Zero-knowledge Location Proof Based on Blockchain
-
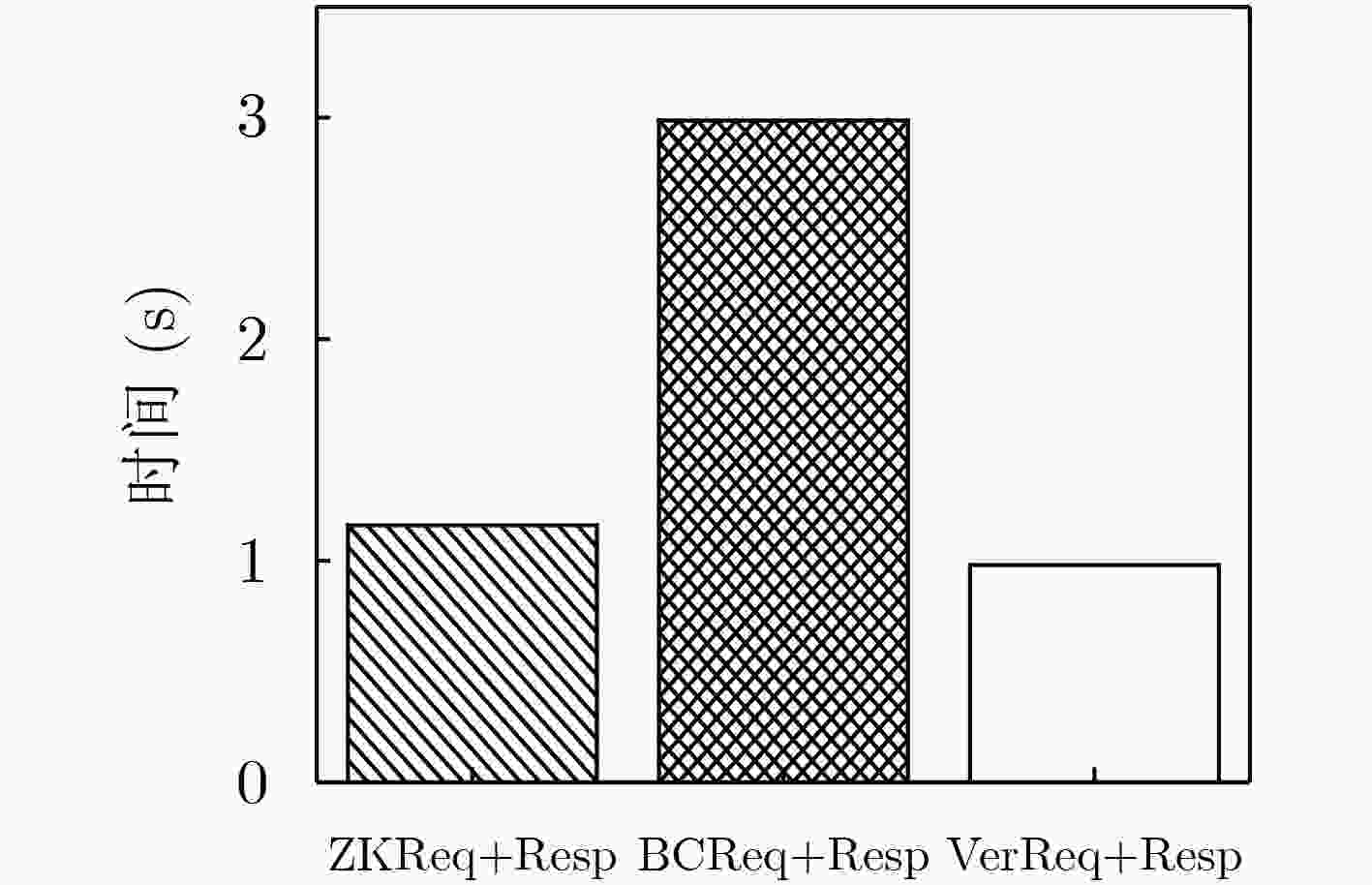
摘要: 地理位置虚拟软件泛滥、民用卫星定位信号易模拟或篡改,致使地理位置可信认证难以实现。针对已有位置证明方案采用中心化架构存在单点失效和易引起集中攻击等安全风险,该文引入去中心化范式思路,利用区块链具有的去中心化、不可篡改、可追溯等特点,并结合零知识证明协议,提出了基于区块链的零知识位置证明方法,实现了以去中心化、保护隐私、高度准确、审查抵制的地理位置认证服务,从而确保用户所提供位置的准确性。该方法不仅能消除中心化位置证明的弊端,确保位置数据的机密性,而且被证明位置数据一旦上链后不可篡改,实现了不可抵赖性。测试分析结果表明:完整的证明流程(包含证明生成验证和上链全过程)实际测试每次平均用时约5 s,其中证明生成和验证的总耗时是50.5~55.5 ms。因此,算法具有较好的性能开销,可满足实际应用需求。Abstract: Due to the proliferation of geographic location virtual software and the easy simulation or tampering of civil satellite positioning signals, it is difficult to realize the trusted authentication of geographic location. In view of the security risk of single-point failure in the existing location certification scheme using centralized architecture, a zero-knowledge location certification method based on blockchain is proposed, combining with zero knowledge certification protocol, to achieve a decentralized, privacy protected, highly accurate, review offset geographic location certification service, so as to ensure the accuracy of the location provided by users. This method not only ensures the confidentiality of the location data, but also proves that the location data can not tamper once it is linked. The results of the test analysis show that the average performance of the whole proving process is about 5 s/time, and the total time of proof generation and verification is 50.5~55.5 ms. Therefore, the algorithm has better performance overhead, which can meet the actual application requirements.
-
Key words:
- Location proof /
- Blockchain /
- Zero-knowledge proof /
- Smart contract
-
表 1 零知识证明生成算法1
输入:证明者和见证者的经度、纬度和海拔、与以见证者位置为圆心的半径$R$, 输出:零知识证明结果${\rm{pf}}$; (1) 挑选随机大数$a,{b_1},{b_2},{b_3},{b_4},{b_5},{e_1},{e_2},{e_3},{e_4},{f_1},{f_2},{f_3},{f_4},k,{l_1},{l_2},{l_3},{l_4},n,{q_1},{q_2},s$; (2) ${\alpha _1},{\alpha _2},{\alpha _3} \leftarrow $经纬度海拔之差,$D \leftarrow {\rm{getDis}}({\alpha _1},{\alpha _2},{\alpha _3})$; (3) if ${R^2} \ge {D^{\rm{2} } }$ do //判断是否在圆内 (4) 挑选两个大素数,相乘得到N,并舍弃掉两个素数;
(5) $\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^4 {c_i^2} \leftarrow {R^2} - {D^2}$;${d_1} \leftarrow \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^3 {e_i^2} + \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^4 {f_i^2} (od N)$;(6) ${d_2} \leftarrow \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^4 { {c_i}{f_i} } + \displaystyle\prod\nolimits_{i = 1}^3 { {e_i}{\alpha _i} } (od N)$;$m \leftarrow b_4^n \displaystyle\prod\nolimits_{i = 1}^4 {l_i^{ {f_i} } } (od N)$; (7) $g \leftarrow \displaystyle\prod\nolimits_{i = 1}^4 {b_i^{ {e_i} } } (od N)$;$h \leftarrow b_4^k \displaystyle\prod\nolimits_{i = 1}^4 {l_i^{ {c_i} } } (od N)$; (8) $p \leftarrow b_4^{ - {d_1}}b_5^{{q_1}}(od N)$;$r \leftarrow b_4^{ - 2{d_2}}b_5^{{q_2}}(od N)$; (9) ${x_i} \leftarrow s \cdot {\alpha _i} + {e_i}(od N)(i = 1,2,3)$,${x_4} \leftarrow s \cdot a + {e_4}(od N)$; (10) ${\beta _i} \leftarrow s{c_i} + {f_i}(od N)(i = 1,2,3,4)$;$A \leftarrow \displaystyle\prod\nolimits_{i = 1}^3 {b_i^{ {\alpha _i} } } b_4^a(od N)$; (11) $\gamma \leftarrow sk + n(od N),\lambda \leftarrow s{q_1} + {q_2}(od N)$; (12) ${\rm{pf}} \leftarrow \{ N,A,s,{b_i},{x_i},g,R,{\beta _i},\lambda ,p,r,\gamma ,h,{l_i},m\} $; (13) else (14) ${\rm{pf}} \leftarrow {\rm{\{ \} }}$. 表 2 零知识证明验证算法2
输入:零知识证明${\rm{pf}}$, 输出:验证结果$R$; (1) ${v_1} \leftarrow {A^{ - s} }\displaystyle\prod\nolimits_{i = 1}^4 {b_i^{ {x_i} } } (od N)$; (2) if ${v_1}! = g$ do (3) $R \leftarrow F$;//返回验证失败
(4) ${v_2} \leftarrow {s^2}{R^2} - \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 3}^3 {x_i^2} - \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^4 {\beta _i^2}$;
${v_3} \leftarrow b_4^{{v_2}}b_5^\lambda (od N)$;(5) if ${v_3}! = {\rm{p}}{{\rm{r}}^s}(od N)$ do
(6) $R \leftarrow F$;(7) ${v_4} \leftarrow b_4^\gamma {h^{ - s} }\displaystyle\prod\nolimits_{i = 1}^4 {l_i^{ {\beta _i} } } (od N)$; (8) if ${v_4}! = m$ do (9) $R \leftarrow F$; (10) $R \leftarrow T$;//返回验证通过。 -
ZHU Zhichao and CAO Guohong. APPLAUS: A privacy-preserving location proof updating system for location-based services[C]. 2011 IEEE INFOCOM, Shanghai, China, 2011: 1889–1897. doi: 10.1109/INFCOM.2011.5934991. ZHU Zhichao and CAO Guohong. Toward privacy preserving and collusion resistance in a location proof updating system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2013, 12(1): 51–64. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2011.237 ZHENG Yao, LI Ming, LOU Wenjing, et al. SHARP: Private proximity test and secure handshake with cheat-proof location tags[C]. The 17th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security - ESORICS, Pisa, Italy, 2012. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-33167-1_21. LUO Wanying and URS Hengartner. Veriplace: A privacy-aware location proof architecture[C]. The 18th SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, San Jose, USA, 2010: 23–32. doi: 10.1145/1869790.1869797. SCHUMMER J and VOHRA R V. Strategy-proof location on a network[J]. Journal of Economic Theory, 2002, 104(2): 405–428. doi: 10.1006/jeth.2001.2807 LI Yi, ZHOU Lu, ZHU Haojin, et al. Privacy-preserving location proof for securing large-scale database-driven cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2016, 3(4): 563–571. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2015.2481926 KHAN R, ZAWOAD S, HAQUE M M, et al. ‘Who, When, and Where?’ Location proof assertion for mobile devices[C]. The 28th Annual IFIP WG 11.3 Working Conference on Data and Applications Security and Privacy XXVIII, Vienna, Austria, 2014: 146–162. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-43936-4_10. 李佩丽, 徐海霞. 区块链用户匿名与可追踪技术[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1061–1067. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190813LI Peili and XU Haixia. Blockchain user anonymity and traceability technology[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1061–1067. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190813 NAKAMOTO S. Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system[EB/OL]. http://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf, 2009. FOUNDATION E. Ethereum: Blockchain app platform[EB/OL]. https://ethereum.github.io/yellowpaper/paper.pdf, 2019. YOUSSEF J R, ZACHAREWICZ G, and CHEN D. Developing an Enterprise Operating System (EOS) - requirements and architecture[C]. The 25th IEEE International Conference on Enabling Technologies: Infrastructure for Collaborative Enterprises (WETICE), Paris, France, 2016: 130–135. doi: 10.1109/WETICE.2016.36. PlatONE Corp. PlatONE_Whitepaper[EB/OL]. https://platone.juzix.net/static-new/pdf/zh/PlatONE_Whitepaper_ZH.pdf, 2019. TROUW A, LEVIN M, and SCHEPER S. The XY oracle network: The proof-of-origin based cryptographic location-network[EB/OL]. https://docs.xyo.network/XYO-White-Paper.pdf, 2018. Foamspace Corp. FOAM whitepaper[EB/OL]. https://www.foam.space/publicAssets/FOAM_Whitepaper.pdf, 2018. NASRULIN B, MUZAMMAL M, and QU Qiang. A robust spatio-temporal verification protocol for blockchain[C]. The 19th International Conference on Web Information Systems Engineering, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2018: 52–67. 冯登国, 张敏, 李昊. 大数据安全与隐私保护[J]. 计算机学报, 2014, 37(1): 246–258. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2014.00246FENG Dengguo, ZHANG Min, and LI Hao. Big data security and privacy protection[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2014, 37(1): 246–258. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2014.00246 曹素珍, 王斐, 郎晓丽, 等. 基于无证书的多方合同签署协议[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(11): 2691–2698. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190166CAO Suzhen, WANG Fei, LANG Xiaoli, et al. Multi-party contract signing protocol based on certificateless[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(11): 2691–2698. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190166 -





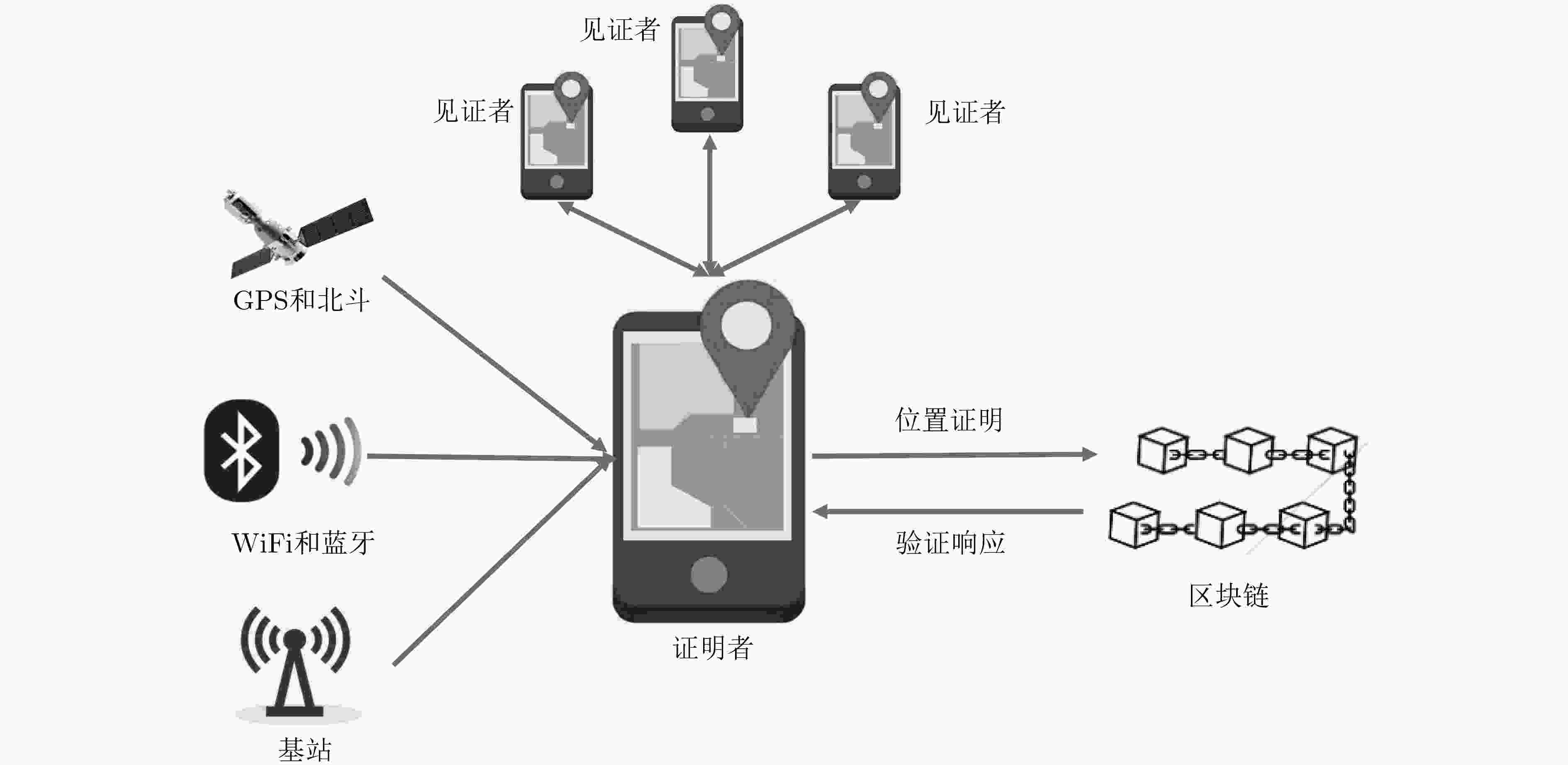
 下载:
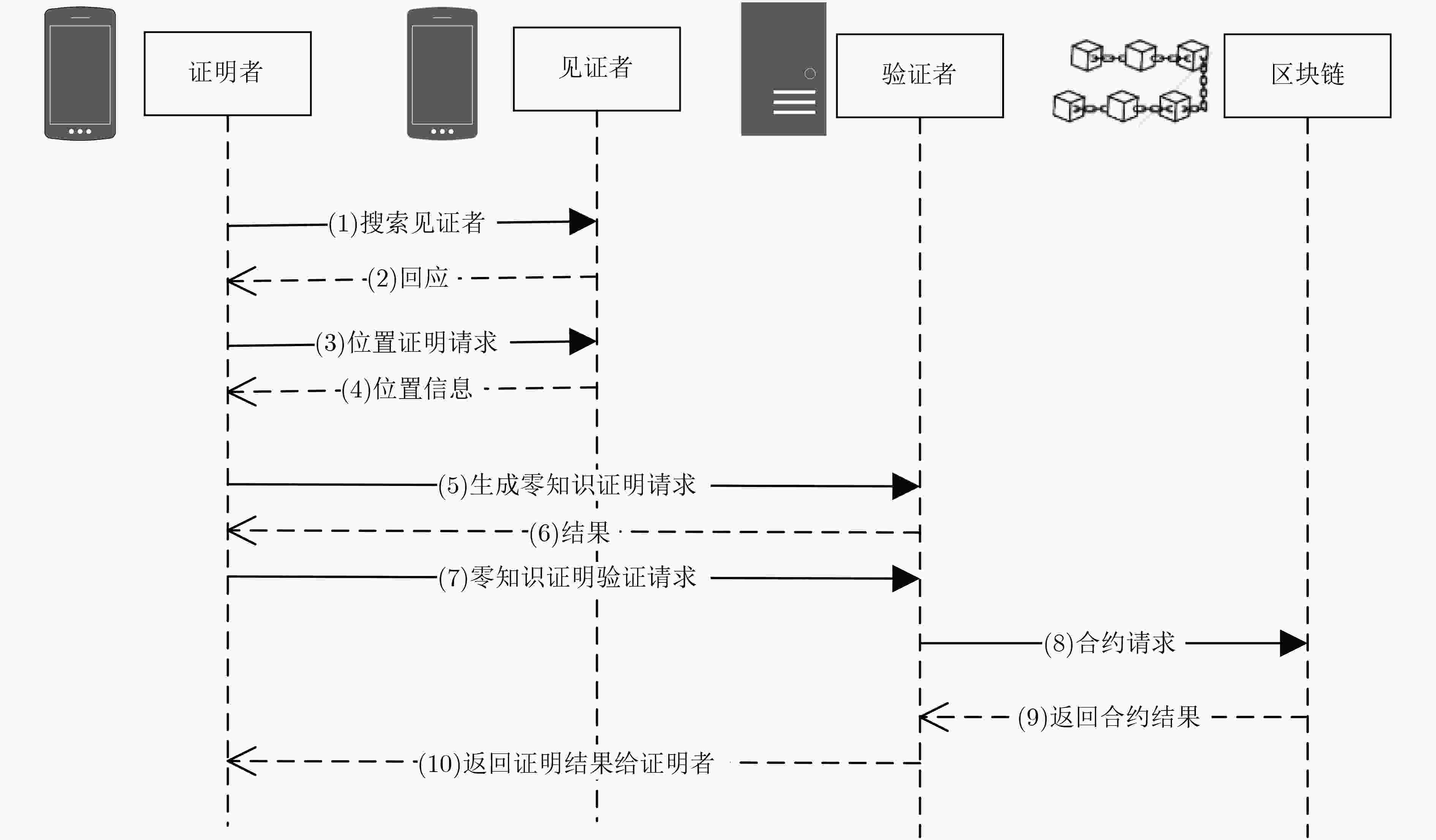
下载:
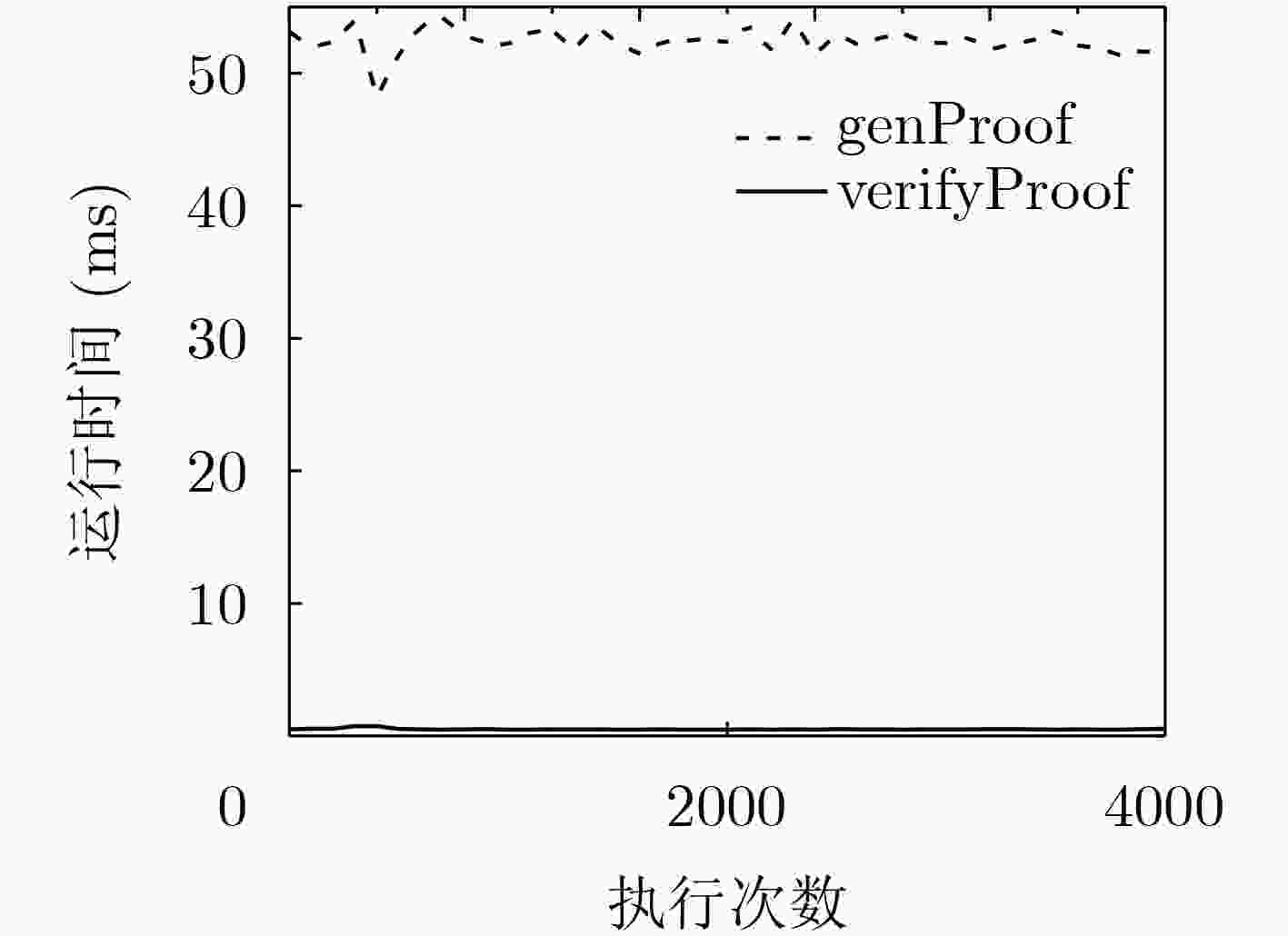
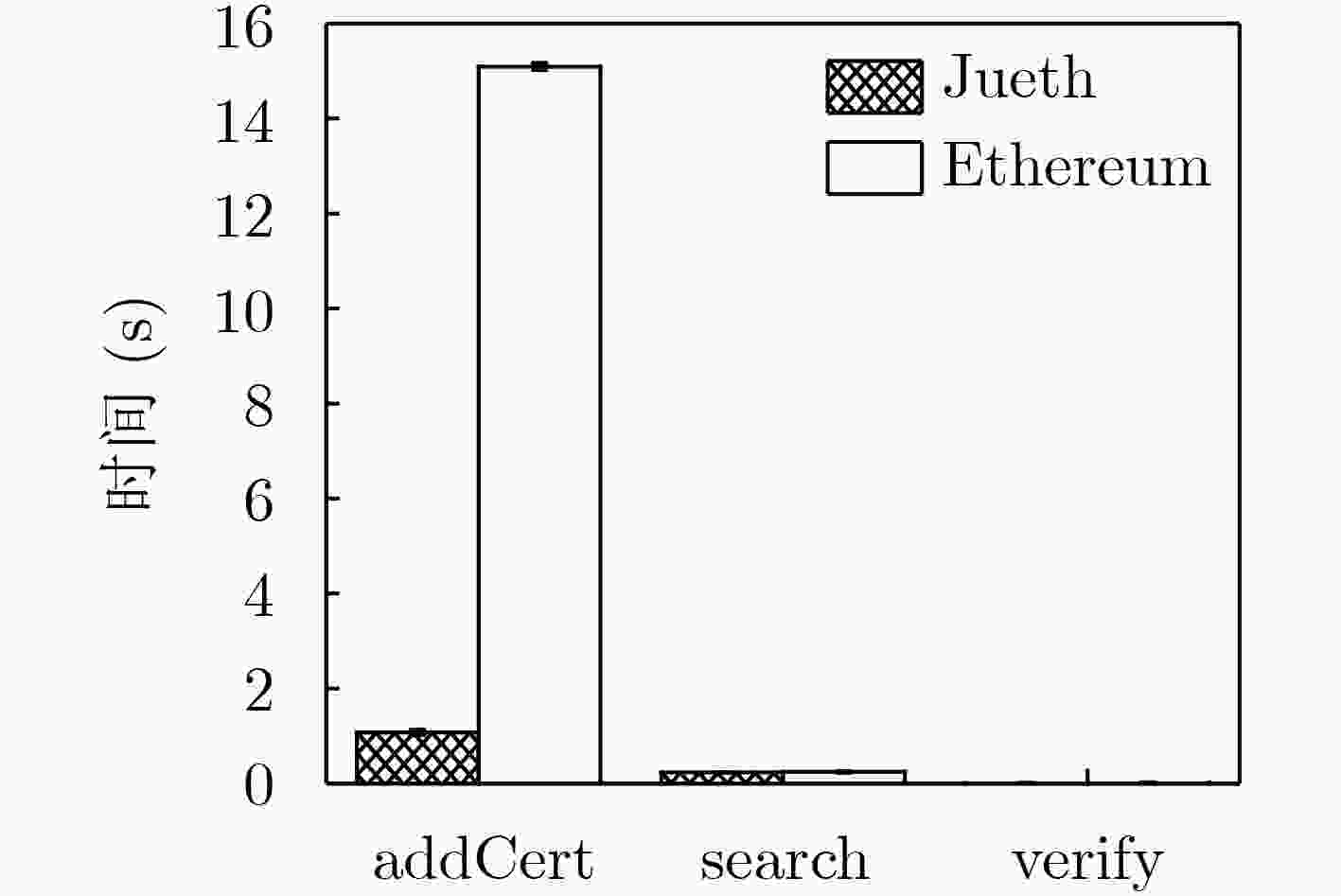


 下载:
下载:
