Aurora Image Classification and Retrieval Method Based on Deep Hashing Algorithm
-
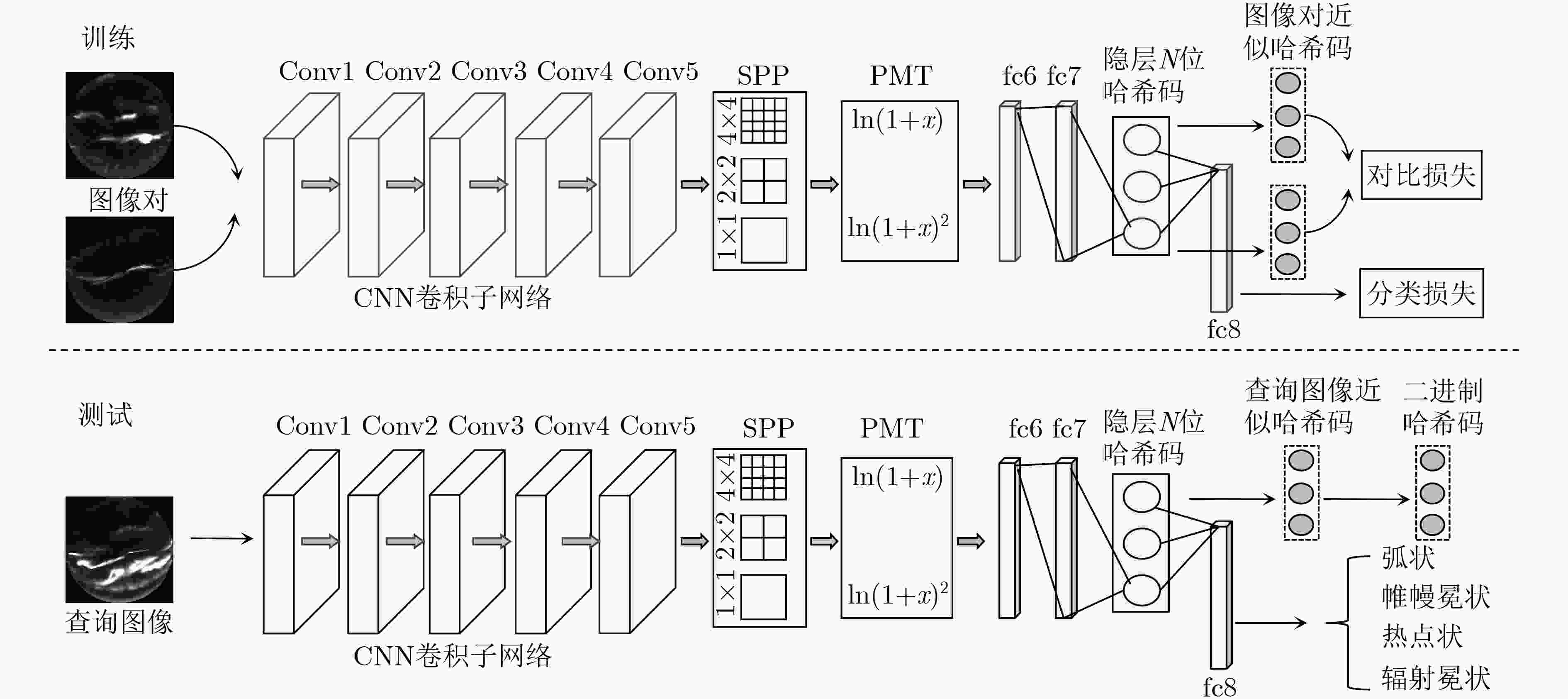
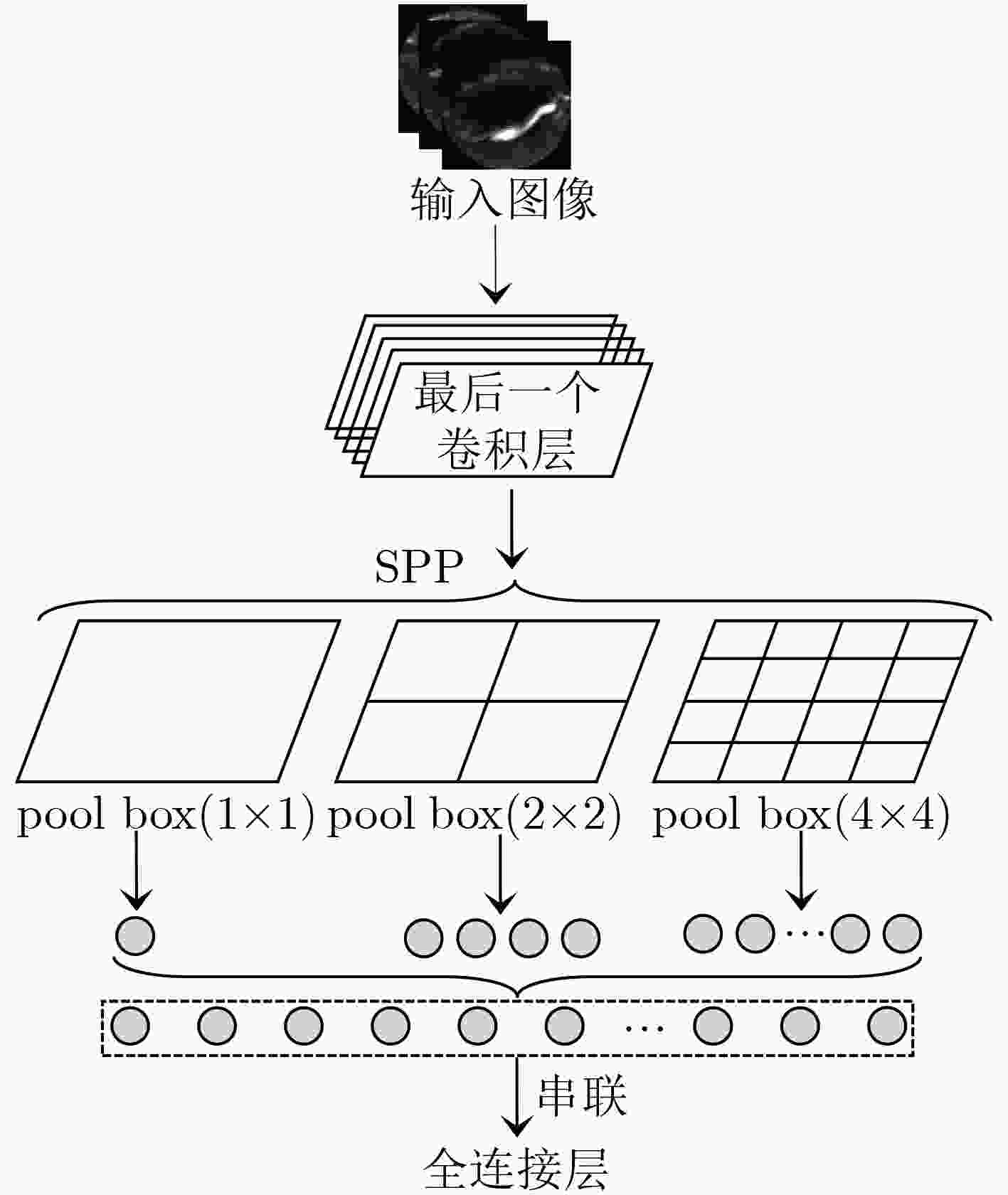
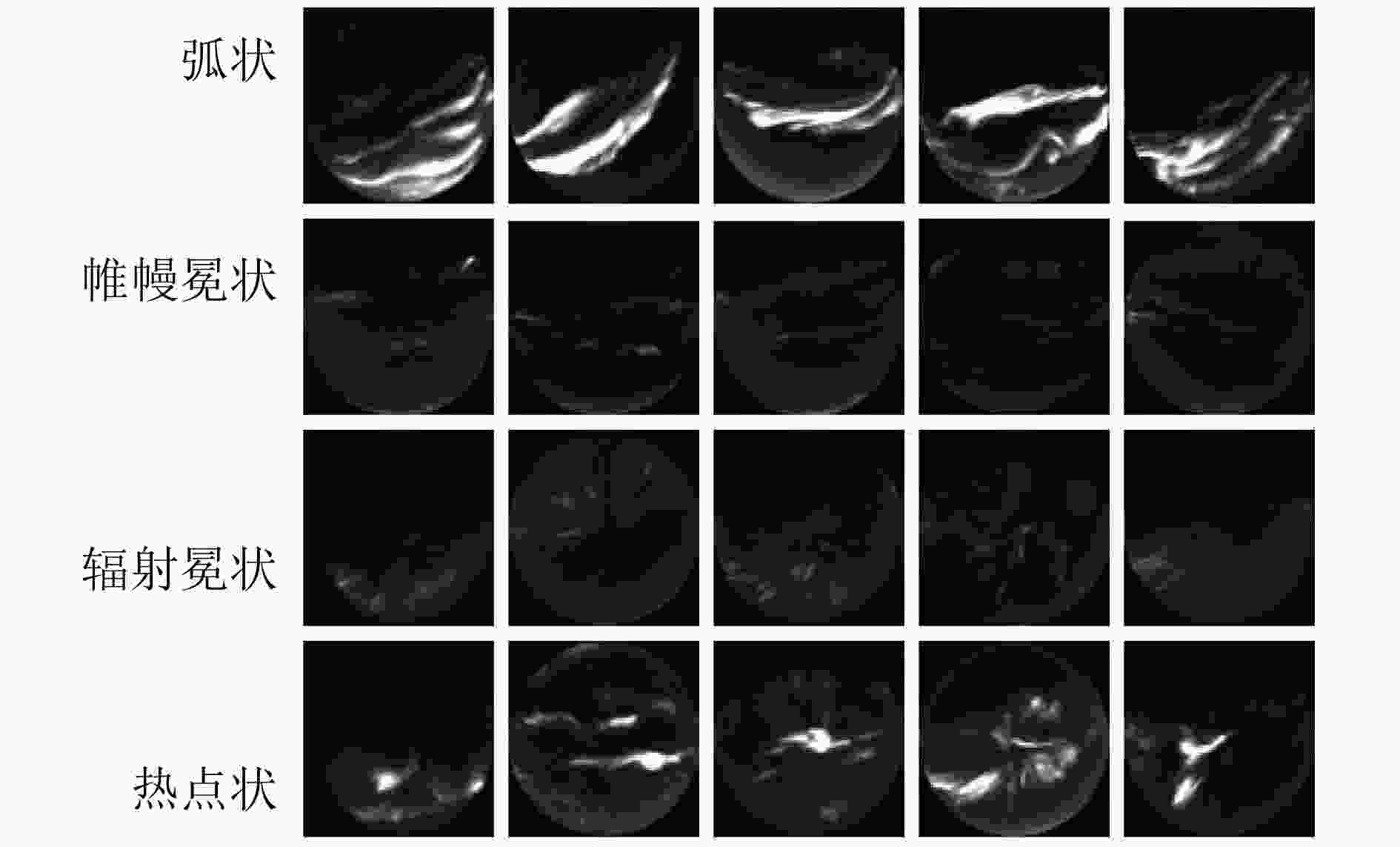
摘要: 面对形态万千、变化复杂的海量极光数据,对其进行分类与检索为进一步研究地球磁场物理机制和空间信息具有重要意义。该文基于卷积神经网络(CNN)对图像特征提取方面的良好表现,以及哈希编码可以满足大规模图像检索对检索时间的要求,提出一种端到端的深度哈希算法用于极光图像分类与检索。首先在CNN中嵌入空间金字塔池化(SPP)和幂均值变换(PMT)来提取图像中多种尺度的区域信息;其次在全连接层之间加入哈希层,将全连接层最能表现图像的高维语义信息映射为紧凑的二值哈希码,并在低维空间使用汉明距离对图像对之间的相似性进行度量;最后引入多任务学习机制,充分利用图像标签信息和图像对之间的相似度信息来设计损失函数,联合分类层和哈希层的损失作为优化目标,使哈希码之间可以保持更好的语义相似性,有效提升了检索性能。在极光数据集和 CIFAR-10 数据集上的实验结果表明,所提出方法检索性能优于其他现有检索方法,同时能够有效用于极光图像分类。Abstract: It is of great significance to classify and retrieve the vast amount of aurora data with various forms and complex changes for the further study of the physical mechanism of the geomagnetic field and spatial information. In this paper, an end-to-end deep hashing algorithm for aurora image classification and retrieval is proposed based on the good performance of CNN in image feature extraction and the fact that hash coding can meet the retrieval time requirment of large-scale image retrieval. Firstly, Spatial Pyramidal Pooling(SPP) and Power Mean Transformtion(PMT) are embedded in Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to extract multi-scale region information in the image. Secondly, a Hash layer is added between the fully connected layer to Mean Average Precision(MAP) the high-dimensional semantic information that can best represent the image into a compact binary Hash code, and the hamming distance is used to measure the similarity between the image pairs in the low-dimensional space. Finally, a multi-task learning mechanism is introduced to design the loss fuction by making full use of similarity informtion between the image label information and the image pairs. The loss of classification layer and Hash layer are combined as the optimization objective, so that a better semantic similarity between Hash code can be maintained, and the retrieval performance can be effectively improved. The results show that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-art retrieval algorithms on aurora dataset and CIFAR-10 datasets, and it can also be used in aurora image classification effectively.
-
表 1 有无哈希层损失两种方法对比
方法 MAP 准确率 不考虑哈希层损失 0.7563 0.8705 考虑哈希层损失 0.8554 0.9073 表 2 有无SPP_PMT层两种方法对比
方法 MAP 准确率 不加SPP_PMT 0.8554 0.9073 加入SPP_PMT 0.8963 0.9367 表 3 3种方法的MAP以及在bit=48下模型参数大小(MB)和训练时间(min)
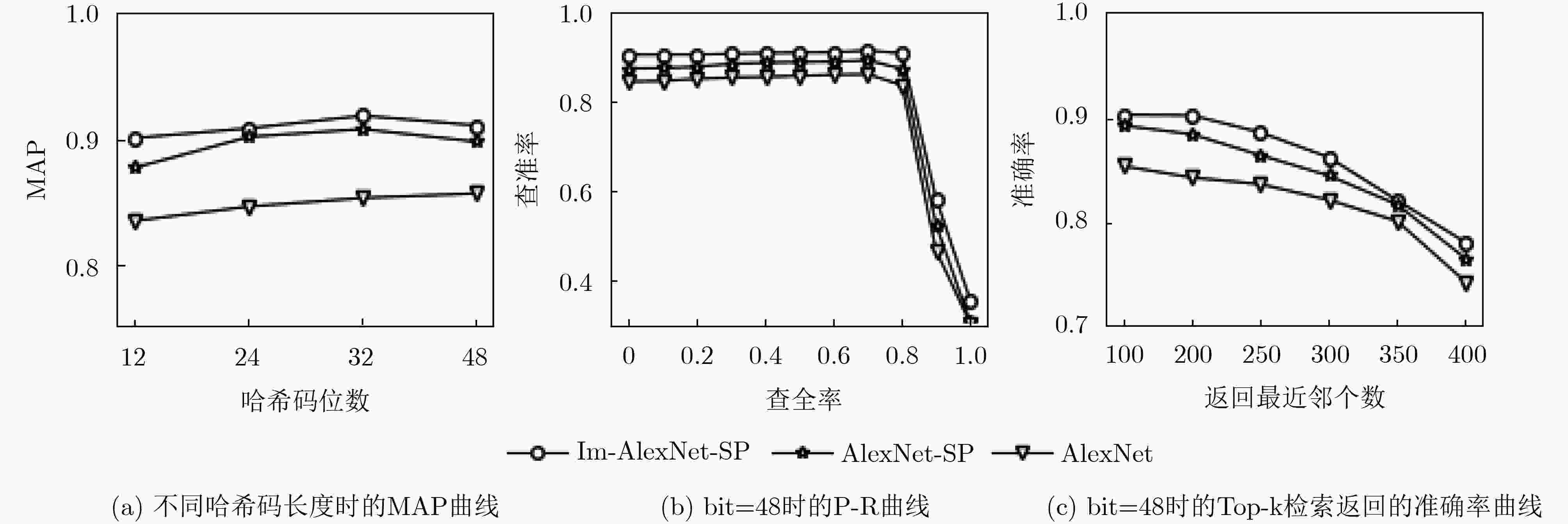
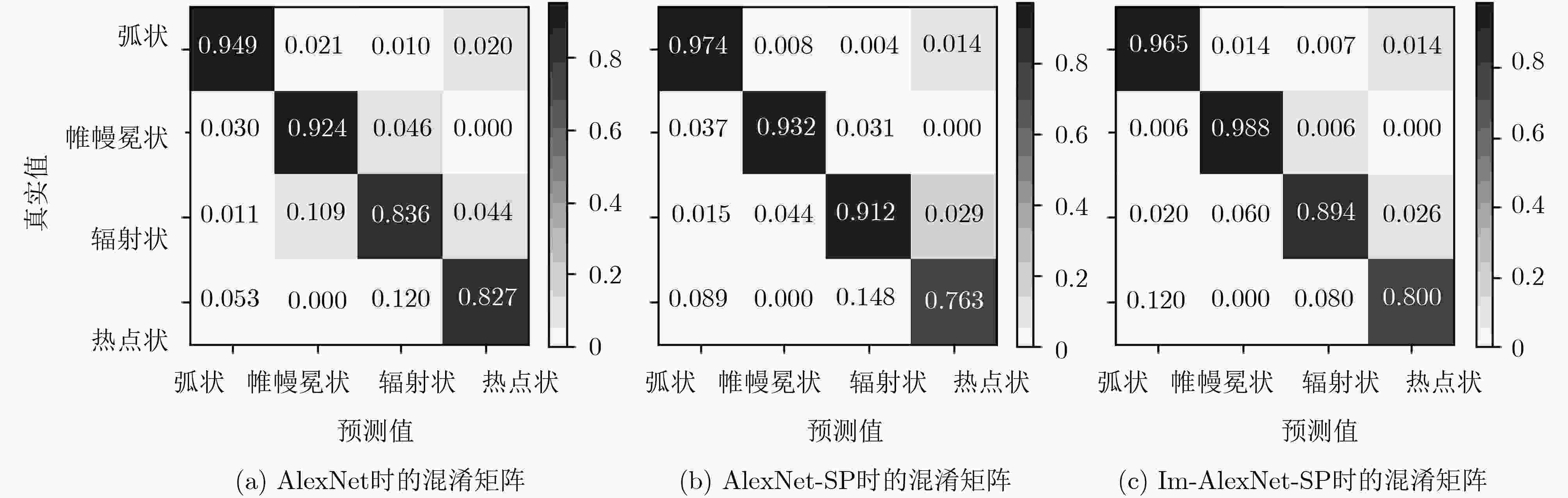
方法 不同哈希码长度(bit)下的MAP 参数大小 训练时间 12 24 32 48 AlexNet 0.8336 0.8450 0.8518 0.8554 218.20 158 AlexNet-SP 0.8729 0.9004 0.9066 0.8963 179.15 115 Im-AlexNet-SP 0.8995 0.9072 0.9173 0.9095 100.77 80 表 4 3种方法在不同哈希码长度下的准确率
方法 不同哈希码长度(bit)下的准确率 12 24 32 48 AlexNet 0.8964 0.8995 0.8988 0.9073 AlexNet-SP 0.9312 0.9298 0.9325 0.9367 Im-AlexNet-SP 0.9320 0.9305 0.9410 0.9384 表 5 本文方法与其他极光检索算法的MAP以及平均查询时间对比(s)
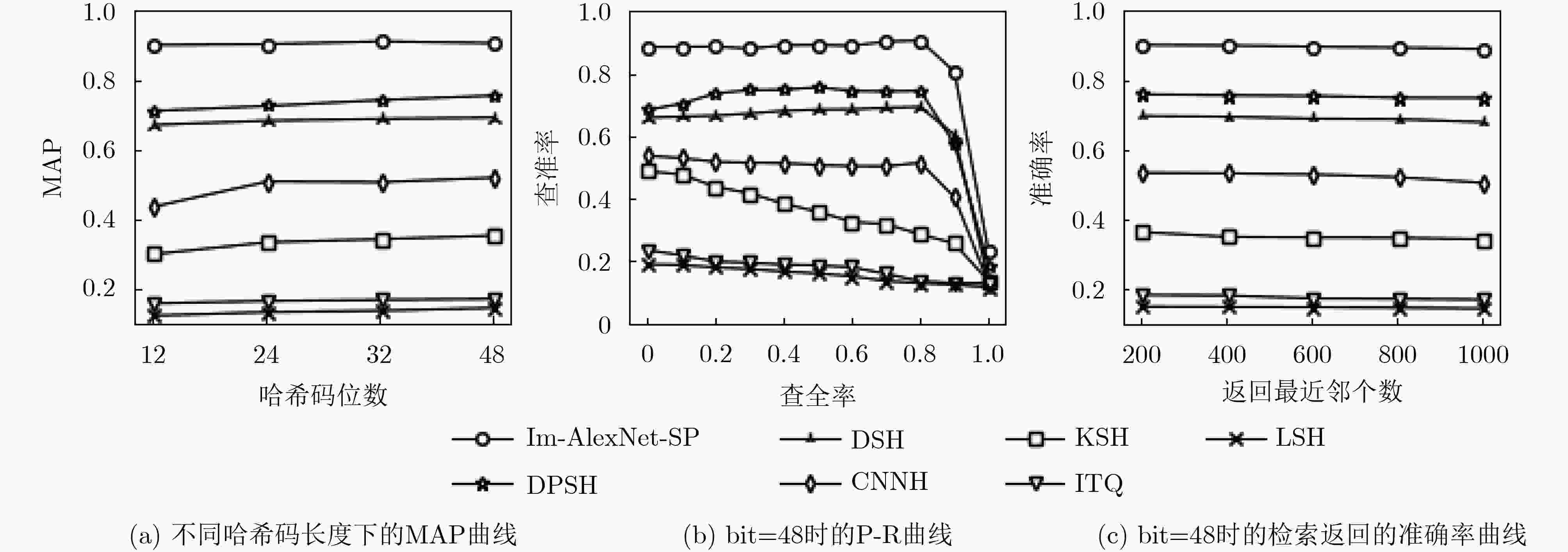
方法 MAP 平均查询时间 HE 0.5253 0.65 VLAD 0.5868 0.52 MAC 0.6558 1.22 MS-RMAC 0.6901 2.89 本文Im-AlexNet-SP 0.9095 0.43 表 6 不同哈希算法在CIFAR-10不同哈希码长度下的MAP
方法 不同哈希码长度(bit)下的MAP 12 24 32 48 本文Im-AlexNet-SP 0.902 0.904 0.912 0.907 DPSH 0.713 0.727 0.744 0.757 DSH 0.673 0.685 0.690 0.694 CNNH 0.439 0.511 0.509 0.522 KSH 0.303 0.337 0.346 0.356 ITQ 0.162 0.169 0.172 0.175 LSH 0.127 0.137 0.141 0.149 -
WANG Qian, LIANG Jimin, HU Zejun, et al. Spatial texture based automatic classification of dayside aurora in all-sky images[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2010, 72(5/6): 498–508. doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2010.01.011 韩冰, 杨辰, 高新波. 融合显著信息的LDA极光图像分类[J]. 软件学报, 2013, 24(11): 2758–2766. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2013.04481HAN Bing, YANG Chen, and GAO Xinbo. Aurora image classification based on LDA combining with saliency information[J]. Journal of Software, 2013, 24(11): 2758–2766. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2013.04481 SYRJÄSUO M T, DONOVAN E F, and COGGER L L. Content-based retrieval of auroral images - thousands of irregular shapes[C]. The 4th IASTED International Conference Visualization, Imaging, and Image Processing, Marbella, Spain, 2004. FU Rong, GAO Xinbo, LI Xuelong, et al. An integrated aurora image retrieval system: Aurora Eye[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2010, 21(8): 787–797. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2010.06.002 YANG Xi, GAO Xinbo, SONG Bin, et al. Aurora image search with contextual CNN feature[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 281: 67–77. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.11.059 葛芸, 马琳, 江顺亮, 等. 基于高层特征图组合及池化的高分辨率遥感图像检索[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(10): 2487–2494. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190017GE Yun, MA Lin, JIANG Shunliang, et al. The combination and pooling based on high-level feature map for high-resolution remote sensing image retrieval[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(10): 2487–2494. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190017 刘冶, 潘炎, 夏榕楷, 等. FP-CNNH: 一种基于深度卷积神经网络的快速图像哈希算法[J]. 计算机科学, 2016, 43(9): 39–46, 51. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2016.09.007LIU Ye, PAN Yan, XIA Rongkai, et al. FP-CNNH: A fast image hashing algorithm based on deep convolutional neural network[J]. Computer Science, 2016, 43(9): 39–46, 51. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2016.09.007 LI Wujun, WANG Sheng, and KANG Wangcheng. Feature learning based deep supervised hashing with pairwise labels[C]. The 25th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2016: 1711–1717. LIU Haomiao, WANG Ruiping, SHAN Shiguang, et al. Deep supervised hashing for fast image retrieval[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2064–2072. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.227. KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904–1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 赵斐, 张文凯, 闫志远, 等. 基于多特征图金字塔融合深度网络的遥感图像语义分割[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(10): 2525–2531. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190047ZHAO Fei, ZHANG Wenkai, YAN Zhiyuan, et al. Multi-feature map pyramid fusion deep network for semantic segmentation on remote sensing data[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(10): 2525–2531. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190047 ZHANG Chenlin and WU Jianxin. Improving CNN linear layers with power mean non-linearity[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 89: 12–21. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.12.029 JEGOU H, DOUZE M, and SCHMID C. Hamming embedding and weak geometric consistency for large scale image search[C]. The 10th European Conference on Computer Vision, Marseille, France, 2008: 304–317. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-88682-2_24. XIA Yan, HE Kaiming, WEN Fang, et al. Joint inverted indexing[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 2013: 3416–3423. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2013.424. TOLIAS G, SICRE R, and JÉGOU H. Particular object retrieval with integral max-pooling of CNN activations[C]. The 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2016: 1–12. LI Yang, XU Yulong, WANG Jiabao, et al. MS-RMAC: Multiscale regional maximum activation of convolutions for image retrieval[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(5): 609–613. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2017.2665522 DATAR M, IMMORLICA N, INDYK P, et al. Locality- sensitive hashing scheme based on p-stable distributions[C]. The 20th Annual Symposium on Computational Geometry, Brooklyn, USA, 2004: 253–262. doi: 10.1145/997817.997857. GONG Yunchao and LAZEBNIK S. Iterative quantization: A procrustean approach to learning binary codes[C]. The 24th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2011: 817–824. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2011.5995432. LIU Wei, WANG Jun, JI Rongrong, et al. Supervised hashing with kernels[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 2074–2081. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2012.6247912. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
