Fuzzy C-Means Clustering with Fast and Adaptive Non-local Spatial Constraint and Membership Linking for Noise Image Segmentation
-
摘要:
针对传统模糊C-均值聚类(FCM)算法难以对噪声图像进行分割的问题,该文提出一种快速自适应非局部空间加权与隶属度连接的模糊FCM抗噪图像分割算法。首先,利用一种非局部空间信息快速计算方法,将以图像所有像素为循环的原始非局部信息计算方法,改为以搜索窗口尺寸为循环,利用空间位移图像与递归高斯滤波的计算方法,克服非局部空间信息计算复杂的问题;其次,计算原始图像与非局部信息项的差值的平方,将其作为非局部信息项的自适应权重,并将差值的平方作倒数变换,作为原始图像的自适应权重;最后,将每个聚类簇中所有像素隶属度之和的对数平方加入目标函数的分母,形成隶属度连接,减少目标函数迭代次数。含噪人工与自然图像分割实验表明,该算法在分割准确度、平均交并比、归一化互信息、运行时间与迭代次数等性能方面优于其他几种FCM算法。
Abstract:Considering the problem of the low anti-noise performance when Fuzzy C-Means clustering (FCM) algorithm is applied to image segmentation, a FCM clustering algorithm with fast and adaptive non-local spatial constraint and membership linking is proposed in this paper. Firstly, in order to increase the computing speed of non-local spatial term, a fast method is proposed by modifying the loop based on all pixels in an image into a loop based on search window and by utilising spatial shift image and recursive Gaussian filter. Next, the squared difference between original image and non-local spatial term is calculated as adaptive weight of non-local information term. The squared difference is reciprocally transformed as adaptive weight of the original image. Finally, the membership linking is established to reduce the iteration steps before convergence by adding the square of the sum of all the membership degrees in every cluster in logarithmic form as the denominator of the objectvie function. Experiments on noisy artificial and natural images prove that this proposed algorithm has superior performance in terms of Segmentation accuracy, mean intersection over union, normalized mutual information, running time and iteration steps.
-
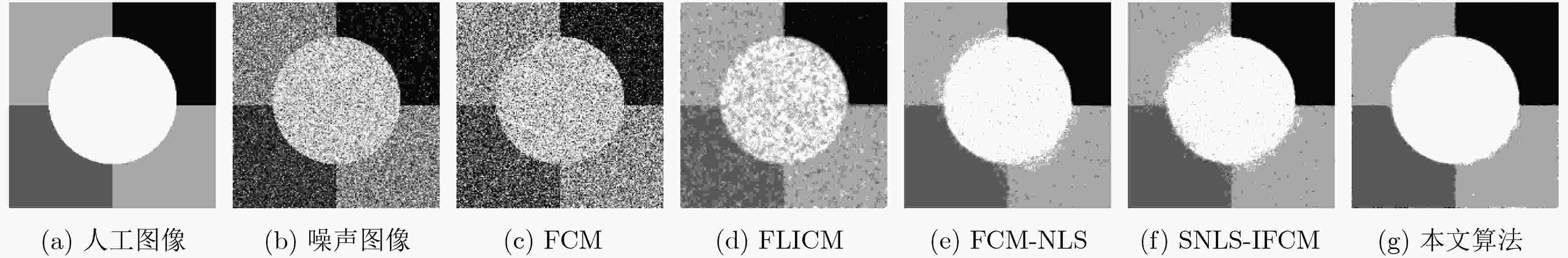
表 1 5种算法对含不同混合噪声人工图像的分割结果
分割指标 SA(%) mIoU(%) NMI(%) 运行时间(s) 迭代次数 噪声大小(%) 5 10 15 20 5 10 15 20 5 10 15 20 5 10 15 20 5 10 15 20 FCM 55.09 43.77 31.21 28.21 52.65 48.48 35.41 30.41 25.34 14.42 9.09 7.13 0.48 0.63 0.67 0.69 18 36 32 35 FLICM 89.54 70.89 60.00 52.08 84.95 64.25 55.16 49.51 73.32 50.10 38.71 30.90 7.52 7.94 7.23 8.02 108 125 106 130 FCM-NLS 96.83 91.48 76.26 59.43 96.35 87.40 68.46 47.80 85.93 76.97 53.63 38.10 185.57 194.82 195.57 195.14 24 33 47 47 SNLS-IFCM 97.66 92.23 77.04 61.02 96.67 88.75 70.12 54.59 86.00 79.18 57.83 40.13 184.12 196.07 196.40 196.83 17 40 51 73 本文算法 98.02 97.30 95.26 90.12 97.70 95.54 92.40 86.71 92.23 89.88 84.35 74.84 1.85 1.92 2.09 2.09 10 10 16 17 表 2 5种算法对含不同混合噪声图像的分割结果
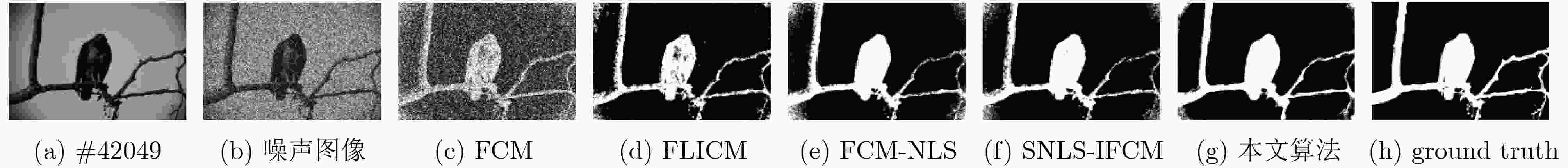
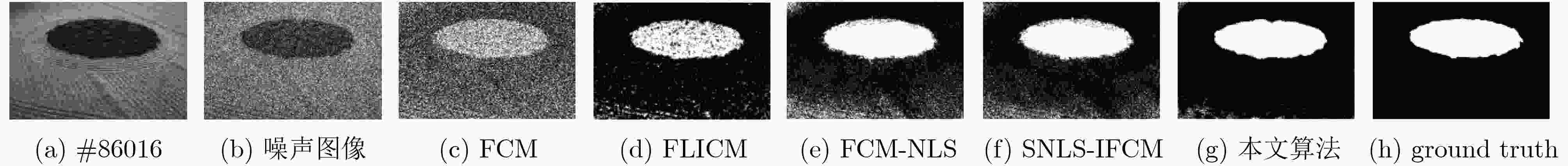
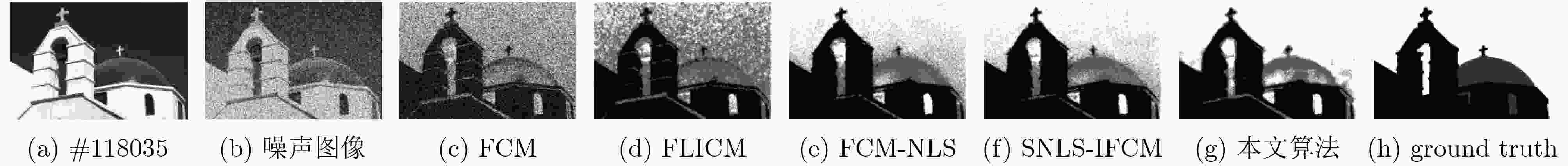
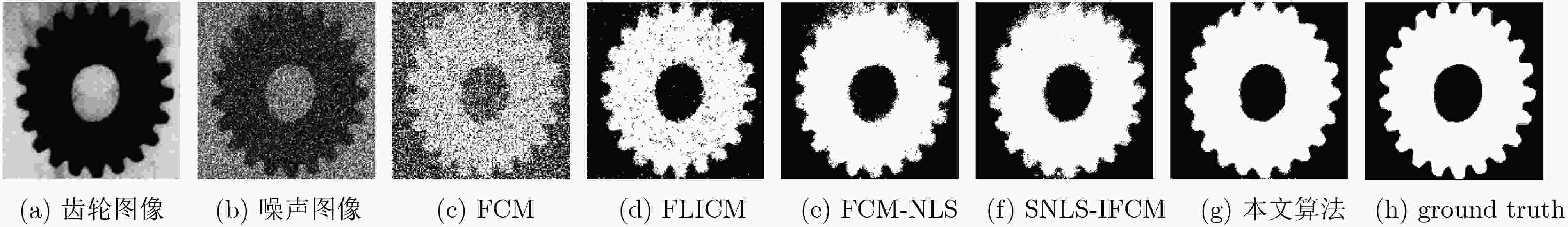
分割指标 SA(%) mIoU(%) NMI(%) 运行时间(s) 迭代次数 噪声大小(%) 5 10 15 20 5 10 15 20 5 10 15 20 5 10 15 20 5 10 15 20 FCM 90.58 81.82 74.57 70.88 82.60 68.88 58.82 54.41 54.99 31.42 17.80 12.32 0.18 0.20 0.15 0.18 15 16 16 18 71.56 63.16 58.74 55.83 51.16 42.74 38.74 36.26 15.74 7.56 4.50 3.02 0.46 0.44 0.35 0.22 23 21 16 11 61.87 57.51 54.04 51.51 40.96 36.52 34.03 32.04 8.19 3.27 2.22 1.33 0.37 0.58 0.28 0.34 18 19 14 16 55.87 49.23 46.77 23.50 36.50 30.73 28.12 12.35 19.45 9.96 6.11 4.11 1.02 0.76 0.52 0.70 35 25 17 23 FLICM 98.83 98.11 96.68 94.41 97.68 96.27 93.52 89.36 90.80 86.44 78.90 69.03 1.60 4.52 3.66 4.29 64 79 88 109 95.33 93.19 90.76 88.61 86.31 80.92 75.39 70.90 63.81 52.86 42.46 34.63 12.32 11.41 13.69 16.14 158 148 177 212 92.19 92.88 85.82 84.07 78.59 78.10 65.45 61.08 52.91 46.01 28.02 19.98 13.22 9.58 23.61 22.00 157 100 300 300 62.15 54.53 44.45 37.20 46.35 39.20 30.85 24.99 49.01 37.81 27.21 20.47 18.85 23.17 18.47 13.09 132 194 151 108 FCM-NLS 98.84 98.16 97.38 95.87 97.68 96.35 94.84 91.98 90.98 86.94 82.90 76.62 189.77 190.08 188.92 197.12 13 16 16 25 95.30 93.53 83.52 71.62 86.26 82.39 65.37 51.49 63.69 55.42 31.17 17.26 472.53 474.82 468.91 473.51 29 29 36 30 96.13 84.85 71.70 63.39 88.00 65.12 50.88 42.73 70.85 37.34 21.15 11.77 473.12 470.12 454.68 472.68 29 28 31 28 85.85 79.31 72.22 61.25 67.48 60.08 52.31 41.84 62.82 55.36 44.63 36.43 478.75 473.25 479.75 480.75 35 53 49 49 SNLS-IFCM 98.92 98.05 97.31 95.50 97.83 96.14 94.70 91.29 91.43 86.40 82.50 75.51 188.42 189.15 188.50 196.30 11 12 13 18 96.75 93.89 84.72 72.61 89.64 82.86 67.01 52.56 73.57 56.67 33.03 18.48 470.25 465.61 470.42 472.76 20 25 42 31 96.80 86.21 71.96 63.01 89.76 65.51 51.21 42.49 79.81 41.55 21.99 12.23 470.30 468.14 452.14 467.14 23 20 28 24 87.92 79.33 71.63 63.11 70.80 59.87 51.72 43.86 65.78 54.15 44.72 35.16 474.25 471.81 470.25 472.25 30 39 24 35 本文算法 99.23 98.26 97.40 96.89 98.12 96.55 95.19 93.90 92.07 87.70 83.54 81.32 1.75 2.06 1.90 1.80 6 6 6 8 98.89 94.36 94.34 93.40 96.04 84.55 83.45 82.15 87.01 61.06 58.27 55.88 4.53 4.41 4.78 4.44 7 12 14 13 98.97 97.72 97.46 91.87 96.31 92.34 91.38 78.10 87.79 78.32 75.44 53.15 4.53 5.51 4.53 4.37 7 10 7 11 90.71 87.40 87.82 79.06 72.75 66.27 67.85 60.03 69.84 65.58 63.13 54.46 4.86 4.37 4.81 4.92 9 7 9 17 表 3 5种算法的时间复杂度
分割算法 计算步骤$E$ 计算步骤函数$E(n)$ 时间复杂度 FCM $H \times W \times K \times {\rm{iter} }$ ${n^4}$ $O({n^4})$ FLICM $H \times W \times K \times {k^2} \times {\rm{iter} }$ ${n^6}$ $O({n^6})$ FCM-NLS $H \times W \times {(2S + 1)^2} \times {(2s + 1)^2} + H \times W \times K \times {\rm{iter} }$ ${n^2}{(n + 1)^4} + {n^4}$ $O({n^6})$ SNLS-IFCM $H \times W \times {(2S + 1)^2} \times {(2s + 1)^2} + H \times W \times (K - 1) \times K \times {\rm{iter} }$ ${n^2}{(n + 1)^4} + {n^4}(n - 1)$ $O({n^6})$ 本文算法 $H \times W \times [{(2S + 1)^2} - 1] + (2 \times H \times W) \times K \times {\rm{iter} }$ ${n^2}[{(n + 1)^2} - 1] + 2{n^4}$ $O({n^4})$ -
范九伦, 雷博. 倒数粗糙熵图像阈值化分割算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 214–221. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190559FAN Jiulun and LEI Bo. Image thresholding segmentation method based on reciprocal rough entropy[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 214–221. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190559 许新征, 丁世飞, 史忠植, 等. 图像分割的新理论和新方法[J]. 电子学报, 2010, 38(2A): 76–82.XU Xinzheng, DING Shifei, SHI Zhongzhi, et al. New theories and methods of image segmentation[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2010, 38(2A): 76–82. 姜枫, 顾庆, 郝慧珍, 等. 基于内容的图像分割方法综述[J]. 软件学报, 2017, 28(1): 160–183. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005136JIANG Feng, GU Qing, HAO Huizhen, et al. Survey on content-based image segmentation methods[J]. Journal of Software, 2017, 28(1): 160–183. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005136 申铉京, 刘翔, 陈海鹏. 基于多阈值Otsu准则的阈值分割快速计算[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(1): 144–149. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160248SHEN Xuanjing, LIU Xiang, and CHEN Haipeng. Fast computation of threshold based on multi-threshold Otsu criterion[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(1): 144–149. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160248 KHAIRE P A and THAKUR N V. An overview of image segmentation algorithms[J]. International Journal of Image Processing and Vision Sciences, 2012, 1(2): 62–68. 雷涛, 张肖, 加小红, 等. 基于模糊聚类的图像分割研究进展[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(8): 1776–1791. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.08.023LEI Tao, ZHANG Xiao, JIA Xiaohong, et al. Research progress on image segmentation based on fuzzy clustering[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(8): 1776–1791. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.08.023 WAZARKAR S and KESHAVAMURTHY B N. A survey on image data analysis through clustering techniques for real world applications[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2018, 55: 596–626. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2018.07.009 ZADEH L A. Fuzzy sets[J]. Information and Control, 1965, 8(3): 338–435. doi: 10.1016/S0019-9958(65)90241-X FAN Jiulun, ZHEN Wenzhi, and XIE Weixin. Suppressed fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2003, 24(9/10): 1607–1612. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8655(02)00401-4 AHMED M N, YAMANY S M, MOHAMED N, et al. A modified fuzzy C-means algorithm for bias field estimation and segmentation of MRI data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2002, 21(3): 193–199. doi: 10.1109/42.996338 ZHU Lin, CHUNG F L, and WANG Shitong. Generalized fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm with improved fuzzy partitions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics) , 2009, 39(3): 578–591. doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2008.2004818 KRINIDIS S and CHATZIS V. A robust fuzzy local information c-means clustering algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(5): 1328–1337. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2040763 ZHAO Feng, JIAO Licheng, and LIU Hanqiang. Fuzzy c-means clustering with non local spatial information for noisy image segmentation[J]. Frontiers of Computer Science in China, 2011, 5(1): 45–56. doi: 10.1007/s11704-010-0393-8 CHEN Songcan and ZHANG Daoqiang. Robust image segmentation using FCM with spatial constraints based on new kernel-induced distance measure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics) , 2004, 34(4): 1907–1916. doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2004.831165 ZHAO Feng. Fuzzy clustering algorithms with self-tuning non-local spatial information for image segmentation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2013, 106: 115–125. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2012.10.022 兰蓉, 林洋. 抑制式非局部空间直觉模糊C-均值图像分割算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(6): 1472–1479. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180651LAN Rong and LIN Yang. Suppressed non-local Spatial intuitionistic fuzzy C-means image segmentation algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(6): 1472–1479. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180651 施伟锋, 卓金宝, 兰莹. 一种基于属性空间相似性的模糊聚类算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(11): 2722–2728. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180974SHI Weifeng, ZHUO Jinbao, and LAN Ying. A novel fuzzy clustering algorithm based on similarity of attribute space[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(11): 2722–2728. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180974 GONG Maoguo, LIANG Yan, SHI Jiao, et al. Fuzzy C-means clustering with local information and kernel metric for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(2): 573–584. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2219547 ELAZAB A, WANG Changmiao, JIA Fucang, et al. Segmentation of brain tissues from magnetic resonance images using adaptively regularized kernel-based fuzzy C-means clustering[J]. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2015, 2015: 485495. doi: 10.1155/2015/485495 MEMON K H and LEE D H. Generalised kernel weighted fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm with local information[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2018, 340: 91–108. doi: 10.1016/j.fss.2018.01.019 BUADES A, COLL B, and MOREL J M. A non-local algorithm for image denoising[C]. 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, USA, 2005: 60–65. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2005.38. VAN VLIET L J, YOUNG I T, and VERBEEK P W. Recursive Gaussian derivative filters[C]. The 14th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Brisbane, Australia, 1998: 509–514. doi: 10.1109/ICPR.1998.711192. -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
