE文件校验和修改 节表 导入表添加冗余导入函数 节表模块重命名 节表冗余信息填充 节表新模块添加 PE文件 加壳、脱壳操作 表 2 实验数据统计信息
样本 训练集 测试集 良性样本 7059 784 恶意样本 6593 732 总数 13652 1516 表 3 恶意代码检测引擎检测结果
评测样本集 良性样本误报 恶意样本误报 误报样本综述 模型检测准确率(%) 原始样本集 7 10 17 98.88 初代对抗样本集 37 9 46 96.97 优化后的对抗样本集 228 11 239 84.23 表 4 厂商产品的检测成功率
恶意代码检测引擎 误报样本数 检测逃逸率(%) Cylance 111 46.45 Endgame 43 17.99 Sophos ML 50 20.92 Trapmine 35 14.64 -
LANDAGE J and WANKHADE M P. Malware and malware detection techniques: A survey[J]. International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology, 2013, 2(12): 61–68. SAXE J and BERLIN K. Deep neural network based malware detection using two dimensional binary program features[C]. The 10th International Conference on Malicious and Unwanted Software (MALWARE), Fajardo, USA, 2015: 11–20. doi: 10.1109/MALWARE.2015.7413680. ARP D, SPREITZENBARTH M, HUBNER M, et al. Drebin: Effective and explainable detection of android malware in your pocket[C]. Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, San Diego, USA, 2014: 23–26. doi: 10.14722/ndss.2014.23247. RAFF E, SYLVESTER J, and NICHOLAS C. Learning the PE header, malware detection with minimal domain knowledge[C]. The 10th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security, Dallas, USA, 2017: 121–132. doi: 10.1145/3128572.3140442. RAFF E, ZAK R, COX R, et al. An investigation of byte n-gram features for malware classification[J]. Journal of Computer Virology and Hacking Techniques, 2018, 14(1): 1–20. doi: 10.1007/s11416-016-0283-1 Cylance Inc. What’s new in CylancePROTECT and CylanceOPTICS[EB/OL]. https://s7d2.scene7.com/is/content/cylance/prod/cylance-web/en-us/resources/knowledge-center/resource-library/briefs/Whats-New-CylancePROTECT-and-CylanceOPTICS.pdf, 2020. Sophos Inc. Sophos central migration tool articles, documentation and resources[EB/OL]. https://community.sophos.com/kb/en-us/122264#Product%20Information, 2020. 梁光辉, 庞建民, 单征. 基于代码进化的恶意代码沙箱规避检测技术研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(2): 341–347. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180257LIANG Guanghui, PANG Jianmin, and SHAN Zheng. Malware sandbox evasion detection based on code evolution[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(2): 341–347. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180257 GROSSE K, PAPERNOT N, MANOHARAN P, et al. Adversarial perturbations against deep neural networks for malware classification[J]. arXiv, 2016, 1606.04435. XU Weilin, QI Yanjun, and EVANS D. Automatically evading classifiers[C]. The 23rd Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, San Diego, USA, 2016: 21–24. doi: 10.14722/ndss.2016.23115. HU Weiwei and TAN Ying. Generating adversarial malware examples for black-box attacks based on GAN[J]. arXiv, 2017, 1702.05983. HU Weiwei and TAN Ying. Black-box attacks against RNN based malware detection algorithms[C]. The Workshops of the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018. RAFF E, BARKER J, SYLVESTER J, et al. Malware detection by eating a whole exe[C]. The Workshops of the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 268–276. TOTAL V. VirusTotal-free online virus, malware and url scanner[EB/OL]. https//www.virustotal.com/en, 2012. PASCANU R, STOKES J W, SANOSSIAN H, et al. Malware classification with recurrent networks[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brisbane, Australia, 2015: 1916–1920. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2015.7178304. KOLOSNJAJI B, ZARRAS A, WEBSTER G, et al. Deep learning for classification of malware system call sequences[C]. The 29th Australasian Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Hobart, Australia, 2016: 137–149. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50127-7_11. HUANG Wenyi and STOKES J W. MtNet: A multi-task neural network for dynamic malware classification[C]. The 13th International Conference on Detection of Intrusions and Malware, and Vulnerability Assessment, San Sebastián, Spain, 2016: 399–418. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-40667-1_20. MANNING C D, RAGHAVAN P, and SCHÜTZE H. Introduction to Information Retrieval[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2008. HAN K S, LIM J H, KANG B, et al. Malware analysis using visualized images and entropy graphs[J]. International Journal of Information Security, 2015, 14(1): 1–14. doi: 10.1007/s10207-014-0242-0 KANCHERLA K and MUKKAMALA S. Image visualization based malware detection[C]. 2013 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Cyber Security (CICS), Singapore, 2013: 40–44. doi: 10.1109/CICYBS.2013.6597204. LIU Xinbo, LIN Yaping, LI He, et al. A novel method for malware detection on ML-based visualization technique[J]. Computers & Security, 2020, 89: 101682. doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2019.101682 Skylight. Cylance, I kill you![ EB/OL]. https://skylightcyber.com/2019/07/18/cylance-i-kill-you/, 2019. MOHURLE S and PATIL M. A brief study of wannacry threat: Ransomware attack 2017[J]. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science, 2017, 8(5): 1938–1940. doi: 10.26483/ijarcs.v8i5.4021 DANG Hung, HUANG Yue, and CHANG E C. Evading classifiers by morphing in the dark[C]. 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Dallas, USA, 2017: 119–133. doi: 10.1145/3133956.3133978. 戚利. Windows PE权威指南[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2011: 67–68.QI Li. Windows PE: The Definitive Guide[M]. Beijing: Machinery Industry Press, 2011: 67–68. KOZA J R. Genetic Programming II: Automatic Discovery of Reusable Subprograms[M]. Cambridge, MA, USA: MIT Press, 1994: 32. Cuckoo Sandbox. Cuckoo Sandbox–Automated malware analysis[EB/OL]. http://www.cuckoosandbox.org, 2017. BANON S. Elastic endpoint security[EB/OL]. https://www.elastic.co/cn/blog/introducing-elastic-endpoint-security, 2019. Trapmine Inc. TRAPMINE integrates machine learning engine into VirusTotal[EB/OL]. https://trapmine.com/blog/trapmine-machine-learning-virustotal/, 2018. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
