Channel’s Price-based Resource Allocation for Wireless Virtual Network: A Hierarchical Matching/ Stackelberg Game Approach
-
摘要:
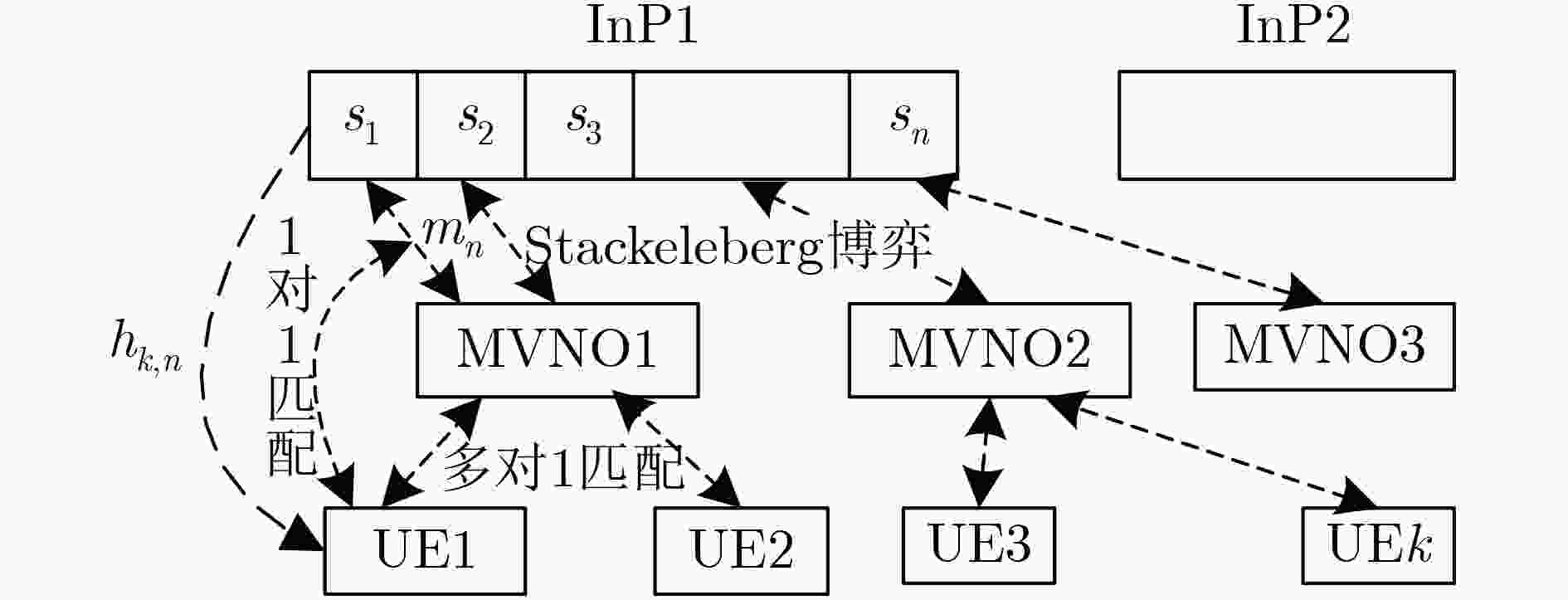
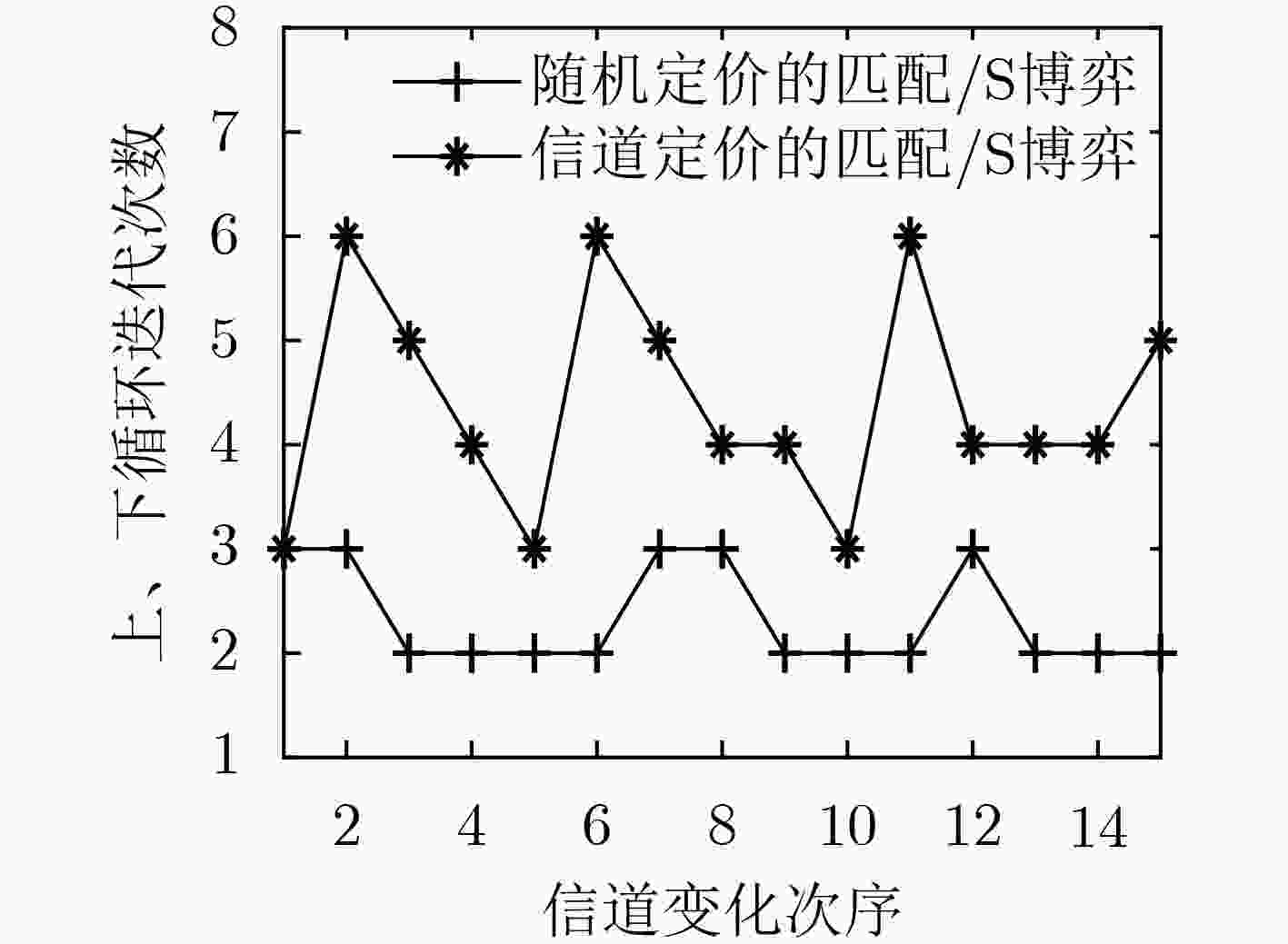
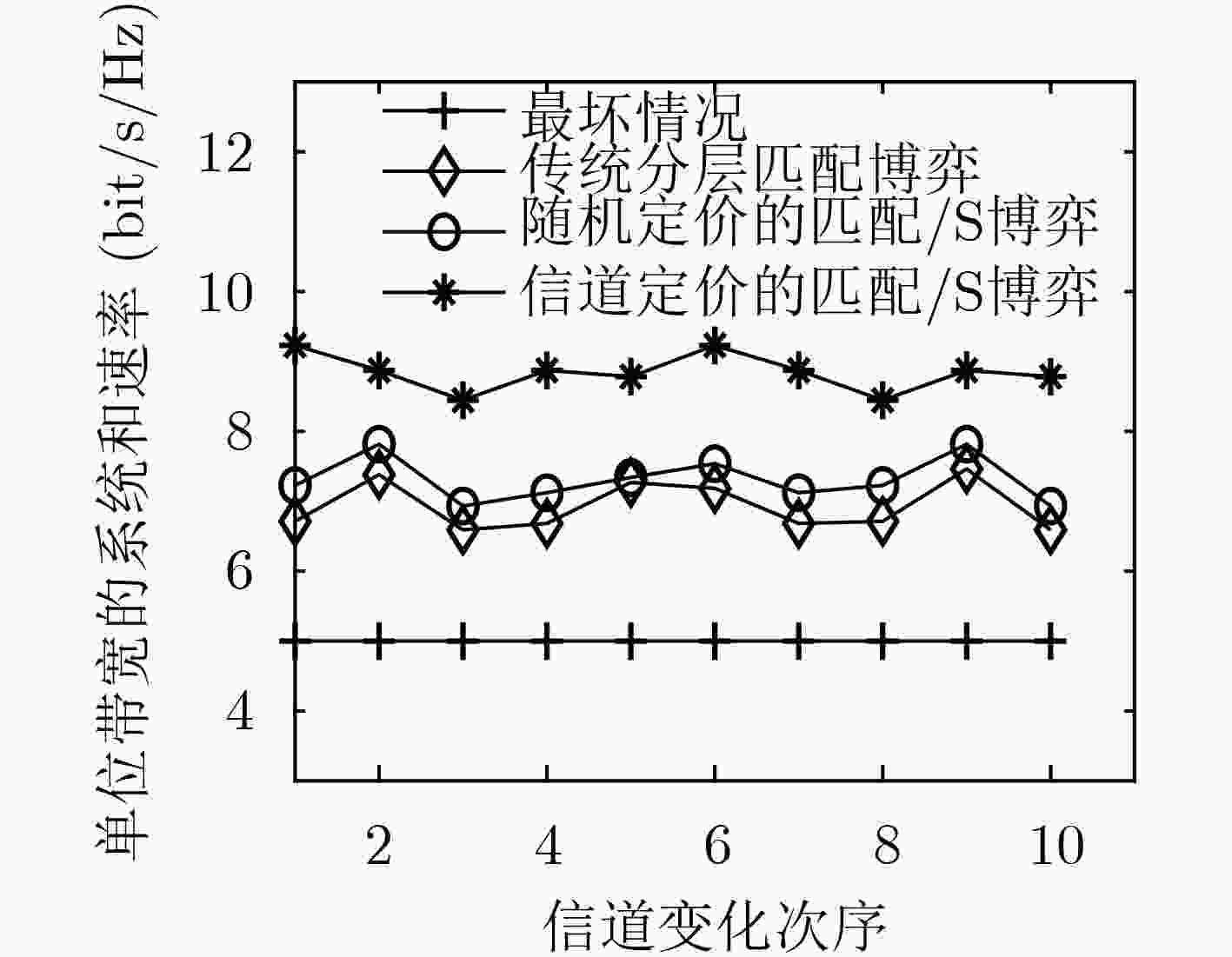
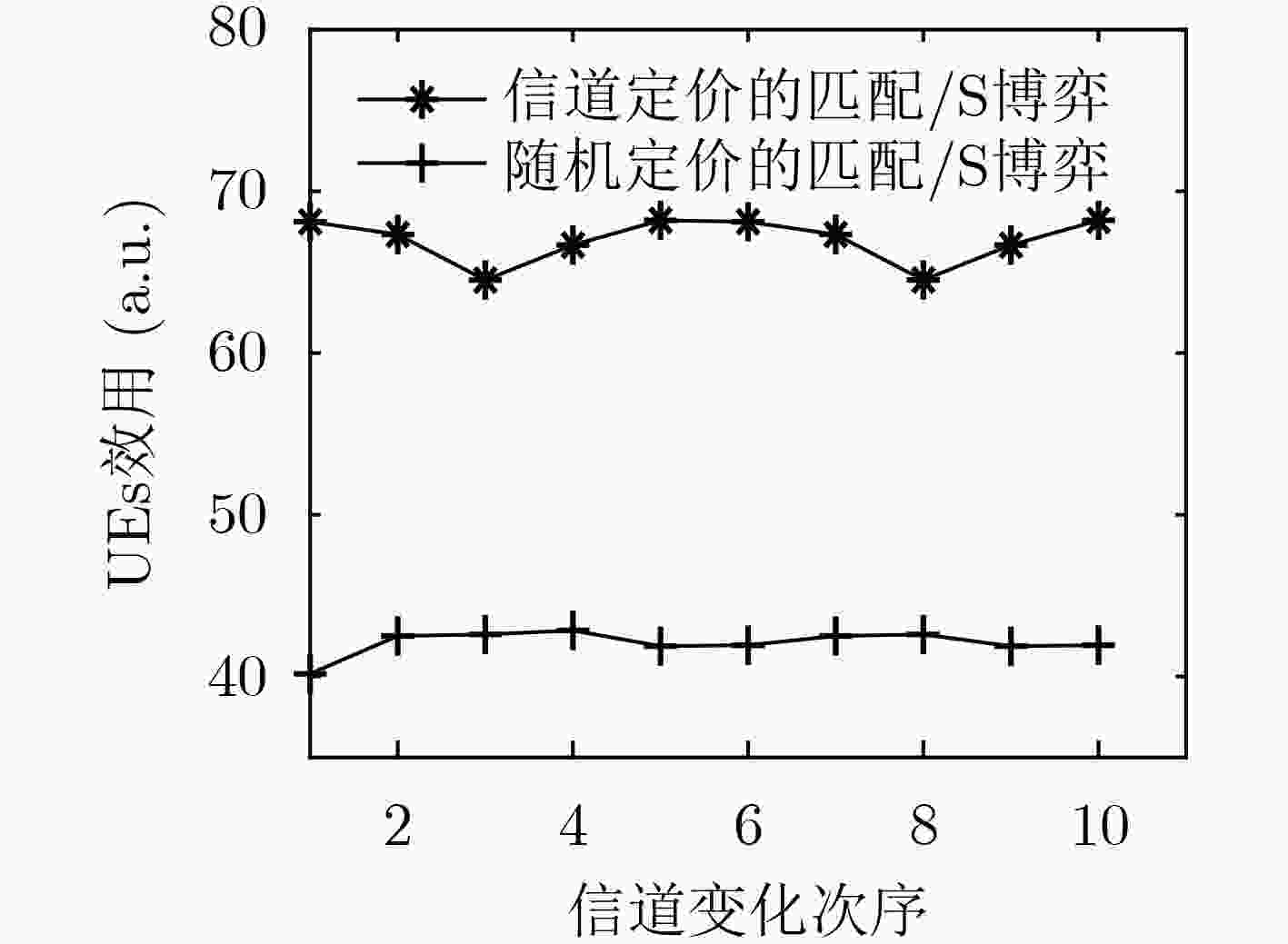
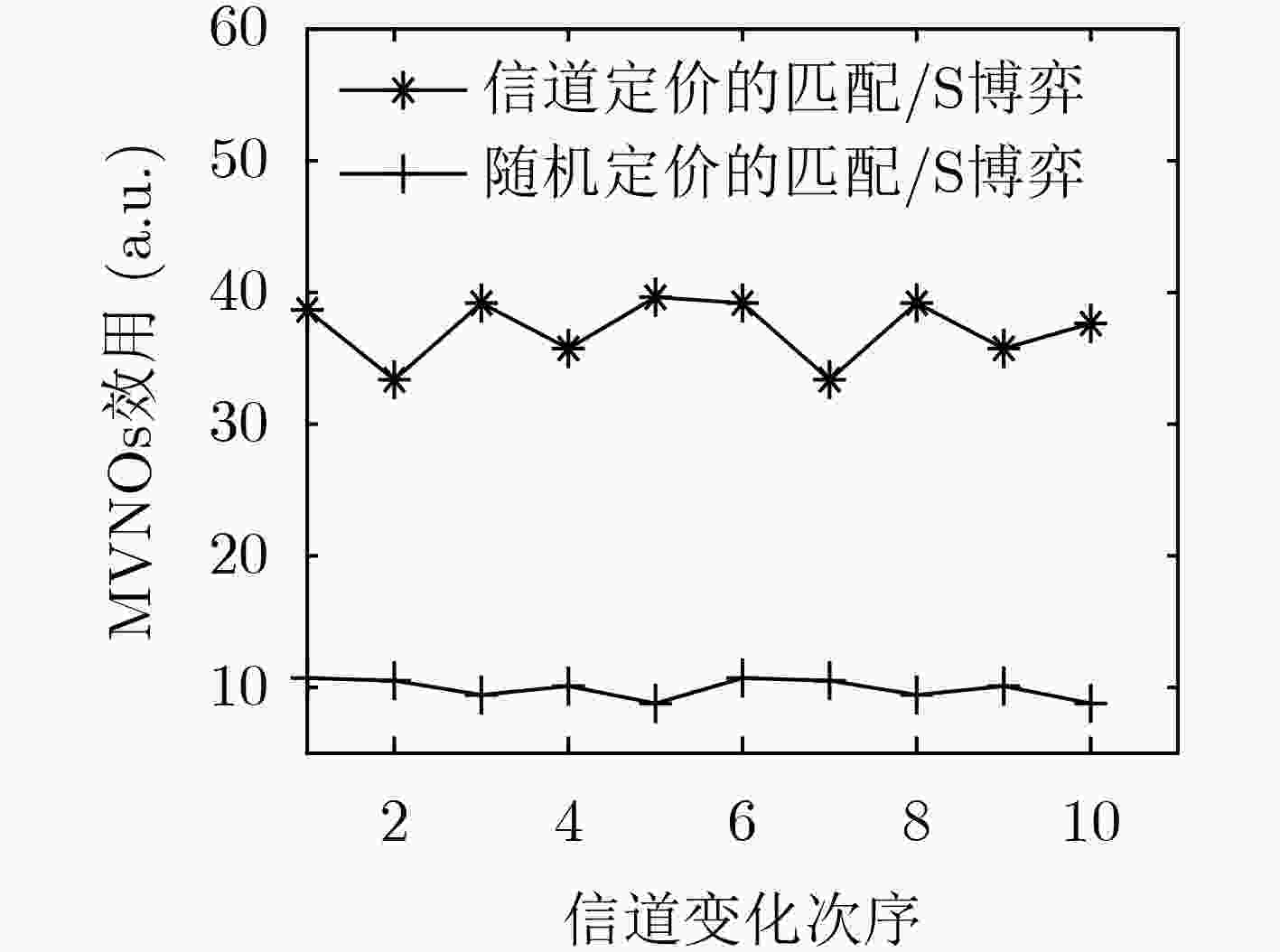
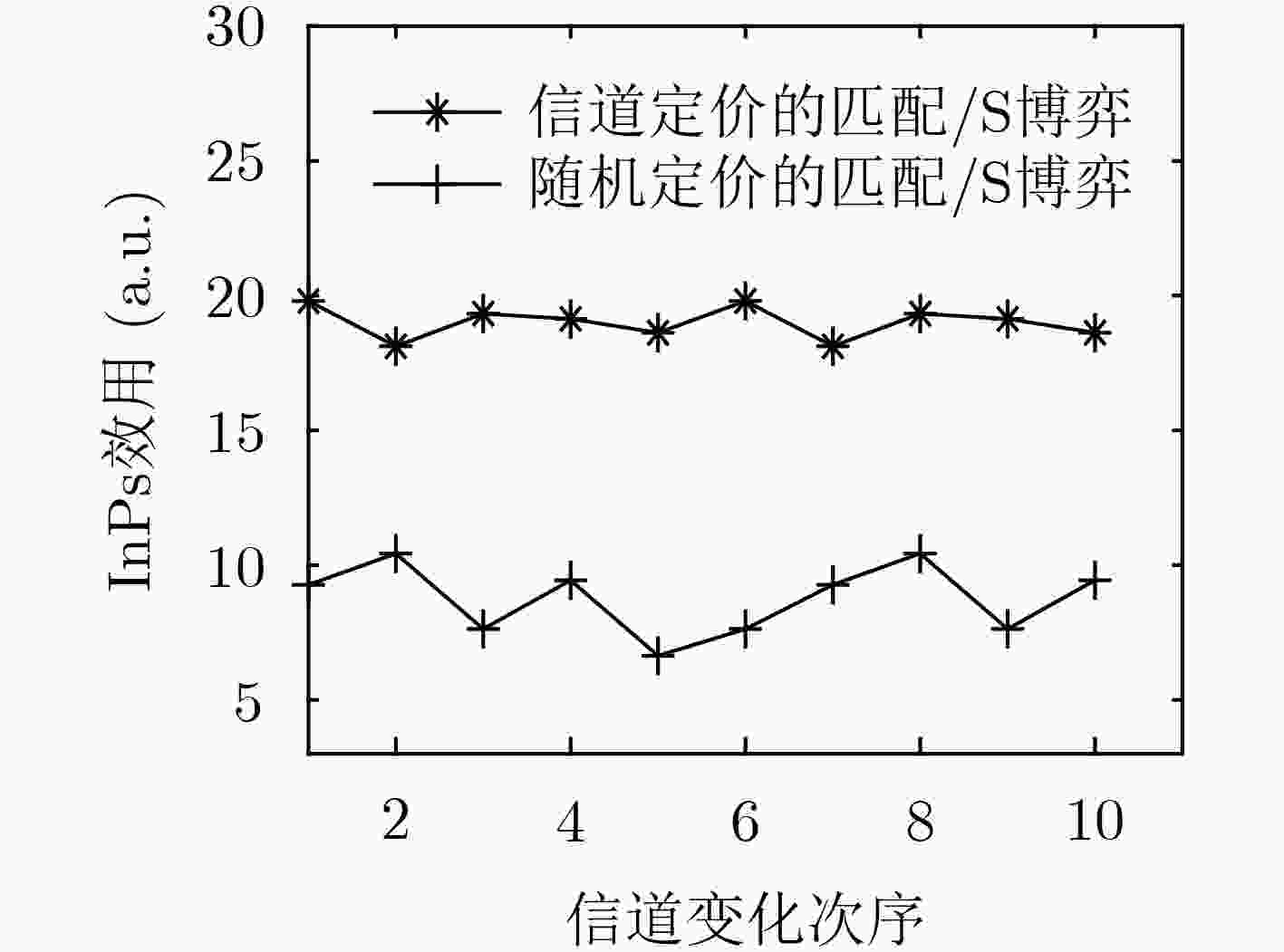
针对分层匹配博弈不能跟踪信道变化以及循环迭代收敛慢等问题,该文提出一种基于信道定价的无线虚拟网络资源分配策略:匹配/Stackelberg分层博弈。分别以基于流带宽的用户满意度、系统带宽及切片功率作为报酬函数建立3级联合优化模型,并采用匹配/Stackelberg分层博弈求解。在博弈下层,定义移动虚拟网络操作者(MVNOs)m—切片n对mn及其与用户(UEs)的1对1匹配博弈以代替UEs与MVNOs的多对1匹配,对
\begin{document}${m_n}$\end{document} 定义基于信道平均信息的切片功率价格,加速上、下一致收敛并使UEs适应信道选择最优
,证明均衡点存在并给出了低复杂度的分布式拒绝-接收算法;在博弈上层,基于UEs与
已匹配关系,形成基础资源提供者(InPs)与
的Stackelberg博弈,给出了基于局部信道信息的功率定价和分配策略,使系统效用及频谱效率基于信道最优。最后定义了双层循环稳定条件及过程。仿真表明,该策略在信道跟踪、频谱效率、效用方面均优于随机定价的匹配/Stackelberg分层博弈以及传统分层匹配博弈。
-
关键词:
- 无线虚拟网络 /
- 分层博弈 /
- 匹配博弈 /
- Stackelberg博弈 /
- 信道定价
Abstract:For the low iteration convergence rate and the disability to track the change of channels in hierarchical matching game, a new resource allocation strategy for wireless virtual networks, i.e., the channel’s price-based hierarchical matching/Stackelberg game is proposed in this paper. A three-level joint optimization model is established on each layer reward function based on stream’s bandwidth-based user’s satisfaction, the system’s bandwidth and the slice’s power. The hierarchical matching/Stackelberg game is adopted to solve the optimizing problem. In the lower layer of the hierarchical game, the
\begin{document}${m_n}$\end{document} is defined to present Mobile Virtual Network Operator(MVNO) m-InPn and one-to-one matching game between it and UEs is constructed to displace the many-to-one matching game between UEs and MVNOs, where a price based on the global information of channels is given to speed up the identical convergence between the upper and the lower layer and make UEs select the optimal
adapting the channel. After proving the existing of equilibrium, the rejecting-receiving algorithm for one-to-one matching game is proposed. In the upper layer of the hierarchical game, a Stackelberg game between the InPs and many
is formed based on the connection between those users and
, and an optimized power pricing and allocation strategy based on local information of channel are given, which makes the optimal system utility and resource utilization based on channels. Finally, the process for the two-tier cycling is given and the stability of the hierarchical game is characterized. Simulation results show that the channel’s price-based hierarchical matching/Stackelberg game strategy outperforms the random pricing hierarchical matching/Stackelberg game and the conventional hierarchical matching game in the aspect of tracking channel’s changing and spectrum efficiency and system’s utility.
-
Key words:
- Wireless virtual network /
- Hierarchical game /
- Matching game /
- Stackelberg game /
- Channel pricing
-
LIANG Chengchao and YU F R. Wireless network virtualization: A survey, some research issues and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2015, 17(1): 358–380. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2014.2352118 LIANG Chengchao and YU F R. Wireless virtualization for next generation mobile cellular networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2015, 22(1): 61–69. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2015.7054720 PARSAEEFARD S, DAWADI R, DERAKHSHANI M, et al. Joint user-association and resource-allocation in virtualized wireless networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 2738–2750. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2560218 DAWADI R, PARSAEEFARD S, DERAKHSHANI M, et al. Energy-efficient resource allocation in multi-cell virtualized wireless networks[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Ubiquitous Wireless Broadband, Montreal, 2015. doi: 10.1109/ICUWB.2015.7324446. 王汝言, 李宏娟, 吴大鹏. 基于Stackelberg博弈的虚拟化无线传感网络资源分配策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(2): 377–384. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180277WANG Ruyan, LI Hongjuan, and WU Dapeng. Stackelberg game-based resource allocation strategy in virtualized wireless sensor network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(2): 377–384. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180277 KOKKU R, MAHINDRA R, ZHANG Honghai, et al. NVS: A substrate for virtualizing wireless resources in cellular networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2012, 20(5): 1333–1346. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2011.2179063 AL-KHATIB O, HARDJAWANA W, and VUCETIC B. Spectrum sharing in multi-tenant 5G Cellular networks: Modeling and planning[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 7: 1602–1616. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2886447 NGUYEN D H N, ZHANG Yanru, and HAN Zhu. Contract-based spectrum allocation for wireless virtualized networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(11): 7222–7235. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2865924 LIU Bin and TIAN Hui. A bankruptcy game-based resource allocation approach among virtual mobile operators[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2013, 17(7): 1420–1423. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2013.052013.130959 梁靓, 武彦飞, 冯钢. 基于在线拍卖的网络切片资源分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1187–1193. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180636LIANG Liang, WU Yanfei, and FENG Gang. Resource allocation algorithm of network slicing based on online auction[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1187–1193. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180636 ZHU Kun and HOSSAIN E. Virtualization of 5G cellular networks as a hierarchical combinatorial auction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2016, 15(10): 2640–2654. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2015.2506578 KAZMI S M A, TRAN N H, HO T M, et al. Hierarchical matching game for service selection and resource purchasing in wireless network virtualization[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(1): 121–124. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2701803 YIN Rui, ZHONG Caijun, YU Guanding, et al. Joint spectrum and power allocation for D2D communications underlaying cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(4): 2185–2195. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2424395 FENG Zhiyong, JI Lei, ZHANG Qixun, et al. A supply-demand approach for traffic-Oriented wireless resource virtualization with testbed analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(9): 6077–6090. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2718527 ZHANG Xi and ZHU Qixuan. Scalable virtualization and offloading-based software-defined architecture for heterogeneous statistical QoS provisioning over 5G multimedia mobile wireless networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2018, 36(12): 2787–2804. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2018.2871327 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
