Correlation Filter Algorithm Based on Adaptive Context Selection and Multiple Detection Areas
-
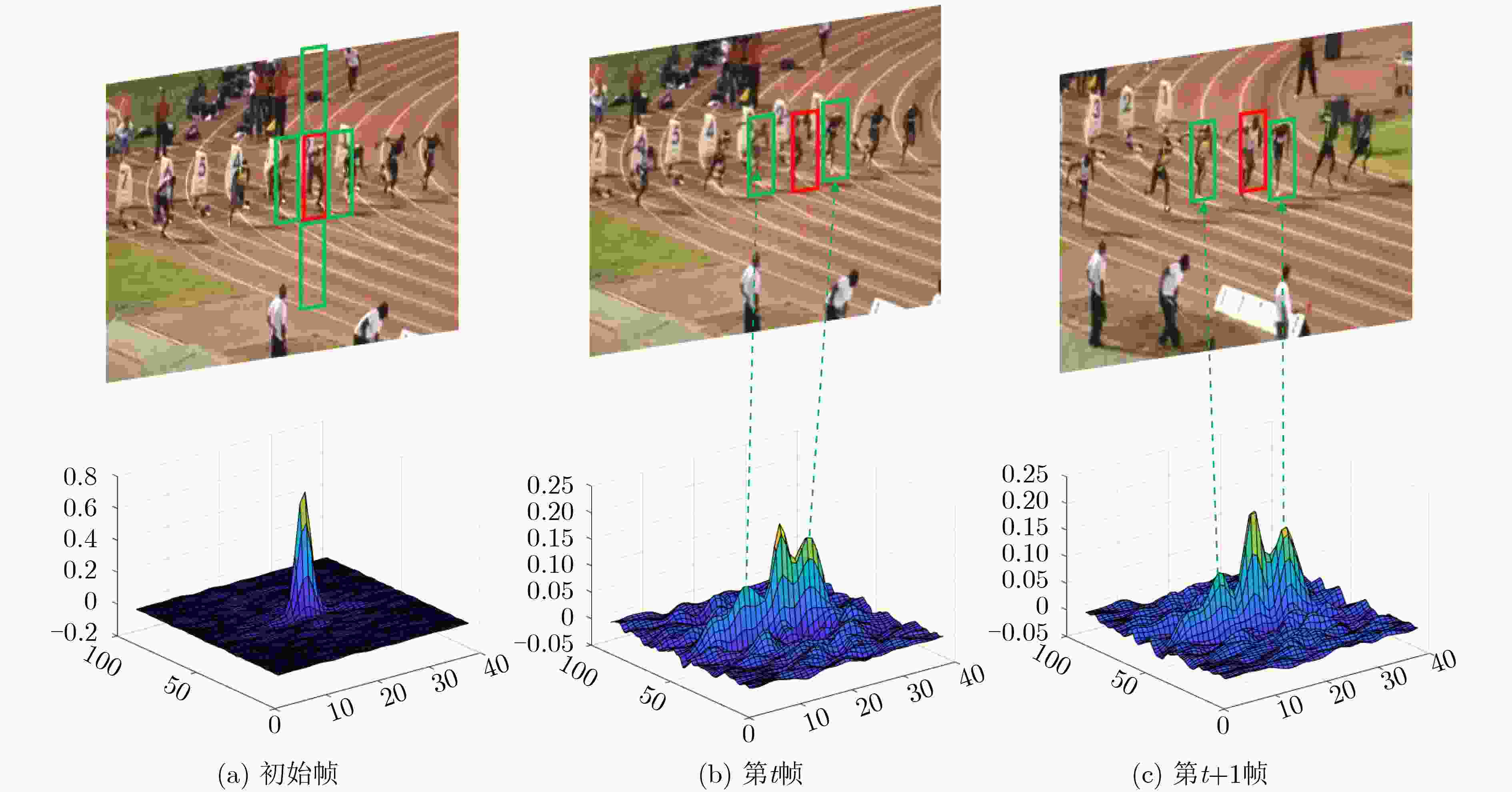
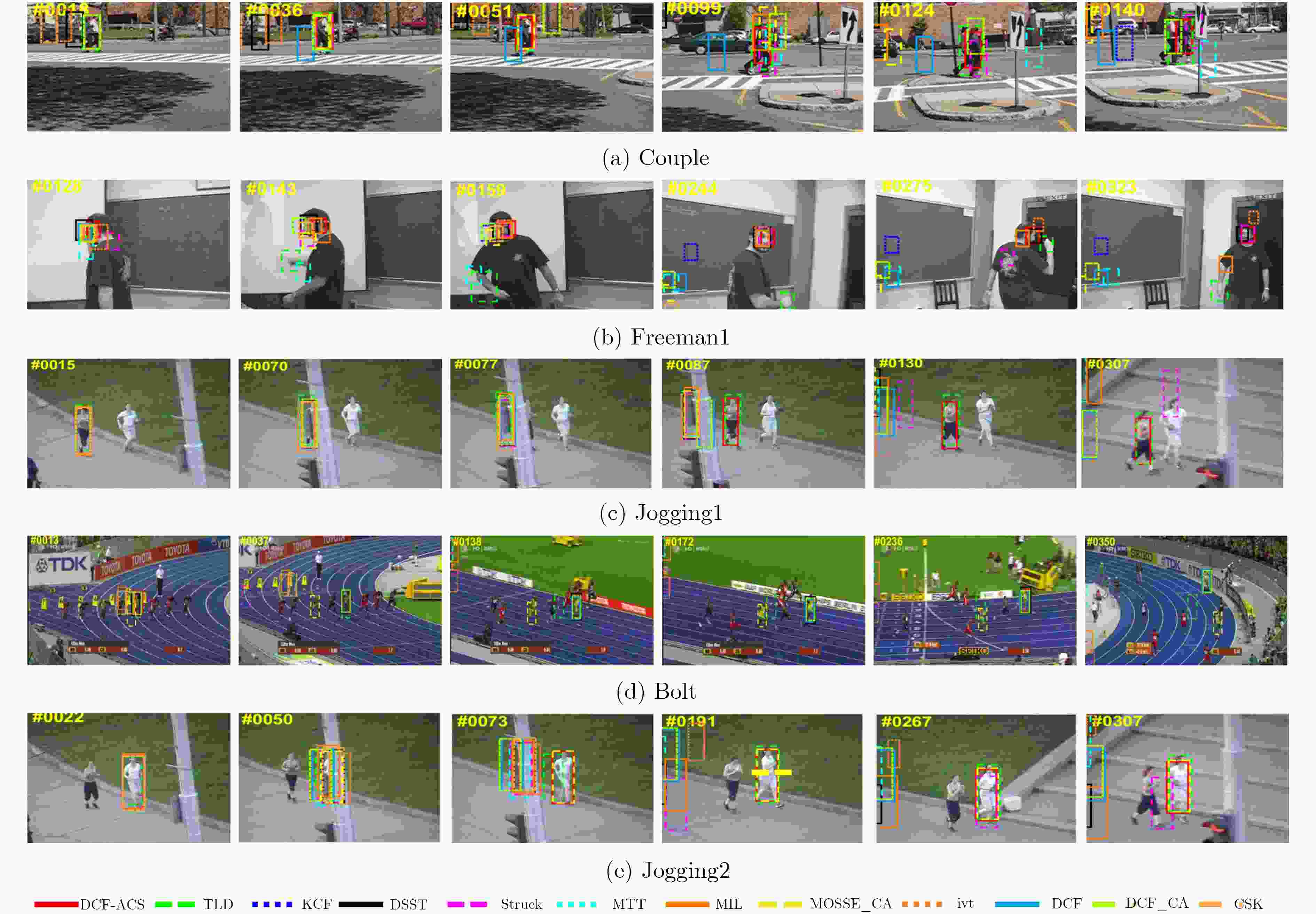
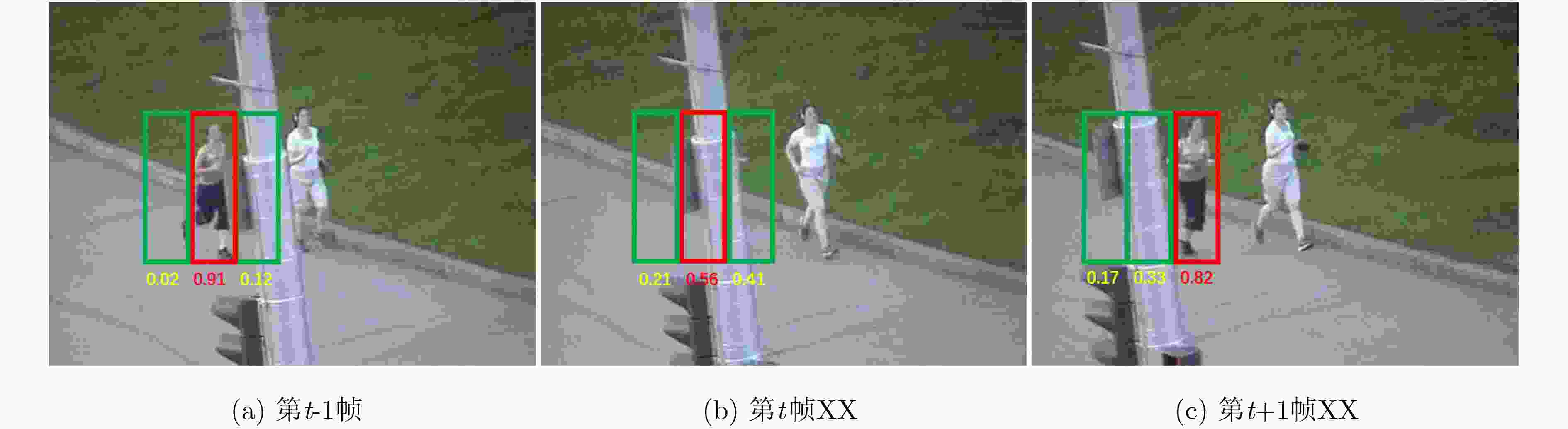
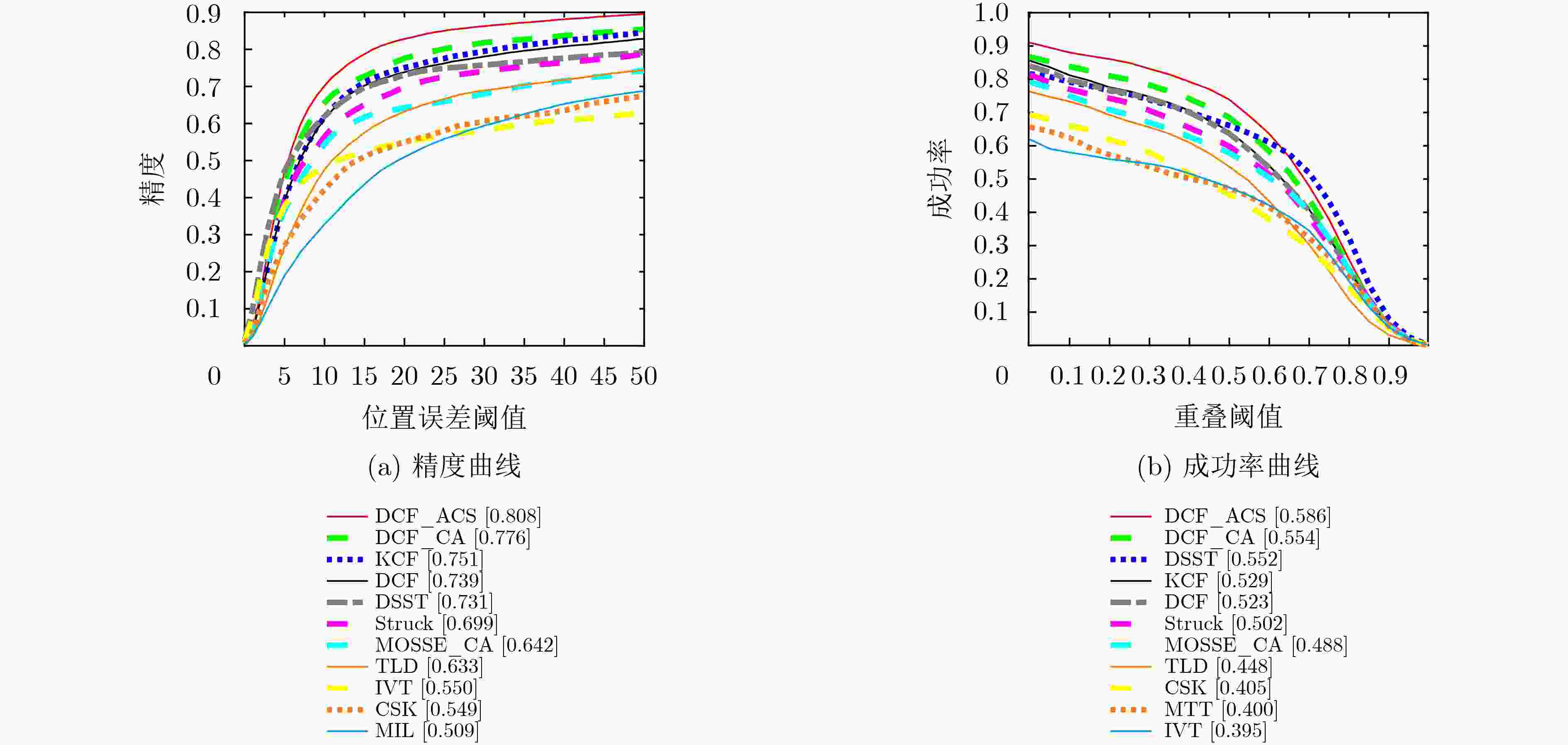
摘要: 为了进一步提高相关滤波算法的判别力和对快速运动、遮挡等复杂场景的应对能力,该文提出一种基于自适应背景选择和多检测区域的跟踪框架。首先对检测后的响应图进行峰值分析,当响应为单峰的时候,提取目标上下左右的4块区域作为负样本对模型进行训练,当响应为多峰的时候,采用峰值提取技术和阈值选择方法提取较大几个峰值区域作为负样本。为了进一步提高算法对遮挡的应对能力,该文提出了一种多检测区域的搜索策略。将该框架和传统的相关滤波算法进行结合,实验结果表明,相对于基准算法,该算法在精度上提高了6.9%,在成功率上提高了6.3%。Abstract: In order to improve further the discrimination ability of the correlation filtering algorithm and the ability to deal with fast motion and occlusion, a tracking framework based on adaptive context selection and multiple detection areas is proposed. Firstly, the peak value of the detected response map is analyzed. When the response is single peak, four areas surrounding the target are extracted as negative samples to train the model. When the response is multi-peak, the peak value extraction technology and threshold selection are used to extract several larger peak areas as negative samples. In order to improve further the ability to deal with occlusion, a multi detection area search strategy is proposed. Combining the framework with the traditional correlation filter algorithm, the experimental results show that the proposed algorithm improves the accuracy by 6.9% and the success rate by 6.3%.
-
Key words:
- Visual tracking /
- Correlation filter /
- Occlusion /
- Context selection
-
表 1 基于自适应背景选择和多检测区域的相关滤波算法
输入:图像序列I1, I2, ···, In,目标初始位置p0=(x0, y0)。 输出:每帧图像的跟踪结果pt=(xt, yt)。 对于t=1, 2, ···, n, do: (1) 定位目标中心位置 (a) 利用前一帧目标位置pt-1确定第t帧ROI区域,并提取
HOG特征;(b) 利用式(3)在多个检测区域进行计算,获得多个响应图; (c) 提取多个响应图的最大值作为目标的中心位置pt。 (2) 模型更新 (a) 对得到的响应图计算峰值个数; (b) 当为单峰时,提取上下左右4个背景块进行模型更新; (c) 当为多峰时,选取峰值位置的背景块作为负样本,对模型
进行训练;(d) 采用式(7)对模型进行更新。 结束 表 2 算法跟踪速度对比
本文算法 DCF_CA DCF DSST TLD MOSSE_CA 成功率 0.586 0.566 0.523 0.552 0.448 0.488 跟踪精度 0.808 0.776 0.739 0.731 0.633 0.642 跟踪速度(FPS) 53.5 82.3 333.0 28.3 33.4 115.0 -
SMEULDERS A W M, CHU D M, CUCCHIARA R, et al. Visual tracking: An experimental survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(7): 1442–1468. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.230 HE Anfeng, LUO Chong, TIAN Xinmei, et al. A twofold Siamese network for real-time object tracking[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4834–4843. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00508. LI Bo, YAN Junjie, WU Wei, et al. . High performance visual tracking with Siamese region proposal network[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8971–8980. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00935. LI Peixia, CHEN Boyu, OUYANG Wanli, et al. GradNet: Gradient-guided network for visual object tracking[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 6162–6171. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00626. BOLME D S, BEVERIDGE J R, DRAPER B A, et al. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters[C]. 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 2544–2550. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2010.5539960. HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels[C]. 12th European Conference on Computer Vision on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012: 702–715. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-33765-9_50. HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 583–596. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2014.2345390 DANELLJAN M, KHAN F S, FELSBERG M, et al. Adaptive color attributes for real-time visual tracking[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 1090–1097. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2014.143. DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, KHAN F S, et al. Convolutional features for correlation filter based visual tracking[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 58–66. doi: 10.1109/ICCVW.2015.84. QI Yuankai, ZHANG Shengping, QIN Lei, et al. Hedged deep tracking[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 4303–4311. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.466. MA Chao, HUANG Jiabin, YANG Xiaokang, et al. Hierarchical convolutional features for visual tracking[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 3074–3082. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.352. WANG Haijun, ZHANG Shengyan, GE Hongjuan, et al. Robust visual tracking via semiadaptive weighted convolutional features[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2018, 25(5): 670–674. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2018.2819622 QI Yuankai, ZHANG Shengping, QIN Lei, et al. Hedging deep features for visual tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(5): 1116–1130. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2828817 ZHANG Tianzhu, XU Changsheng, and YANG M H. Learning multi-task correlation particle filters for visual tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(2): 365–378. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2797062 DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, KHAN F S, et al. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4310–4318. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.490. 蒲磊, 冯新喜, 侯志强, 等. 基于空间可靠性约束的鲁棒视觉跟踪算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1650–1657. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180780PU Lei, FENG Xinxi, HOU Zhiqiang, et al. Robust visual tracking based on spatial reliability constraint[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1650–1657. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180780 GALOOGAHI H K, SIM T, LUCEY S. Correlation filters with limited boundaries[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 4630–4638. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299094. PU Lei, FENG Xinxi, and HOU Zhiqiang. Learning temporal regularized correlation filter tracker with spatial reliable constraint[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 81441–81450. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2922416 LI Feng, TIAN Cheng, ZUO Wangmeng, et al. Learning spatial-temporal regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4904–4913. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00515. 侯志强, 王帅, 廖秀峰, 等. 基于样本质量估计的空间正则化自适应相关滤波视觉跟踪[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(8): 1983–1991. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180921HOU Zhiqiang, WANG Shuai, LIAO Xiufeng, et al. Adaptive regularized correlation filters for visual tracking based on sample quality estimation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(8): 1983–1991. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180921 MUELLER M, SMITH N, GHANEM B, et al. Context-aware correlation filter tracking[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1396–1404. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.152. WANG Mengmeng, LIU Yong, HUANG Zeyi, et al. Large margin object tracking with circulant feature maps[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4021–4029. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.510. WU Yi, LIM J, and YANG M H. Object tracking benchmark[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1834–1848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2388226 DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, KHAN F S, et al. Accurate scale estimation for robust visual tracking[C]. British Machine Vision Conference 2014, Nottingham, UK, 2014: 65.1–65.11. doi: 10.5244/C.28.65. HARE S, GOLODETZ S, SAFFARI A, et al. Struck: Structured output tracking with kernels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(10): 2096–2109. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2509974 KALAL Z, MIKOLAJCZYK K, and MATAS J. Tracking-learning-detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(7): 1409–1422. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.239 ZHANG Tianzhu, GHANEM B, LIU Si, et al. Robust visual tracking via multi-task sparse learning[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 2042–2049. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2012.6247908. BABENKO B, YANG M H, and BELONGIE S. Visual tracking with online multiple instance learning[C]. 2019 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 983–990. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206737. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
