Cryptographic Approaches for Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning
-
摘要: 新一代人工智能技术的特征,表现为借助GPU计算、云计算等高性能分布式计算能力,使用以深度学习算法为代表的机器学习算法,在大数据上进行学习训练,来模拟、延伸和扩展人的智能。不同数据来源、不同的计算物理位置,使得目前的机器学习面临严重的隐私泄露问题,因此隐私保护机器学习(PPM)成为目前广受关注的研究领域。采用密码学工具来解决机器学习中的隐私问题,是隐私保护机器学习重要的技术。该文介绍隐私保护机器学习中常用的密码学工具,包括通用安全多方计算(SMPC)、隐私保护集合运算、同态加密(HE)等,以及应用它们来解决机器学习中数据整理、模型训练、模型测试、数据预测等各个阶段中存在的隐私保护问题的研究方法与研究现状。Abstract: The characteristics of the new generation of artificial intelligence technology are shown as follows: with the help of GPU computing, cloud computing and other high-performance distributed computing capabilities, machine learning algorithms represented by deep learning algorithms are used for learning and training on big data to simulate, extend and expand human intelligence. Different data sources and computing physical locations make the current machine learning face serious privacy leakage problem, so the Privacy Protection of Machine (PPM) Learning has become a widely concerned research area. Using cryptography technology to solve the problem of privacy in machine learning is an important technology to protect the privacy of machine learning. Cryptographic tools used in privacy-preserving machine learning are introduced, such as general Secure Multi-Party Computing (SMPC), privacy protection set operation and Homomorphic Encryption (HE), describes the status and developments applying the tools to solving the problems of privacy protection in various stages of machine learning, such as data processing, model training, model testing, and data prediction.
-
表 1 MiniONN效率实验结果
数据集 MNIST CIFAR10 精确度(%) 99.52 91.5 运行时间(s) 320 11686 数据传输(MB) 336.7 1803 #p/h 163840 2524 表 2 文献[42]效率分析
通信 计算 存储 用户端 $O\left( {\left( {\lambda + \mu } \right)m + nr} \right)$ $O\left( {m{ {\left( {\lg\left( m \right)} \right)}^2} + \left( {l + 1} \right) \cdot c\left( {r,n} \right)} \right)$ $O\left( {4k\lambda + \mu \left( {m + 3\left\lceil {\dfrac{l}{2} } \right\rceil } \right) + nr} \right)$ 服务器端 $O\left( { {m^2}\mu + nmr + \dfrac{ {ml} }{2} } \right)$ $O\left( {{m^2} + \left( {m - \zeta } \right) \cdot l \cdot c\left( {r,n} \right)} \right)$ $O\left( {mnr + {m^2}\mu + \dfrac{ {ml\mu } }{2} } \right)ght)$ -
YAO A C. Protocols for secure computations[C]. The 23rd Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Chicago, USA, 1982: 160–164. YAO A C C. How to generate and exchange secrets[C]. The 27th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Toronto, Canada, 1986: 162–167. GOLDREICH O, MICALI S, and WIGDERSON A. How to play ANY mental game[C]. The 19th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, New York, USA, 1987: 218–229. BEN-OR M, GOLDWASSER S, and WIGDERSON A. Completeness theorems for non-cryptographic fault-tolerant distributed computation[C]. The 20th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Chicago, USA, 1988: 1–10. 蒋瀚, 徐秋亮. 实用安全多方计算协议关键技术研究进展[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2015, 52(10): 2247–2257. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2015.20150763JIANG Han and XU Qiuliang. Advances in key techniques of practical secure multi-party computation[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2015, 52(10): 2247–2257. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2015.20150763 BEAVER D. Efficient multiparty protocols using circuit randomization[C]. Annual International Cryptology Conference, Santa Barbara, USA, 1992: 420–432. BENDLIN R, DAMGÅRD I, ORLANDI C, et al. Semi-homomorphic encryption and multiparty computation[C]. The 30th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Tallinn, Estonia, 2011: 169–188. DAMGÅRD I, PASTRO V, SMART N, et al. Multiparty computation from somewhat homomorphic encryption[C]. The 32nd Annual International Cryptology Conference, Santa Barbara, USA, 2012: 643–662. PAILLIER P. Public-key cryptosystems based on composite degree residuosity classes[C]. International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Prague, Czech Republic, 1999: 223–238. GENTRY C. A fully homomorphic encryption scheme[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Stanford University, 2009. VAN DIJK M, GENTRY C, HALEVI S, et al. Fully homomorphic encryption over the integers[C]. The 29th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, French Riviera, France, 2010: 24–43. BRAKERSKI Z, GENTRY C, and VAIKUNTANATHAN V. (Leveled) fully homomorphic encryption without bootstrapping[J]. ACM Transactions on Computation Theory, 2014, 6(3): No.13. DUCAS L and MICCIANCIO D. FHEW: Bootstrapping homomorphic encryption in less than a second[C]. The 34th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Sofia, Bulgaria, 2015: 617–640. 孙茂华, 胡磊, 朱洪亮, 等. 布尔电路上保护隐私集合并集运算的研究与实现[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(6): 1412–1418. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150911SUN Maohua, HU Lei, ZHU Hongliang, et al. Research and implementation of privacy preserving set union in Boolean circuits[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(6): 1412–1418. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150911 KOLESNIKOV V, KUMARESAN R, ROSULEK M, et al. Efficient batched oblivious PRF with applications to private set intersection[C]. 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Vienna, Austria, 2016: 818–829. KOLESNIKOV V, ROSULEK M, TRIEU N, et al. Scalable private set union from symmetric-key techniques[EB/OL]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2019/776, 2019. BARNI M, ORLANDI C, and PIVA A. A privacy-preserving protocol for neural-network-based computation[C]. The 8th Workshop on Multimedia and Security, Geneva, Switzerland, 2006: 146–151. ORLANDI C, PIVA A, and BARNI M. Oblivious neural network computing via homomorphic encryption[J]. EURASIP Journal on Information Security, 2007, 2007(1): 037343. doi: 10.1186/1687-417X-2007-037343 GRAEPEL T, LAUTER K, and NAEHRIG M. ML confidential: Machine learning on encrypted data[C]. The 15th International Conference on Information Security and Cryptology, Seoul, Korea, 2012: 1–21. ZHANG Qingchen, YANG L T, and CHEN Zhikui. Privacy preserving deep computation model on cloud for big data feature learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2016, 65(5): 1351–1362. doi: 10.1109/TC.2015.2470255 HESAMIFARD E, TAKABI H, GHASEMI M, et al. Privacy-preserving machine learning in cloud[C]. 2017 ACM Cloud Computing Security Workshop, Dallas, USA, 2017: 39–43. ROUHANI B D, RIAZI M S, and KOUSHANFAR F. DeepSecure: Scalable provably-secure deep learning[C]. The 55th ACM/ESDA/IEEE Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2018: 1–6. NIKOLAENKO V, WEINSBERG U, IOANNIDIS S, et al. Privacy-preserving ridge regression on hundreds of millions of records[C]. 2013 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, Berkeley, USA, 2013: 334–348. MOHASSEL P and ZHANG Yupeng. SecureML: A system for scalable privacy-preserving machine learning[C]. 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Jose, USA, 2017: 19–38. CHANDRAN N, GUPTA D, RASTOGI A, et al. EzPC: Programmable, efficient, and scalable secure two-party computation for machine learning[EB/OL]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2017/1109, 2017. DEMMLER D, SCHNEIDER T, and ZOHNER M. ABY-A framework for efficient mixed-protocol secure two-party computation[C]. 2015 Network and Distributed System Security, San Diego, USA, 2015: 1–15. XIE Pengtao, BILENKO M, FINLEY T, et al. Crypto-nets: Neural networks over encrypted data[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6181, 2014. DOWLIN N, GILAD-BACHRACH R, LAINE K, et al. CryptoNets: Applying neural networks to encrypted data with high throughput and accuracy[C]. The 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, USA, 2016: 201–210. BOS J W, LAUTER K, LOFTUS J, et al. Improved security for a ring-based fully homomorphic encryption scheme[C]. The 14th IMA International Conference on Cryptography and Coding, Oxford, England, 2013: 45–64. CHABANNE H, DE WARGNY A, MILGRAM J, et al. Privacy-preserving classification on deep neural network[EB/OL]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2017/035, 2017. HESAMIFARD E, TAKABI H, and GHASEMI M. CryptoDL: Deep neural networks over encrypted data[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.05189, 2017. LIU Jian, JUUTI M, LU Yao, et al. Oblivious neural network predictions via MiniONN transformations[C]. 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Dallas, USA, 2017: 619–631. COURBARIAUX M, HUBARA I, SOUDRY D, et al. Binarized neural networks: Training deep neural networks with weights and activations constrained to +1 or –1[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.02830, 2016. BOURSE F, MINELLI M, MINIHOLD M, et al. Fast homomorphic evaluation of deep discretized neural networks[C]. The 38th Annual International Cryptology Conference, Santa Barbara, USA, 2018: 483–512. SANYAL A, KUSNER M J, GASCÓN A, et al. TAPAS: Tricks to accelerate (encrypted) prediction as a service[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.03461, 2018. SADEGH RIAZI M, SAMRAGH M, CHEN Hao, et al. XONN: XNOR-based oblivious deep neural network inference[C]. The 28th USENIX Conference on Security Symposium, Santa Clara, USA, 2019: 1501–1518. MCMAHAN H B, MOORE E, RAMAGE D, et al. Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data[C]. The 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, USA, 2017: 1272–1282. KONEČNÝ J, MCMAHAN B, and RAMAGE D. Federated optimization: Distributed optimization beyond the datacenter[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.03575, 2015, KONEČNÝ J, MCMAHAN H B, YU F X, et al. Federated learning: Strategies for improving communication efficiency[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1610.05492, 2016. 杨立君, 丁超, 吴蒙. 一种同时保障隐私性与完整性的无线传感器网络可恢复数据聚合方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(12): 2808–2814. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150208YANG Lijun, DING Chao, and WU Meng. A recoverable privacy-preserving integrity-assured data aggregation scheme for wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(12): 2808–2814. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150208 BONAWITZ K, IVANOV V, KREUTER B, et al. Practical secure aggregation for privacy-preserving machine learning[C]. 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Dallas, USA, 2017: 1175–1191. MANDAL K, GONG Guang, and LIU Chuyi. NIKE-based fast privacy-preserving high-dimensional data aggregation for mobile devices[R]. CACR Technical Report, CACR 2018–10, 2018. MANDAL K and GONG Guang. PrivFL: Practical privacy-preserving federated regressions on high-dimensional data over mobile networks[EB/OL]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2019/979, 2019. -





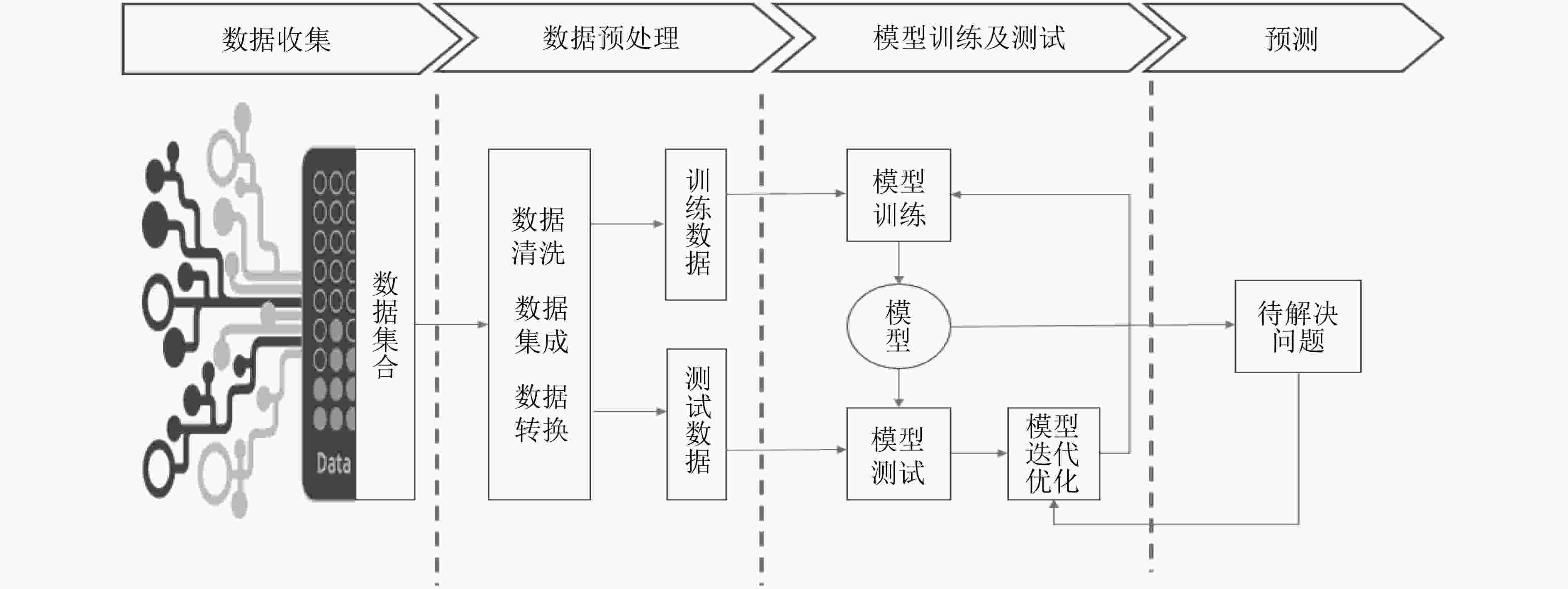
 下载:
下载:
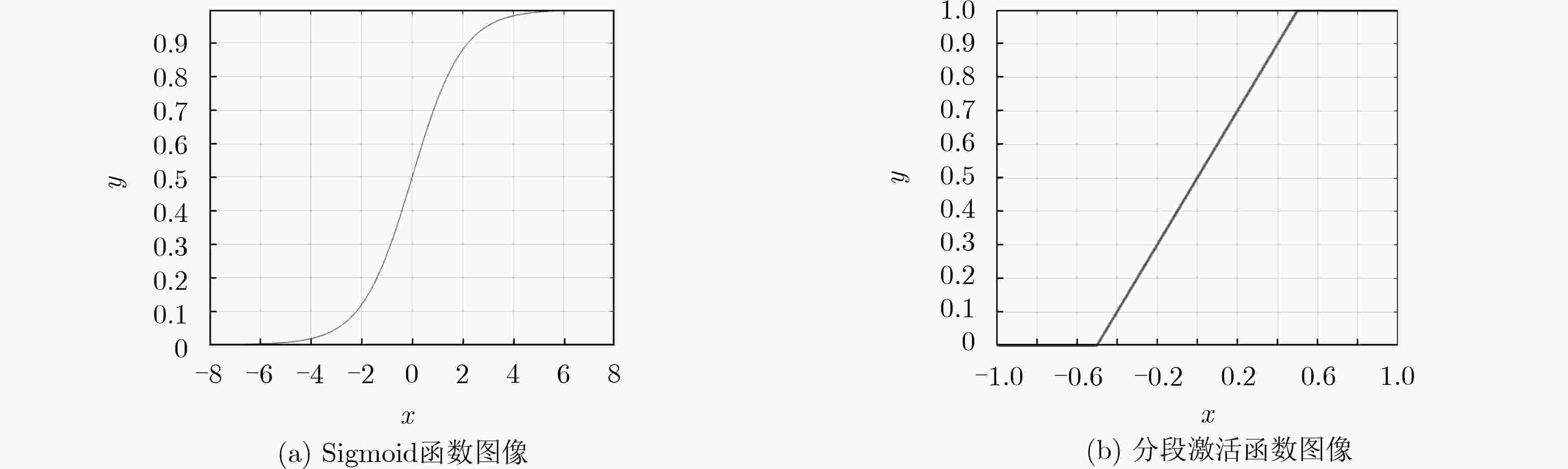
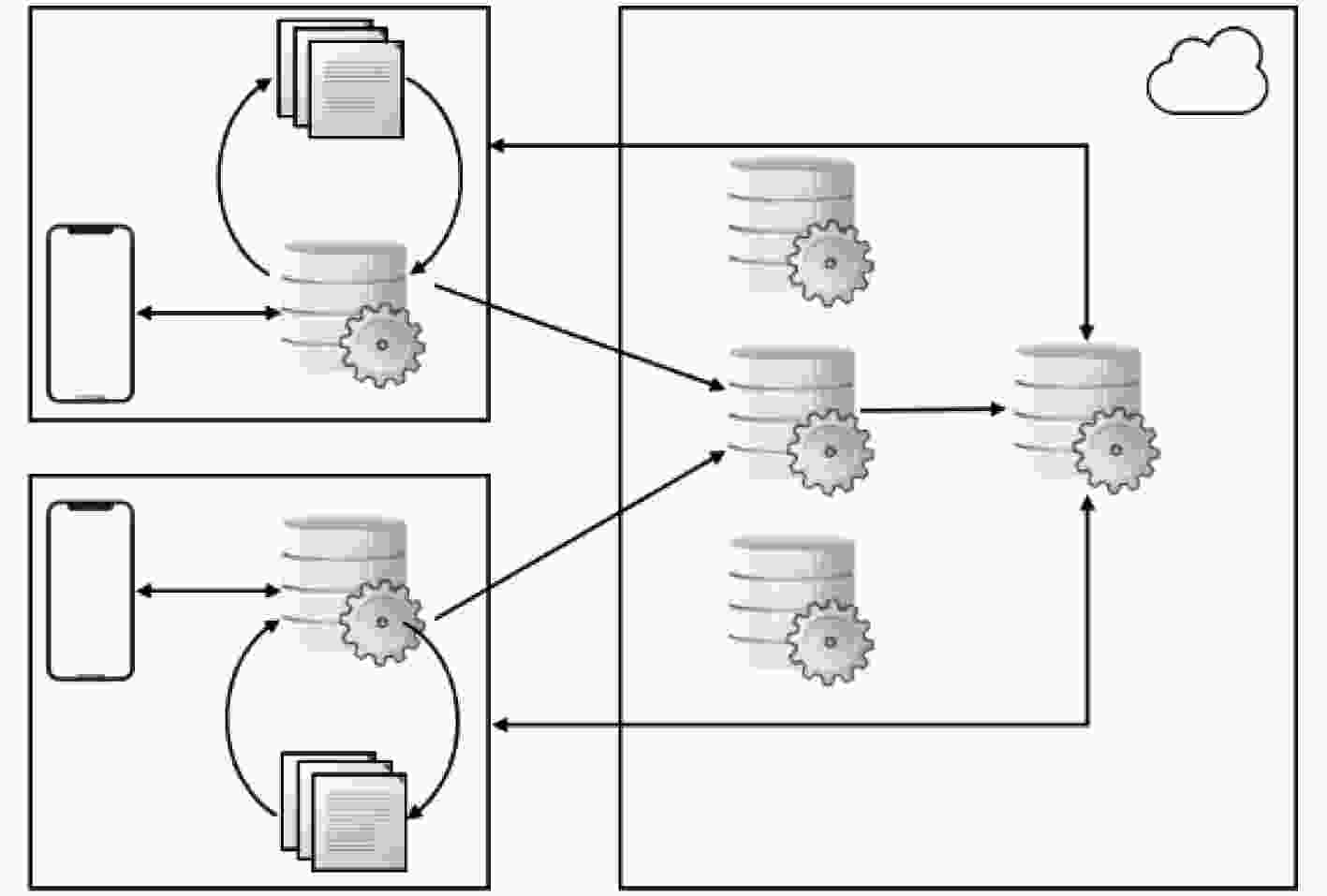



 下载:
下载:
