|
VAN ROON E N, FLIKWEERT S, LE COMTE M, et al. Clinical relevance of drug-drug interactions[J]. Drug Safety, 2005, 28(12): 1131–1139. doi: 10.2165/00002018-200528120-00007
|
|
CHOU Tingchao. Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies[J]. Pharmacological Reviews, 2006, 58(3): 621–681. doi: 10.1124/pr.58.3.10
|
|
LEHÁR J, KRUEGER A S, AVERY W, et al. Synergistic drug combinations tend to improve therapeutically relevant selectivity[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2009, 27(7): 659–666. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1549
|
|
CHAIT R, CRANEY A, and KISHONY R. Antibiotic interactions that select against resistance[J]. Nature, 2007, 446(7136): 668–671. doi: 10.1038/nature05685
|
|
VENKATAKRISHNAN K, VON MOLTKE L L, OBACH R S, et al. Drug metabolism and drug interactions: Application and clinical value of in vitro models[J]. Current Drug Metabolism, 2003, 4(5): 423–459. doi: 10.2174/1389200033489361
|
|
PIRMOHAMED M and ORME M L. Drug Interactions of Clinical Importance[M]. DAVIES D M, FERNER R E, and DE GLANVILLE H. Davies's Textbook of Adverse Drug Reactions. 5th ed. London: Chapman & Hall, 1998: 888–912.
|
|
TAKEDA T, HAO Ming, CHENG Tiejun, et al. Predicting drug-drug interactions through drug structural similarities and interaction networks incorporating pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics knowledge[J]. Journal of Cheminformatics, 2017, 9: 16. doi: 10.1186/s13321-017-0200-8
|
|
FOKOUE A, SADOGHI M, HASSANZADEH O, et al. Predicting drug-drug interactions through large-scale similarity-based link prediction[C]. The 13th International Conference European Semantic Web Conference, Heraklion, Greece, 2016: 774–789. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-34129-3_47.
|
|
VILAR S, HARPAZ R, URIARTE E, et al. Drug—drug interaction through molecular structure similarity analysis[J]. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 2012, 19(6): 1066–1074. doi: 10.1136/amiajnl-2012-000935
|
|
VILAR S, URIARTE E, SANTANA L, et al. Detection of drug-drug interactions by modeling interaction profile fingerprints[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(3): e58321. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058321
|
|
KASTRIN A, FERK P, and LESKOŠEK B. Predicting potential drug-drug interactions on topological and semantic similarity features using statistical learning[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(5): e0196865. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196865
|
|
CHENG Feixiong and ZHAO Zhongming. Machine learning-based prediction of drug-drug interactions by integrating drug phenotypic, therapeutic, chemical, and genomic properties[J]. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 2014, 21(e2): e278–e286. doi: 10.1136/amiajnl-2013-002512
|
|
RYU J Y, KIM H U, and LEE S Y. Deep learning improves prediction of drug-drug and drug-food interactions[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(18): E4304–E4311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1803294115
|
|
LUO Heng, ZHANG Ping, HUANG Hui, et al. DDI-CPI, a server that predicts drug-drug interactions through implementing the chemical-protein interactome[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42(W1): W46–W52. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku433
|
|
ZHANG Ping, WANG Fei, HU Jianying, et al. Label propagation prediction of drug-drug interactions based on clinical side effects[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 12339. doi: 10.1038/srep12339
|
|
LIU Lili, CHEN Lei, ZHANG Yuhang, et al. Analysis and prediction of drug-drug interaction by minimum redundancy maximum relevance and incremental feature selection[J]. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 2017, 35(2): 312–329. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2016.1138142
|
|
TAKARABE M, SHIGEMIZU D, KOTERA M, et al. Network-based analysis and characterization of adverse drug-drug interactions[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2011, 51(11): 2977–2985. doi: 10.1021/ci200367w
|
|
GOTTLIEB A, STEIN G Y, ORON Y, et al. INDI: A computational framework for inferring drug interactions and their associated recommendations[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2012, 8: 592. doi: 10.1038/msb.2012.26
|
|
WISHART D S, FEUNANG Y D, GUO A C, et al. DrugBank 5.0: A major update to the DrugBank database for 2018[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 46(D1): D1074–D1082. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037
|
|
CORTES C and VAPNIK V. Support-vector networks[J]. Machine Learning, 1995, 20(3): 273–297. doi: 10.1007/bf00994018
|
|
陈素根, 吴小俊. 基于特征值分解的中心支持向量机算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(3): 557–564. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150693CHEN Sugen and WU Xiaojun. Eigenvalue proximal support vector machine algorithm based on eigenvalue decoposition[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(3): 557–564. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150693
|
|
汪廷华, 田盛丰, 黄厚宽. 特征加权支持向量机[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(3): 514–518. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.01711WANG Tinghua, TIAN Shengfeng, and HUANG Houkuan. Feature weighted support vector machine[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(3): 514–518. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.01711
|
|
WU Shaomin and FLACH P. A scored AUC metric for classifier evaluation and selection[C]. ICML 2005 Workshop on ROC Analysis in Machine Learning, Bonn, Germany, 2005.
|
|
HOSSIN M and SULAIMAN M N. A review on evaluation metrics for data classification evaluations[J]. International Journal of Data Mining & Knowledge Management Process, 2015, 5(2): 1–11. doi: 10.5121/ijdkp.2015.5201
|
|
ARLOT S and CELISSE A. A survey of cross-validation procedures for model selection[J]. Statistics Surveys, 2010, 4: 40–79. doi: 10.1214/09-SS054
|
|
LIU Weiping and LÜ Linyuan. Link prediction based on local random walk[J]. EPL (Europhysics Letters) , 2010, 89(5): 58007. doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/89/58007
|
|
TANG Jiliang, ALELYANI S, and LIU Huan. Feature Selection for Classification: A Review[M]. AGGARWAL C C. Data Classification: Algorithms and Applications. New York: CRC Press, 2014: 37.
|





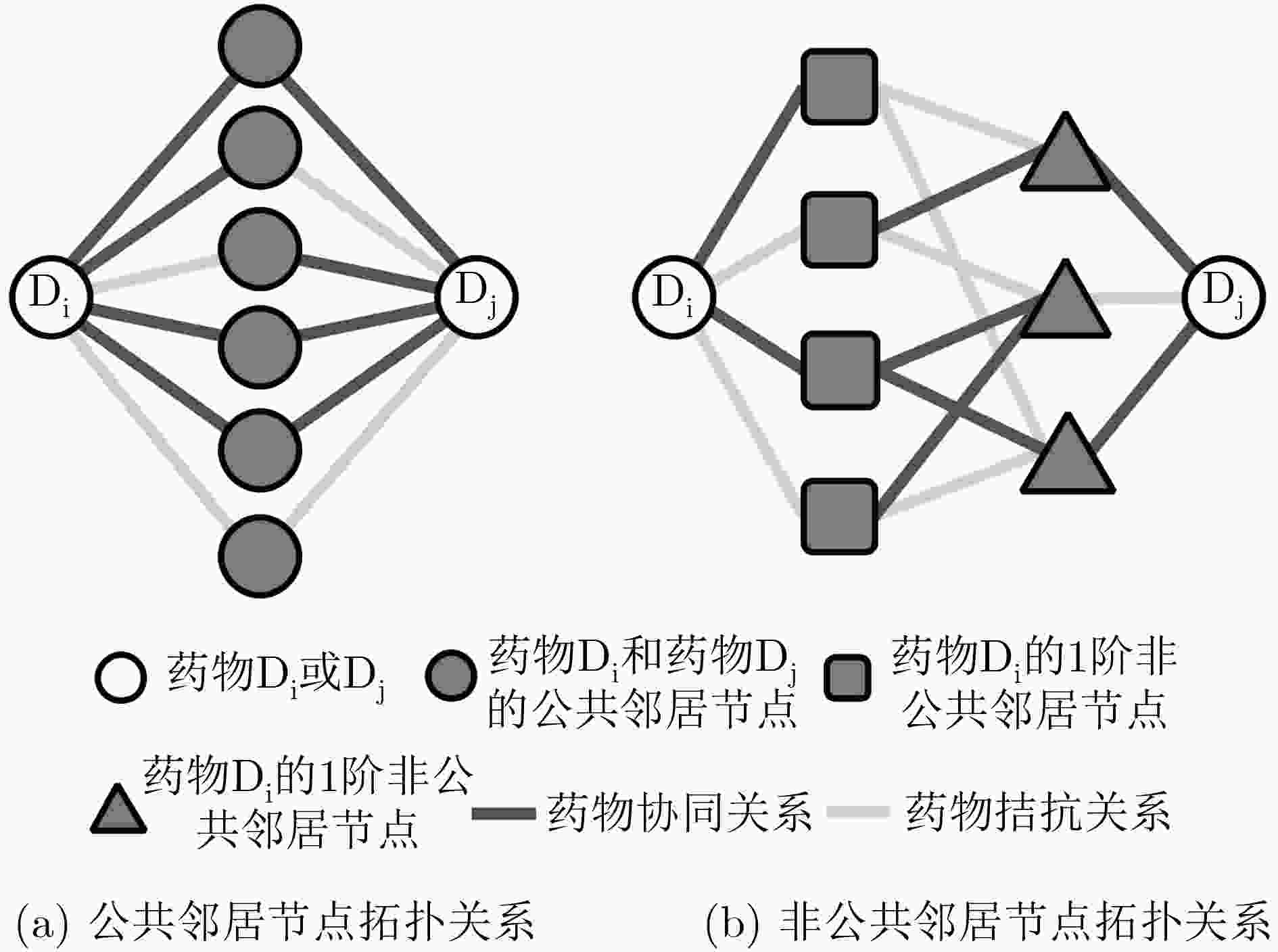
 下载:
下载:
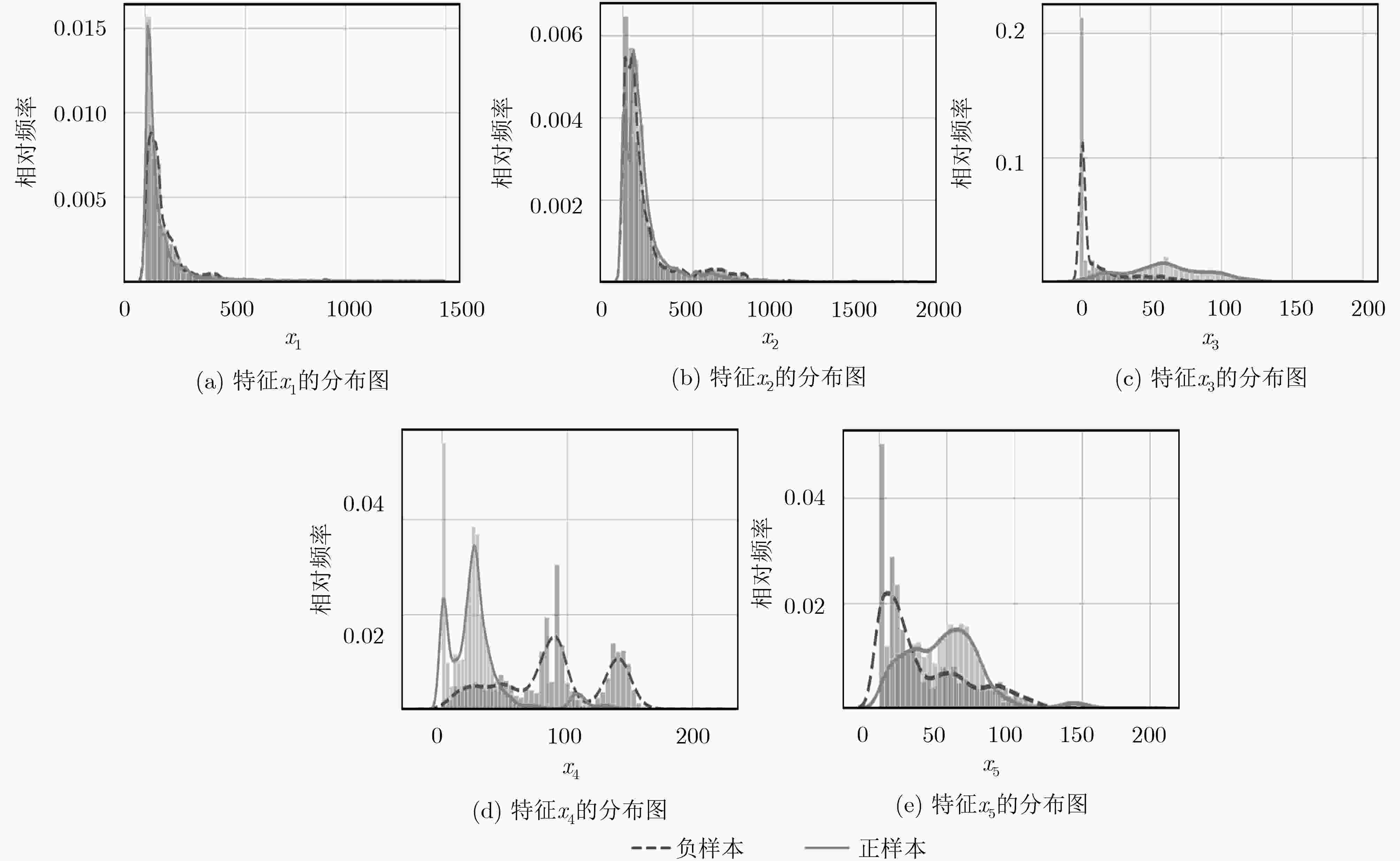
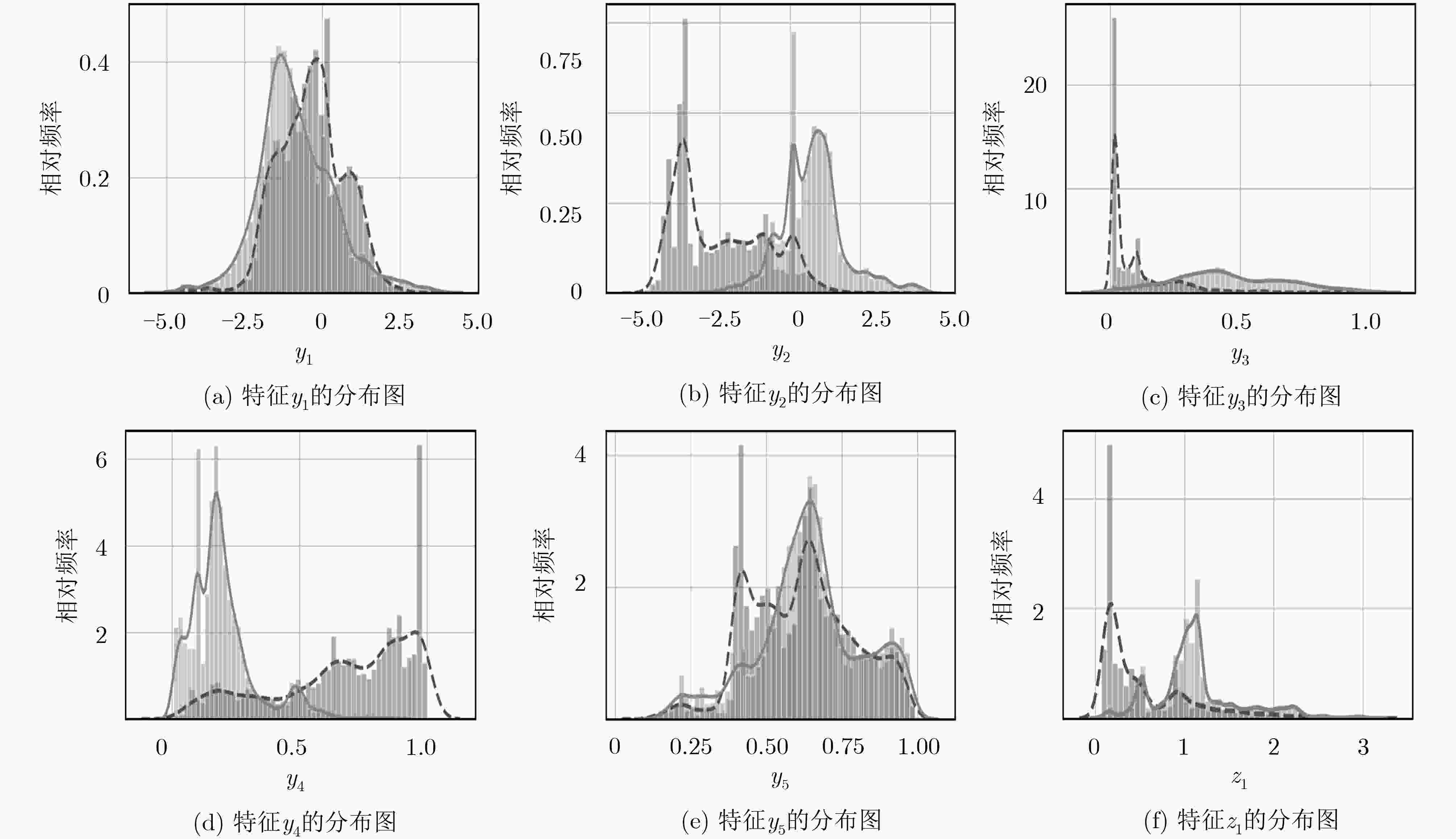
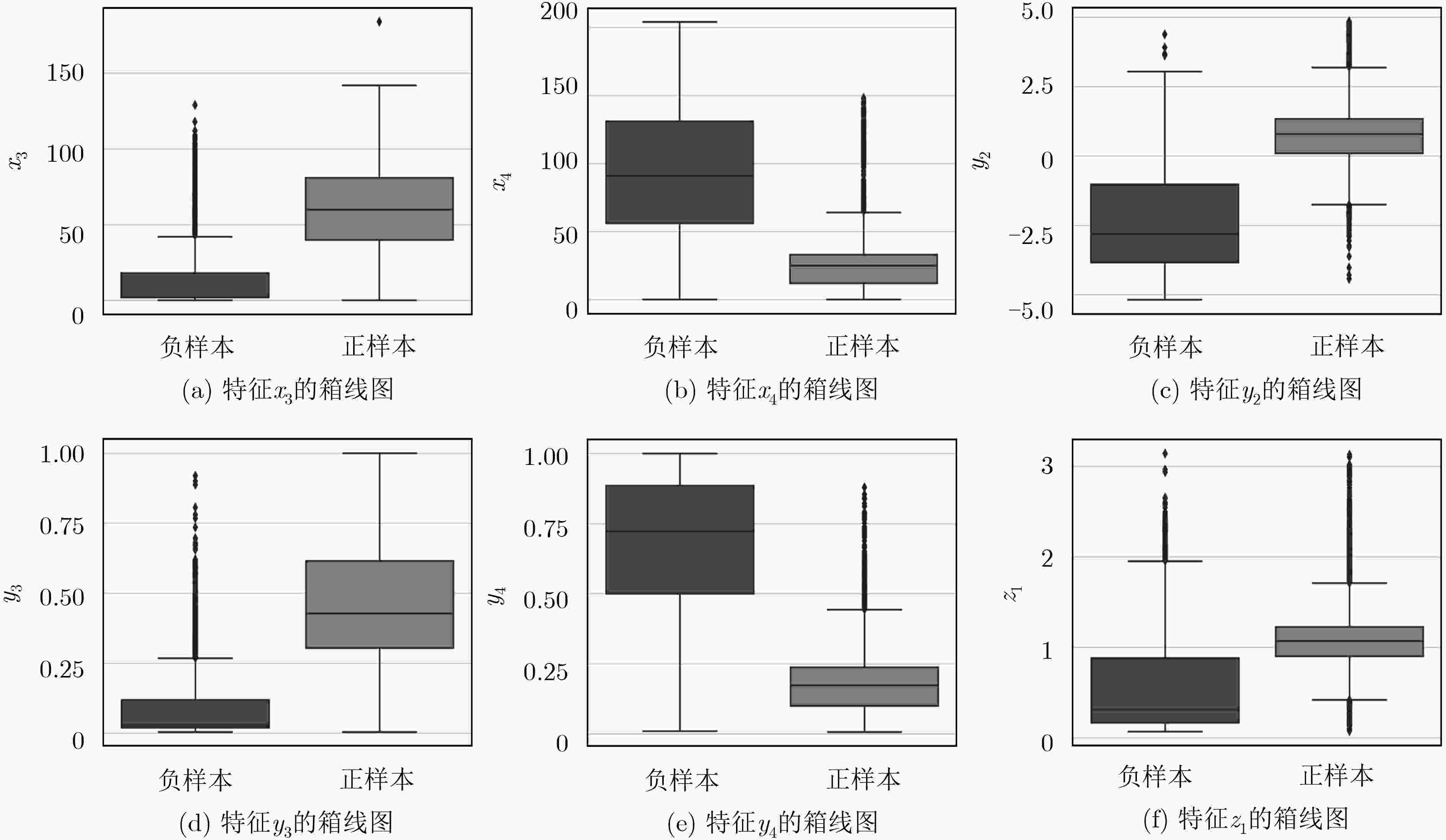
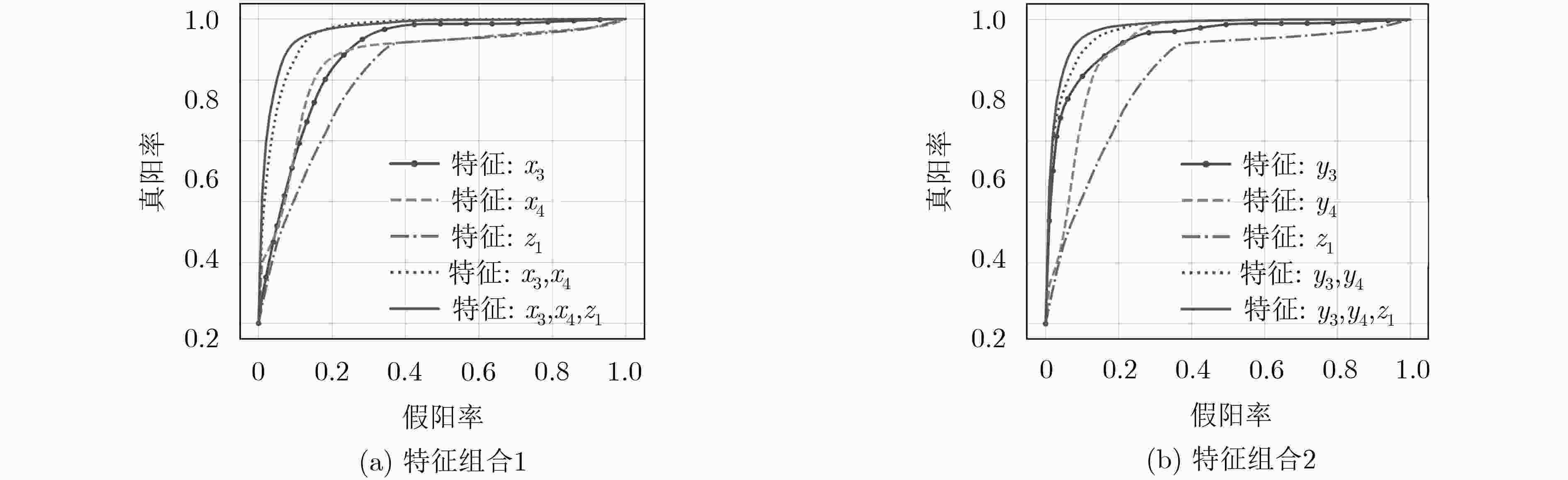
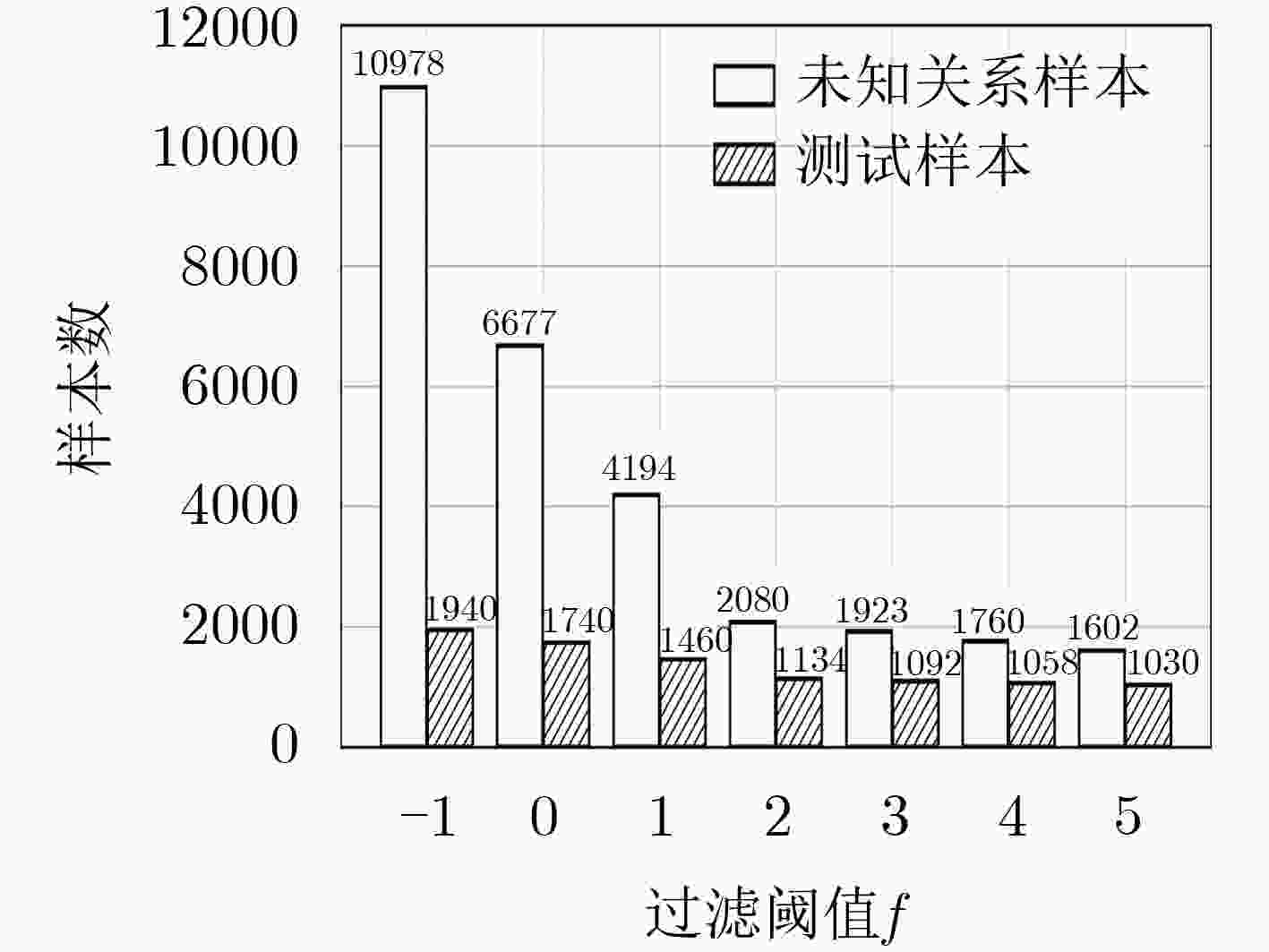
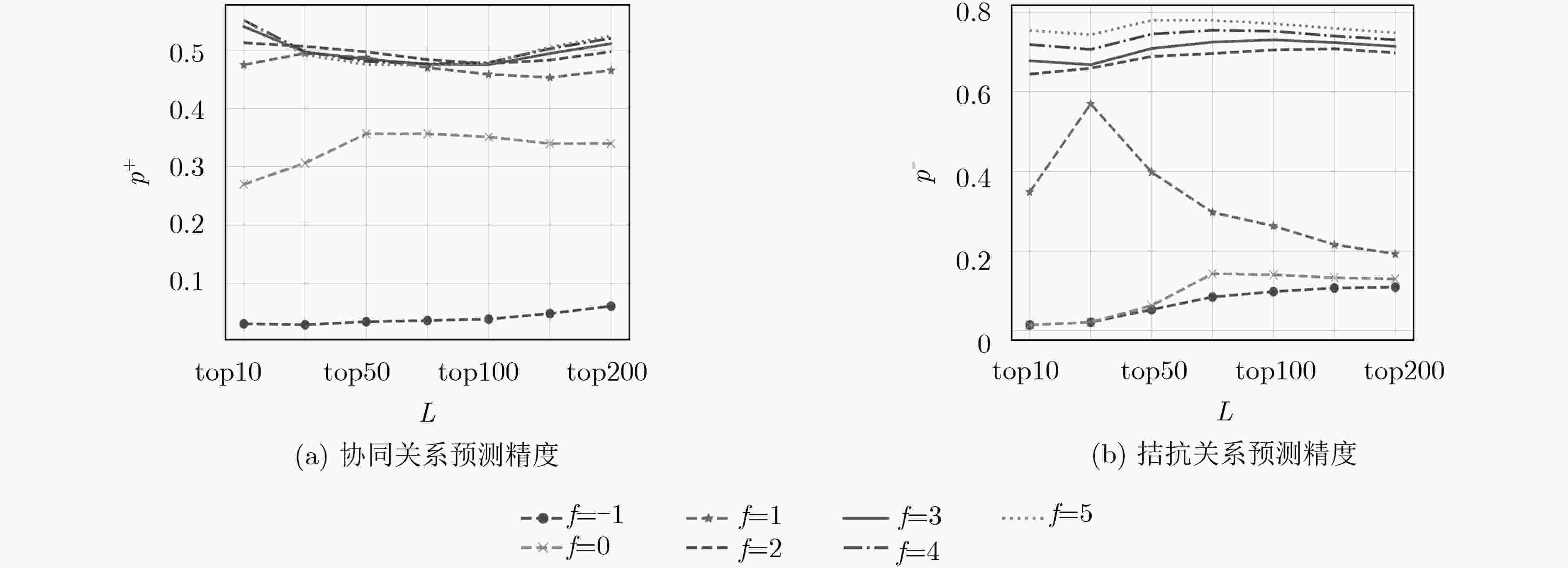


 下载:
下载:
