Two-segment Continuous Alignment and Error Analysis Method Based on Dual Antenna Assistance
-
摘要:
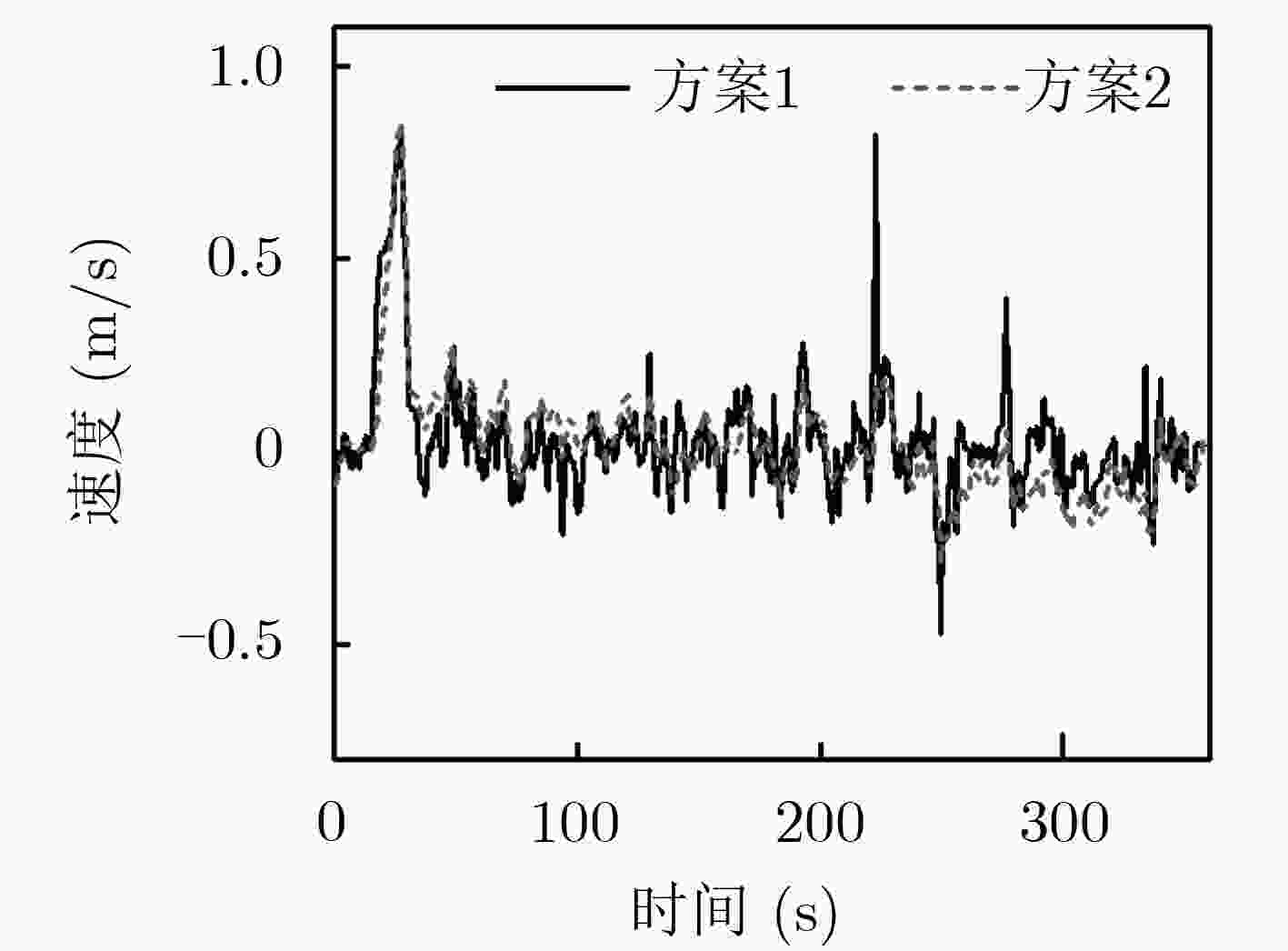
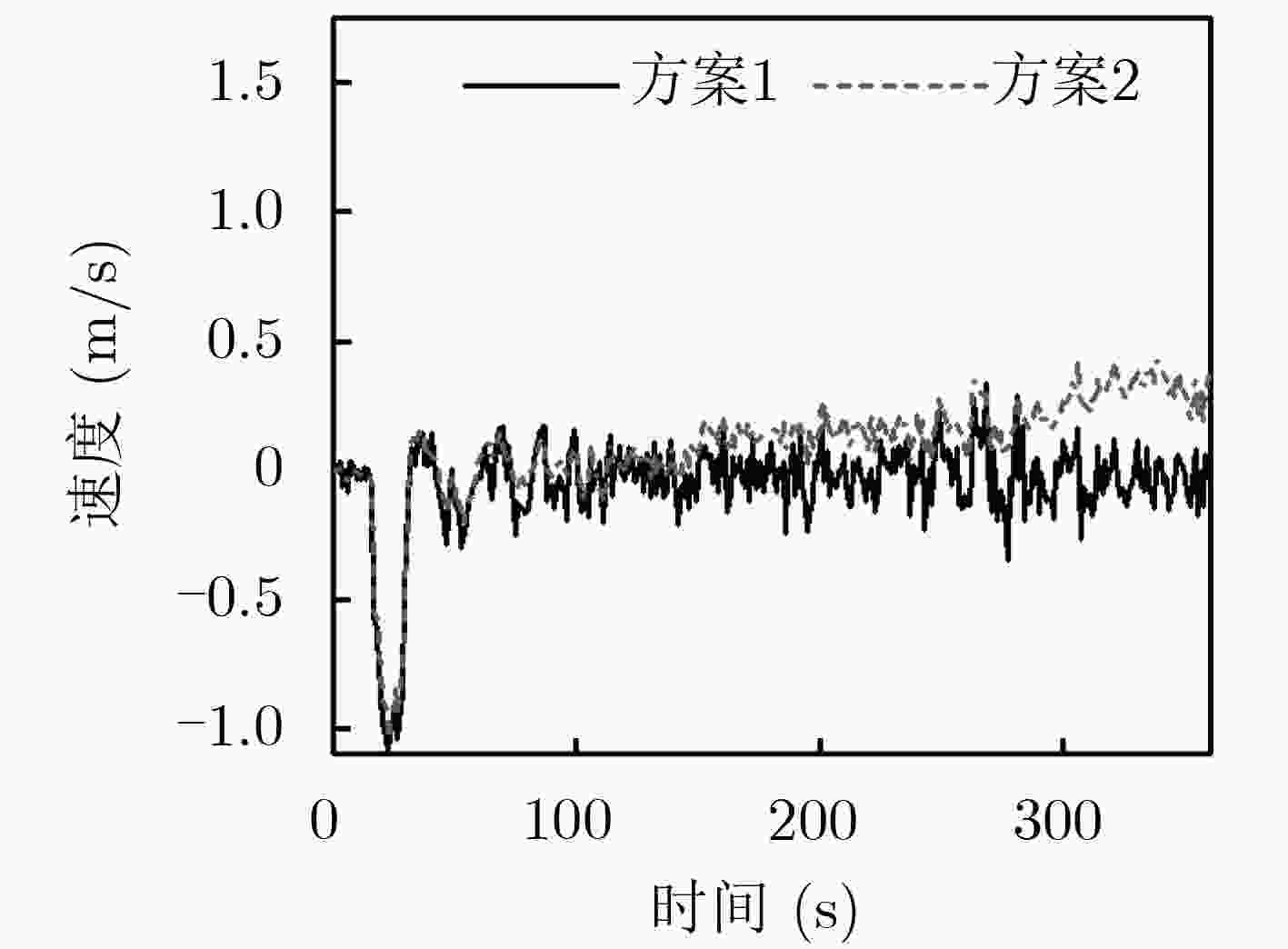
针对低精度微惯性测量单元/全球导航卫星系统 (IMU/GNSS)松组合导航系统中初始方位难以精确得到和行进间航向容易发散的问题,该文设计了一种双天线辅助的两段连续式对准方法。首先分析了初始方位误差对航向精度的影响;其次,由于GNSS测向系统精度高、无姿态漂移误差的特点,基于双天线基线矢量推导了一种最小二乘算法的测姿模型,进行初始对准;最后针对行进间对准,研究扩展了基于航向差值的1维量测以抑制航向发散。设计试验探讨了双天线基线矢量对初始对准与行进间航向精度的影响,改进方法可以使得初始方位误差优于0.7°,行进间航向能够更准确地被跟踪。针对目标的初始对准与行进间对准,双天线可提供辅助信息,其效果优于单天线IMU/GNSS的组合,且方法计算量适中。
Abstract:Considering the problem that it is difficult to obtain the initial position accurately in the low-precision Inertial Measurement Unit/Global Navigation Satellite System (IMU/GNSS) loose integrated navigation system and the course divergence is easy to travel. A two-segment continuous alignment method assisted by dual antennas is designed. Firstly, the influence of initial bearing error on heading accuracy is analyzed. Secondly, due to the characteristics of high accuracy and poor dynamic response of the GNSS direction-finding system, a least-squares attitude estimation model is derived based on the dual-antenna baseline vector for initial alignment. Finally, for the alignment between travels, the research extendes the one-dimensional measurement based on the heading difference to suppress the heading error. The design experiment explores the influence of the dual antenna baseline vector on the initial alignment and the heading accuracy between travels. The improved method can make the initial azimuth error better than 0.7°. At the same time, the heading angle between travels can be tracked more accurately. For the initial alignment of the target and the alignment between the traveling, the dual antenna can provide auxiliary information, its effect is better than the single antenna IMU/GNSS combination, and the method calculation is moderate.
-
Key words:
- Dual antenna /
- Alignment /
- Baseline
-
表 1 仿真方位误差
序号 仿真条件 陀螺漂移0°/h,加表漂移200 μg 陀螺漂移0.05°/h,加表漂移200 μg 初始方位误差 50 s 100 s 50 s 100 s 1 0° –0.0259 –0.0132 0.1852 0.1744 2 1° –0.0456 –0.0164 0.1896 0.1801 3 2° –0.0459 –0.0221 0.2106 0.2087 4 3° 0.0536 –0.0049 0.2235 0.2151 5 4° 0.0566 0.0549 0.2446 0.2158 6 5° 0.0928 0.0643 0.2710 0.2502 表 2 不同基线的航向、俯仰误差与标差对比
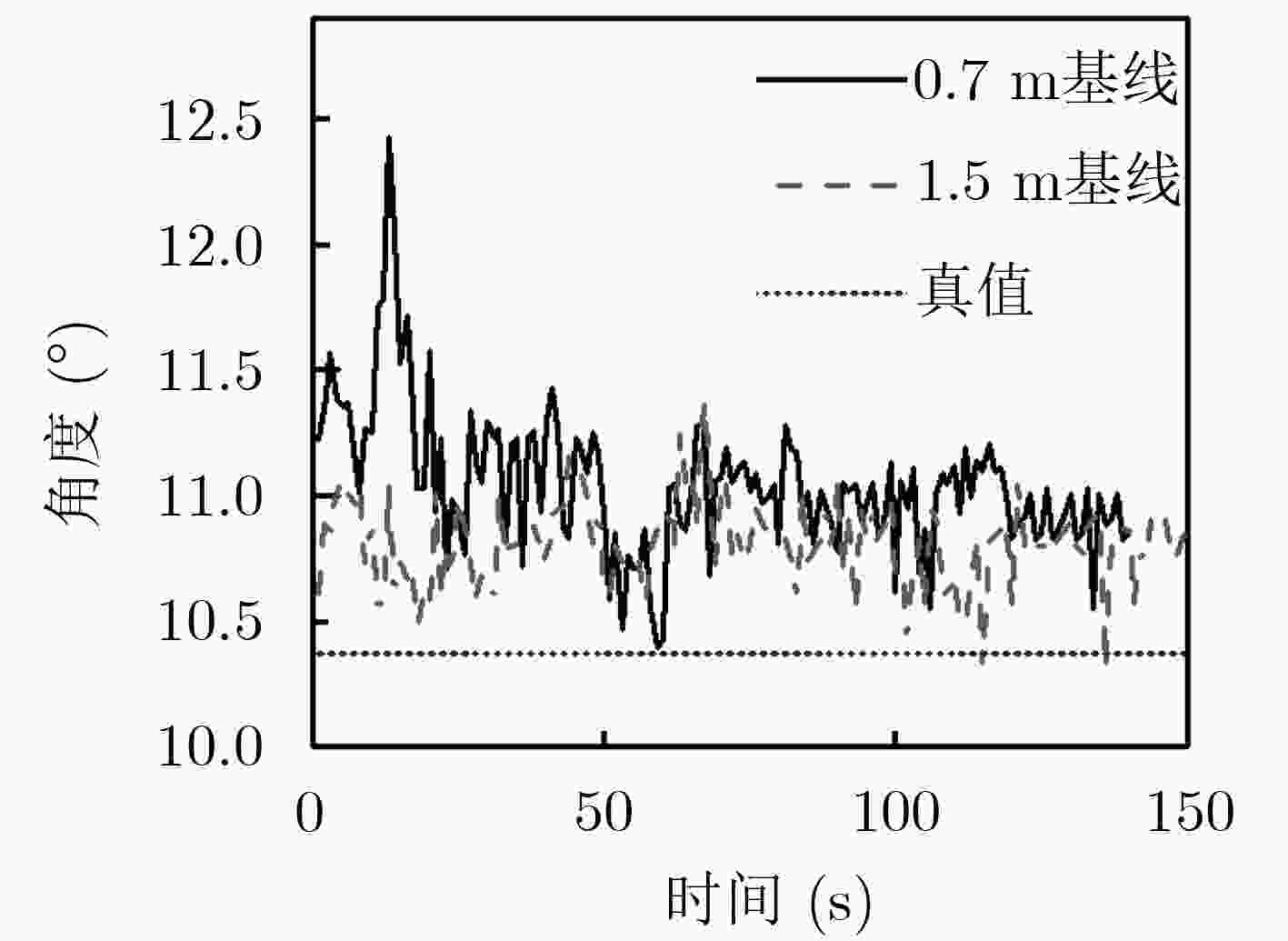
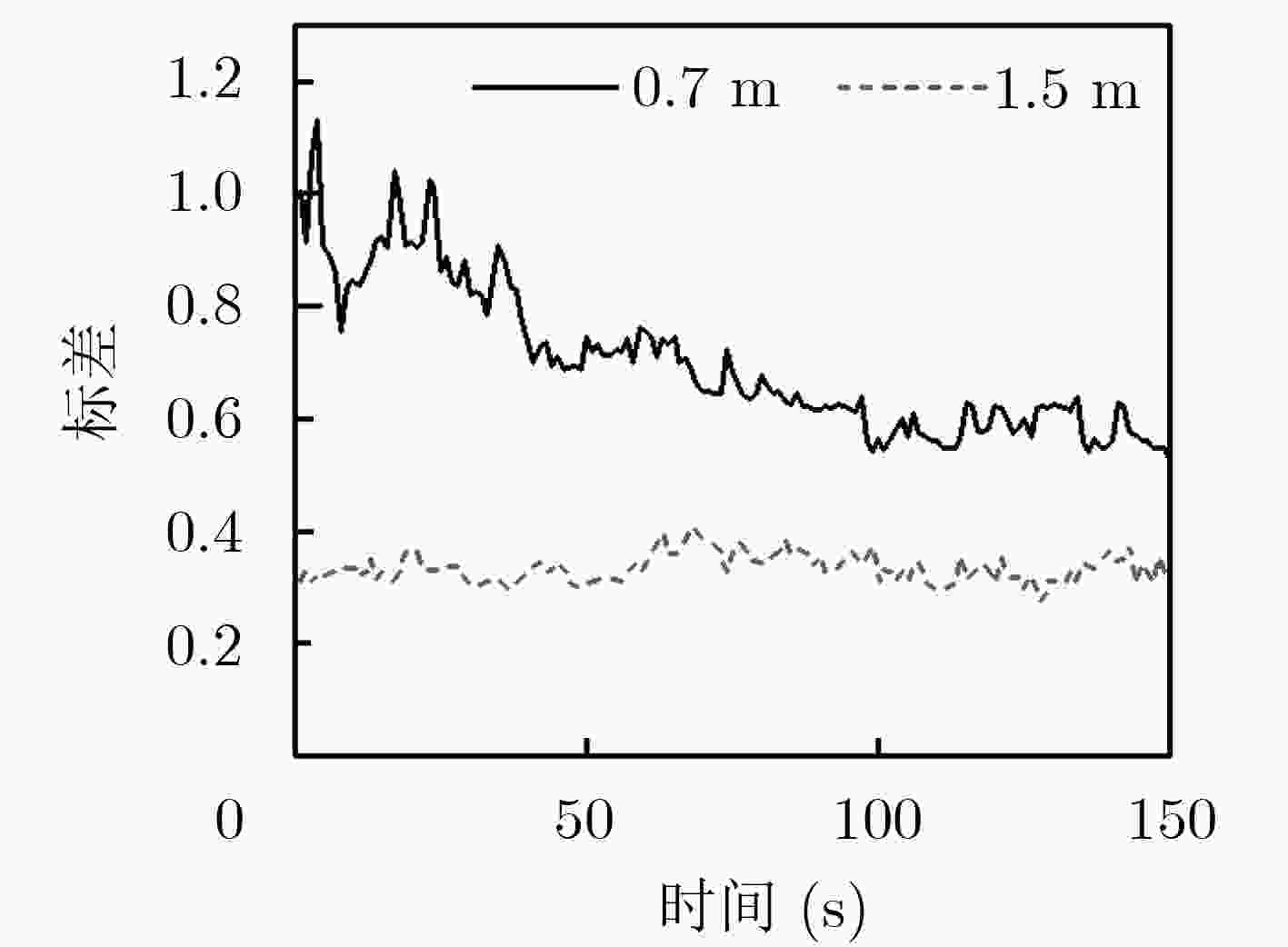
序号 单位(°) 单位(m) 航向(均值) 航向误差 俯仰(均值) 俯仰误差 航向标差 俯仰标差 基线长度 1 12.7585 2.3973 –1.9938 0.6634 0.6986 1.3569 0.3 2 11.6900 1.3188 –0.4225 0.8879 0.5072 1.2269 0.5 3 10.9793 0.6081 –0.2156 1.1148 0.3144 0.7169 0.7 4 12.5680 2.1968 –0.1551 1.1753 0.2661 0.5105 0.9 5 12.6673 2.2961 –0.5753 0.7551 0.2333 0.4548 1.1 6 11.7562 1.383 –0.3468 0.9836 0.1757 0.3178 1.3 7 10.8113 0.4401 –0.2260 1.1044 0.1601 0.3331 1.5 8 12.0038 1.6326 –0.2109 1.1195 0.1555 0.3028 1.7 表 3 航向、速度的误差均值与RMS
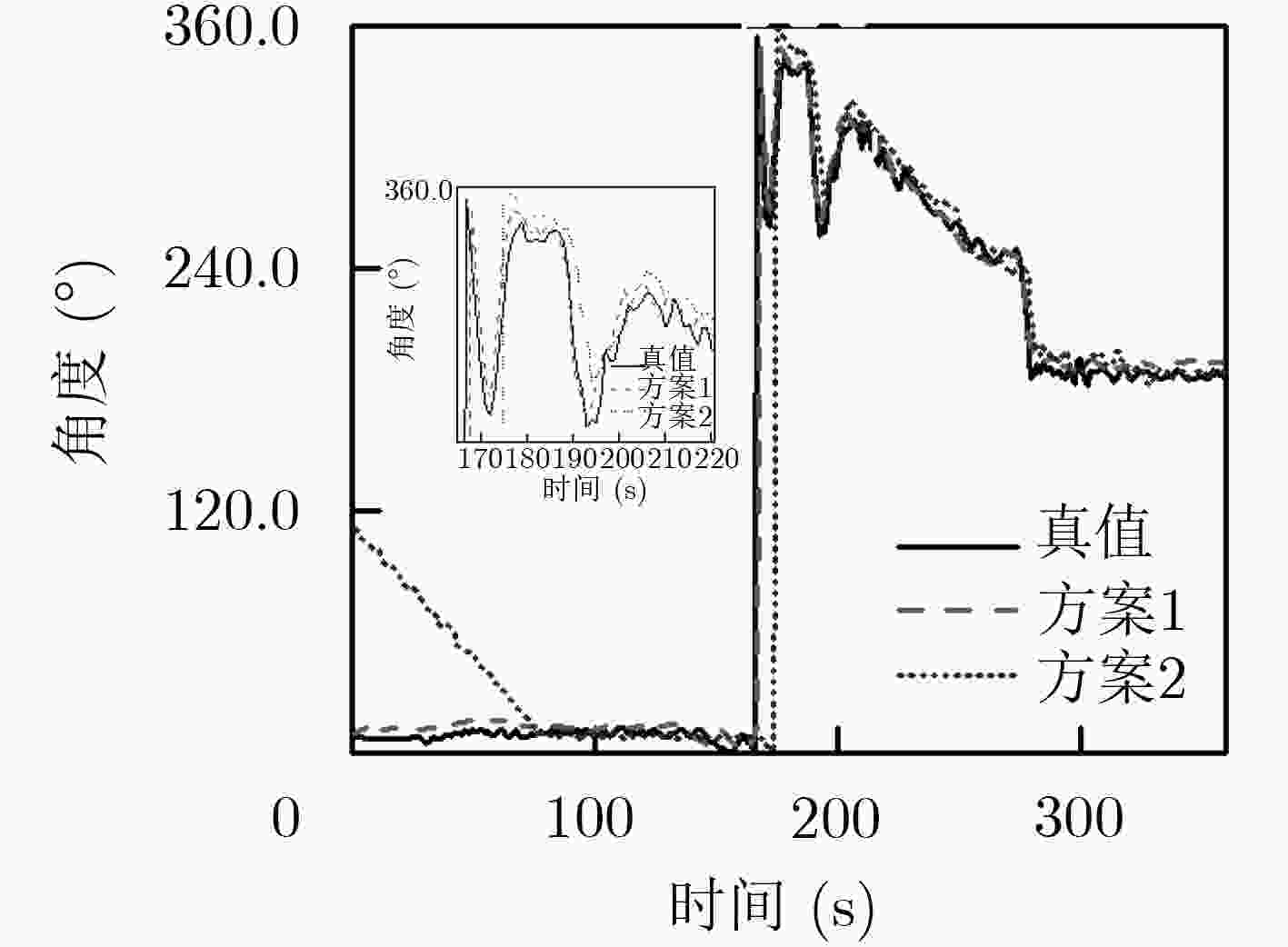
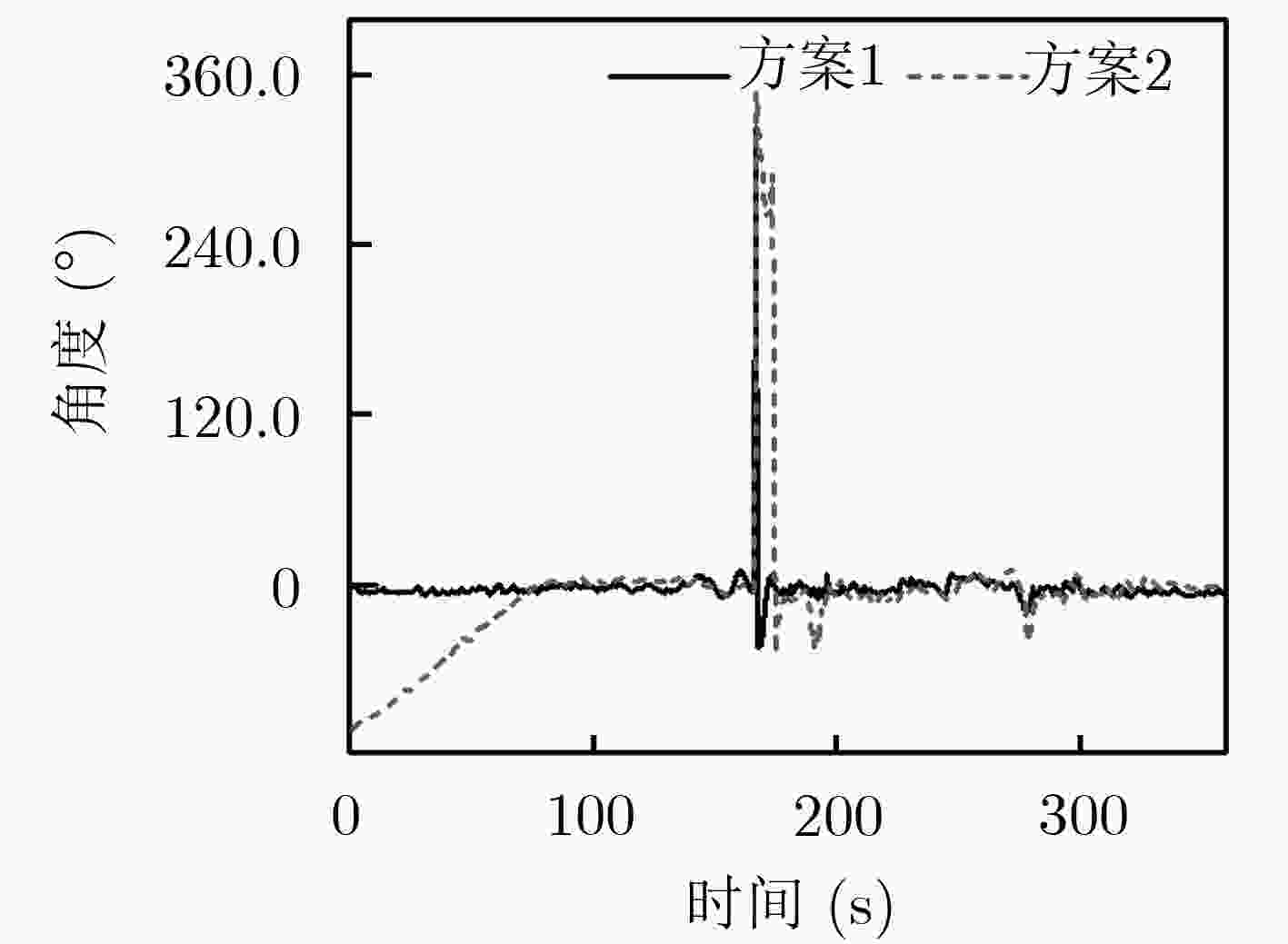
方法 航向(°) 东向速度(m/s) 北向速度(m/s) 误差均值 改进前 21.3608 0.1874 0.1123 改进后 5.5263 0.1103 0.0982 RMS 改进前 50.0653 0.3035 0.1691 改进后 17.3301 0.2495 0.1468 -
李杨, 孙伟强, 王兴岭, 等. 空间不一致在动态对准中影响分析及补偿方法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2018, 26(5): 567–570. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2018.05.002LI Yang, SUN Weiqiang, WANG Xingling, et al. Influence of space inconsistencyon in-motion alignment and compensation method for large ship[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2018, 26(5): 567–570. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2018.05.002 HAO Yushi, XU Aigong, SUI Xin, et al. A modified extended Kalman filter for a two-antenna GPS/INS vehicular navigation system[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(11): 3809. doi: 10.3390/s18113809 ISMAIL M and ABDELKAWY E. A hybrid error modeling for MEMS IMU in integrated GPS/INS navigation system[J]. The Journal of Global Positioning Systems, 2018, 16(1): 6. doi: 10.1186/s41445-018-0016-5 KHALAF W, CHOUAIB I, and WAINAKH M. Novel adaptive UKF for tightly-coupled INS/GPS integration with experimental validation on an UAV[J]. Gyroscopy and Navigation, 2017, 8(4): 259–269. doi: 10.1134/S2075108717040083 陈光武, 程鉴皓, 杨菊花, 等. 基于改进神经网络增强自适应UKF的组合导航系统[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1766–1773. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181171CHEN Guangwu, CHENG Jianhao, YANG Juhua, et al. Improved neural network enhanced navigation system of adaptive UKF[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1766–1773. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181171 庞春雷, 赵修斌, 余永林, 等. 低精度SINS初始对准/GPS双天线测向互辅算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 41(6): 167–173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2014.06.028PANG Chunlei, ZHAO Xiubin, YU Yonglin, et al. Interact arithmetic of low-accuracy SINS’initial alignment and GPS orientation measurement with two antennas[J]. Journal of Xidian University:Natural Science, 2014, 41(6): 167–173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2014.06.028 张方照, 柴艳菊, 柴华, 等. 两种多天线GNSS定姿方法的精度分析[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2016, 24(1): 30–35. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2016.01.007ZHANG Fangzhao, CHAI Yanju, CHAI Hua, et al. Analysis on precision of two attitude determination methods using GNSS multi-antenna data[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2016, 24(1): 30–35. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2016.01.007 蔡体菁, 陈仁, 王鑫, 等. 北斗短基线双天线旋转快速定向方法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2018, 26(3): 305–309. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2018.03.005CAI Tijing, CHEN Ren, WANG Xin, et al. Fast orientation method by BeiDou short baseline dual-antennas rotation[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2018, 26(3): 305–309. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2018.03.005 LI Wanli, TANG Kanghua, LU Liangqing, et al. Optimization-based INS in-motion alignment approach for underwater vehicles[J]. Optik, 2013, 124(20): 4581–4585. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2013.01.069 KANG Taizhong, FANG Jiancheng, and WANG Wei. Quaternion-optimization-based in-flight alignment approach for airborne POS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2012, 61(11): 2916–2923. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2012.2202989 EMEL’YANTSEV G I, STEPANOV A P, and BLAZHNOV B A. Attitude determination by INS/GNSS system aided by phase and magnetometer measurements for spinning vehicles[J]. Gyroscopy and Navigation, 2014, 5(4): 205–212. doi: 10.1134/S207510871404004X 周广涛, 王晴晴, 高远. 基于ZIHR航向角修正方法的行人导航算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(1): 170–177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.01.24ZHOU Guangtao, WANG Qingqing, and GAO Yuan. Pedestrian navigation algorithm based on ZIHR heading angle correction method[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(1): 170–177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.01.24 何东旭, 葛磊, 张鑫, 等. 罗经方位对准的收敛时间分析[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2019, 14(5): 159–166. doi: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.01522HE Dongxu, GE Lei, ZHANG Xin, et al. Analysis on convergence time of gyrocompass azimuth alignment[J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2019, 14(5): 159–166. doi: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.01522 李杰, 杨雁宇, 冯凯强, 等. 一种融合互补滤波和卡尔曼滤波高精度姿态测量算法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2018, 26(1): 51–55, 86. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2018.01.009LI Jie, YANG Yanyu, FENG Kaiqiang, et al. High-precision attitude measurement algorithm based on complementary filtering and Kalman filtering[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2018, 26(1): 51–55, 86. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2018.01.009 -





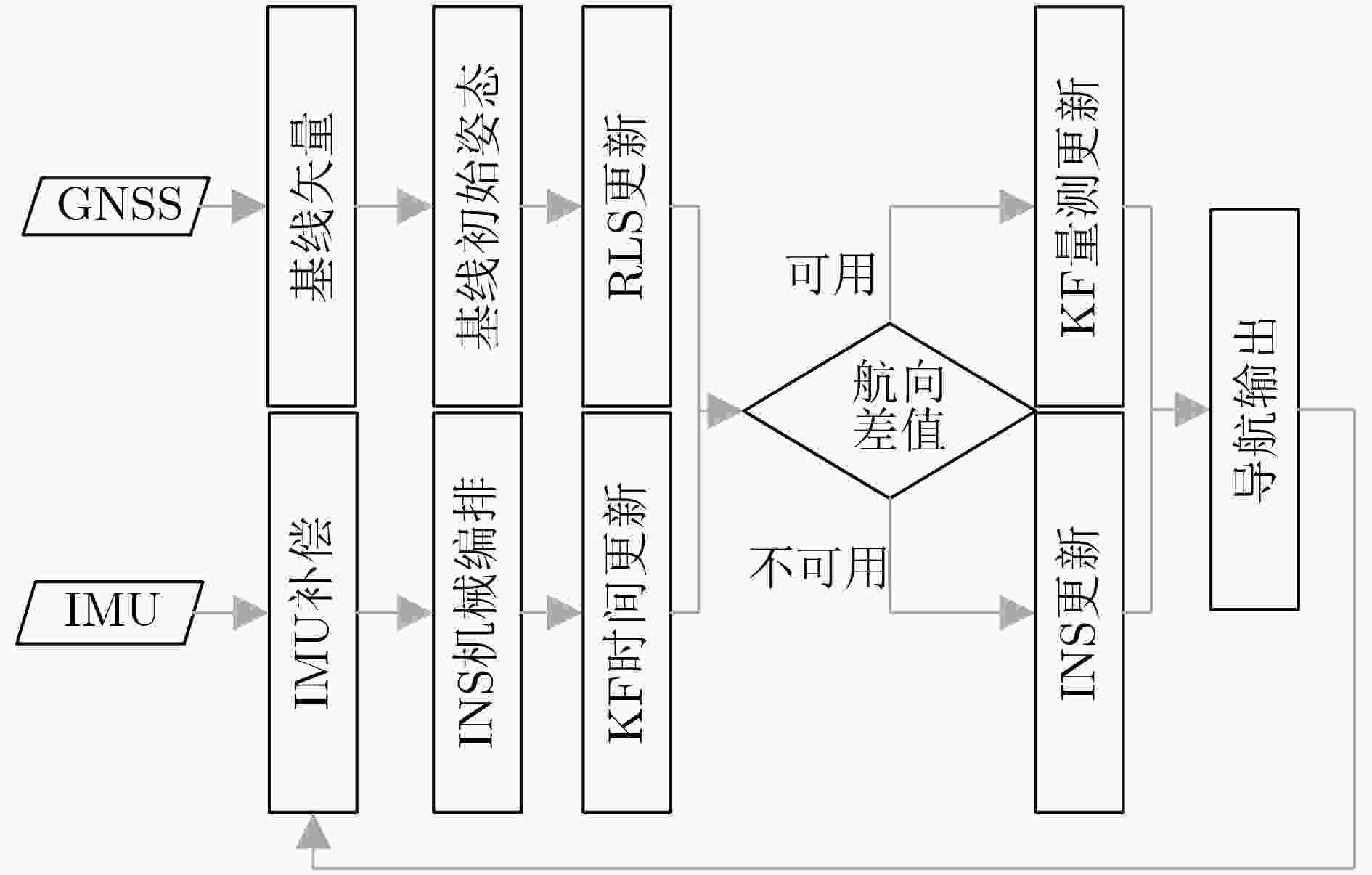
 下载:
下载:
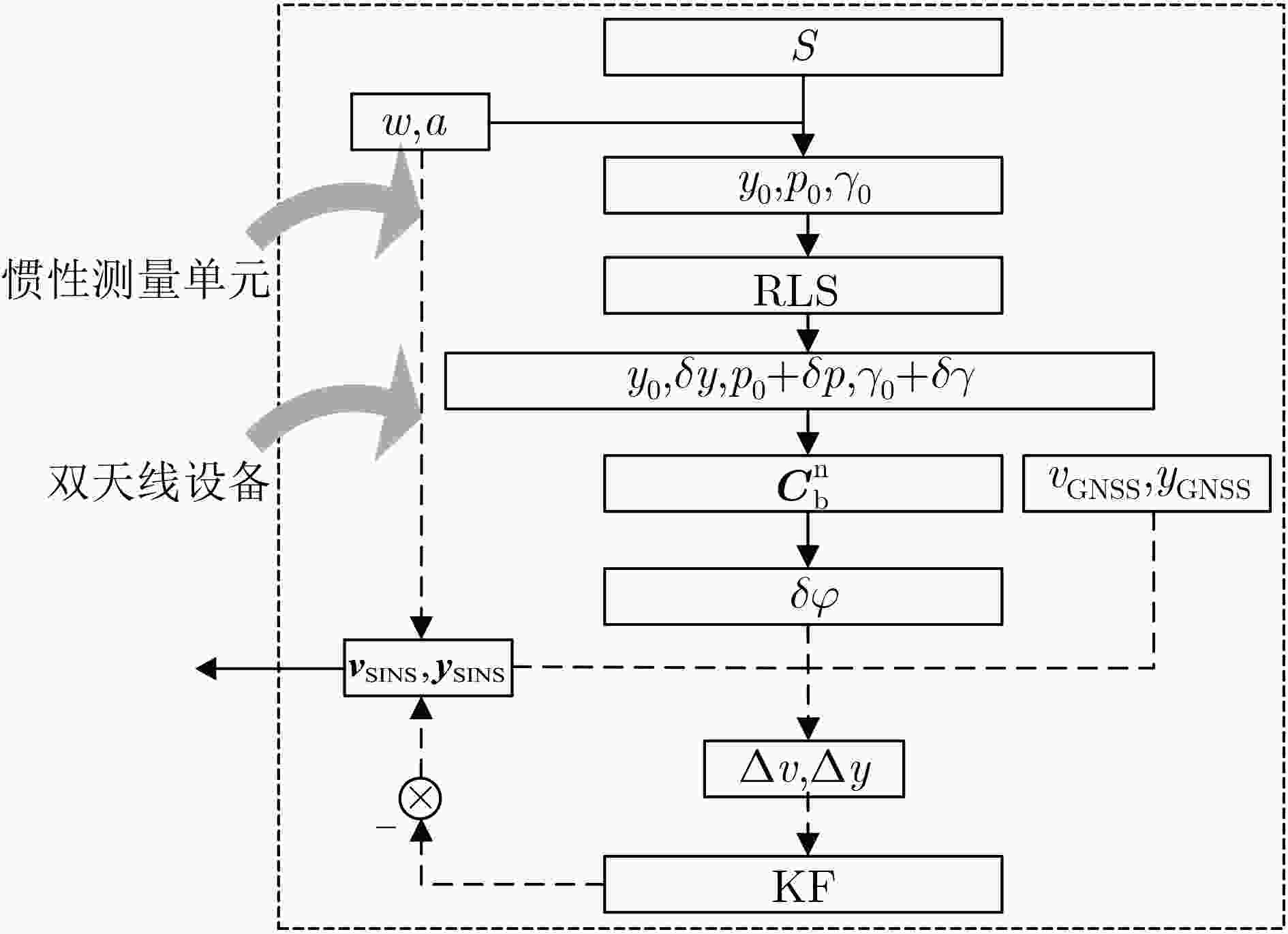
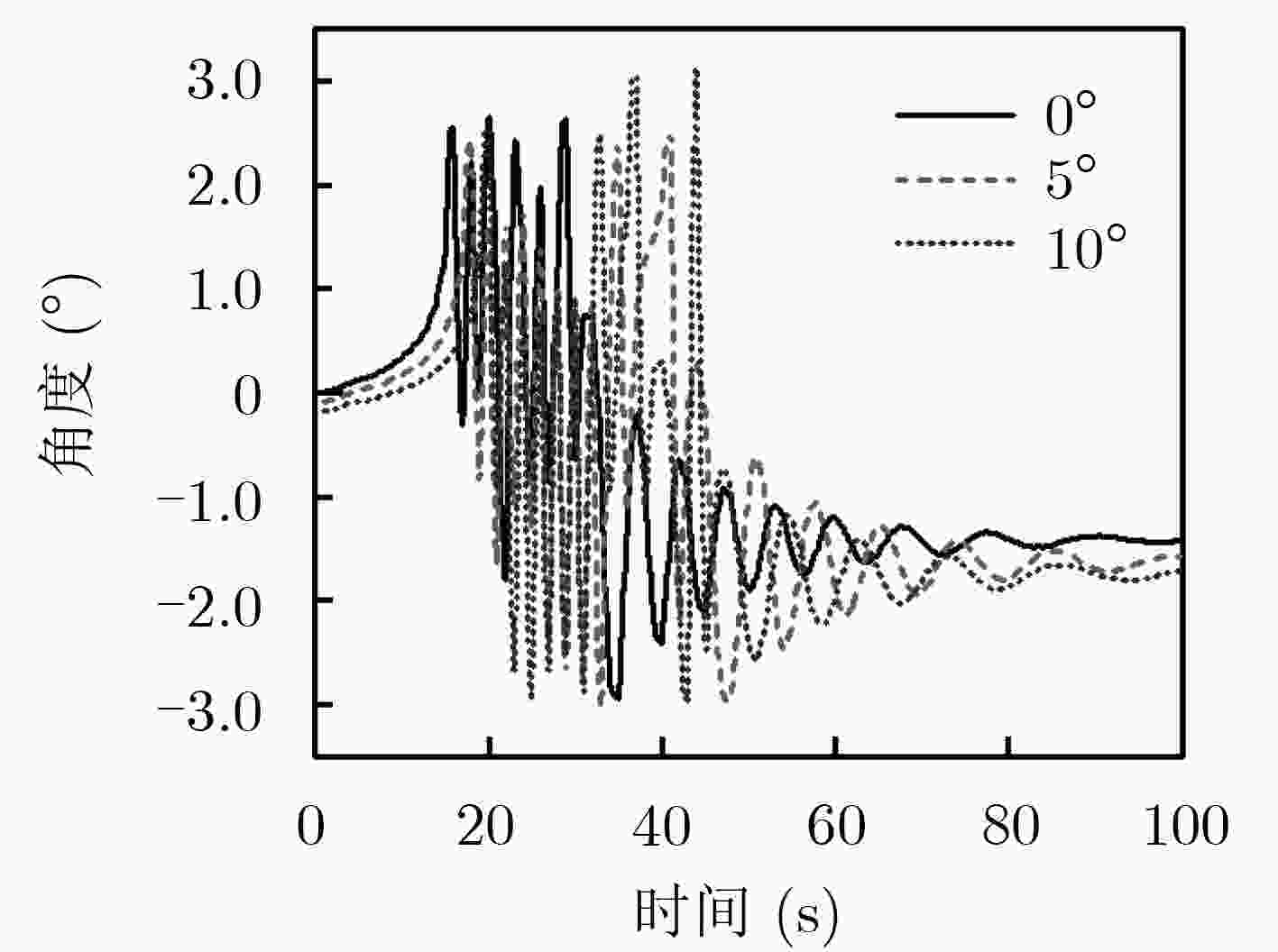
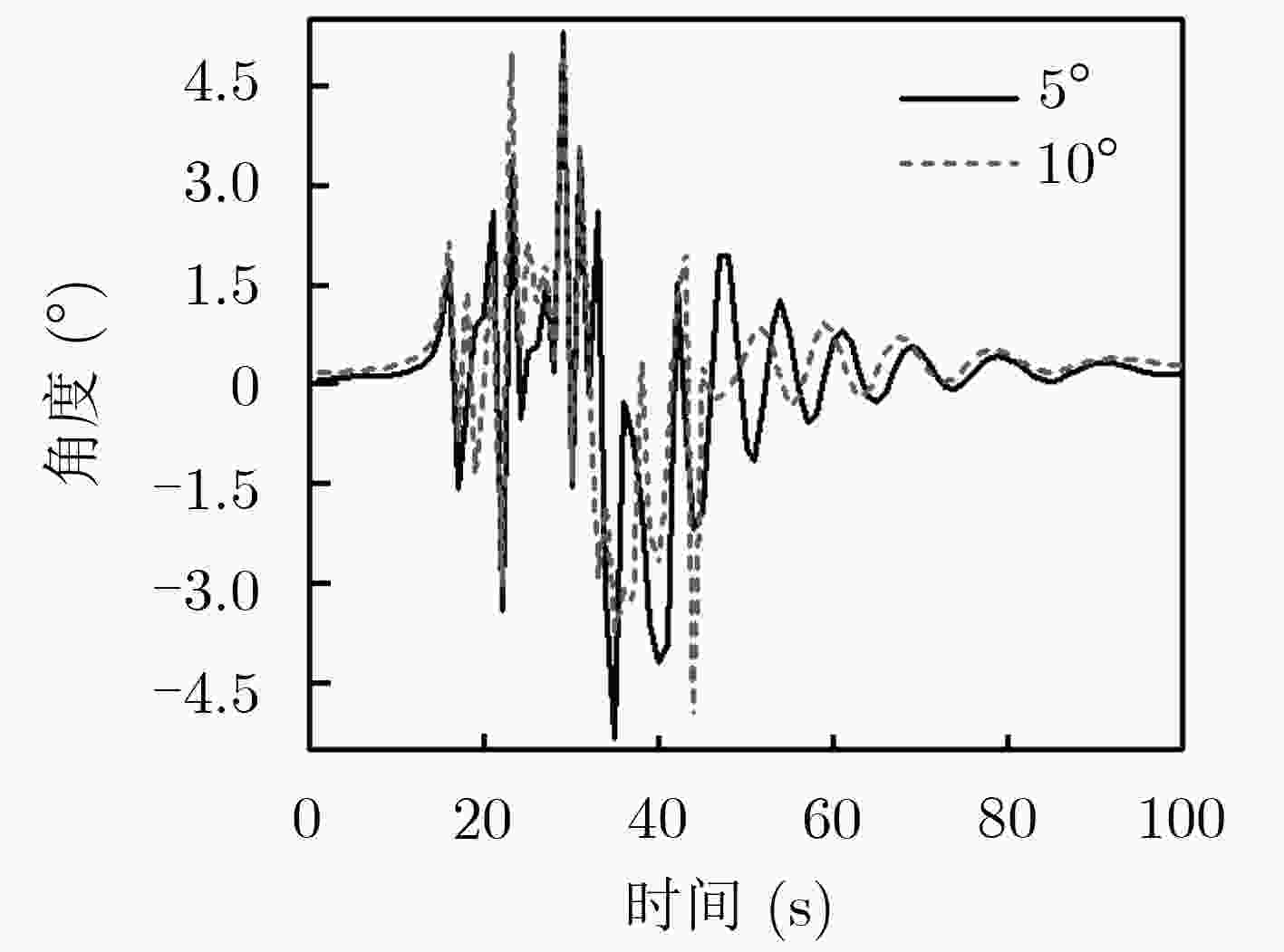


 下载:
下载:
