Pilot Iris Recognition Based on Spherical Haar Wavelet and Convolutional Neural Network
-
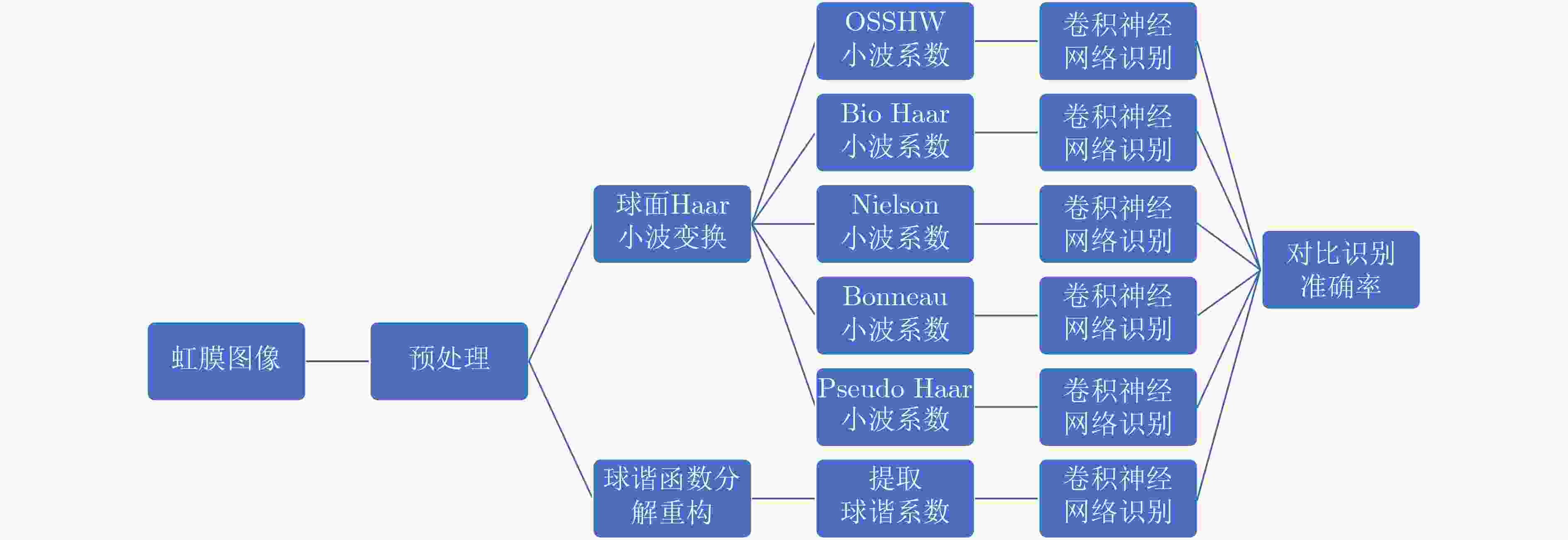
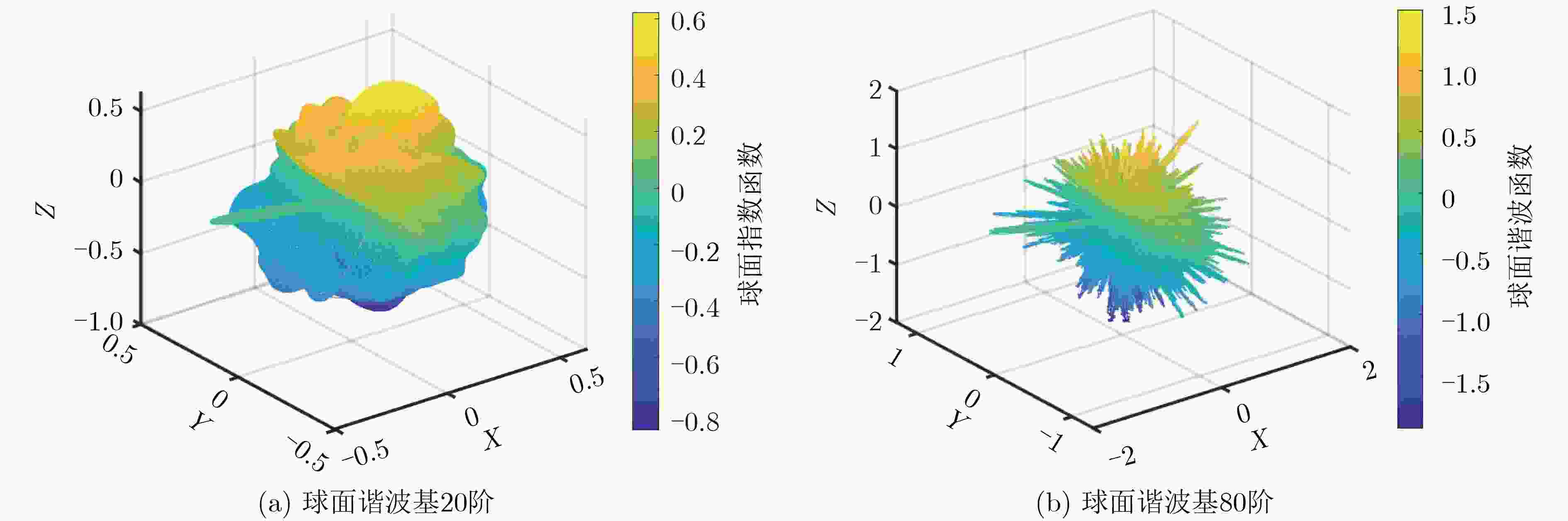
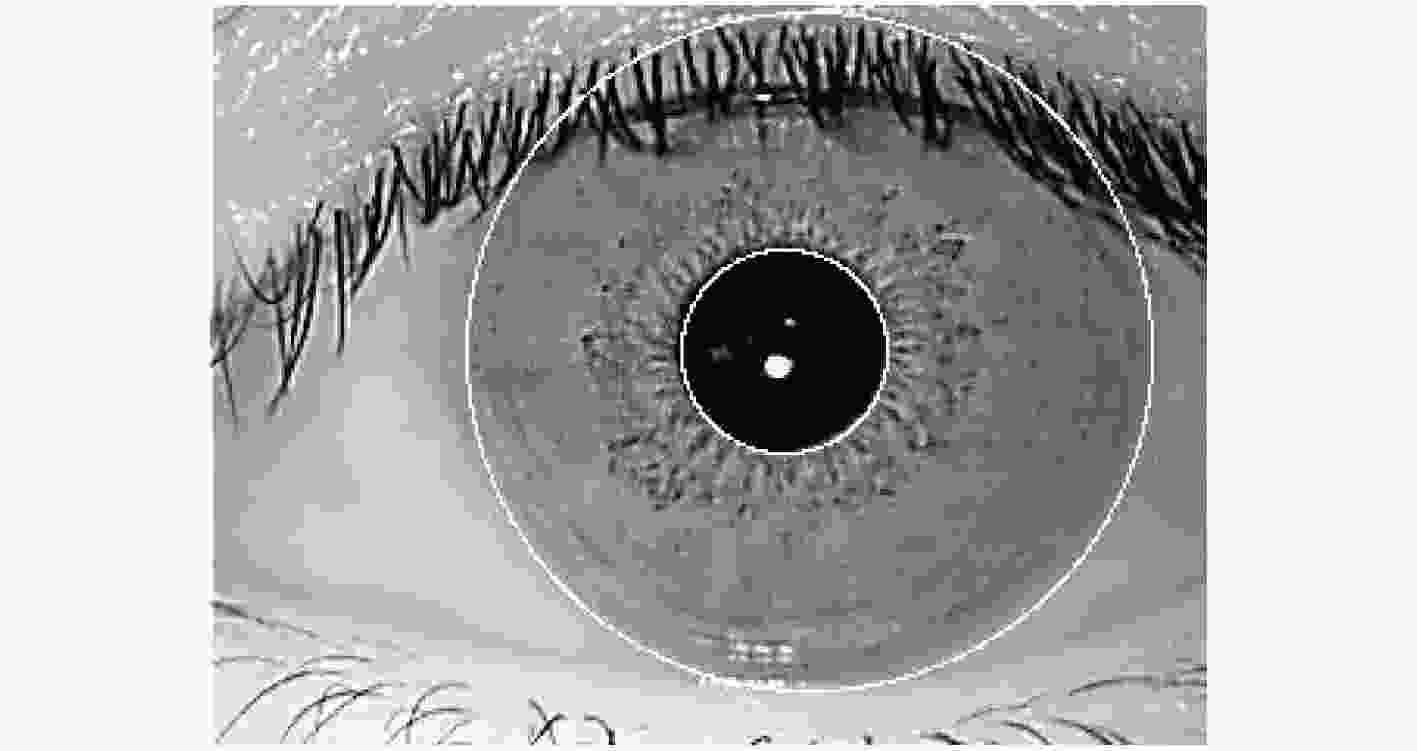
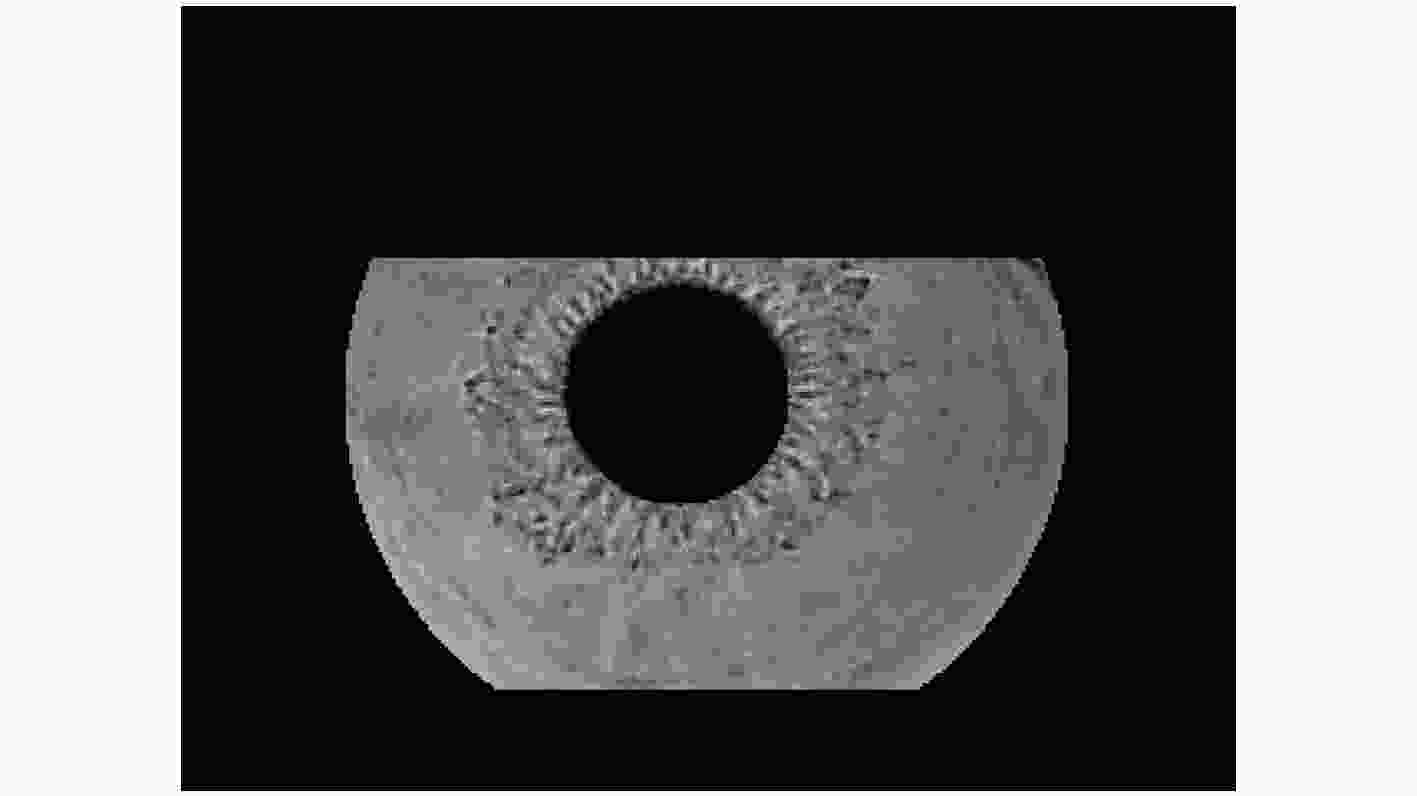
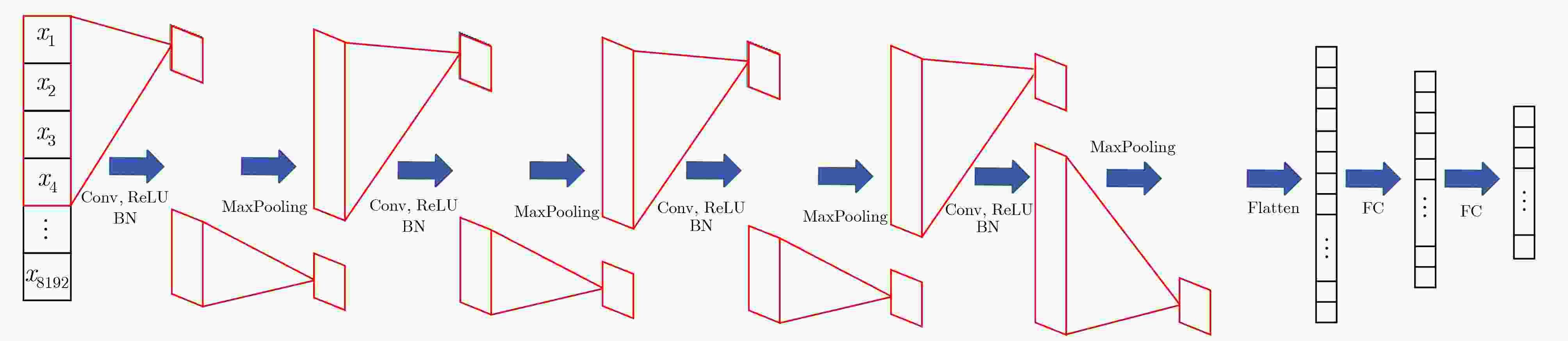
摘要: 虹膜识别面临两个重要的问题:一是如何精细分解与重构虹膜球面图像;二是如何识别虹膜图特征。虹膜表面几何位置信息是一种重要的信号,传统的虹膜识别通常使用虹膜图像的平面特征,然而人的眼睛是一种球体,从平面图像难以提取到虹膜球体的几何特征。针对平面特征容易出现虹膜纹理的扭曲和失真等问题,该文建议一种正交对称的球面Haar小波(OSSHW)基,对球面虹膜信号进行多尺度分解与重构,获得更精细的虹膜曲面几何特征,同时对比球谐函数和半正交或正交球面Haar小波基的虹膜球面信号特征提取能力。在此基础上,该文提出一种基于卷积神经网络(CNN)和正交对称的球面Haar小波的虹膜识别方法,它能够有效捕获虹膜球体曲面的局部精细特征,比半正交或正交球面Haar小波基具有更强的虹膜识别能力。Abstract: Iris recognition faces two important issues. they are how to decompose finely and reconstruct the spherical image of the iris, and how to identify the characteristics of the iris. Conventional iris recognition uses usually the planar features of these iris images. However, the human eye is a sphere. The geometric position information of the iris surface is an important signal, but it is difficult to extract the geometric features of the iris sphere from the planar image. Considering the issue that the plane features are prone to distortion and lack fidelity of iris texture, an Orthogonal and Symmetric Spherical Haar Wavelet (OSSHW) basis is proposed to decompose and reconstruct the spherical iris signal to obtain stronger geometric features of iris surface. The comparison of the feature extraction ability to spherical signal by the spherical harmonics and the typical semi-orthogonal or nearly orthogonal spherical Haar wavelet is also presented. And then, an iris recognition method based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) + OSSHW is proposed, which can effectively capture the local fine features of iris spherical surface, and has stronger ability in iris recognition than semi-orthogonal or nearly orthogonal spherical Haar wavelet bases.
-
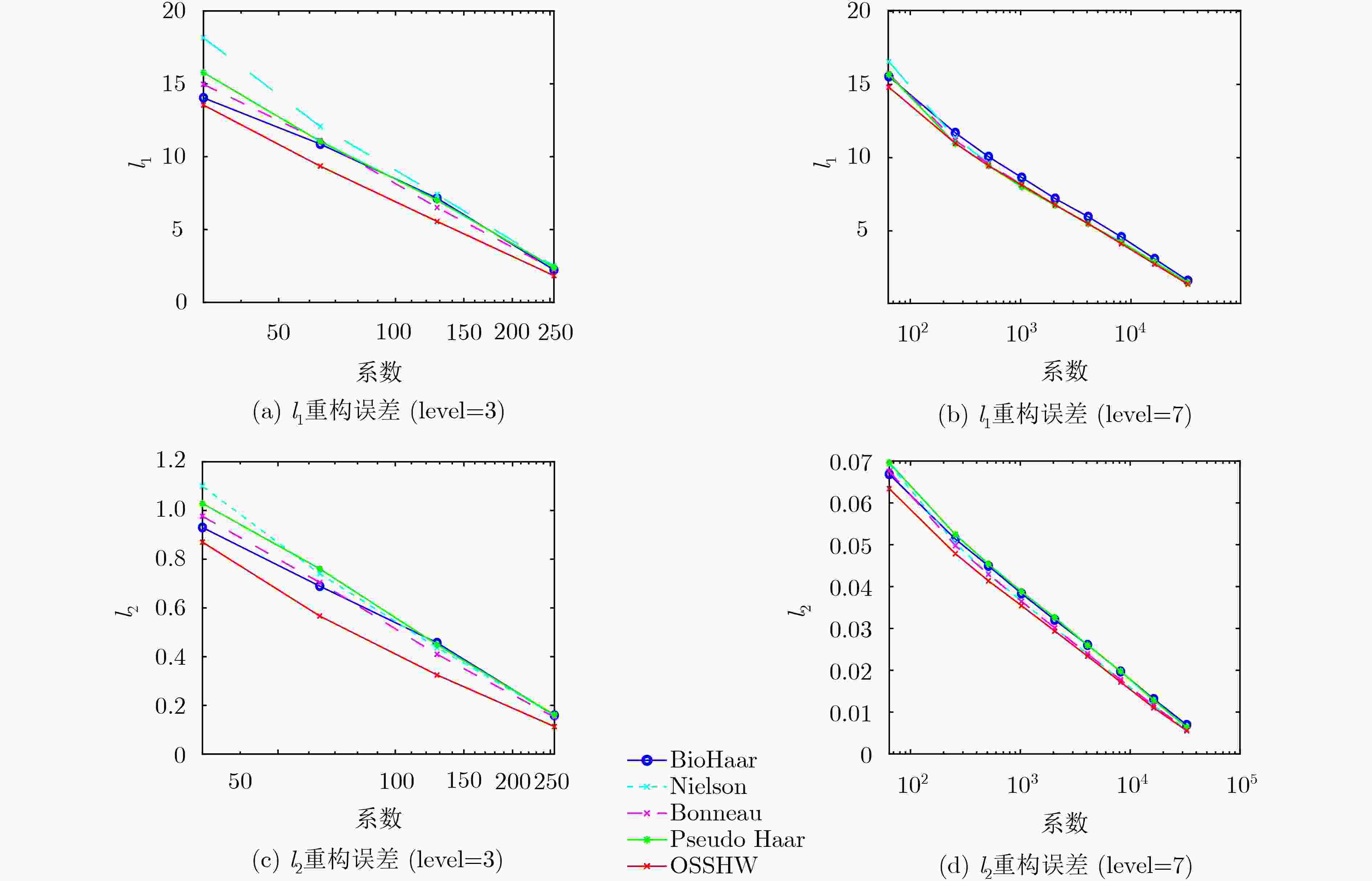
表 1 使用5种球面Haar小波基进行虹膜信号重构
$ {l}_{2} $ 误差(保留1.56%的小波系数,level=5)小波基 虹膜信号 Bio Haar Nielson Bonneau Pseudo Haar OSSHW 1 0.2671 0.2432 0.2448 0.2535 0.2282 2 0.1917 0.1744 0.1717 0.1813 0.1690 3 0.2967 0.2720 0.2716 0.2860 0.2676 4 0.2519 0.2345 0.2340 0.2446 0.2310 5 0.2636 0.2457 0.2483 0.2571 0.2432 -
MA Li, WANG Yunhong, and TAN Tieniu. Iris recognition based on multichannel Gabor filtering[C]. The 5th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Melbourne, Australia, 2002: 279–283. YAO Peng, LI Jun, YE Xueyi, et al. Iris recognition algorithm using modified log-Gabor filters[C]. The 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR’06), Hong Kong, China, 2006: 461–464. NABTI M and BOURIDANE A. An effective and fast iris recognition system based on a combined multiscale feature extraction technique[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2008, 41(3): 868–879. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2007.06.030 PROENÇA H and SANTOS G. Fusing color and shape descriptors in the recognition of degraded iris images acquired at visible wavelengths[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2012, 116(2): 167–178. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2011.10.008 SANTOS G and HOYLE E. A fusion approach to unconstrained iris recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2012, 33(8): 984–990. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2011.08.017 TAN Tieniu, ZHANG Xiaobo, SUN Zhenan, et al. Noisy iris image matching by using multiple cues[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2012, 33(8): 970–977. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2011.08.009 HUO Guang, LIU Yuanning, ZHU Xiaodong, et al. Secondary iris recognition method based on local energy-orientation feature[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2015, 24(1): 013033. doi: 10.1117/1.JEI.24.1.013033 KUMAR A, POTNIS A, and SINGH A. Iris recognition and feature extraction in iris recognition system by employing 2D DCT[J]. IRJET International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2016, 3(12): 503–510. 刘元宁, 刘帅, 朱晓冬, 等. 基于特征加权融合的虹膜识别算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(1): 221–229.LIU Yuanning, LIU Shuai, ZHU Xiaodong, et al. Iris recognition algorithm based on feature weighted fusion[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Engineering and Technology Edition, 2019, 49(1): 221–229. OUYANG Wanli, ZHAO Tianle, CHAM W K, et al. Fast full-search-equivalent pattern matching using asymmetric haar wavelet packets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2016, 28(4): 819–833. doi: 10.1109/tcsvt.2016.2629621 WU E Q, ZHOU Guirong, ZHU Limin, et al. Rotated sphere haar wavelet and deep contractive auto-encoder network with fuzzy Gaussian SVM for pilot’s pupil center detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 51(1): 332–345. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2886012 XU Guangzhu, ZHANG Zaifeng, and MA Yide. A novel method for iris feature extraction based on intersecting cortical model network[J]. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computing, 2018, 26(1/2): 341–352. ALOYSIUS N and GEETHA M. A review on deep convolutional neural networks[C]. 2017 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Chennai, India, 2017: 588–592. DHAGE S S, HEGDE S S, MANIKANTAN K, et al. DWT-based feature extraction and radon transform based contrast enhancement for improved iris recognition[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2015, 45: 256–265. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2015.03.135 BHARATH B V, VILAS A S, MANIKANTAN K, et al. Iris recognition using radon transform thresholding based feature extraction with Gradient-based Isolation as a pre-processing technique[C]. The 9th International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems (ICIIS), Gwalior, India, 2014: 1–8. MINAEE S, ABDOLRASHIDI A. Deepiris: Iris recognition using a deep learning approach[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1907.09380, 2019. CHEN Ying, WANG Wenyuan, ZENG Zhuang, et al. Adapted deep convnets technology for robust iris recognition[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2019, 28(3): 033008. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
