Ship Target Recognition Based on Highly Efficient Scalable Improved Residual Structure Neural Network
-
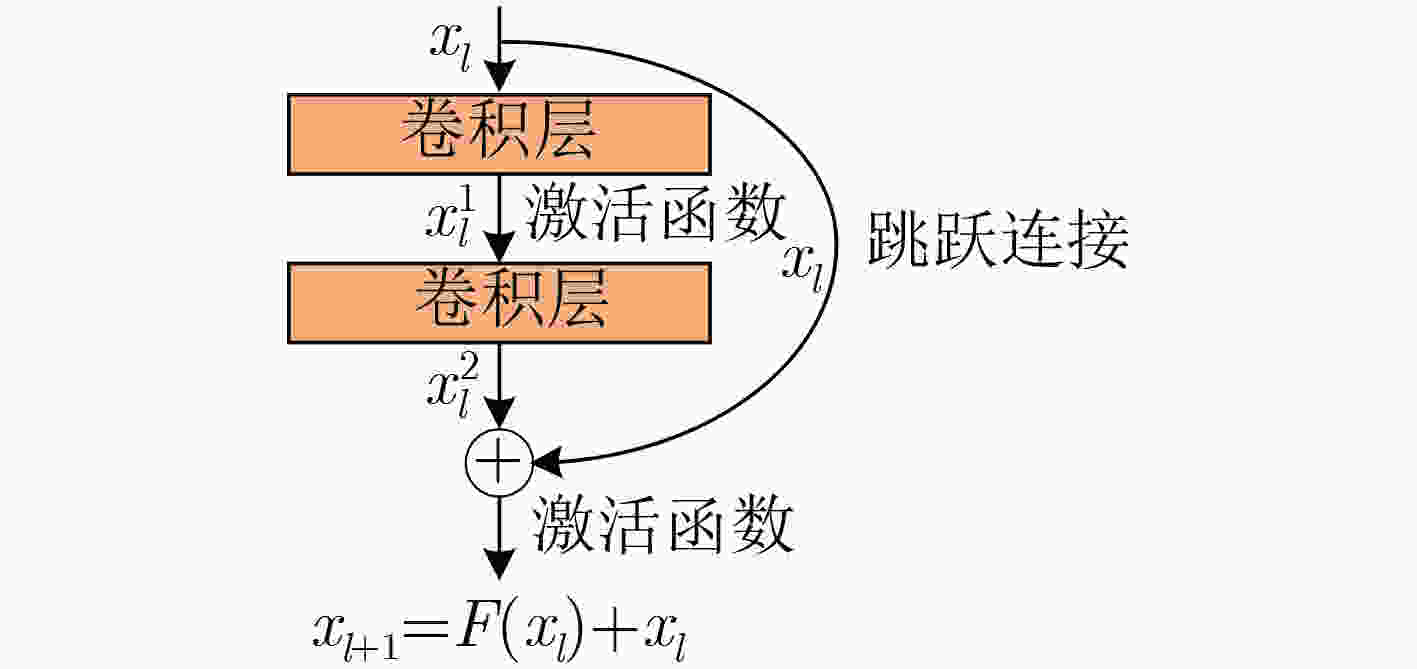
摘要: 神经网络的深度在一定范围内与识别效果成正相关,为解决超出范围后网络层数增加识别准确率却下降的模型饱和问题,该文提出一种具有高效的微块内部结构和残差网络结构的神经网络模型,用于对舰船目标基于高分辨距离像的分类识别。该方法利用具有小尺度卷积核的卷积模块提取目标的稳定可分特征,同时利用联合损失函数约束目标特征的类内距离提高识别能力。仿真结果表明,该模型相比于其他常见网络结构,在模型参数更少的情况下,识别效果更好,同时具有较强的噪声鲁棒性。Abstract: The depth of neural network is positively correlated with the recognition effect in a certain range. In order to solve the problem that model recognition accuracy decreases when the number of network layers increases after exceeding the range. A neural network model with efficient micro internal blocks structure and residual network structure is proposed, which is used for recognition of ship targets based on High Range Resolution Profile (HRRP) data. In this method, the convolution module with a small scale convolution kernel is used to extract automatically the stable and separable features of target. And the intra-class distance of the target is constrained by the joint loss function to improve the recognition ability. Simulation results show that compared with other common network structures, this model has better recognition performance and stronger noise robustness with fewer model parameters.
-
表 1 模型A各阶段参数情况
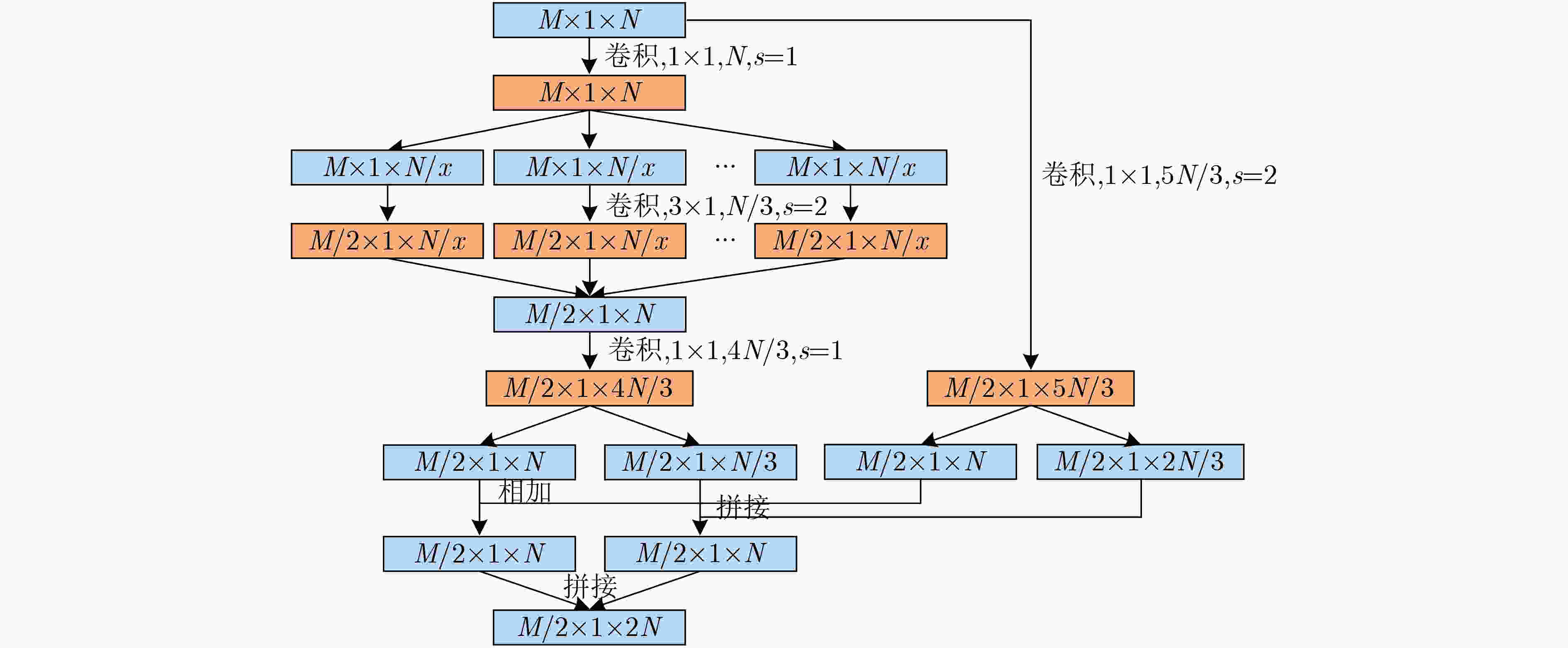
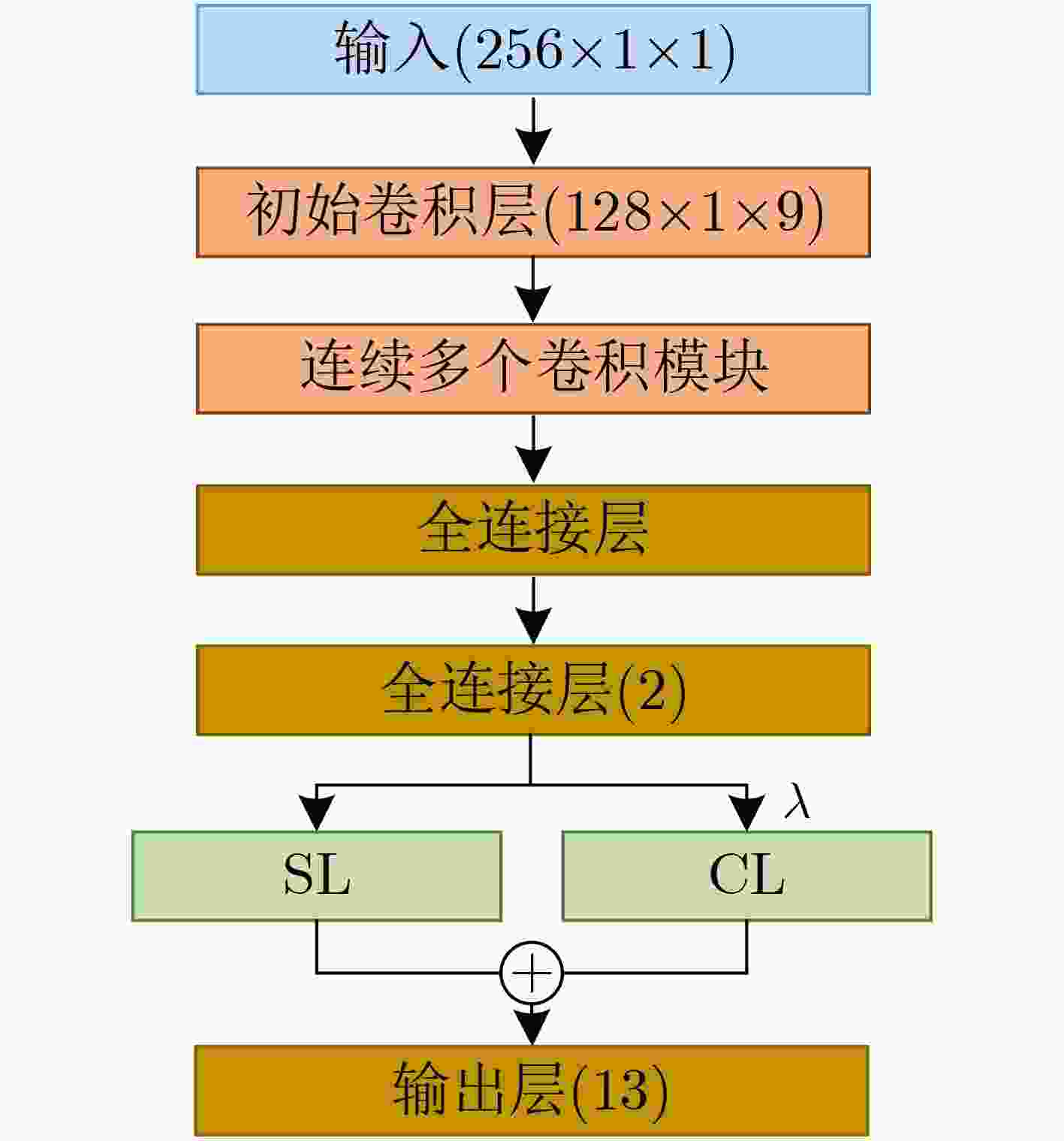
阶段 输出 结构 参数个数 初始卷积层 128×1×9 7×1, 9, s=2 99 左侧支路 右侧支路 卷积模块1 64×1×18 1×1, 9
3×1, 3, s=2, x=3
1×1, 121×1, 15, s=2 585 卷积模块2 32×1×36 1×1, 18
3×1, 6, s=2, x=3
1×1, 241×1, 30, s=2 1980 卷积模块3 16×1×72 1×1, 36
3×1, 12, s=2, x=3
1×1, 481×1, 60, s=2 7200 卷积模块4 8×1×144 1×1, 72
3×1, 24, s=2, x=3
1×1, 961×1, 120, s=2 27360 全连接层1 144 全局平均池化+全局最大值池化 0 全连接层2 2 288 输出层 13 SL+CL 26 参数总数 37538 表 2 不同复杂度模型在不同信噪比数据集下的识别准确率(%)
模型名称 识别时间(μs) 信噪比(dB) 0 5 10 15 模型A 258 60.42 89.41 98.21 99.83 模型B 326 72.95 94.41 99.15 99.89 模型C 323 73.78 93.71 99.07 99.86 表 3 CNN模型结构和参数明细
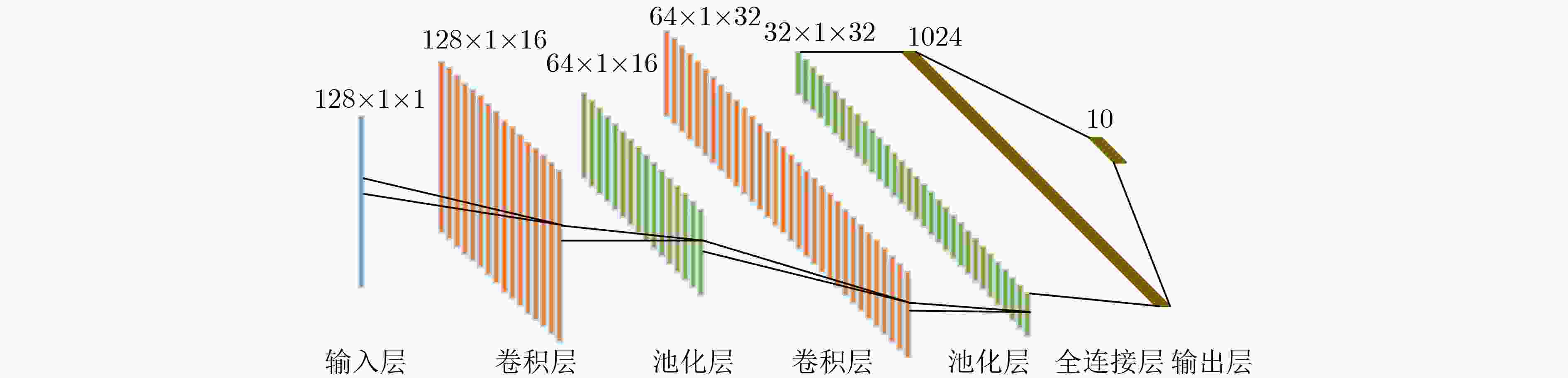
阶段 输出维度 网络结构 参数个数 卷积层1 256×1×8 3×1, 8, s=1 64 池化层1 128×1×8 2×1, s=2 0 卷积层2 128×1×16 3×1, 16, s=1 464 池化层2 64×1×16 2×1, s=2 0 卷积层3 64×1×32 3×1, 32, s=1 1696 池化层3 32×1×32 2×1, s=2 0 卷积层4 32×1×64 3×1, 64, s=1 6464 池化层4 16×1×64 2×1, s=2 0 卷积层5 16×1×64 1×1, 64, s=1 4416 池化层5 8×1×64 2×1, s=2 0 全连接层1 64 32832 全连接层2 2 130 输出层 13 SL 39 参数总数 46105 表 4 SDSAE&KNN模型结构和参数明细
阶段 输出维度 参数个数 隐藏层1 150×1 38550 隐藏层2 100×1 15100 隐藏层3 50×1 5050 隐藏层4 10×1 510 参数总数 59210 表 5 SCAE模型结构和参数明细
阶段 输出维度 网络结构 参数个数 卷积层1 256×1×128 5×1, 128, s=1 768 池化层1 128×1×128 2×1, s=2 0 卷积层2 128×1×64 5×1, 64, s=1 41024 池化层2 64×1×64 2×1, s=2 0 卷积层3 64×1×32 3×1, 32, s=1 6176 池化层3 32×1×32 2×1, s=2 0 卷积层4 32×1×16 3×1, 16, s=1 1552 池化层4 16×1×16 2×1, s=2 0 卷积层5 16×1×8 1×1, 8, s=1 136 池化层5 8×1×8 2×1, s=2 0 输出层 13 SL 845 参数总数 50501 表 6 不同信噪比条件下本节模型与对比模型识别准确率(%)
模型名称 识别时间(μs) 信噪比(dB) 0 5 10 15 模型A 258 60.42 89.41 98.21 99.83 CNN 69 58.22 86.91 95.51 98.79 SCAE 47 54.78 86.58 94.44 98.78 SDSAE&KNN 68 46.50 83.94 93.44 98.65 -
魏存伟, 段发阶, 刘先康. 基于宽带雷达HRRP舰船目标长度估计算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(9): 1960–1965. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.09.10WEI Cunwei, DUAN Fajie, and LIU Xiankang. Length estimation method of ship target based on wide-band radar’s HRRP[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(9): 1960–1965. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.09.10 贺思三, 赵会宁, 张永顺. 基于时频域联合滤波的中段群目标信号分离[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(5): 545–551. doi: 10.12000/JR15008HE Sisan, ZHAO Huining, and ZHANG Yongshun. Signal separation for target group in midcourse based on time-frequency filtering[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(5): 545–551. doi: 10.12000/JR15008 吴佳妮, 陈永光, 代大海, 等. 基于快速密度搜索聚类算法的极化HRRP分类方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(10): 2461–2467. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151457WU Jiani, CHEN Yongguang, DAI Dahai, et al. Target recognition for polarimetric HRRP based on fast density search clustering method[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(10): 2461–2467. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151457 李建伟, 曲长文, 彭书娟, 等. 基于生成对抗网络和线上难例挖掘的SAR图像舰船目标检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(1): 143–149. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180050LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, PENG Shujuan, et al. Ship detection in SAR images based on generative adversarial network and online hard examples mining[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(1): 143–149. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180050 杜兰, 魏迪, 李璐, 等. 基于半监督学习的SAR目标检测网络[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 154–163. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190783DU Lan, WEI Di, LI Lu, et al. SAR target detection network via semi-supervised learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 154–163. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190783 罗会兰, 卢飞, 孔繁胜. 基于区域与深度残差网络的图像语义分割[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(11): 2777–2786. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190056LUO Huilan, LU Fei, and KONG Fansheng. Image semantic segmentation based on region and deep residual network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(11): 2777–2786. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190056 XING Shihong and ZHANG Shaokang. Ship model recognition based on convolutional neural networks[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Changchun, China, 2018: 144-148. doi: 10.1109/ICMA.2018.8484362. 杨宏宇, 王峰岩. 基于深度卷积神经网络的气象雷达噪声图像语义分割方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(10): 2373–2381. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190098YANG Hongyu and WANG Fengyan. Meteorological radar noise image semantic segmentation method based on deep convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(10): 2373–2381. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190098 王鑫, 李可, 宁晨, 等. 基于深度卷积神经网络和多核学习的遥感图像分类方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1098–1105. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180628WANG Xin, LI Ke, NING Chen, et al. Remote sensing image classification method based on deep convolution neural network and multi-kernel learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1098–1105. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180628 郭晨, 简涛, 徐从安, 等. 基于深度多尺度一维卷积神经网络的雷达舰船目标识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(6): 1302–1309. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180677GUO Chen, JIAN Tao, XU Congan, et al. Radar HRRP target recognition based on deep multi-scale 1D convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(6): 1302–1309. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180677 王容川, 庄志洪, 王宏波, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的雷达目标HRRP分类识别方法[J]. 现代雷达, 2019, 41(5): 33–38. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.05.007WANG Rongchuan, ZHUANG Zhihong, WANG Hongbo, et al. HRRP classification and recognition method of radar target based on convolutional neural network[J]. Modern Radar, 2019, 41(5): 33–38. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.05.007 刘兴旺. 一种多层预训练卷积神经网络在图像识别中的应用[D]. [硕士论文], 中南民族大学, 2018.LIU Xingwang. The application of a multi-layers pre-training convolutional neural network in image recognition[D]. [Master dissertation], South-Central University for Nationalities, 2018. 赵飞翔, 刘永祥, 霍凯. 基于栈式降噪稀疏自动编码器的雷达目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 149–156. doi: 10.12000/JR16151ZHAO Feixiang, LIU Yongxiang, and HUO Kai. Radar target recognition based on stacked denoising sparse autoencoder[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 149–156. doi: 10.12000/JR16151 KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Red Hook, United States, 2012: 1097–1105. SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, United States, 2015: 1–14. HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, United States, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. SZEGEDY C, IOFFE S, VANHOUCKE V, et al. Inception-v4, inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]. The 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, United States, 2017: 4278–4284. WEN Yandong, ZHANG Kaipeng, LI Zhifeng, et al. A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 499–515. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46478-7_31. -





 下载:
下载:
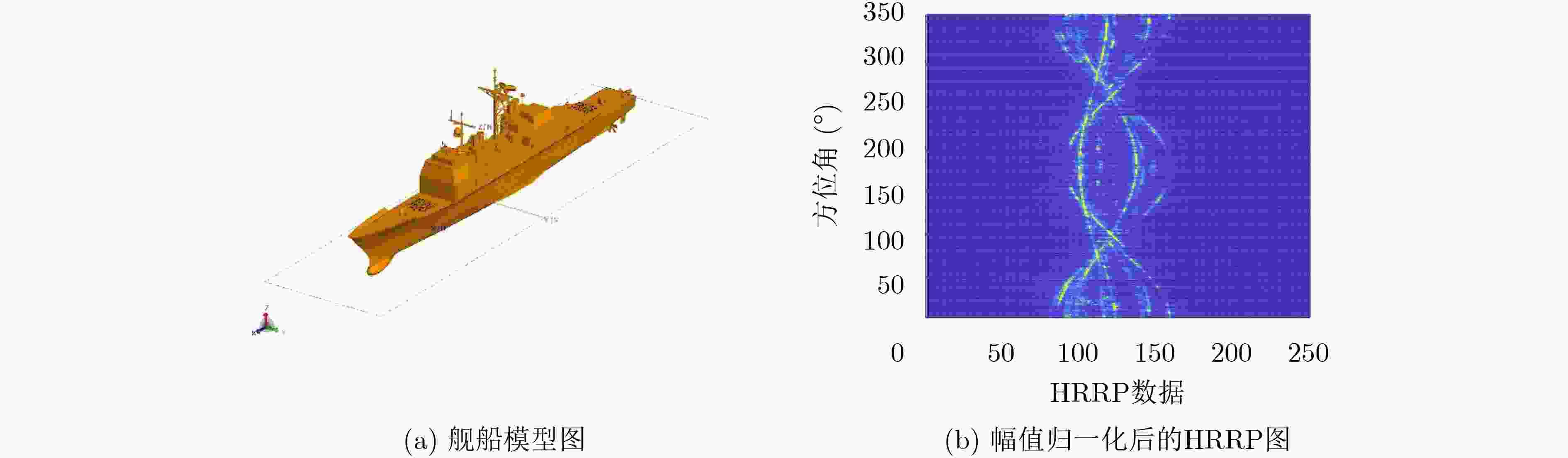
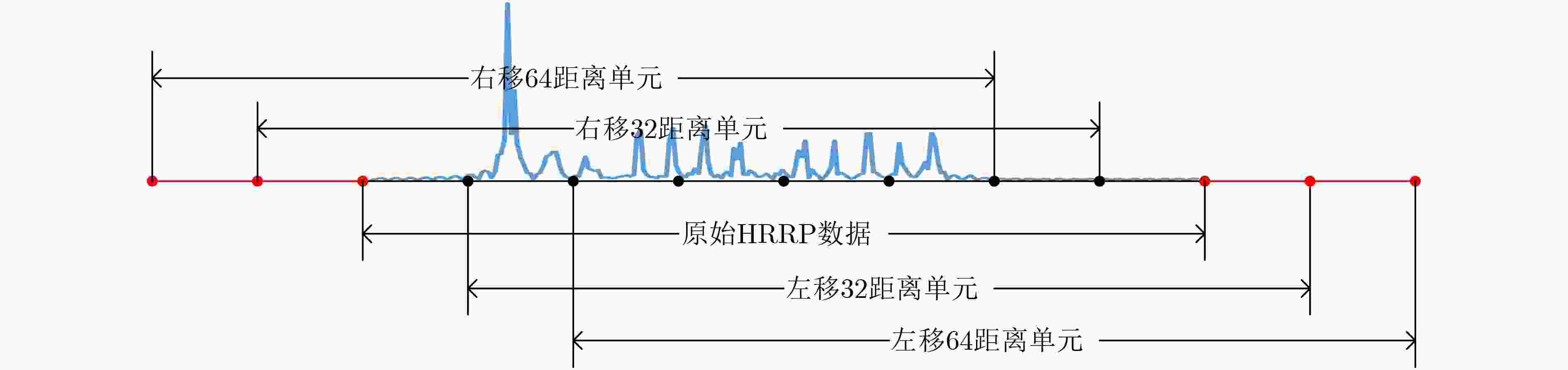
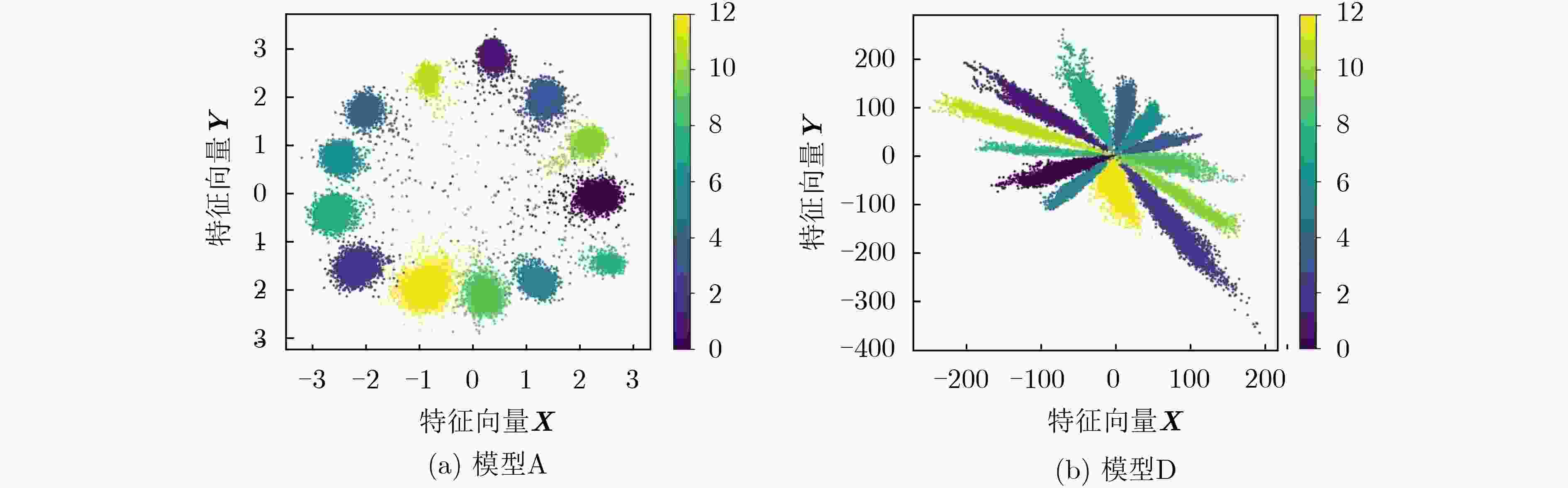


 下载:
下载:
