Sensor Selection Method Based on Multi-objective Optimal Optimization for Mixture Gaussian Noise
-
摘要:
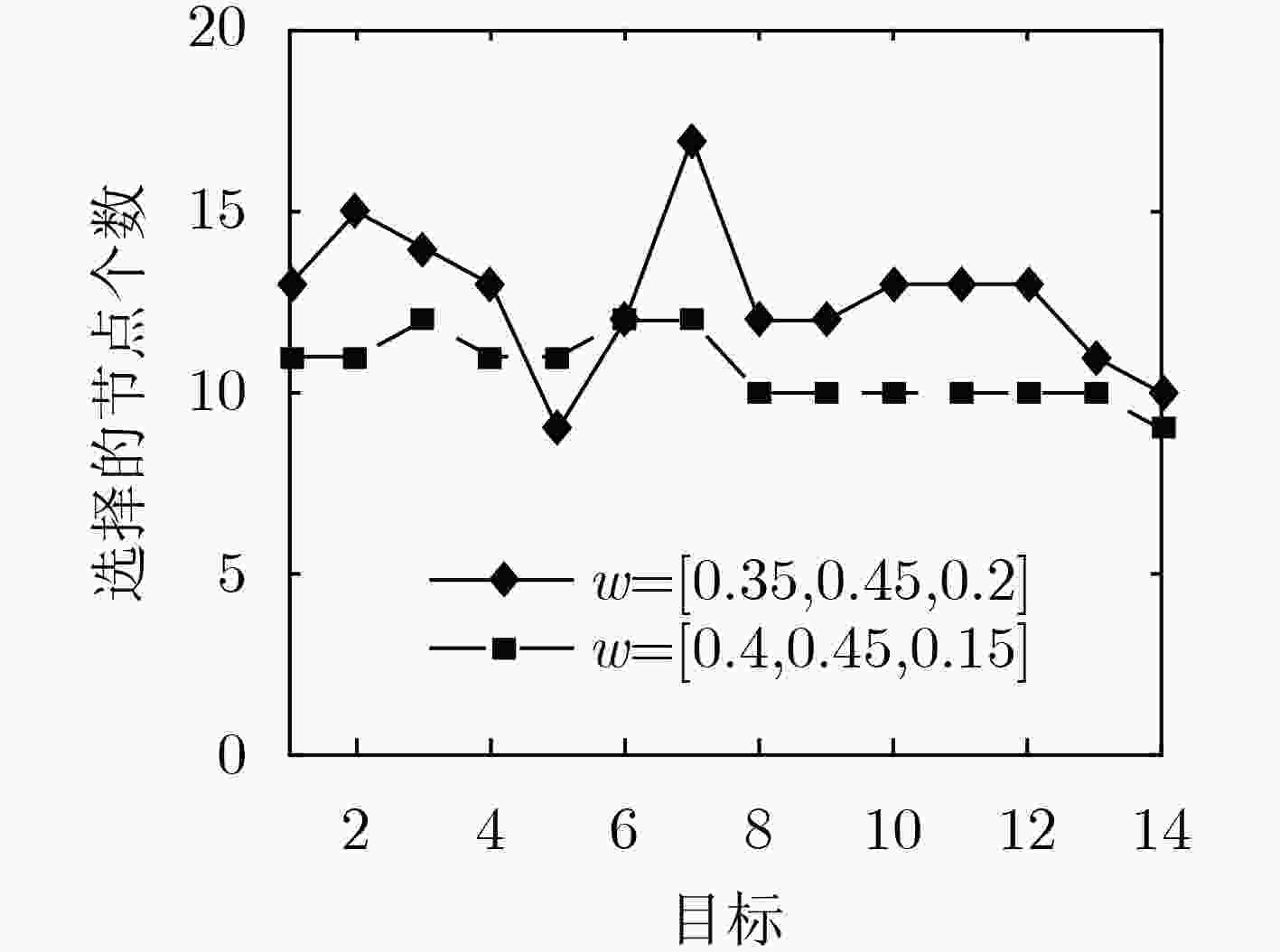
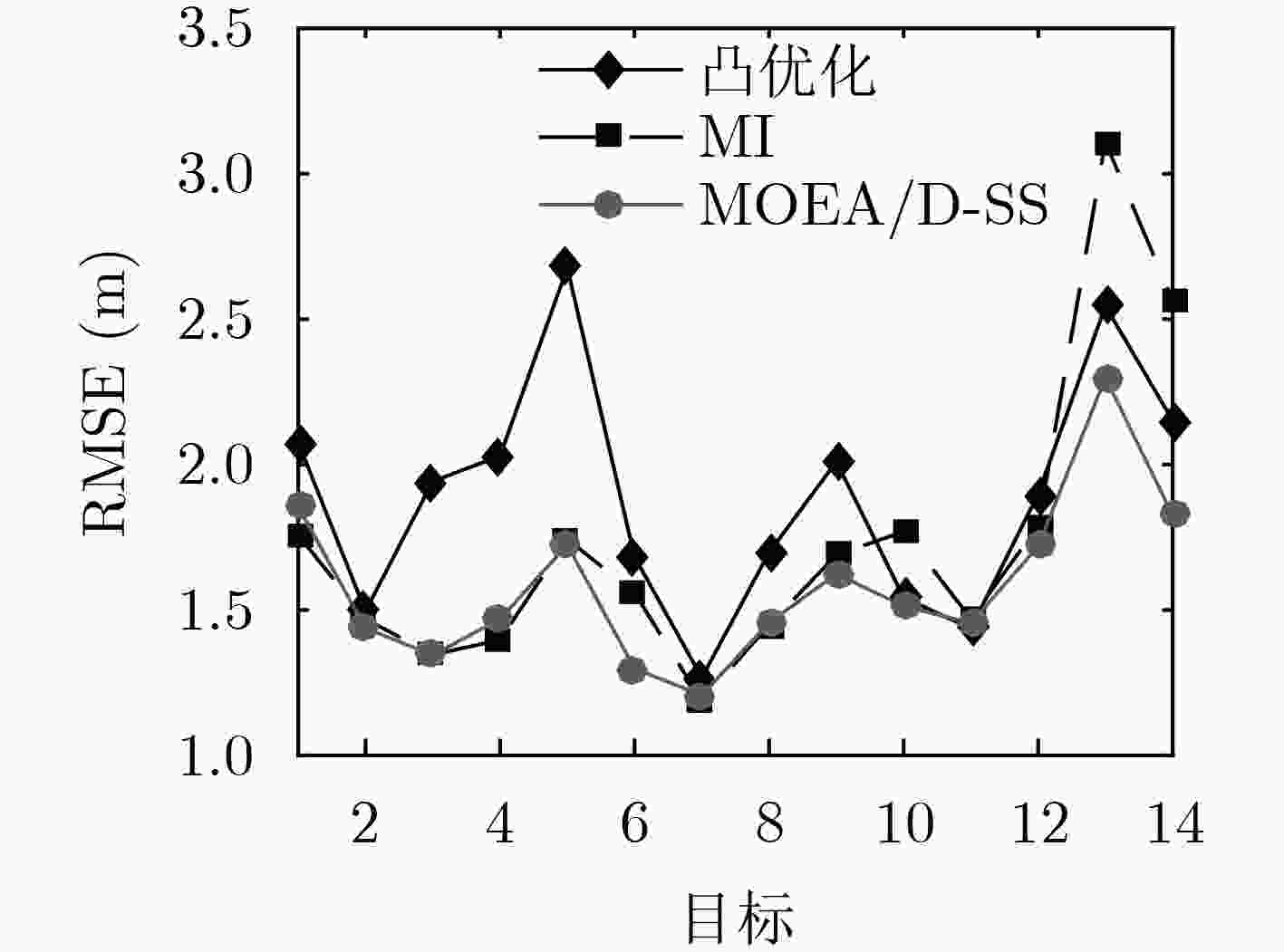
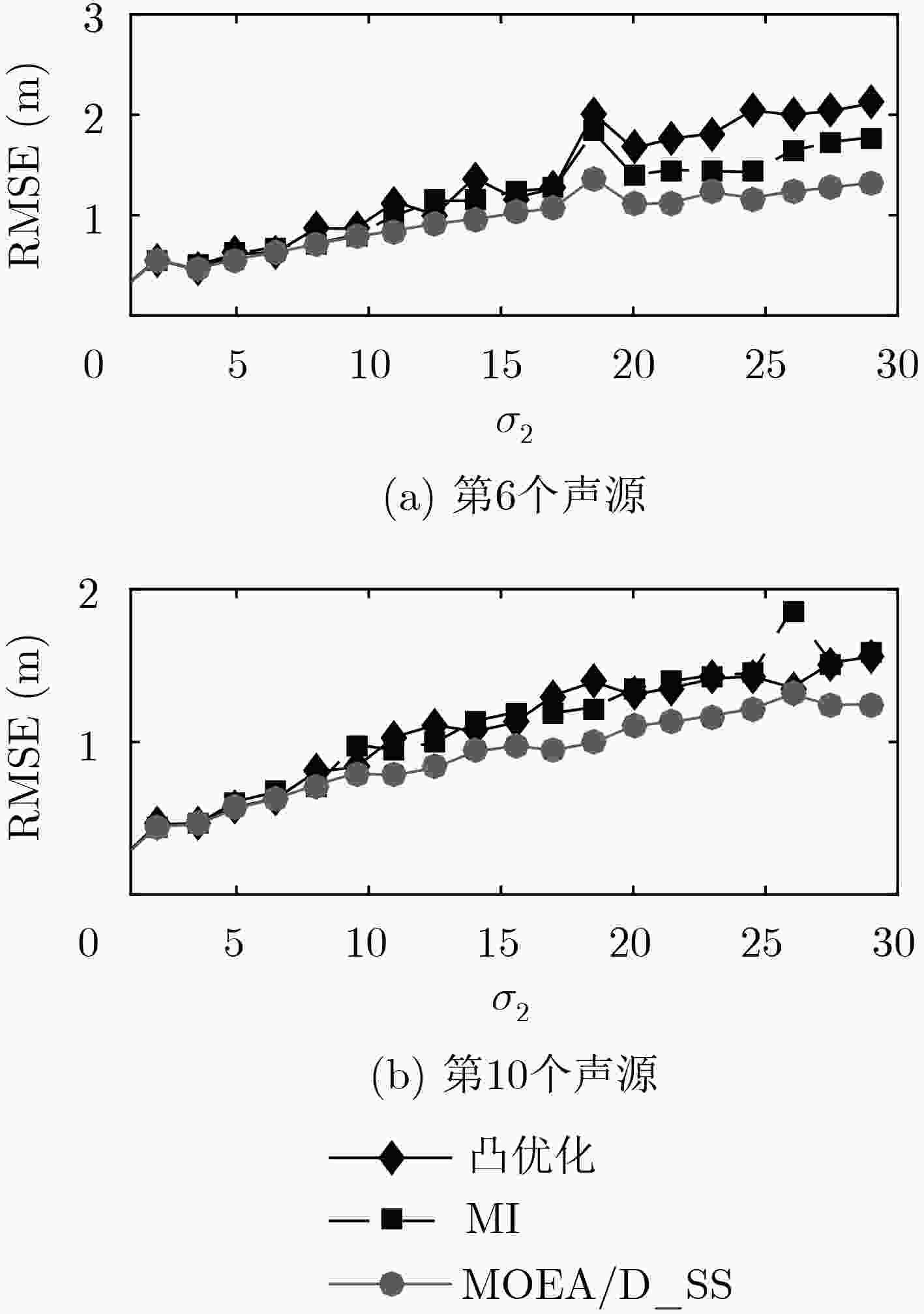
为解决非高斯噪声背景下,基于贝叶斯Fisher信息矩阵和基于互信息的节点选择不一致的问题,该文提出一种基于多目标优化的节点选择方法。推导出节点噪声为混合高斯分布时的贝叶斯Fisher信息矩阵和互信息,将节点个数、选择的节点对应的Fisher信息矩阵和互信息共同作为优化的目标函数。提出利用基于分解的多目标优化方法寻找Pareto最优解,并采用与理想解相似的偏好排序技术(TOPSIS)从所有Pareto最优解中选择最终的节点选择方案。仿真实验结果表明,基于多目标优化的节点选择方法选择的节点具有更优更稳健的定位精度。
Abstract:To overcome the flaw that the sensor selection methods based on either of Bayesian Fisher information matrix or mutual information could not provide coincident results, the multiple objective optimal technology is developed for sensor selection by minimizing the number of sensors, maximizing corresponding Bayesian Fisher information matrix and mutual information of the selected sensors. Then, the Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) approach is proposed to find the candidate that can better trade off the cost and two performance metrics. Comparison results demonstrate that the proposed method can find a better sensor group, and ultimately, its overall localization performance is more stable and accurate.
-
SALVATI D, DRIOLI C, and FORESTI G L. Exploiting CNNs for improving acoustic source localization in noisy and reverberant conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2018, 2(2): 103–116. doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2017.2775237 闫青丽, 陈建峰. 风场环境中声速修正的分布式声源定位算法[J]. 声学学报, 2017, 42(4): 421–426. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2017.04.005YAN Qingli and CHEN Jianfeng. Distributed sound source localization algorithm for sound velocity calibration in windy environment[J]. Acta Acustica, 2017, 42(4): 421–426. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2017.04.005 刘坤, 吴建新, 甄杰, 等. 基于阵列天线和稀疏贝叶斯学习的室内定位方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1158–1164. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190314LIU Kun, WU Jianxin, ZHEN Jie, et al. Indoor localization algorithm based on array antenna and sparse bayesian learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1158–1164. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190314 ERTIN E, FISHER J W, and POTTE L C. Maximum mutual information principle for dynamic sensor query problems[C]. The 2nd International Workshop on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Palo Alto, USA, 2003: 405–416. doi: 10.1007/3-540-36978-3_27. WANG Hanbiao, YAO K, and ESTRIN D. Information-theoretic approaches for sensor selection and placement in sensor networks for target localization and tracking[J]. Journal of Communications and Networks, 2005, 7(4): 438–449. doi: 10.1109/jcn.2005.6387986 ZHAO Feng, SHIN J, and REICH J. Information-driven dynamic sensor collaboration[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2002, 19(2): 61–72. doi: 10.1109/79.985685 KAPLAN L. Global node selection for localization in a distributed sensor network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 113–135. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1603409 KAPLAN L. Local node selection for localization in a distributed sensor network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 136–146. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1603410 CHEPURI S P and LEUS G. Sparsity-promoting sensor selection for non-linear measurement models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(3): 684–698. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2014.2379662 LIU Sijia, CHEPURI S P, FARDAD M, et al. Sensor selection for estimation with correlated measurement noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(13): 3509–3522. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2550005 郝本建, 王林林, 李赞, 等. 面向TDOA被动定位的定位节点选择方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(2): 213–219. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180293HAO Benjian, WANG Linlin, LI Zan, et al. Sensor selection method for TDOA passive localization[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(2): 213–219. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180293 YANG Mengna, JACKSON D R, CHEN Ji, et al. A TDOA localization method for nonline-of-sight scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2019, 67(4): 2666–2676. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2891403 NGUYEN N H, DOĞANÇAY K, and KURUOĞLU E E. An iteratively reweighted instrumental-variable estimator for robust 3-D AOA localization in impulsive noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(18): 4795–4808. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2931210 YAN Qingli, CHEN Jianfeng, OTTOY G, et al. Robust AOA based acoustic source localization method with unreliable measurements[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 152: 13–21. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.05.010 CAO Nianxia, CHOI S, MASAZADE E, et al. Sensor selection for target tracking in wireless sensor networks with uncertainty[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(20): 5191–5204. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2595500 ZHAO Yue, LI Zan, HAO Benjian, et al. Sensor selection for TDOA-based localization in wireless sensor networks with non-line-of-sight condition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(10): 9935–9950. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2936110 GIL P, MARTINS H, and JANUÁRIO F. Outliers detection methods in wireless sensor networks[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2019, 52(4): 2411–2436. doi: 10.1007/s10462-018-9618-2 ZHANG Jiangfan, WANG Xiaodong, BLUM R S, et al. Attack detection in sensor network target localization systems with quantized data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(8): 2070–2085. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2802459 ZHANG Qingfu and LI Hui. MOEA/D: A multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2007, 11(6): 712–731. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2007.892759 SHIH H S, SHYUR H J, and LEE E S. An extension of TOPSIS for group decision making[J]. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 2007, 45(7/8): 801–813. doi: 10.1016/j.mcm.2006.03.023 -





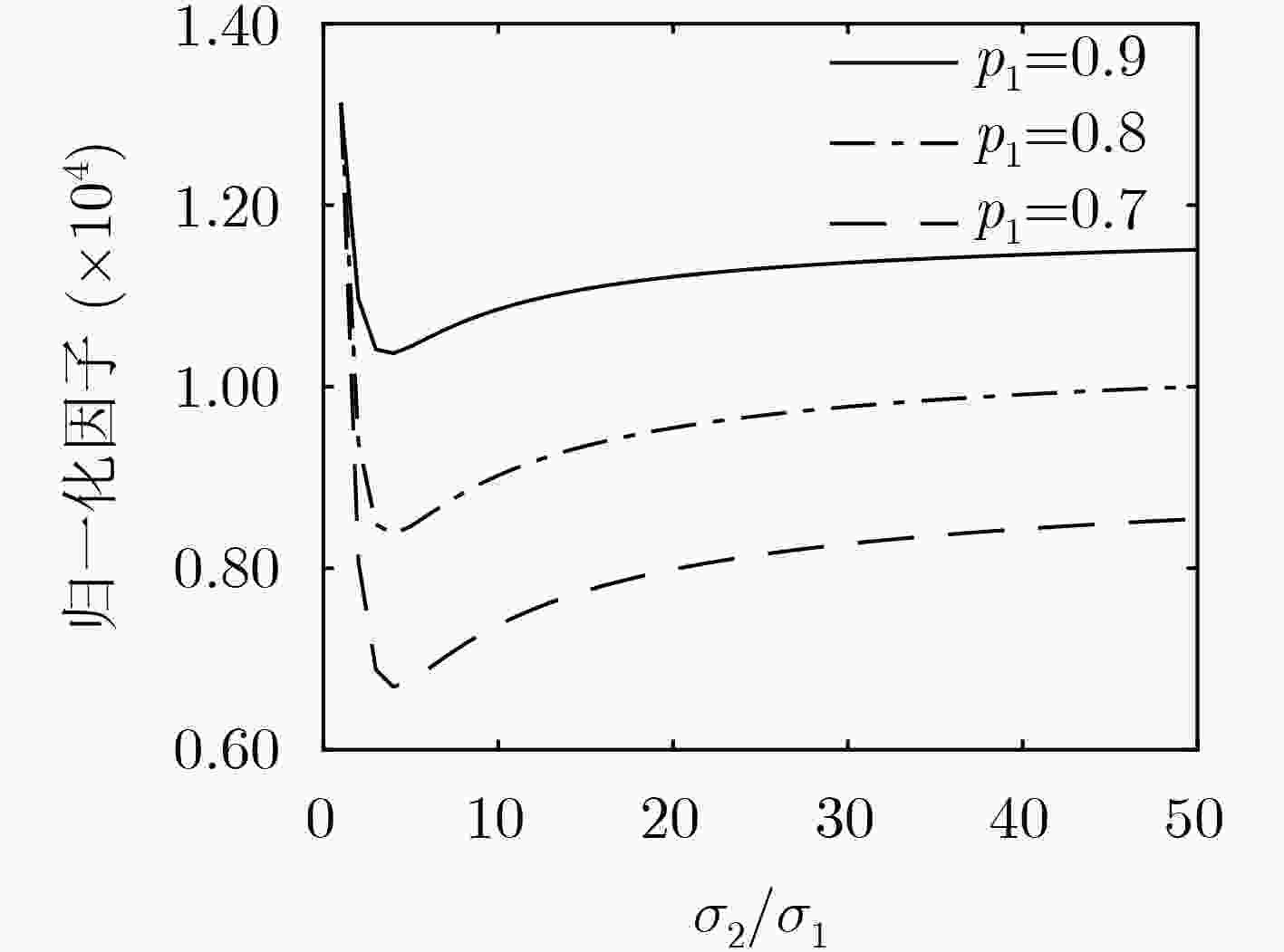

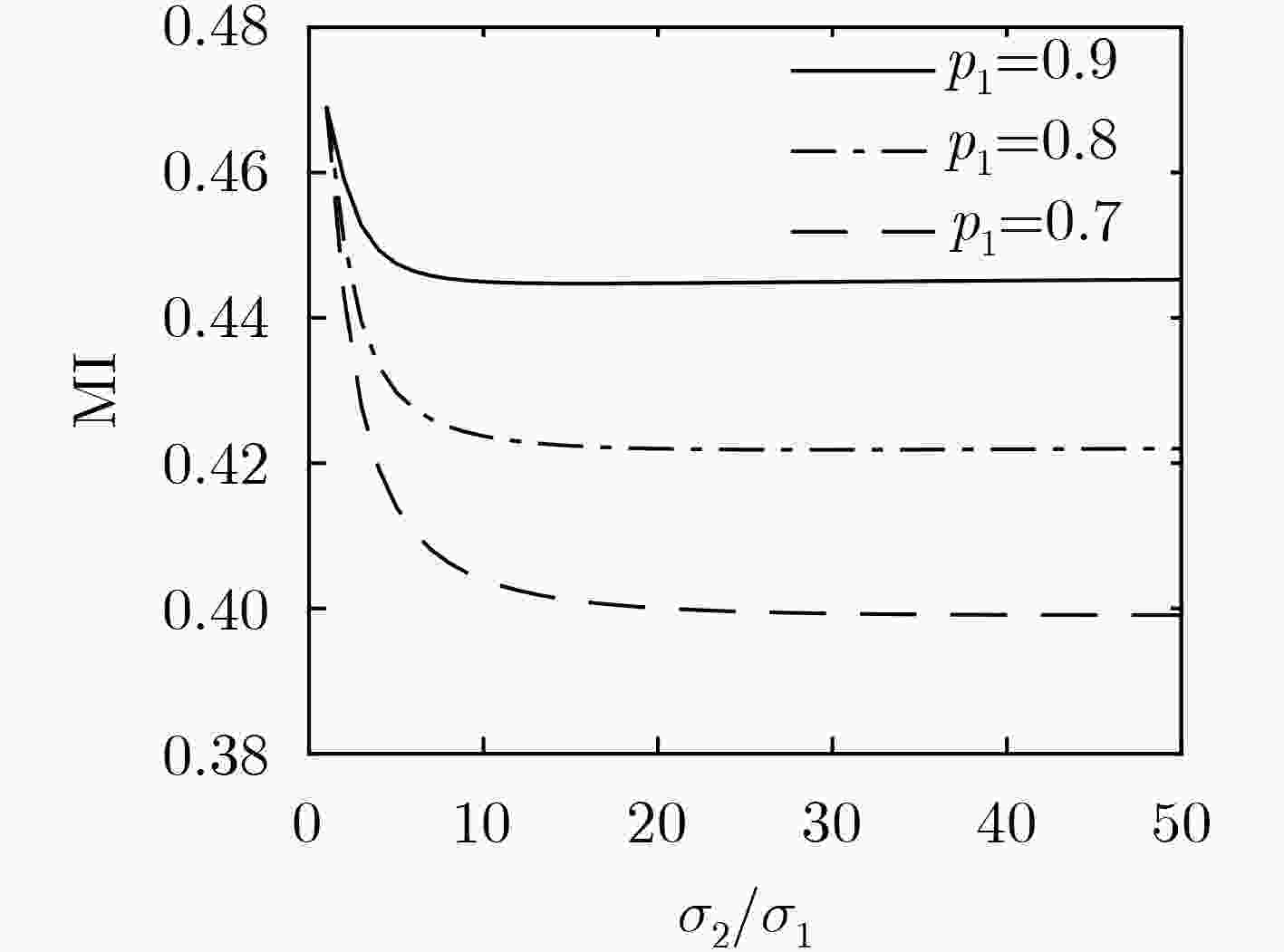
 下载:
下载:


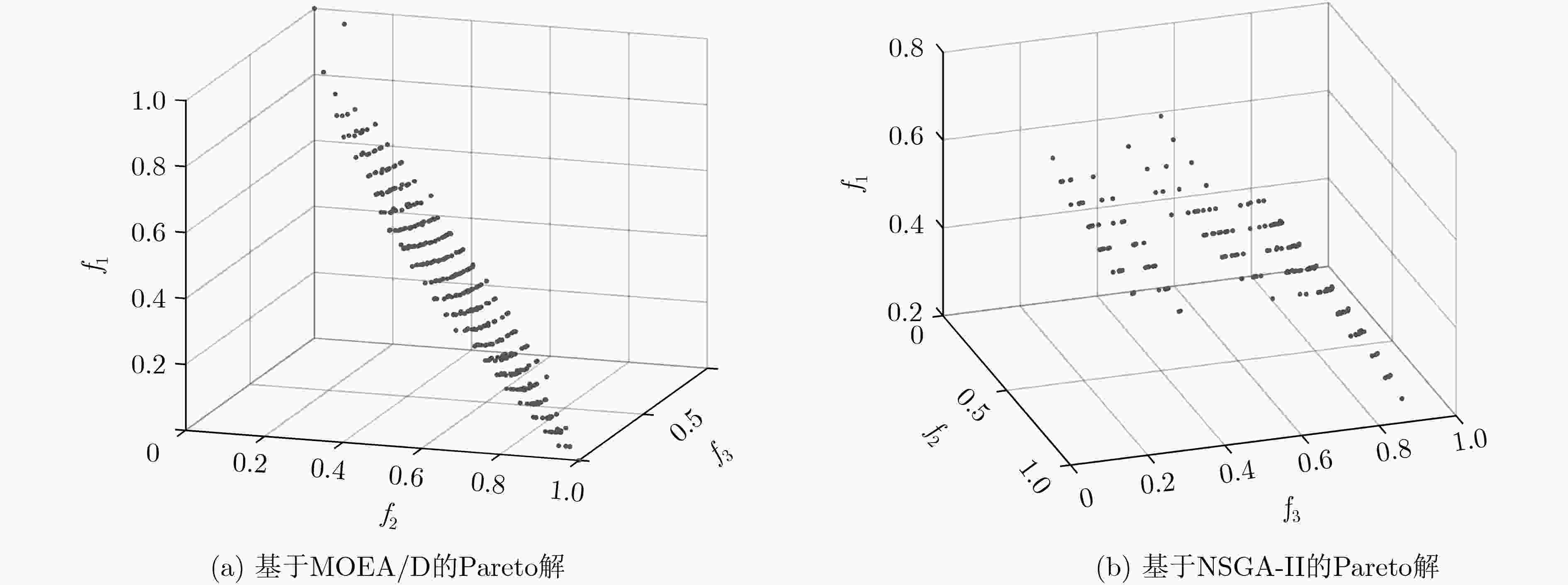
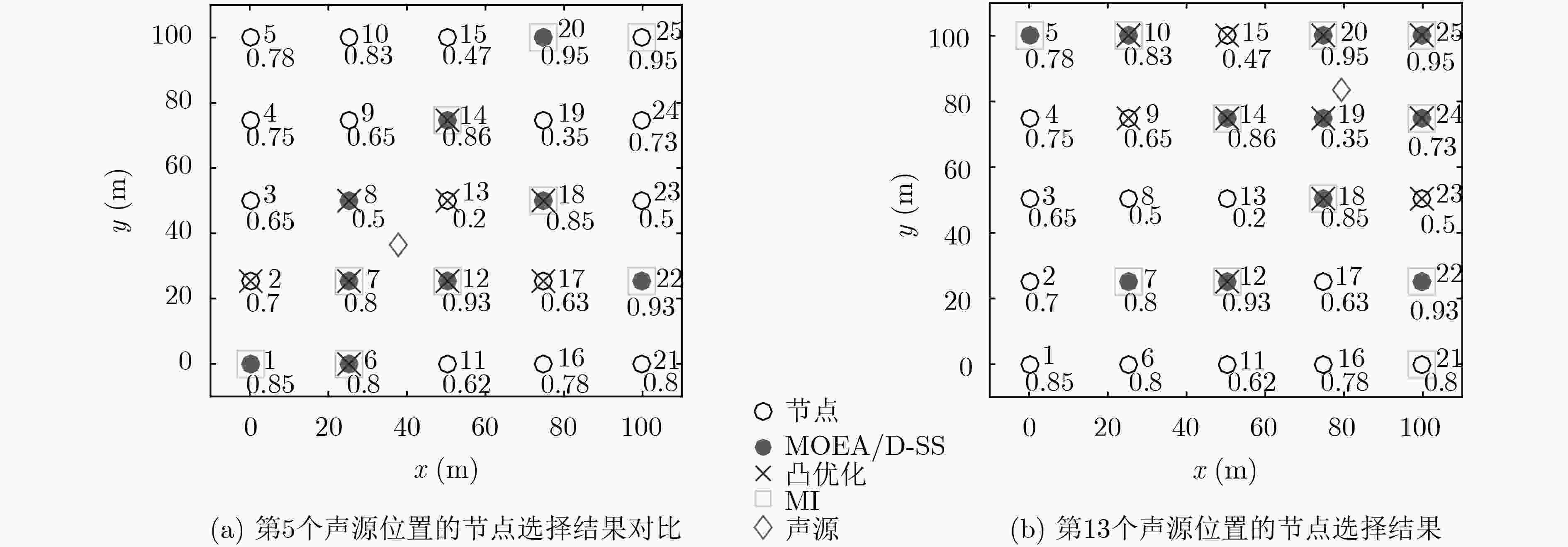



 下载:
下载:
