Molecular Circuit Design of Two-bit Gray Code Subtracter Based on DNA Strand Displacement
-
摘要: DNA链置换技术具有自发性、并行性、可编程性、动态级联性的特点,在DNA计算中占据重要的地位。DNA链置换技术被广泛的应用于解决数学问题,该文采用格雷码编码方式结合DNA链置换技术设计了两位减法器,扩展DNA减法运算。最后利用Visual DSD软件模拟两位减法器,该电路达到预期的功能,且具有并行性和可扩展性,可与其他生化电路结合使用。Abstract: DNA strand displacement technology has the characteristics of spontaneity, parallelism, programmability and dynamic cascade, which is widely used to solve mathematical problems. In this paper, a two-bit subtracter is designed by using Gray code encoding and DNA strand displacement technology to extend the operation of DNA subtraction. Finally, Visual DSD software is used to simulate the two-bit subtracter. The circuit, with the strong parallelism and expansibility, achieves the expected function. It can be used in combination with other biochemical circuits.
-
Key words:
- Molecular circuit /
- DNA strand displacement /
- Gray code /
- Subtracter
-
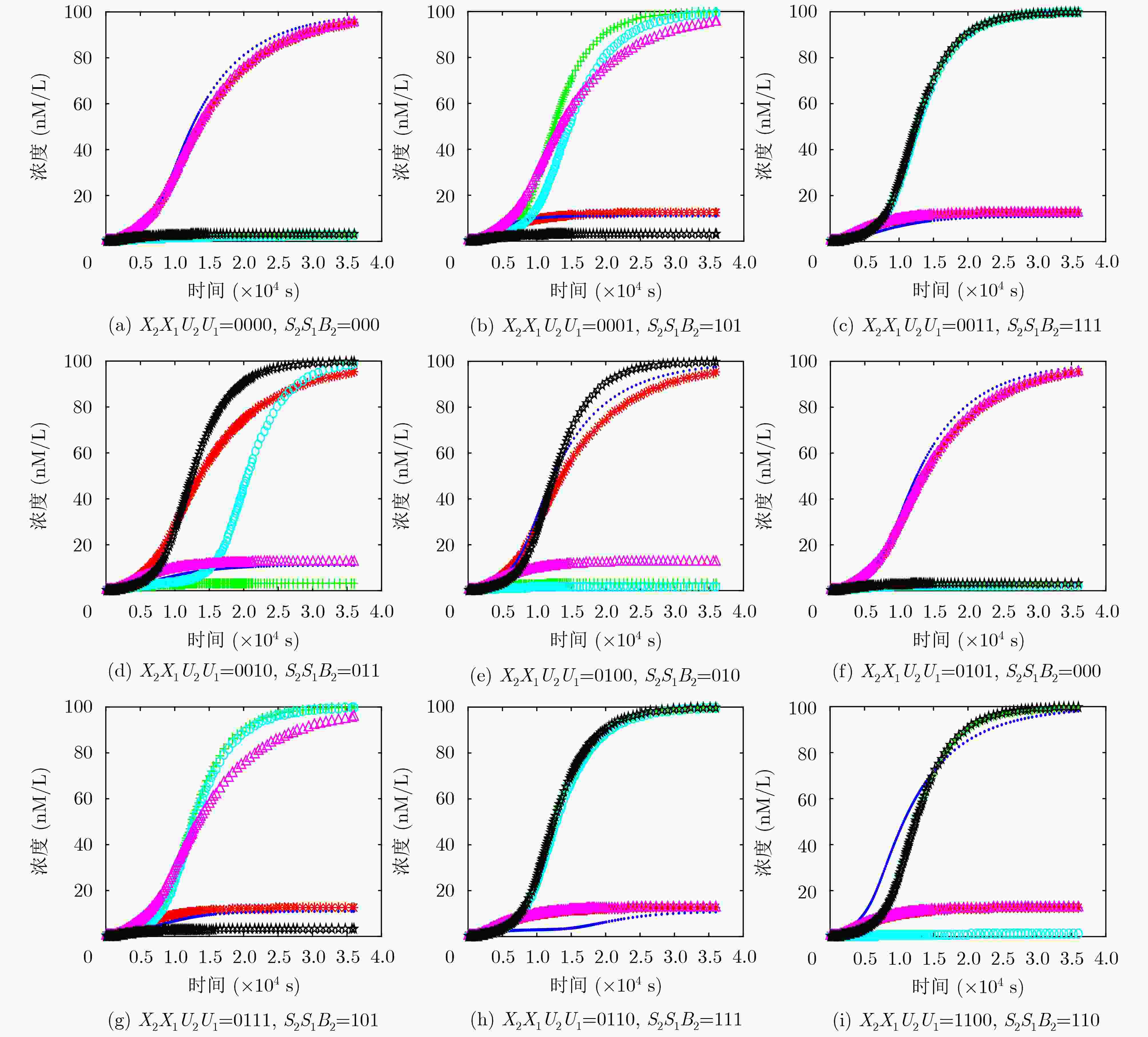
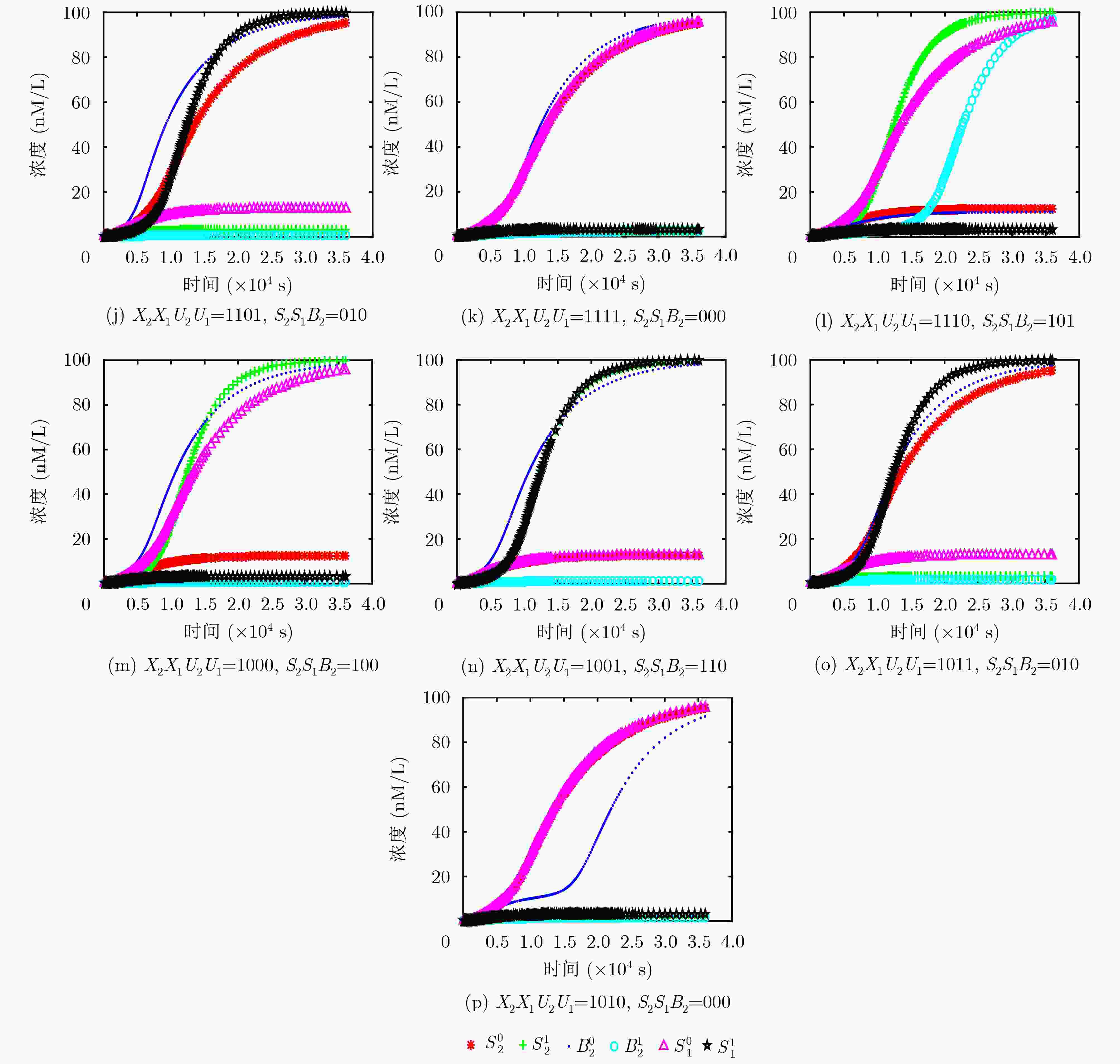
表 1 两位减法器操作运算的真值表
X2X1/减数 U2U1/被减数 S2S1/差值 B2/高位借位 X2X1/减数 U2U1/被减数 S2S1/差值 B2/高位借位 00 00 00 0 11 00 11 0 00 01 10 1 11 01 01 0 00 11 11 1 11 11 00 0 00 10 01 1 11 10 10 1 01 00 01 0 10 00 10 0 01 01 00 0 10 01 11 0 01 11 10 1 10 11 01 0 01 10 11 1 10 10 00 0 -
XU Jin, QIANG Xiaoli, CHENG Kai, et al. A DNA computing model for the graph vertex coloring problem based on a probe graph[J]. Engineering, 2018, 4(1): 61–77. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2018.02.011 SONG Tianqi, GARG S, MOKHTAR R, et al. Analog computation by DNA strand displacement circuits[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(8): 898–912. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.6b00144 THUBAGERE A J, THACHUK C, BERLEANT J, et al. Compiler-aided systematic construction of large-scale DNA strand displacement circuits using unpurified components[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 14373. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14373 ZOU Chengye, WEI Xiaopeng, ZHANG Qiang, et al. Solution of equations based on analog DNA strand displacement circuits[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nanobioscience, 2019, 18(2): 191–204. doi: 10.1109/TNB.2019.2897116 SONG Tianqi, GARG S, MOKHTAR R, et al. Design and analysis of compact DNA strand displacement circuits for analog computation using autocatalytic amplifiers[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(1): 46–53. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.6b00390 李佩佳, 石勇, 汪华东, 等. 基于有序编码的核极限学习顺序回归模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(6): 1287–1293. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170765LI Peijia, SHI Yong, WANG Huadong, et al. Ordered code-based kernel extreme learning machine for ordinal regression[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(6): 1287–1293. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170765 刘伟, 魏志刚, 杜薇, 等. 近阈值电压下可容错的末级缓存结构设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(7): 1759–1766. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170989LIU Wei, WEI Zhigang, DU Wei, et al. Fault-tolerant last level cache architecture design at near-threshold voltage[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(7): 1759–1766. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170989 KONG Jinglin, ZHU Jinbo, CHEN Kaikai, et al. Specific biosensing using DNA aptamers and nanopores[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(3): 1807555. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201807555 CUI Yunxi, FENG Xuenan, WANG Yaxin, et al. An integrated-molecular-beacon based multiple exponential strand displacement amplification strategy for ultrasensitive detection of DNA methyltransferase activity[J]. Chemical Science, 2019, 10(3): 2290–2297. doi: 10.1039/c8sc05102j LI Hua, LIU Jin, and GU Hongzhou. Targeting nucleolin to obstruct vasculature feeding with an intelligent DNA nanorobot[J]. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 2019, 23(3): 2248–2250. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14127 KIELAR C, REDDAVIDE F V, TUBBENHAUER S, et al. Pharmacophore nanoarrays on DNA origami substrates as a single-molecule assay for fragment-based drug discovery[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2018, 130(45): 15089–15093. doi: 10.1002/ange.201806778 TASCIOTTI E. Smart cancer therapy with DNA origami[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(3): 234–235. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4095 CORDEIRO M, OTRELO-CARDOSO A R, SVERGUN D I, et al. Optical and structural characterization of a chronic myeloid leukemia DNA biosensor[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2018, 13(5): 1235–1242. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.8b00029 ELBAZ J, LIOUBASHEVSKI O, WANG Fuan, et al. DNA computing circuits using libraries of DNAzyme subunits[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2010, 5(6): 417–422. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2010.88 QIAN Lulu and WINFREE E. A simple DNA gate motif for synthesizing large-scale circuits[J]. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2011, 8(62): 1281–1297. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2010.0729 QIAN Lulu, WINFREE E, and BRUCK J. Neural network computation with DNA strand displacement cascades[J]. Nature, 2011, 475(7356): 368–372. doi: 10.1038/nature10262 马丽娜, 董亚非, 张成, 等. 基于DNA链置换与荧光标记的0–1规划问题的计算模型[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2013, 43(11): 152–159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2013.11.020MA Lina, DONG Yafei, ZHANG Cheng, et al. A computing model based on DNA strand replacement/fluorescence labeling for 0–1 programming[J]. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2013, 43(11): 152–159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2013.11.020 姚莉娜, 田桂花, 叶盟盟, 等. DNA链置换技术的研究现状与展望[J]. 郑州轻工业学院学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 29(1): 15–21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-476X.2014.01.003YAO Lina, TIAN Guihua, YE Mengmeng, et al. Current situation and prospect of DNA strand displacement technology[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University of Light Industry:Natural Science, 2014, 29(1): 15–21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-476X.2014.01.003 ZOU Chengye, WEI Xiaopeng, ZHANG Qiang, et al. Four-analog computation based on DNA strand displacement[J]. ACS Omega, 2017, 2(8): 4143–4160. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.7b00572 LOPEZ R, WANG Ruofan, and SEELIG G. A molecular multi-gene classifier for disease diagnostics[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2018, 10(7): 746–754. doi: 10.1038/s41557-018-0056-1 -





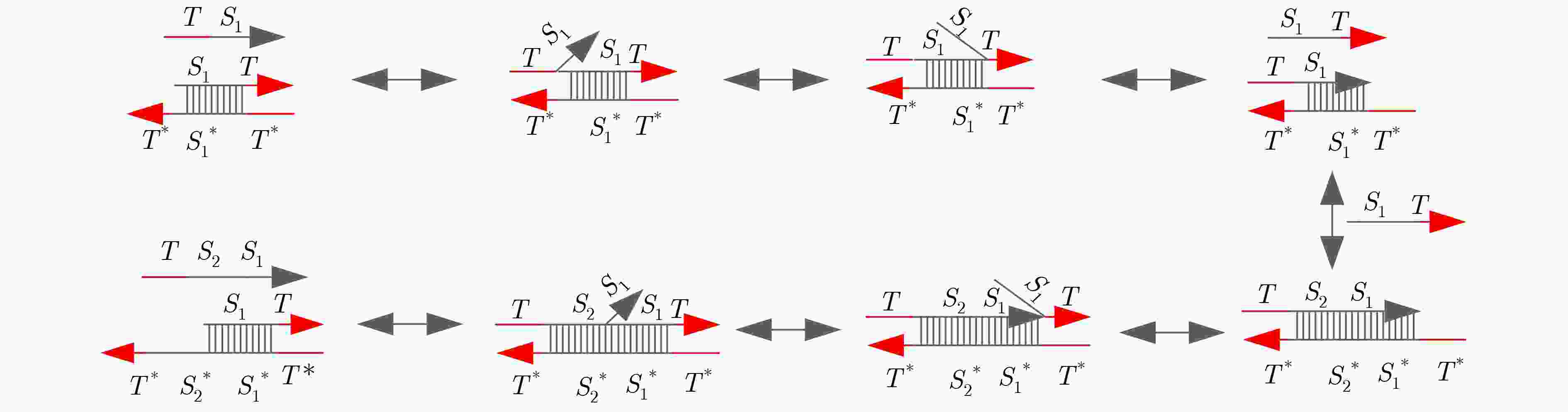
 下载:
下载:
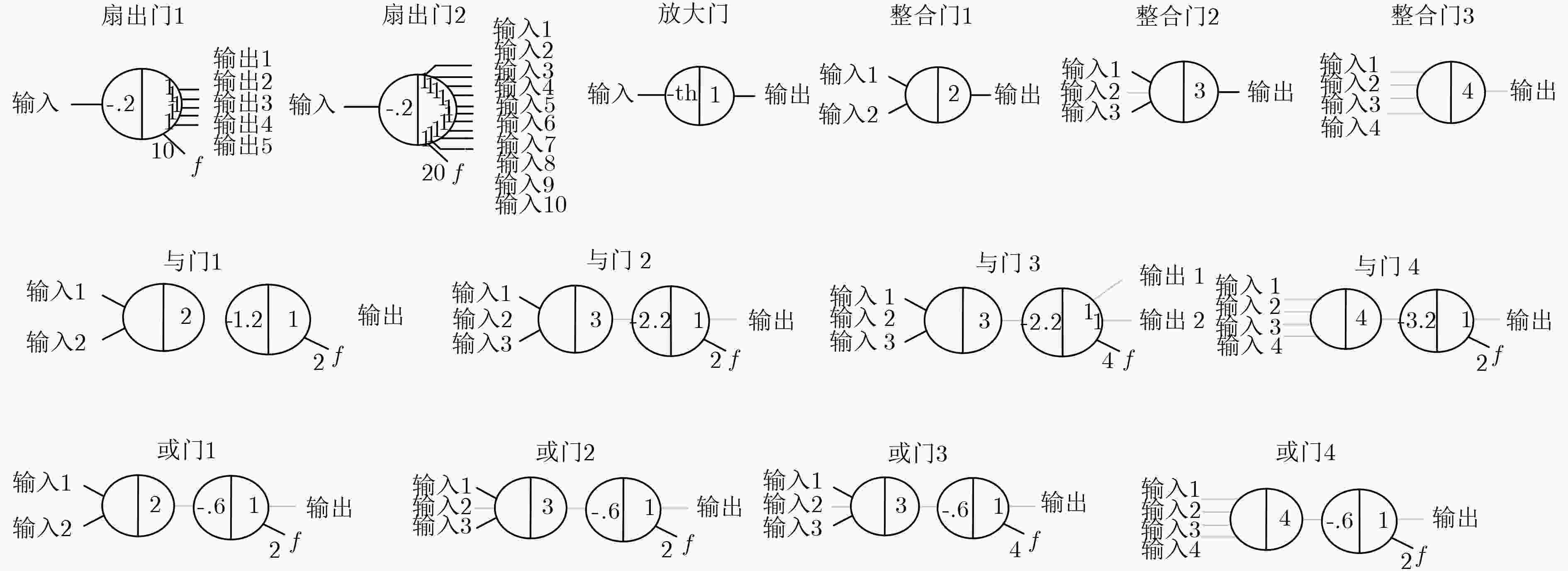
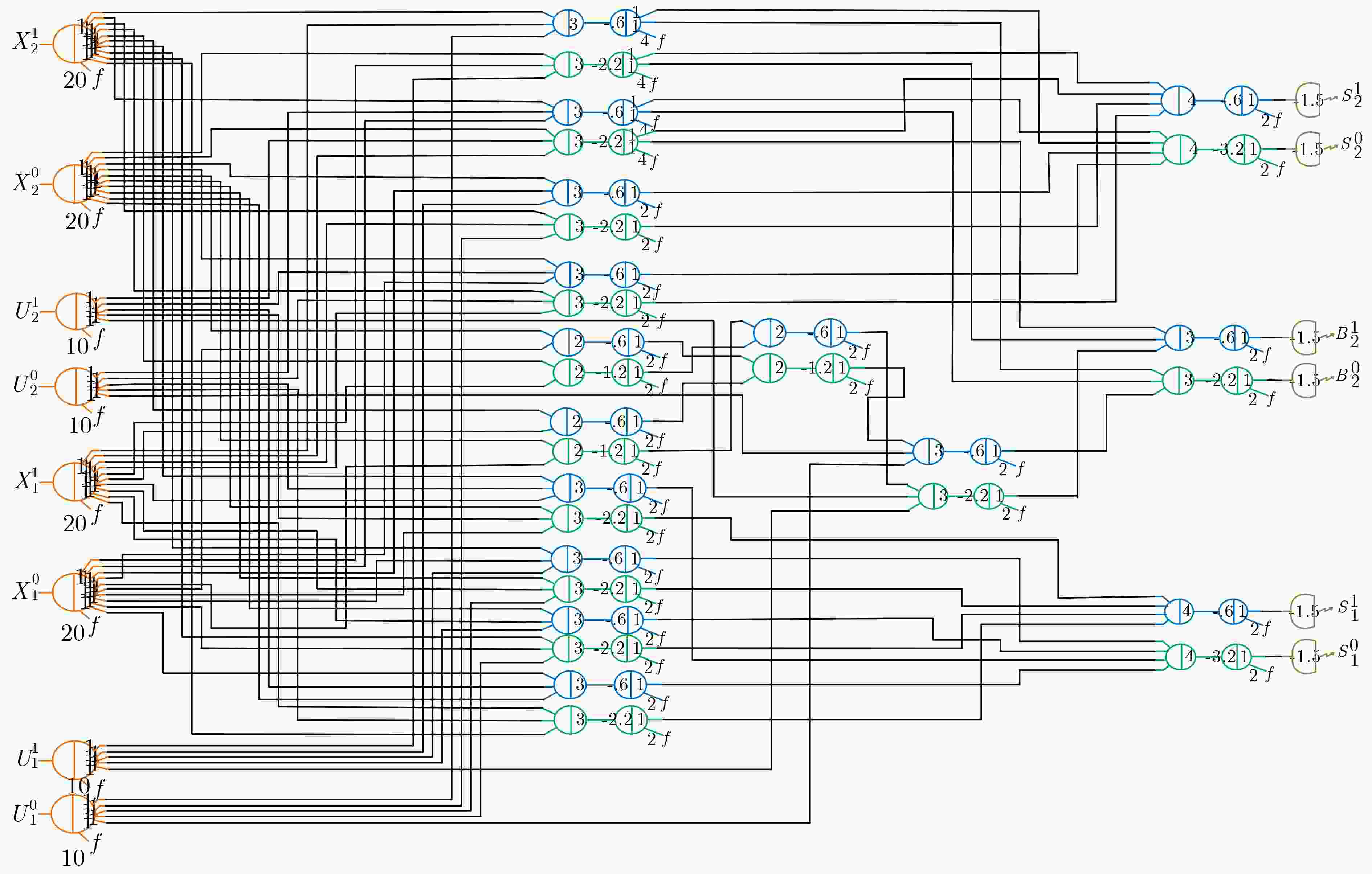
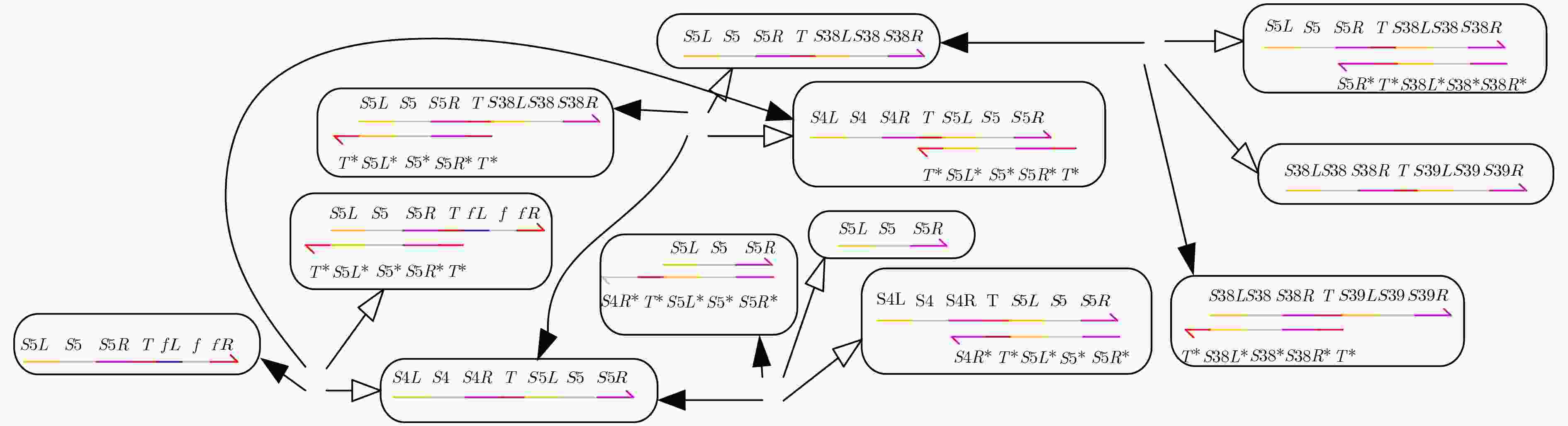


 下载:
下载:
