Analysis of Breast Cancer Subtypes Prediction Based on Alternative Splicing Disorders
-
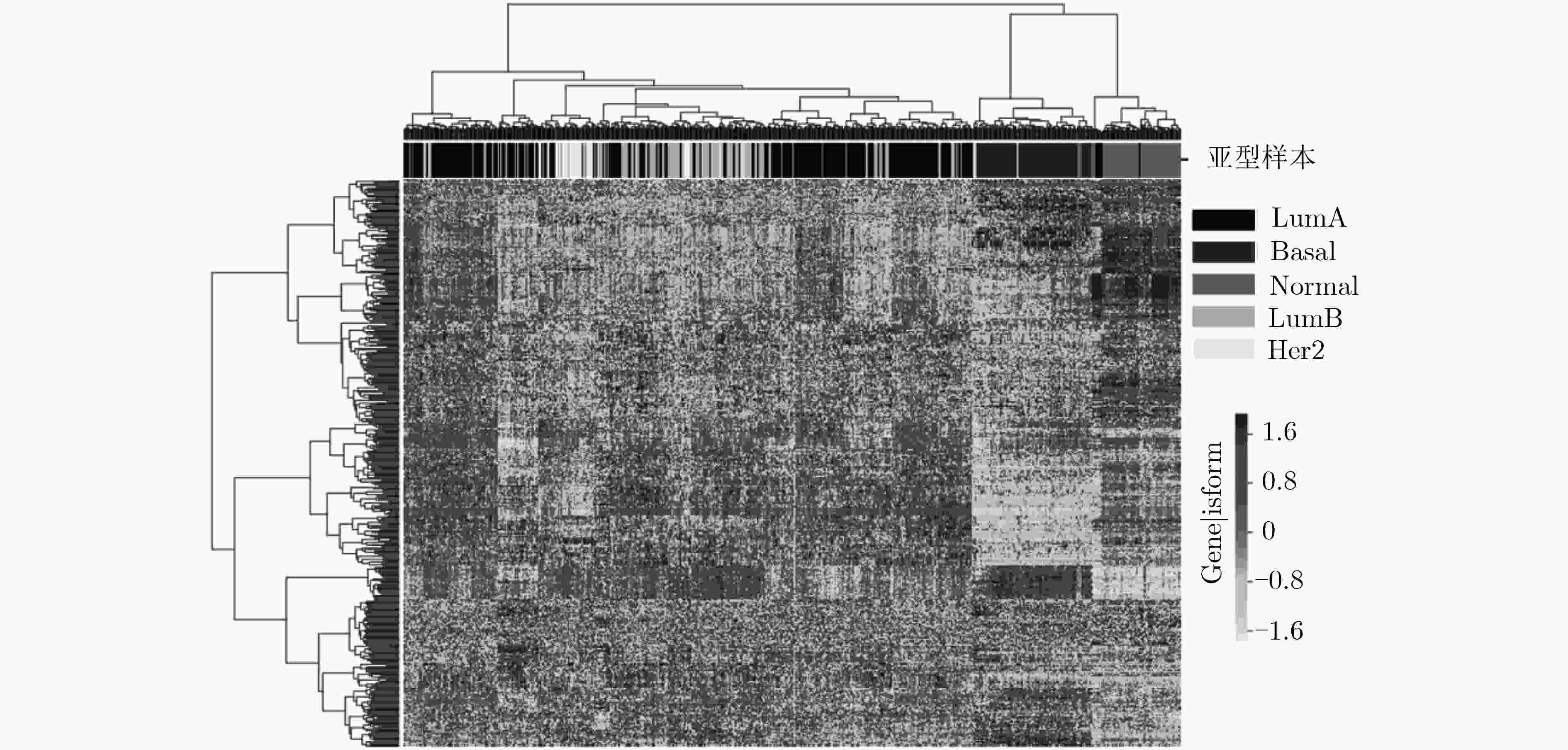
摘要: 可变剪接与多种复杂疾病的发生、发展存在密切的联系,包括肿瘤在内的多种疾病的产生往往伴随着可变剪接的紊乱发生。现有的乳腺癌亚型分析主要是基于单个剪接异构体出发,缺少考虑亚型之间由于可变剪接紊乱造成剪接异构体在整体分布上的差异。因此该文提出了基于可变剪接紊乱的乳腺癌亚型预测方法,主要使用Jensen-Shannon(JS)散度来找寻亚型之间的可变剪接紊乱差异较大的基因,并构建反向传播(BP)神经网络模型对乳腺癌亚型进行分类。结果表明,该方法不仅能有效发现肿瘤异质性分子,在乳腺癌亚型分类方面也有较好的识别结果,其平均F1值达到0.89,且能为患者提供个性化乳腺癌亚型药物推荐。该文的研究将有效促进基于可变剪接紊乱的乳腺癌亚型研究的发展。
-
关键词:
- 乳腺癌亚型预测 /
- 可变剪接 /
- Jensen-Shannon散度 /
- 反向传播神经网络 /
- 药物推荐
Abstract: Alternative splicing is closely related to the occurrence and development of a variety of complex diseases, the emergence of various diseases including tumors is often accompanied by the occurrence of alternative splicing disorders. The existing analysis of breast cancer subtypes is mainly based on single splicing isoform, and the difference in the overall distribution of splicing isoforms caused by alternative splicing disorders among subtypes is not considered. Therefore, a prediction method of breast cancer subtypes based on alternative splicing disorders is proposed, which mainly uses Jensen-Shannon(JS) divergence to find genes with large differences in alternative splicing disorders between subtypes, then constructes Back Propagation(BP) neural network model to classify breast cancer subtypes. The results show that this method could not only effectively detect tumor heterogeneous molecules, but also had good identification results in the classification of breast cancer subtypes, with an average F1-score of 0.89, and could provide personalized drug recommendations for patients with breast cancer subtypes. This study will effectively promote the development of breast cancer subtypes based on alternative splicing disorders. -
表 1 不同乳腺癌亚型的样本数
乳腺癌亚型 样本数 Basal 140 Her2 67 LumA 432 LumB 194 Normal 117 表 2 乳腺癌亚型分类
乳腺癌亚型 精确率 召回率 F1值 Basal 0.97 0.96 0.97 Her2 0.85 0.75 0.79 LumA 0.89 0.92 0.91 LumB 0.81 0.79 0.80 Normal 0.89 0.91 0.90 表 3 乳腺癌亚型的药物推荐
靶基因 药物 Basal Her2 LumA LumB CHEK1 Enzastaurin 0.393 0.369 0.195 0.316 ESR1 Melatonin,Homosalate,Estradiol,2-Amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo(4,5-b)pyridine,Danazol,Fulvestrant,Raloxifene,Custirsen,Tamoxifen,Estrone sulfate,Methyltestosterone,Fluoxymesterone,Afimoxifene 0.305 0.133 0.028 0.025 FOLR2 Folic acid,Methotrexate 0.842 0.025 0.108 0.354 GPER1 Estradiol 0.442 0.438 0.021 0.013 GSN Latrunculin A 0.443 0.419 0.224 0.476 PPARG Curcumin,Isoflavone,Valproic acid,Mesalazine,Nabiximols,Cannabidiol 0.668 0.645 0.030 0.637 AURKB Enzastaurin,AT9283 0.640 0.569 0.352 0.591 ABCC11 Methotrexate,Folic acid 0.431 0.036 0.013 0.040 -
ULE J and BLENCOWE B J. Alternative splicing regulatory networks: Functions, mechanisms, and evolution[J]. Molecular Cell, 2019, 76(2): 329–345. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.09.017 PAN Qun, SHAI O, LEE L J, et al. Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in the human transcriptome by high-throughput sequencing[J]. Nature Genetics, 2008, 40(12): 1413–1415. doi: 10.1038/ng.259 HIRSCH C L, AKDEMIR Z C, WANG Li, et al. Myc and SAGA rewire an alternative splicing network during early somatic cell reprogramming[J]. Genes & Development, 2015, 29(8): 803–816. doi: 10.1101/gad.255109.114 VENABLES J P. Aberrant and alternative splicing in cancer[J]. Cancer Research, 2004, 64(21): 7647–7654. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1910 NARYSHKIN N A, WEETALL M, DAKKA A, et al. SMN2 splicing modifiers improve motor function and longevity in mice with spinal muscular atrophy[J]. Science, 2014, 345(6197): 688–693. doi: 10.1126/science.1250127 GILLINGS A S, BALMANNO K, WIGGINS C M, et al. Apoptosis and autophagy: BIM as a mediator of tumour cell death in response to oncogene-targeted therapeutics[J]. The FEBS Journal, 2009, 276(21): 6050–6062. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07329.x MENON R and OMENN G S. Proteomic characterization of novel alternative splice variant proteins in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2/neu-induced breast cancers[J]. Cancer Research, 2010, 70(9): 3440–3449. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2631 DAVID C J and MANLEY J L. Alternative pre-mRNA splicing regulation in cancer: Pathways and programs unhinged[J]. Genes & Development, 2010, 24(21): 2343–2364. doi: 10.1101/gad.1973010 BLACK D L. Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2003, 72: 291–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161720 ALMENDRO V, MARUSYK A, and POLYAK K. Cellular heterogeneity and molecular evolution in cancer[J]. Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease, 2013, 8: 277–302. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-020712-163923 PAL S, BI Yingtao, MACYSZYN L, et al. Isoform-level gene signature improves prognostic stratification and accurately classifies glioblastoma subtypes[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42(8): e64. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku121 PEROU C M, SØRLIE T, EISEN M B, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours[J]. Nature, 2000, 406(6797): 747–752. doi: 10.1038/35021093 ZHAO Wei, HOADLEY K A, PARKER J S, et al. Identification of mRNA isoform switching in breast cancer[J]. BMC Genomics, 2016, 17: 181. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2521-9 SØRLIE T, TIBSHIRANI R, PARKER J, et al. Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent gene expression data sets[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2003, 100(14): 8418–8423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0932692100 STRICKER T P, BROWN C D, BANDLAMUDI C, et al. Robust stratification of breast cancer subtypes using differential patterns of transcript isoform expression[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2017, 13(3): e1006589. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006589 曾勇, 舒欢, 胡江平, 等. 基于BP神经网络的自适应伪最近邻分类[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(11): 2774–2779. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160133ZENG Yong, SHU Huan, HU Jiangping, et al. Adaptive pseudo nearest neighbor classification based on BP neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(11): 2774–2779. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160133 AKRAM M, IQBAL M, DANIYAL M, et al. Awareness and current knowledge of breast cancer[J]. Biological Research, 2017, 50: 33. doi: 10.1186/s40659-017-0140-9 刘文斌, 陈杰, 方刚, 等. 基于药物互作网络的协同与拮抗预测研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1428–1435. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190867LIU Wenbin, CHEN Jie, FANG Gang, et al. Prediction of drug synergy and antagonism based on drug-drug interaction network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1428–1435. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190867 CALIFANO A and ALVAREZ M J. The recurrent architecture of tumour initiation, progression and drug sensitivity[J]. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2017, 17(2): 116–130. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.124 KIMURA S. AT-9283, a small-molecule multi-targeted kinase inhibitor for the potential treatment of cancer[J]. Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs, 2010, 11(12): 1442–1449. ZHOU Donghu, JIANG Ying, and HE Fuchu. Alternative splicing in lifeomics era[J]. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 2015, 45(12): 1177–1184. doi: 10.1360/N052015-00135 -





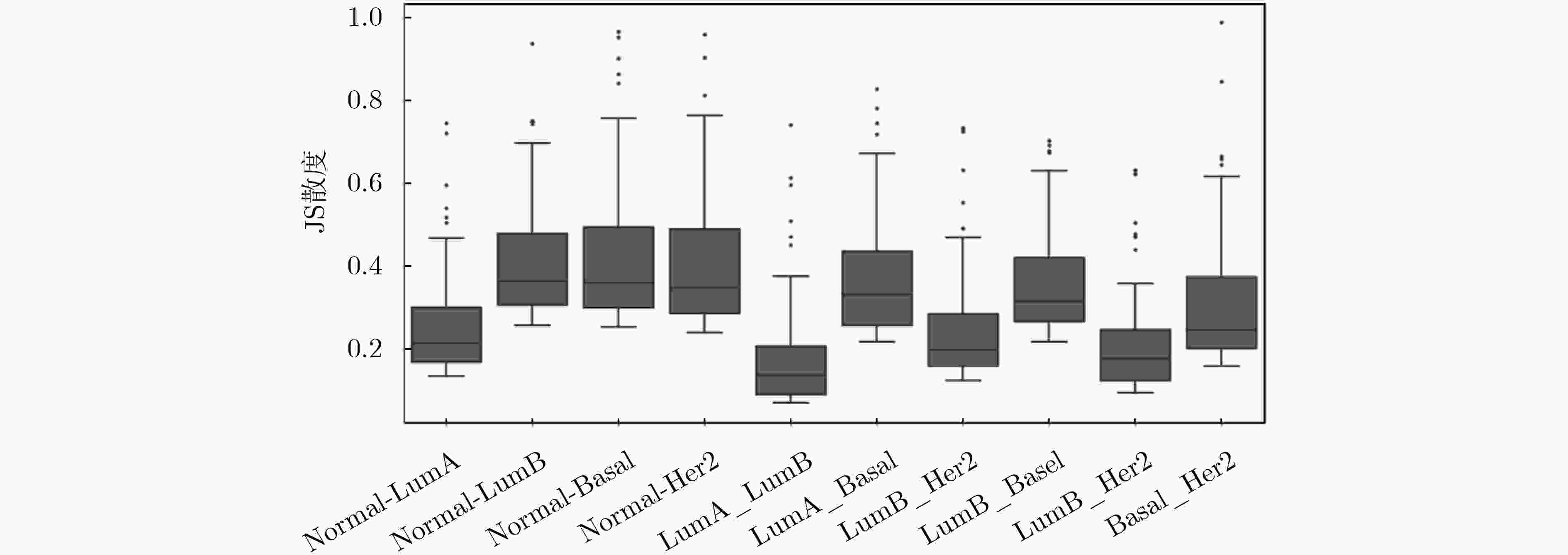
 下载:
下载:
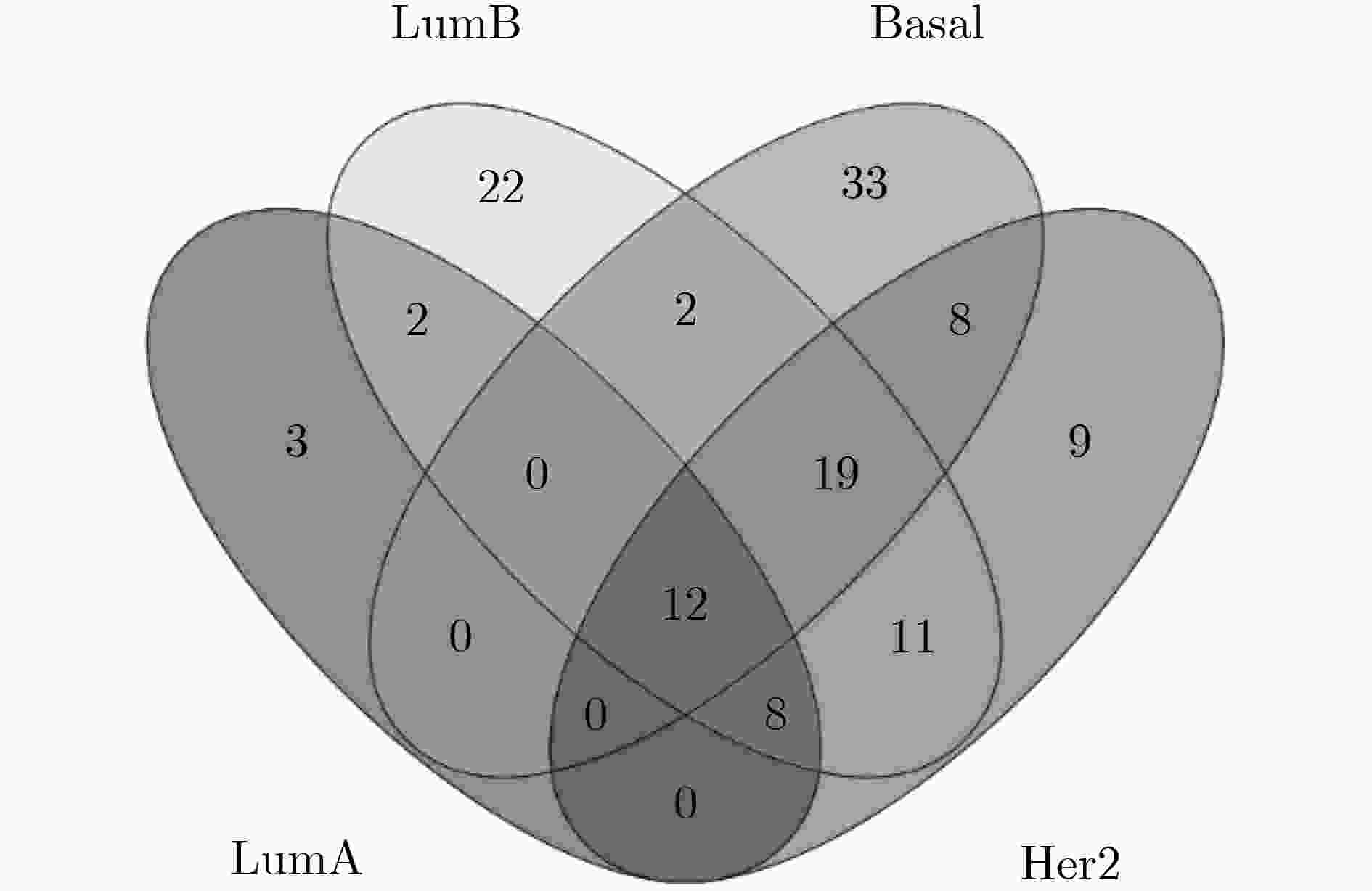
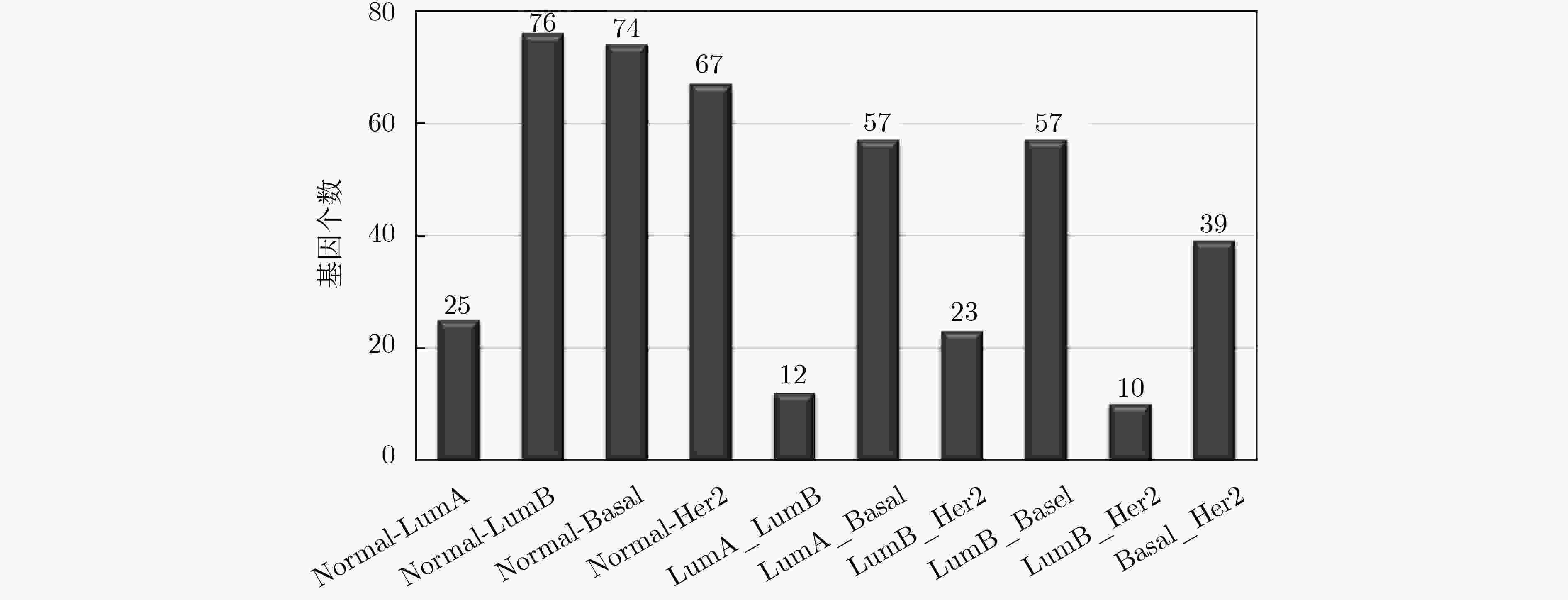

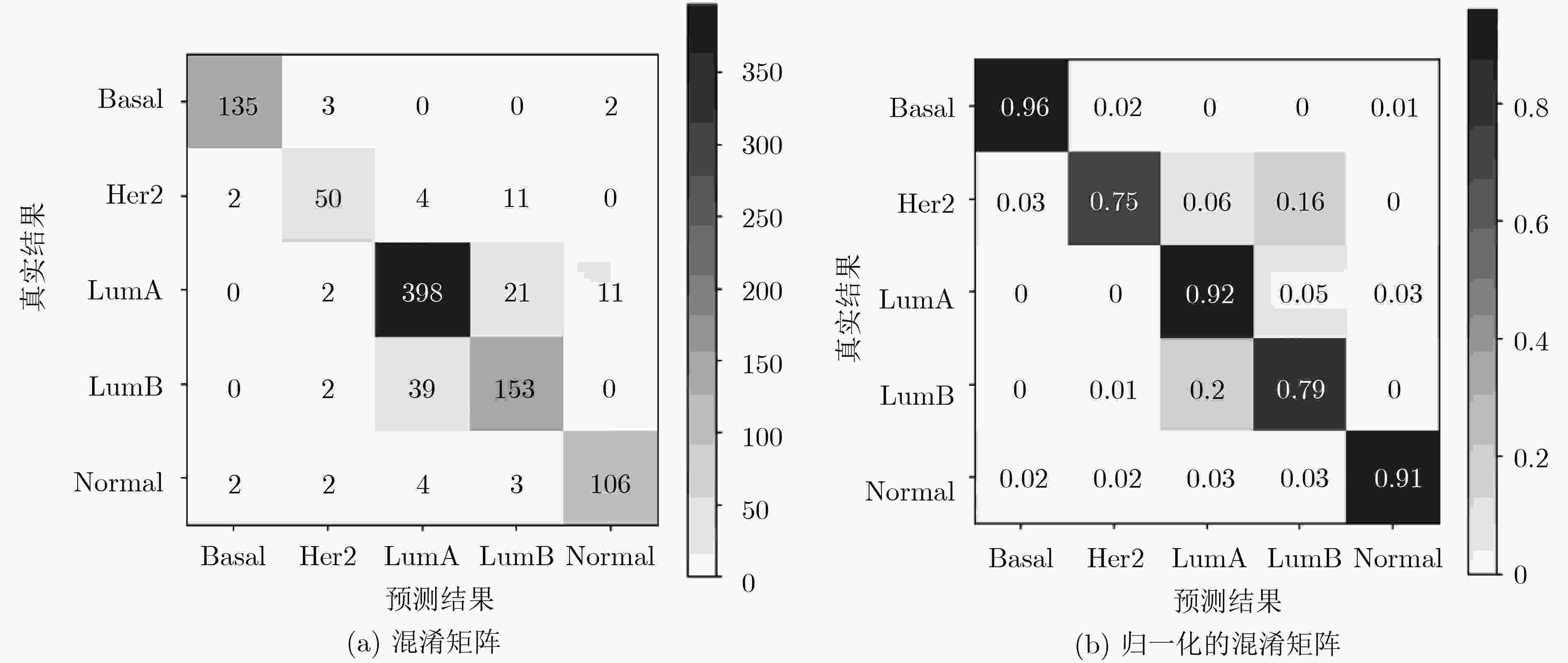


 下载:
下载:
