Universally Composable Two-Party Password-Based Authenticated Key Exchange from Ideal Lattices
-
摘要: 大部分现有基于格的两方口令认证密钥交换协议(2PAKE)都是在基于不可区分的公共参考串模型或Bellare-Pointcheval-Rogaway(BBR)模型下被证明安全的。该文提出一个基于环上带误差学习问题的两方口令认证密钥交换协议,并在通用可组合框架下证明其安全性。与同类协议相比,新协议具有更高的安全性和更高的效率。Abstract: Most of the existing two-party password-based Authenticated Key Exchange (2PAKE) protocols from lattices are proven secure using the indistinguishable common reference string model or the Bellare-Pointcheval-Rogaway model. This paper proposes a two-party password-based authenticated key exchange protocol based on the Ring Learning With Errors (RLWE) problem and proves its security under the Universally Composable (UC) framework. Compared with similar protocols, the new protocol achieves a higher level of security and efficiency.
-
表 1 UC框架不可区分性证明概览
游戏 模型 游戏 模拟器 挑战者 U1 U2 U3 U4 哈希与加解密 ${\rm{G}} 0$ 现实 真实 真实 真实 真实 真实 协议 ${\cal{A}}$ ${\rm{G}} 1$ 混合 真实 真实 真实 真实 模拟 ${\cal{H}}$ ${\cal{A}}$ ${\rm{G}} 2$ 混合 真实 真实 真实 真实 模拟 ${\cal{H}}$ ${\cal{A}}$ ${\rm{G}} 3$ 混合 真实 真实 真实 模拟 模拟 ${\cal{H}}$ ${\cal{A}}$ ${\rm{G}} 4$ 混合 模拟 真实 模拟 真实 模拟 ${\cal{H}}$ ${\cal{A}}$ ${\rm{G}} 5$ 混合 真实 真实 真实 模拟 模拟 ${\cal{H}}$ ${\cal{A}}$ ${\rm{G}} 6$ 混合 真实 模拟 真实 模拟 模拟 ${\cal{H}}$ ${\cal{A}}$ ${\rm{G}} 7$ 理想 模拟 模拟 模拟 模拟 模拟 ${\cal{S}}$ ${\cal{A}}$ 表 2 理想格上口令基2PAKE协议的性能比较
协议 通信开销 环运算次数 安全模型 难题假设 误差调和 RLWE-PAK $2n\;{\log _2}\;q + n$ 4 BPR模型 RLWE Ding式REC RLWE-SRP $2n\;{\log _2}\;q + n$ 5 UC模型 RLWE Ding式REC 本文协议 $2n\;{\log _2}\;q + n$ 4 UC模型 RLWE Peikert式REC -
[1] SHOR P W. Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer[J]. SIAM Review, 1999, 41(2): 303–332. doi: 10.1137/S0036144598347011 [2] HALLGREN S. Fast quantum algorithms for computing the unit group and class group of a number field[C]. The Thirty-Seventh Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Baltimore, USA, 2005: 468–474. doi: 10.1145/1060590.1060660. [3] KATZ J and VAIKUNTANATHAN V. Smooth projective hashing and password-based authenticated key exchange from lattices[C]. The 15th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security: Advances in Cryptology, Tokyo, Japan, 2009: 636–652. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-10366-7_37. [4] JIANG Shaoquan and GONG Guang. Password based key exchange with mutual authentication[C]. The 11th International Workshop on Selected Areas in Cryptography, Waterloo, Canada, 2004: 267–279. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-30564-4_19. [5] DING Yi and FAN Lei. Efficient password-based authenticated key exchange from lattices[C]. The 2011 Seventh International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, Sanya, China, 2011: 934–938. doi: 10.1109/CIS.2011.210. [6] ZHANG Jiang and YU Yu. Two-round PAKE from approximate SPH and instantiations from lattices[C]. The 23rd International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Hong Kong, China, 2017: 37–67. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-70700-6_2. [7] DING Jintai, ALSAYIGH S, LANCRENON J, et al. Provably secure password authenticated key exchange based on RLWE for the post-quantum world[C]. The Cryptographers’ Track at the RSA Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 183–204. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-52153-4_11. [8] LI Zengpeng and WANG Ding. Two-round PAKE protocol over lattices without NIZK[C]. The 14th International Conference on Information Security and Cryptology, Fuzhou, China, 2019: 138–159. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-14234-6_8. [9] KARBASI A H, ATANI R E, and ATANI S E. A new ring-based SPHF and PAKE protocol on ideal lattices[J]. ISeCure, 2019, 11(1): 1–11. doi: 10.22042/ISECURE.2018.109810.398 [10] BELLARE M, POINTCHEVAL D, and ROGAWAY P. Authenticated key exchange secure against dictionary attacks[C]. International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptographic Techniques, Bruges, Belgium, 2000: 139–155. doi: 10.1007/3-540-45539-6_11. [11] CANETTI R, HALEVI S, KATZ J, et al. Universally composable password-based key exchange[C]. The 24th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Aarhus, Denmark, 2005: 404–421. doi: 10.1007/11426639_24. [12] GAO Xinwei, DING Jintai, LIU Jiqiang, et al. Post-quantum secure remote password protocol from RLWE problem[C]. The 13th International Conference on Information Security and Cryptology, Xi'an, China, 2018: 99–116. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-75160-3_8. [13] WU T. The secure remote password protocol[C]. The 1998 Internet Society Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, San Diego, USA, 1998: 97–111. [14] DING Jintai, XIE Xiang, and LIN Xiaodong. A simple provably secure key exchange scheme based on the learning with errors problem[R]. Cryptology ePrint Archive: Report 2012/688, 2012. [15] PEIKERT C. Lattice cryptography for the internet[C]. The 6th International Workshop on Post-Quantum Cryptography, Waterloo, Canada, 2014: 197–219. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-11659-4_12. [16] ABDALLA M, CATALANO D, CHEVALIER C, et al. Efficient two-party password-based key exchange protocols in the UC framework[C]. The Cryptographers’ Track at the RSA Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2008: 335–351. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-79263-5_22. [17] LYUBASHEVSKY V, PEIKERT C, and REGEV O. On ideal lattices and learning with errors over rings[C]. The 29th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, French Riviera, French, 2010: 1–23. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-13190-5_1. [18] 张洋, 刘仁章, 林东岱. 理想格上格基的快速三角化算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 98–104. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190725ZHANG Yang, LIU Renzhang, and LIN Dongdai. Fast triangularization of ideal latttice basis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 98–104. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190725 [19] CANETTI R and RABIN T. Universal composition with joint state[C]. The 23rd Annual International Cryptology Conference on Advances in Cryptology, Santa Barbara, USA, 2003: 265–281. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-45146-4_16. [20] HOFHEINZ D and MÜLLER-QUADE J. Universally composable commitments using random oracles[C]. First Theory of Cryptography Conference on Theory of Cryptography, Cambridge, USA, 2004: 58–76. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-24638-1_4. [21] LISKOV M, RIVEST R L, and WAGNER D. Tweakable block ciphers[C]. The 22nd Annual International Cryptology Conference on Advances in Cryptology, Santa Barbara, USA, 2002: 31–46. doi: 10.1007/3-540-45708-9_3. -





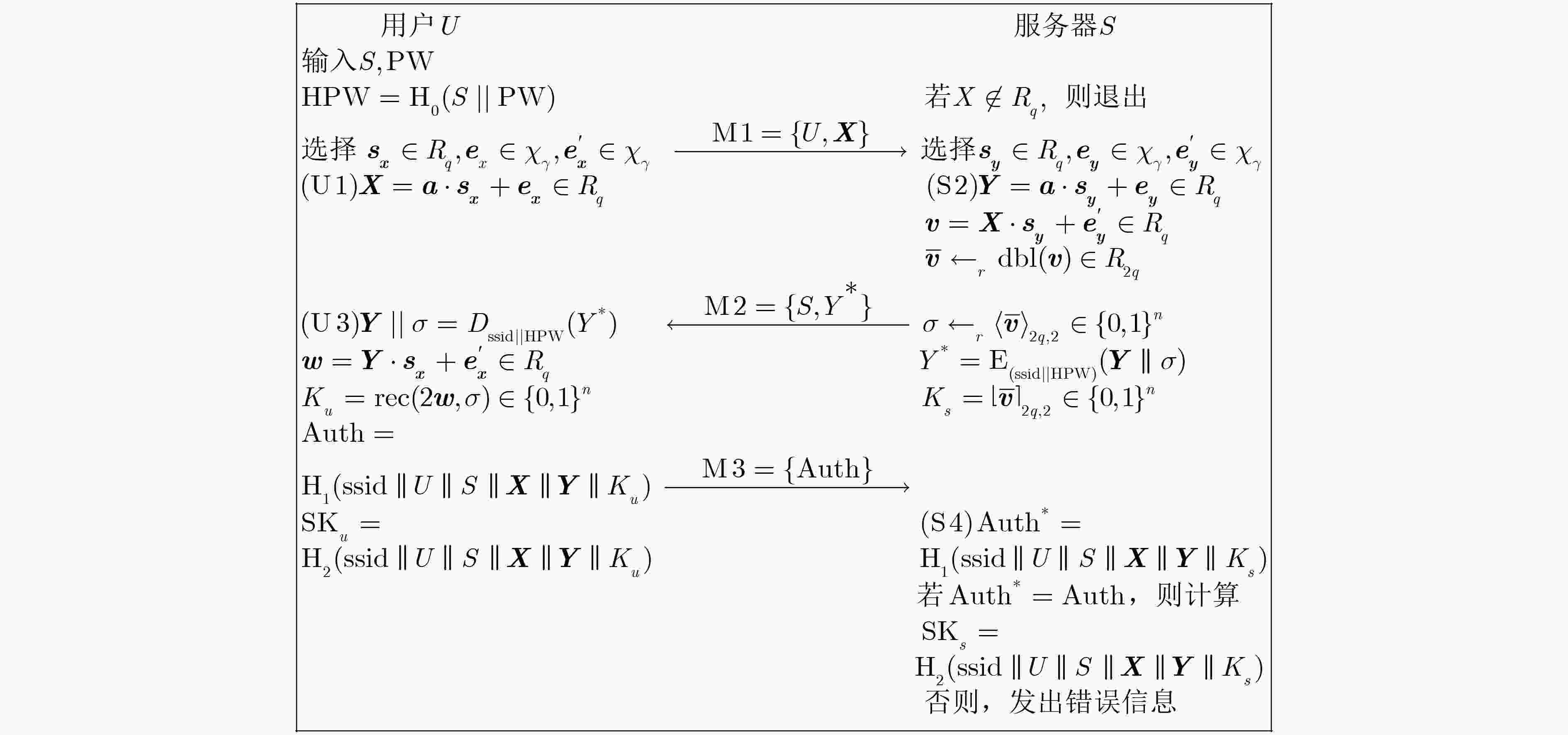
 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
