Field Manipulation Attacks Based on Sniffing Techniques
-
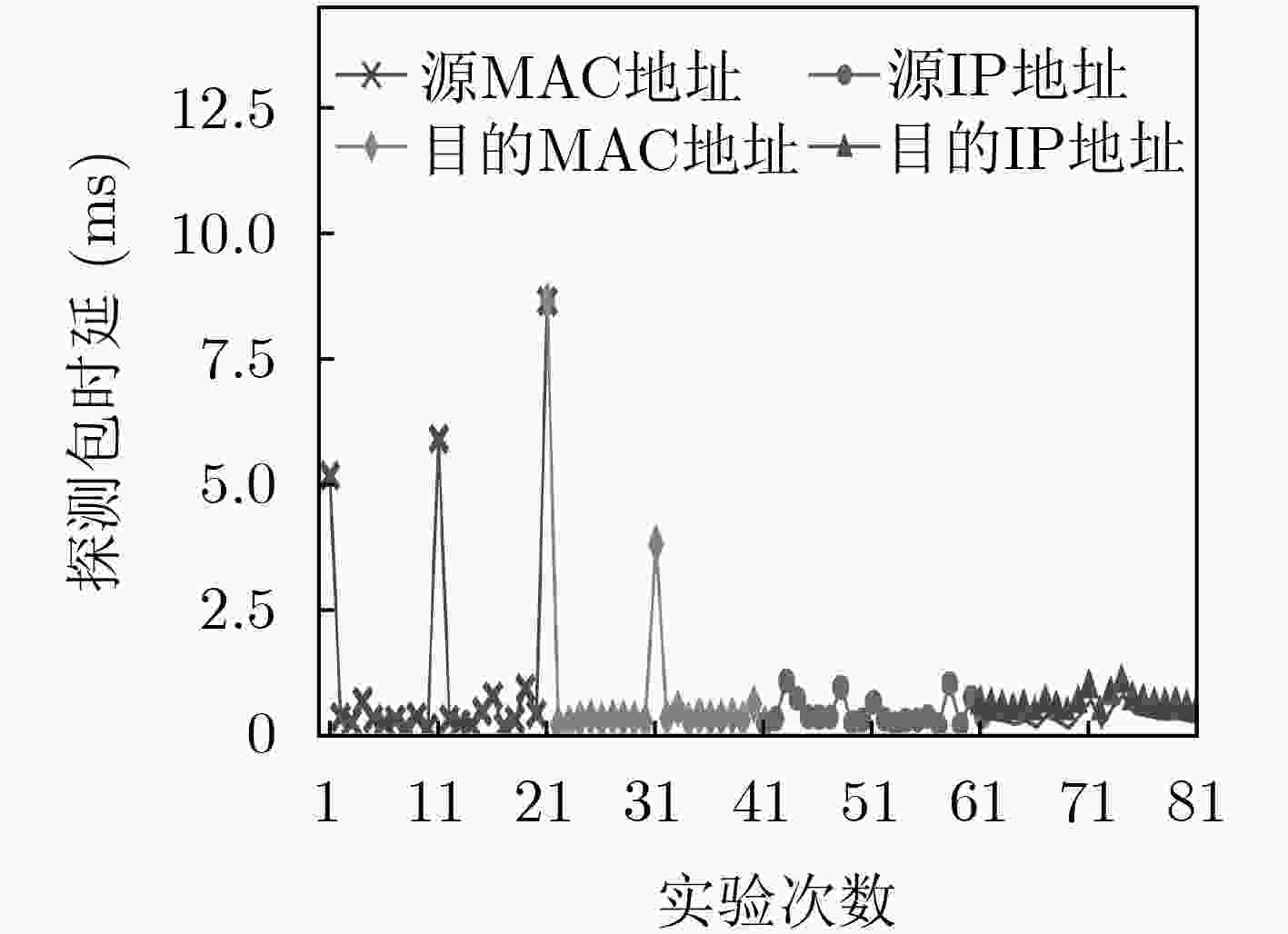
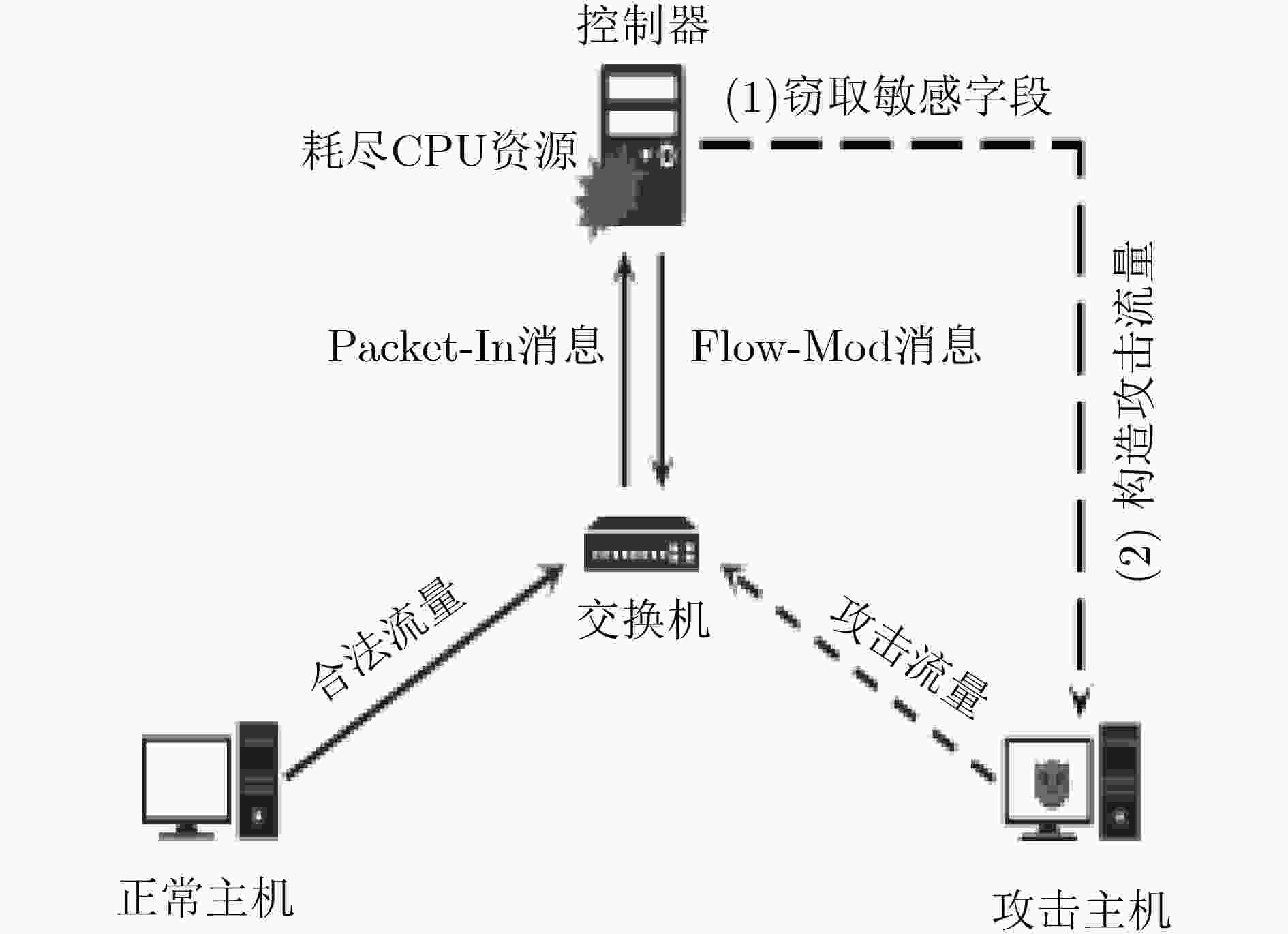
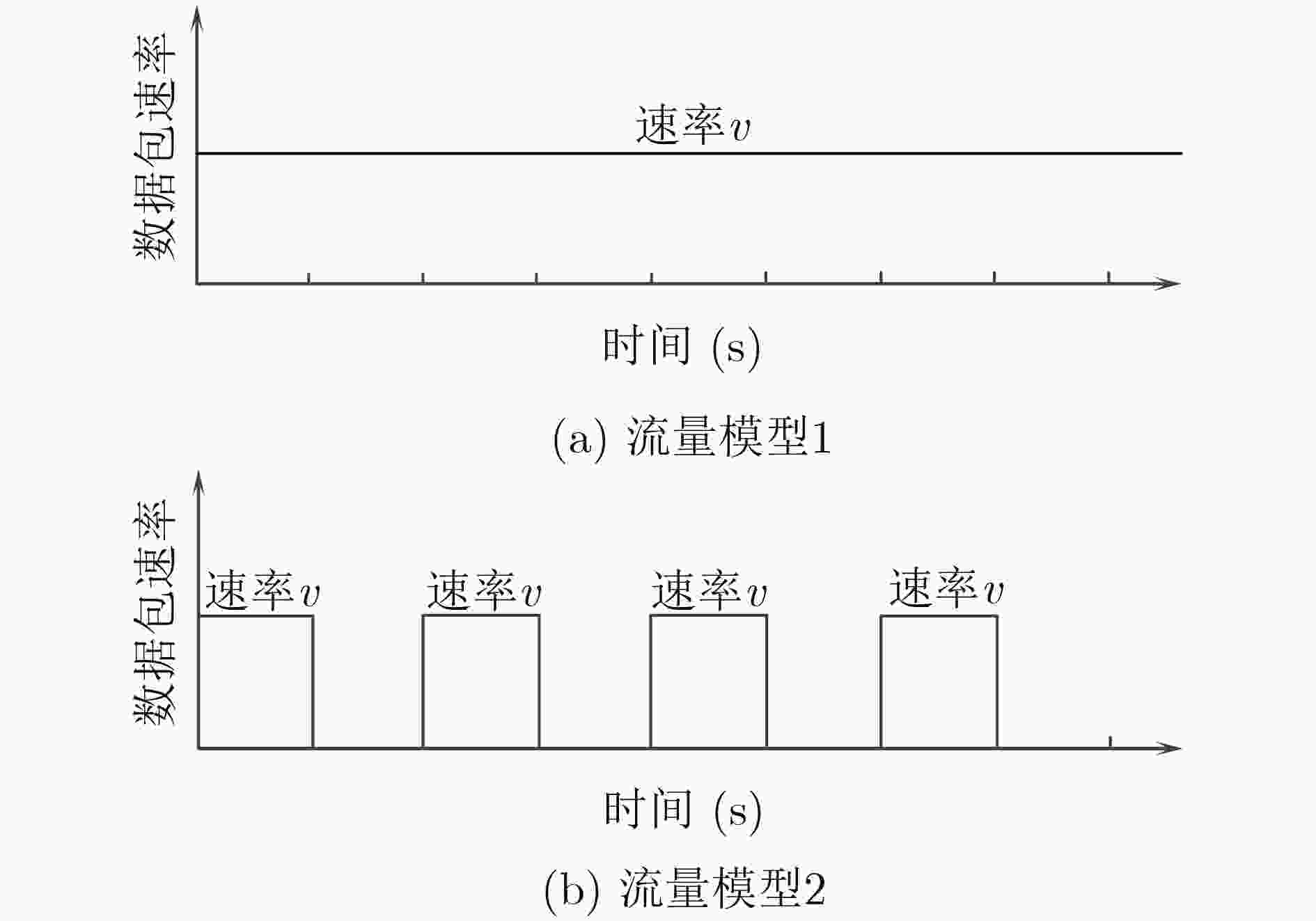
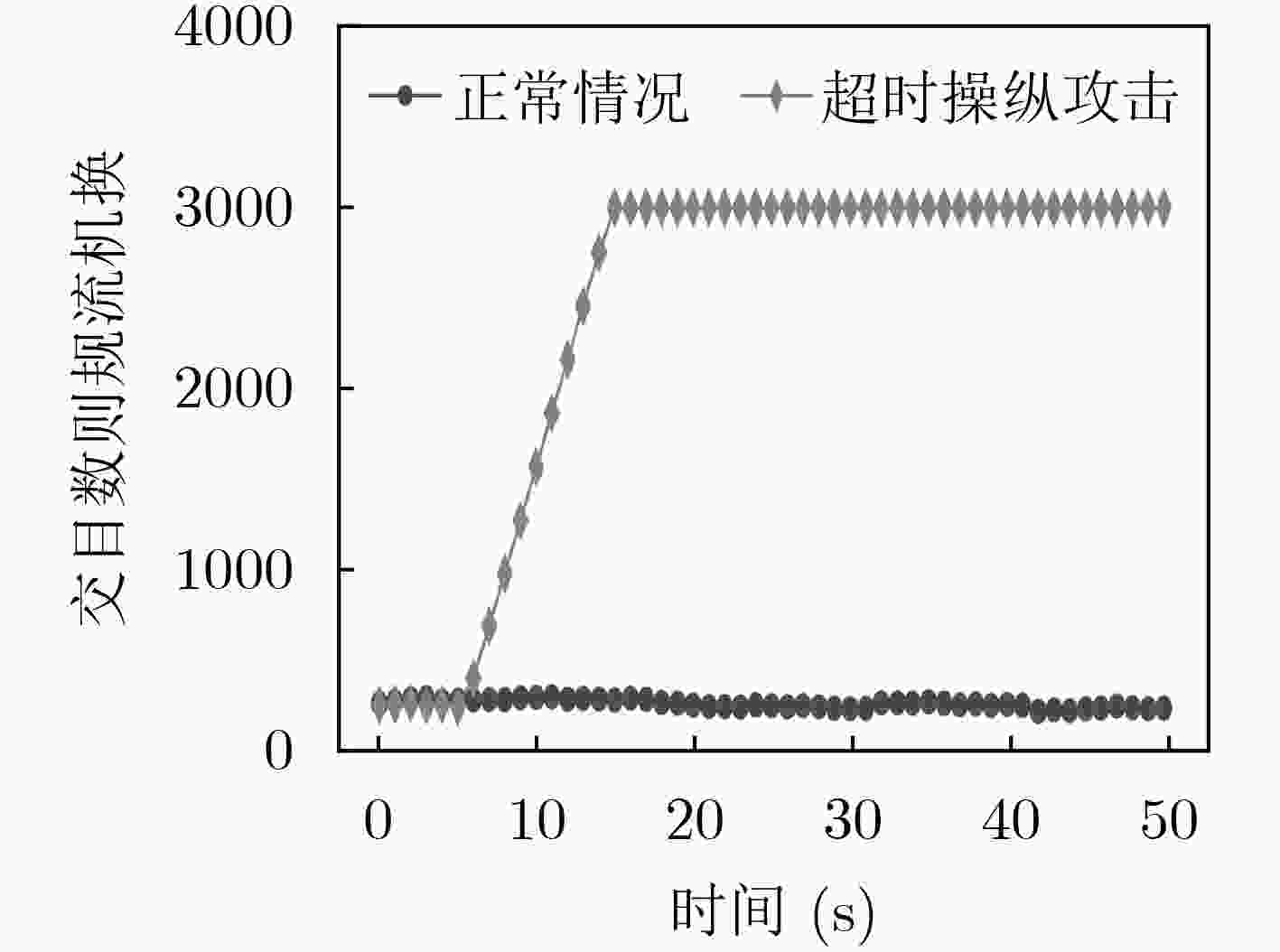
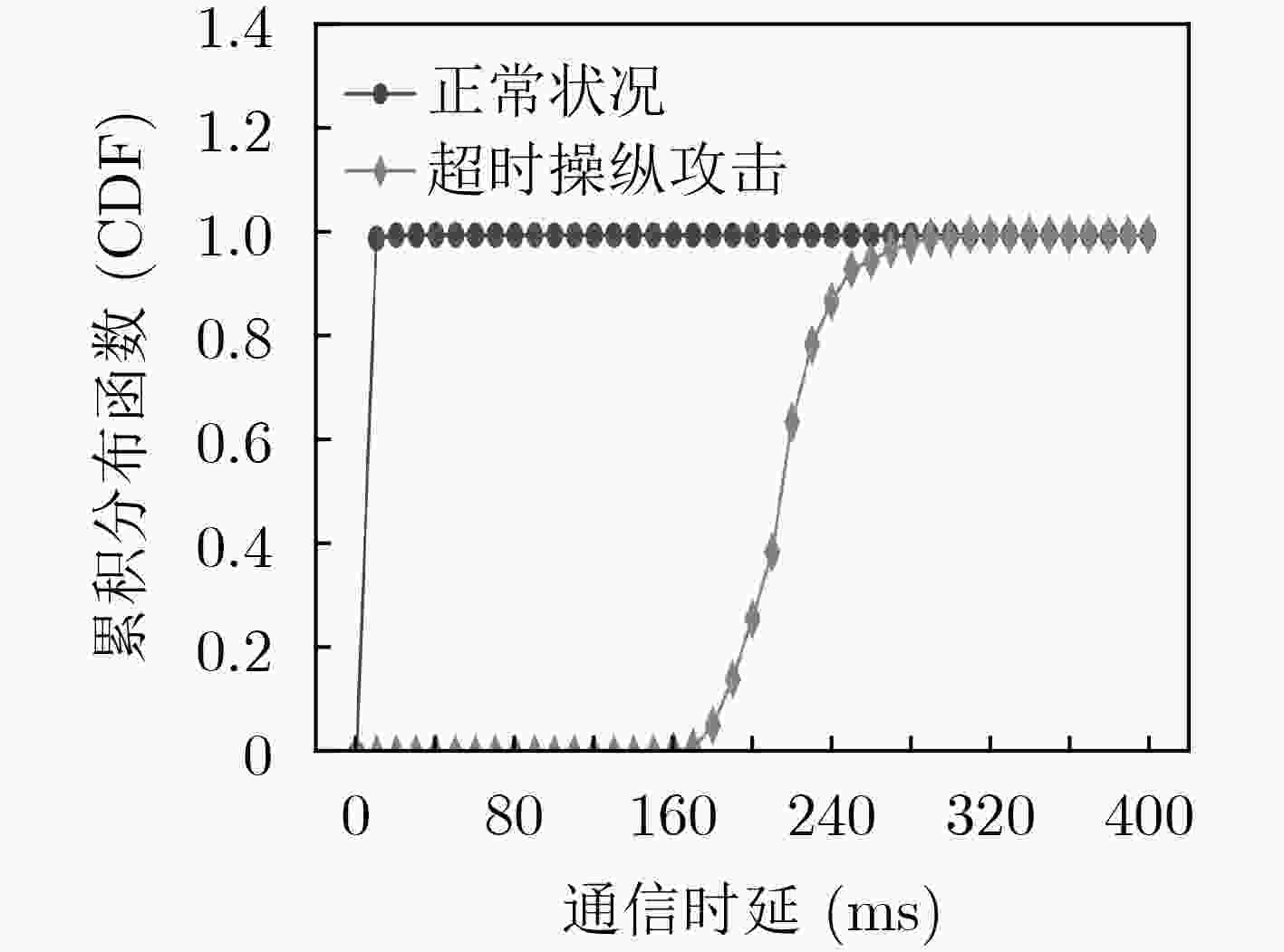
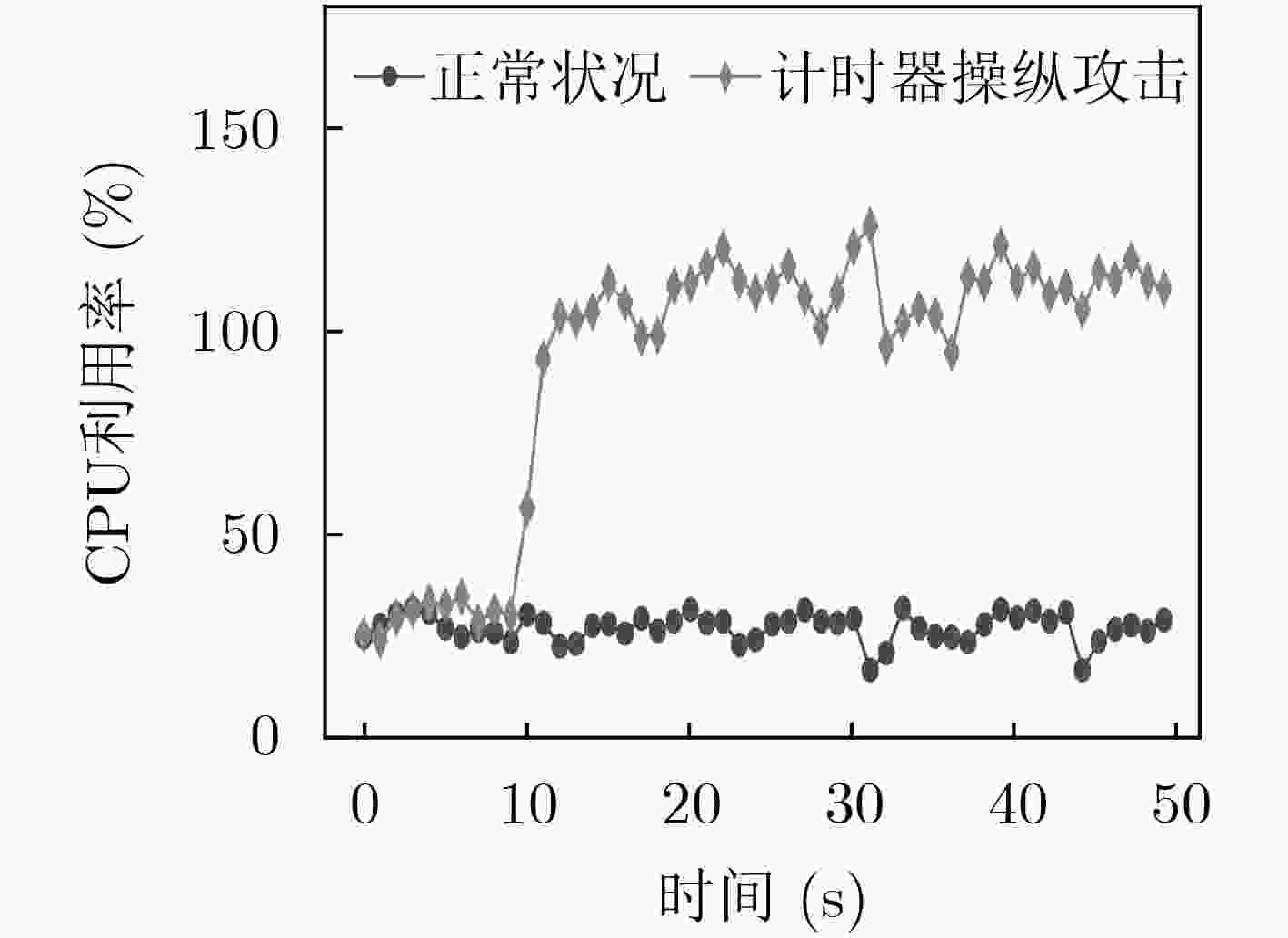
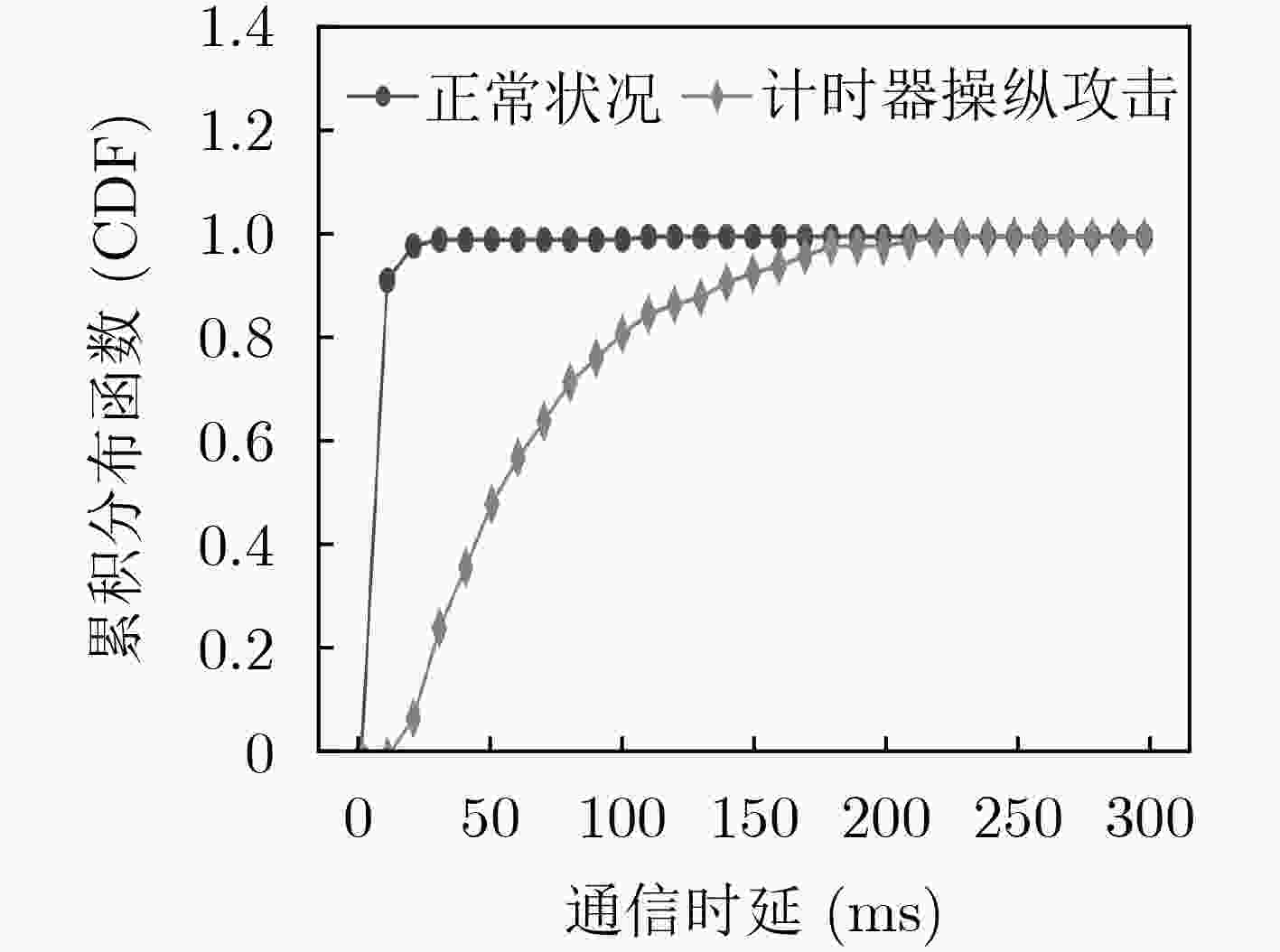
摘要: 软件定义网络(SDN)为网络基础设施提供灵活性、可管理性以及可编程性的同时,引入了诸多新型的攻击向量。该文介绍了攻击者针对OpenFlow关键字段发起的恶意操纵攻击,并设计了3种基于数据包转发时延的嗅探技术以保证字段操纵攻击在真实SDN网络中的可实施性。实验结果表明,字段操纵攻击严重消耗了SDN网络资源,进而导致合法用户之间的通信性能明显降低。Abstract: The flexibility, manageability, and programmability brought by Software-Defined Networking (SDN), however come at the cost of new attack vectors. Malicious manipulation attacks against the key fields in OpenFlow is proposed, and three sniffing technologies based on forwarding delay to ensure the feasibility of manipulation attacks are designed. The experimental results show that the field manipulation attacks consume SDN resources greatly, leading to a significant decrease in the communication performance between legitimate users.
-
Key words:
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN) /
- OpenFlow /
- Field manipulation attack /
- Sniffing
-
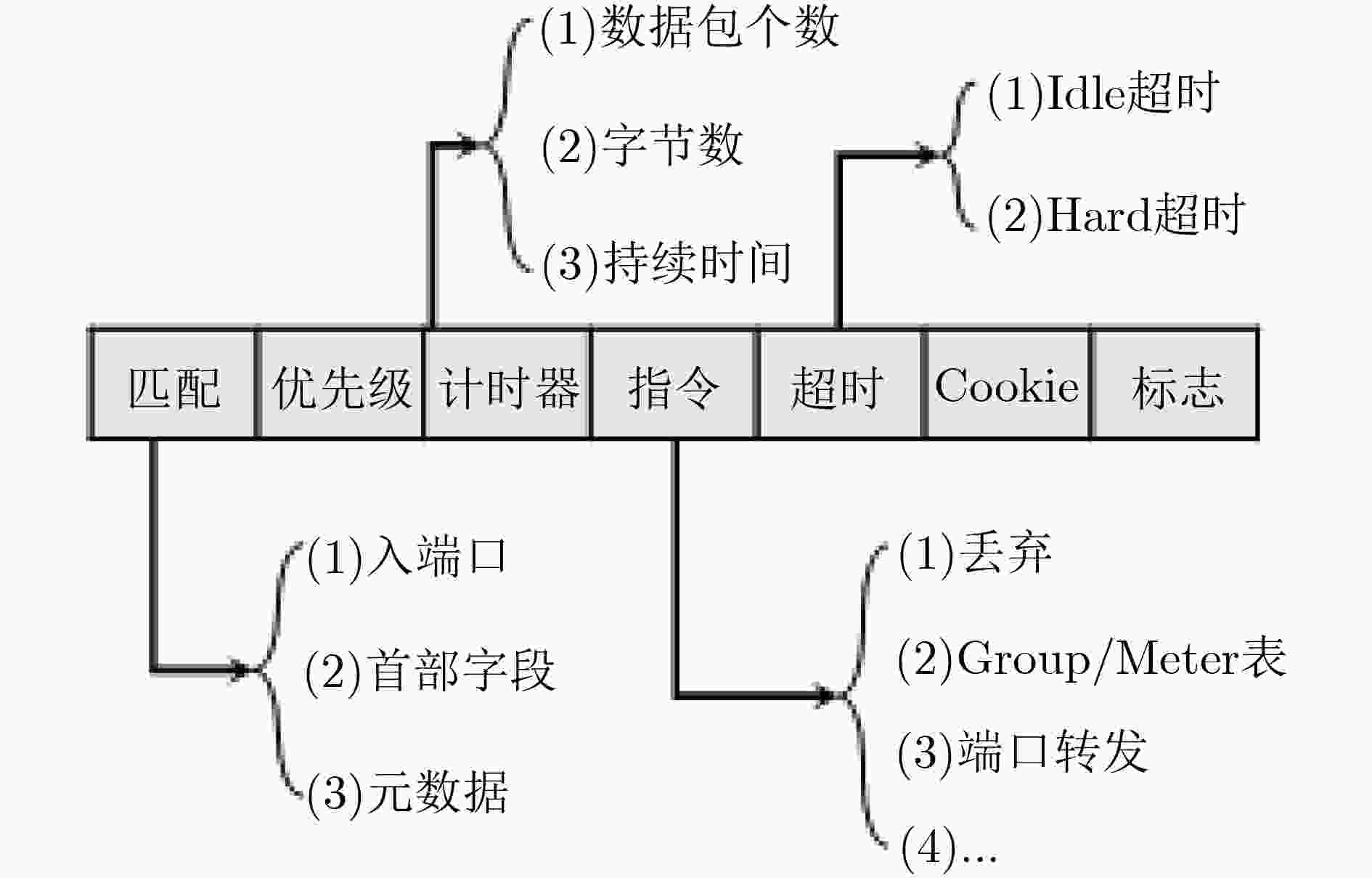
表 1 基于二分法的嗅探技术
初始化:探测包序列$\{ {p_1},{p_2},···,{p_n}\}$;最小超时初始设置为0;最大超时初始设置为$t$(保证$t$时间后规则被剔除); (1) 注入${p_1}$数据包; (2) 循环,对于探测包序列$\{ {p_1},{p_2},···,{p_n}\}$中的每一个数据包${p_i}$: (3) 设置等待时延为(最小超时+最大超时)/2; (4) 等待时延过后,注入${p_i}$数据包,并获得${p_i}$数据包的往返时延; (5) 如果往返时延较大,说明${p_i}$数据包再次触发了流规则安装过程,则: (6) 更新最大超时为(最小超时+最大超时)/2; (7) 否则,说明${p_i}$数据包没有触发了流规则安装过程,然后: (8) 更新最小超时为(最小超时+最大超时)/2; (9) 当全部探测包发送完毕,返回得到的最小超时和最大超时; -
MCKEOWN N, ANDERSON T, BALAKRISHNAN H, et al. OpenFlow: Enabling innovation in campus networks[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2008, 38(2): 69–74. doi: 10.1145/1355734.1355746 ZENG Yue, GUO Songtao, and LIU Guiyan. Comprehensive link sharing avoidance and switch aggregation for software-defined data center networks[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 91: 25–36. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2018.08.034 WANG Haopei, SRIVASTAVA A, XU Lei, et al. Bring your own controller: Enabling tenant-defined SDN apps in IaaS clouds[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Atlanta, USA, 2017: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM.2017.8057137. SAHAY R, MENG Weizhi, ESTAY D A S, et al. CyberShip-IoT: A dynamic and adaptive SDN-based security policy enforcement framework for ships[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 100: 736–750. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.05.049 ZHENG Jing, LI Qi, GU Guofei, et al. Realtime DDoS defense using COTS SDN switches via adaptive correlation analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2018, 13(7): 1838–1853. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2018.2805600 姚琳元, 董平, 张宏科. 基于对象特征的软件定义网络分布式拒绝服务攻击检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(2): 381–388. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160370YAO Linyuan, DONG Ping, and ZHANG Hongke. Distributed denial of service attack detection based on object character in software defined network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(2): 381–388. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160370 武泽慧, 魏强, 任开磊, 等. 基于OpenFlow交换机洗牌的DDoS攻击动态防御方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(2): 397–404. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160449WU Zehui, WEI Qiang, REN Kailei, et al. Dynamic defense for DDoS attack using OpenFlow-based switch shuffling approach[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(2): 397–404. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160449 DENG Shuhua, GAO Xing, LU Zebin, et al. DoS vulnerabilities and mitigation strategies in software-defined networks[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2019, 125: 209–219. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2018.10.011 SKOWYRA R, XU Lei, GU Guofei, et al. Effective topology tampering attacks and defenses in software-defined networks[C]. The 48th Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks, Luxembourg City, 2018: 374–385. doi: 10.1109/dsn.2018.00047. LI Qi, ZOU Xiaoyue, HUANG Qun, et al. Dynamic packet forwarding verification in SDN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2019, 16(6): 915–929. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2018.2810880 CAO Jiahao, LI Qi, XIE Renjie, et al. The crosspath attack: Disrupting the SDN control channel via shared links[C]. The 28th USENIX Conference on Security Symposium, Berkeley, USA, 2019: 19–36. SHIN S and GU Guofei. Attacking software-defined networks: A first feasibility study[C]. The 2nd ACM SIGCOMM Workshop on Hot Topics in Software Defined Networking, Hong Kong, China, 2013: 165–166. doi: 10.1145/2491185.2491220. CAO Jiahao, XU Mingwei, LI Qi, et al. Disrupting sdn via the data plane: A low-rate flow table overflow attack[C]. The 13th International Conference on Security and Privacy in Communication Networks, Niagara Falls, Canada, 2017: 356–376. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-78813-5_18. JAIN S, KUMAR A, MANDAL S, et al. B4: Experience with a globally-deployed software defined wan[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2013, 43(4): 3–14. doi: 10.1145/2486001.2486019 Open Networking Foundation. OpenFlow switch specification 1.5. 1[EB/OL]. https://www.opennetworking.org/software-defined-standards/specifications/, 2019. ZHANG Mengtao, LI Guanyu, XU Lei, et al. Control plane reflection attacks in SDNs: New attacks and countermeasures[C]. The 21st International Symposium on Research in Attacks, Intrusions, and Defenses, Heraklion, Greece, 2018: 161–183. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-00470-5_8. XU Hongli, YU Zhuolong, QIAN Chen, et al. Minimizing flow statistics collection cost of SDN using wildcard requests[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Atlanta, USA, 2017: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM.2017.8056992. ZHU Huikang, FAN Hongbo, LUO Xuan, et al. Intelligent timeout master: Dynamic timeout for SDN-based data centers[C]. The 13th International Symposium on Integrated Network Management, Ottawa, Canada, 2015: 734–737. doi: 10.1109/INM.2015.7140363. -





 下载:
下载:
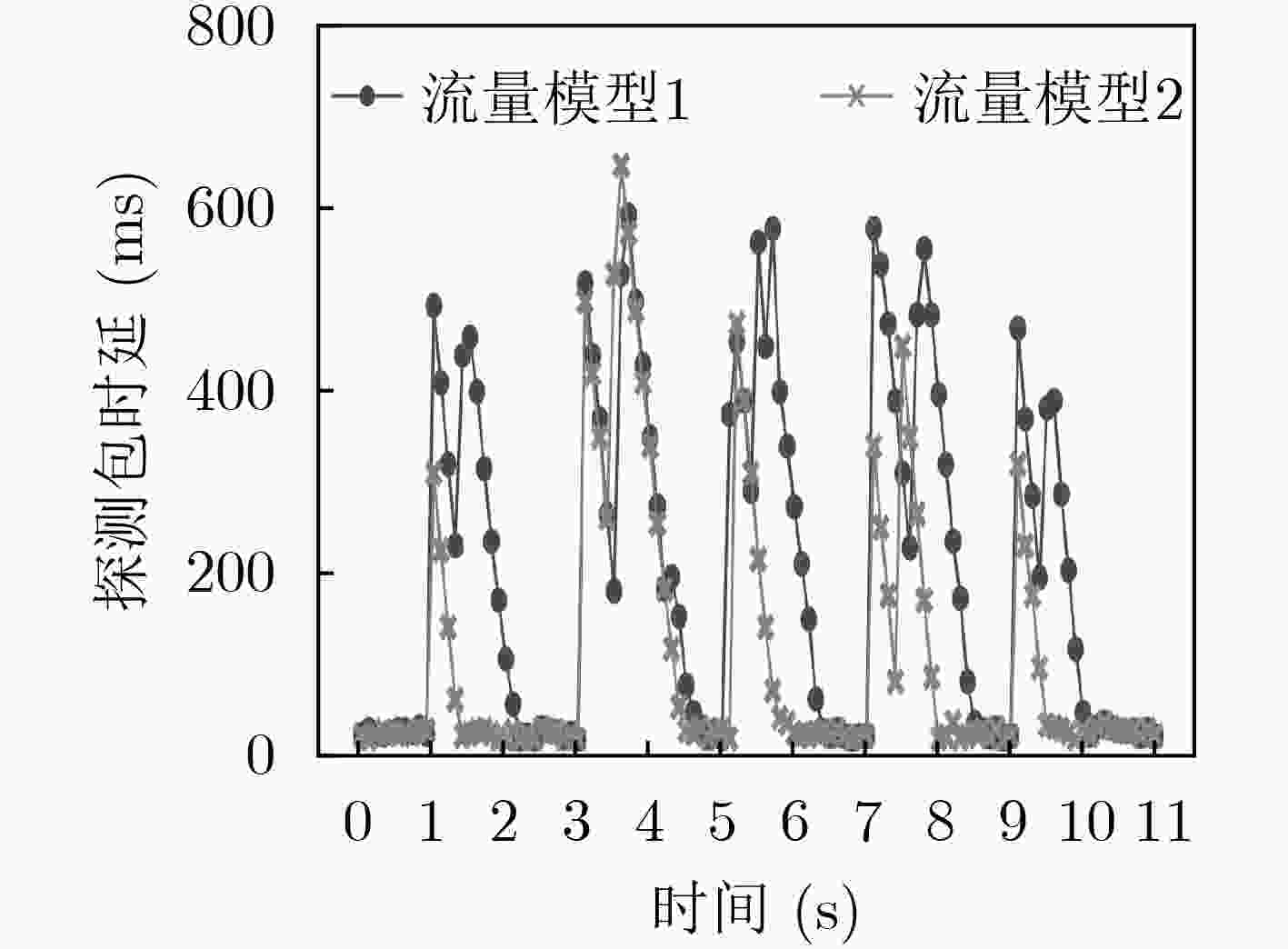
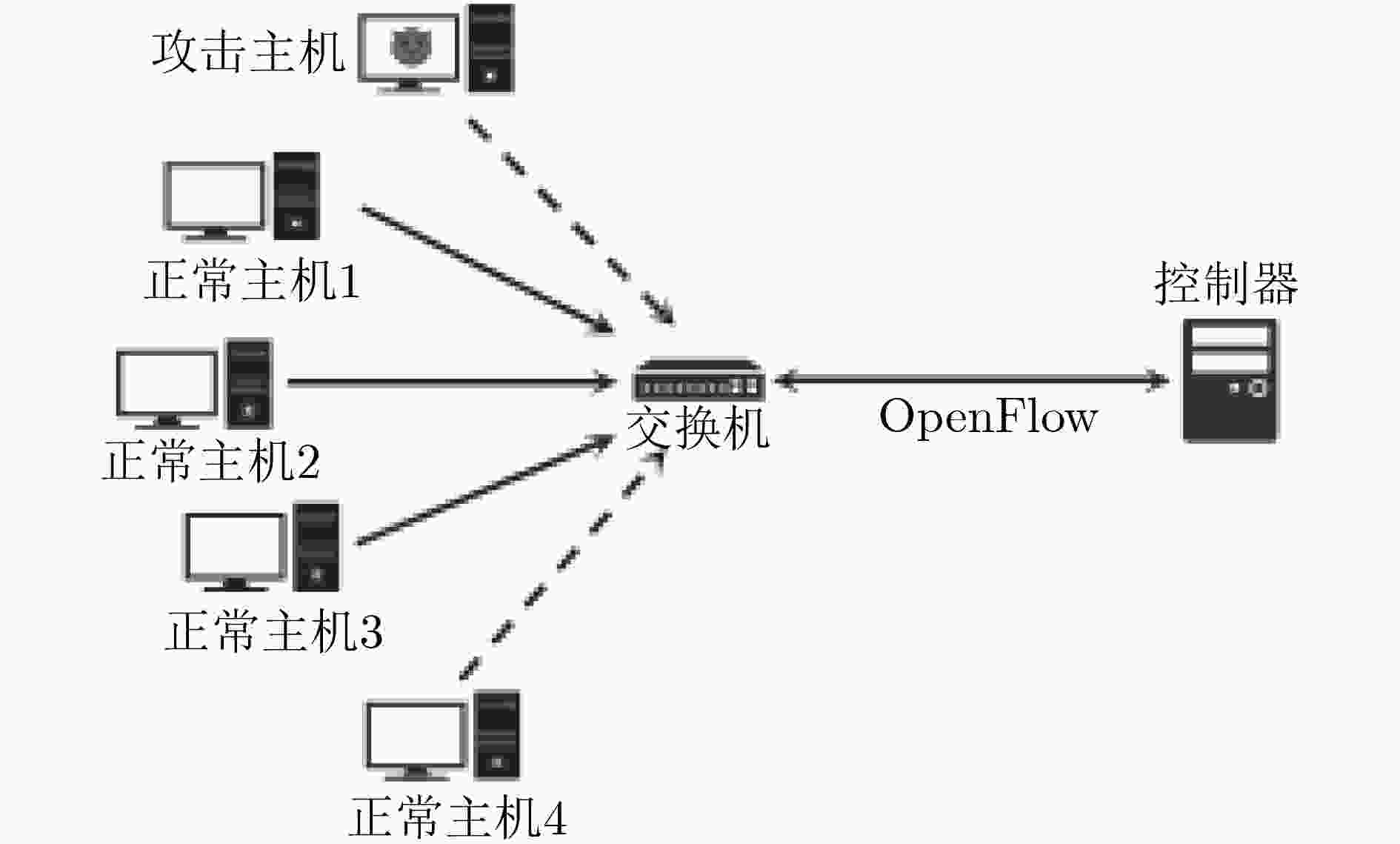
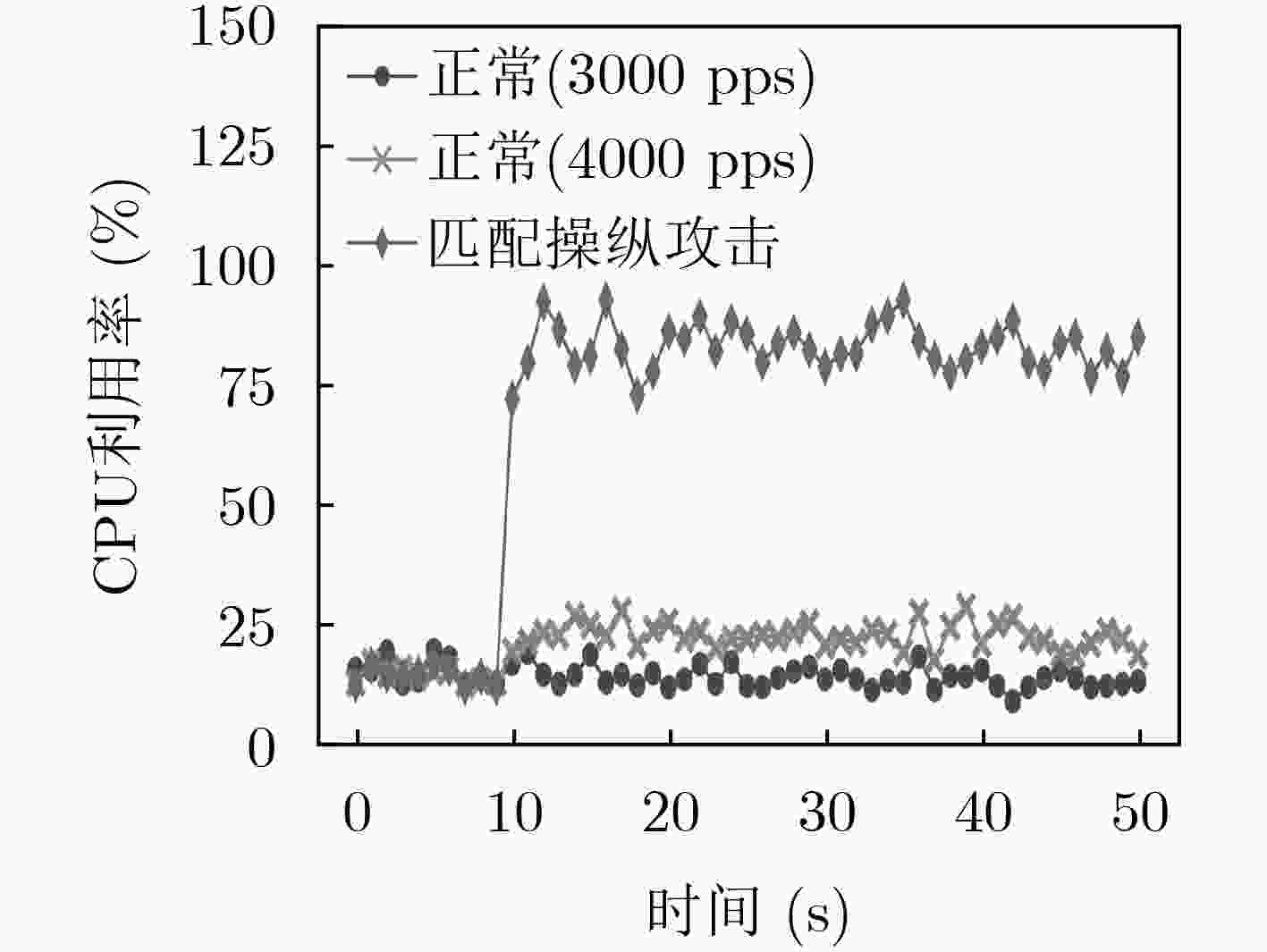
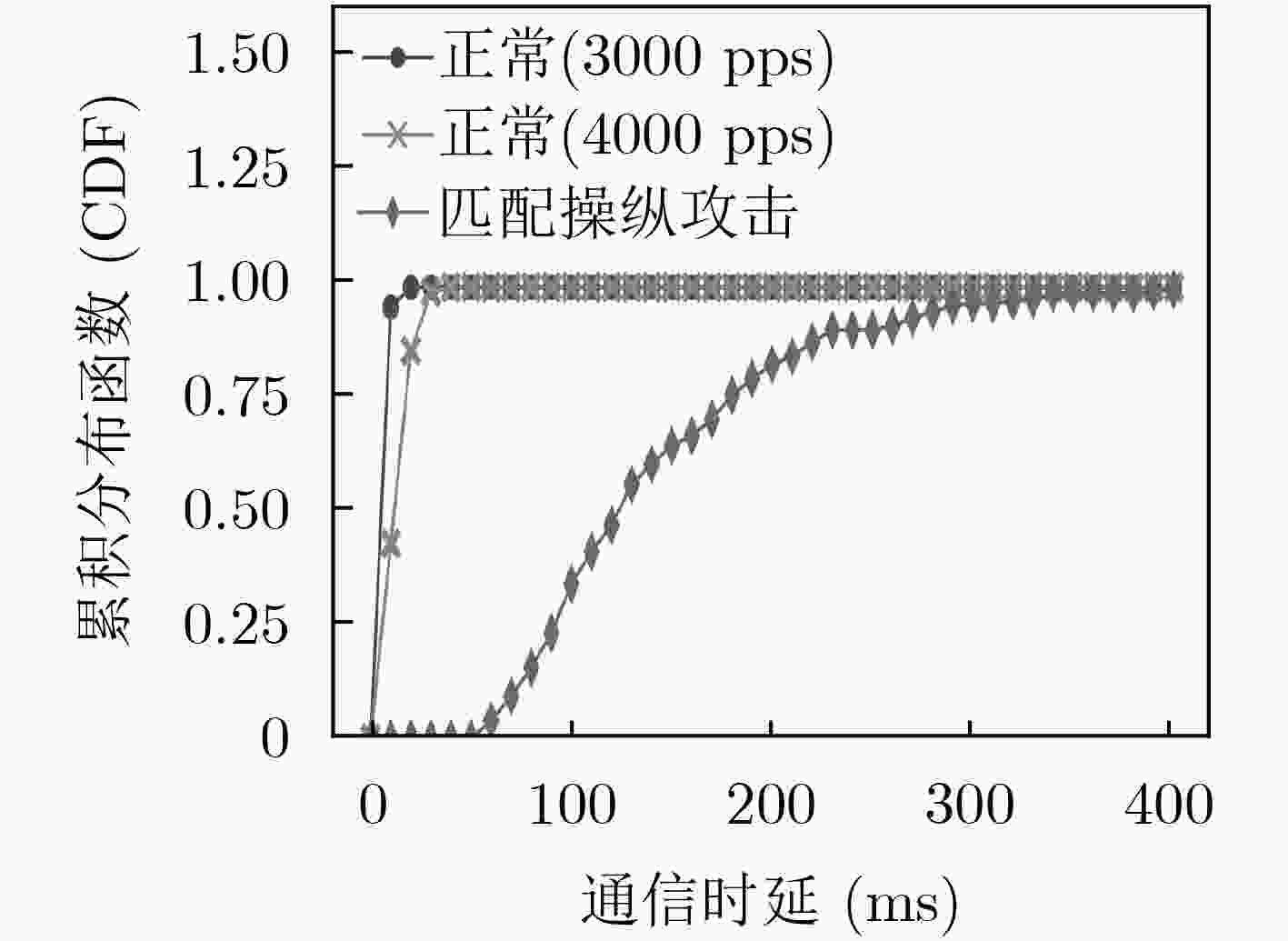


 下载:
下载:
