Initial Sensitive Dynamics in Memristor Synapse-coupled Hopfield Neural Network
-
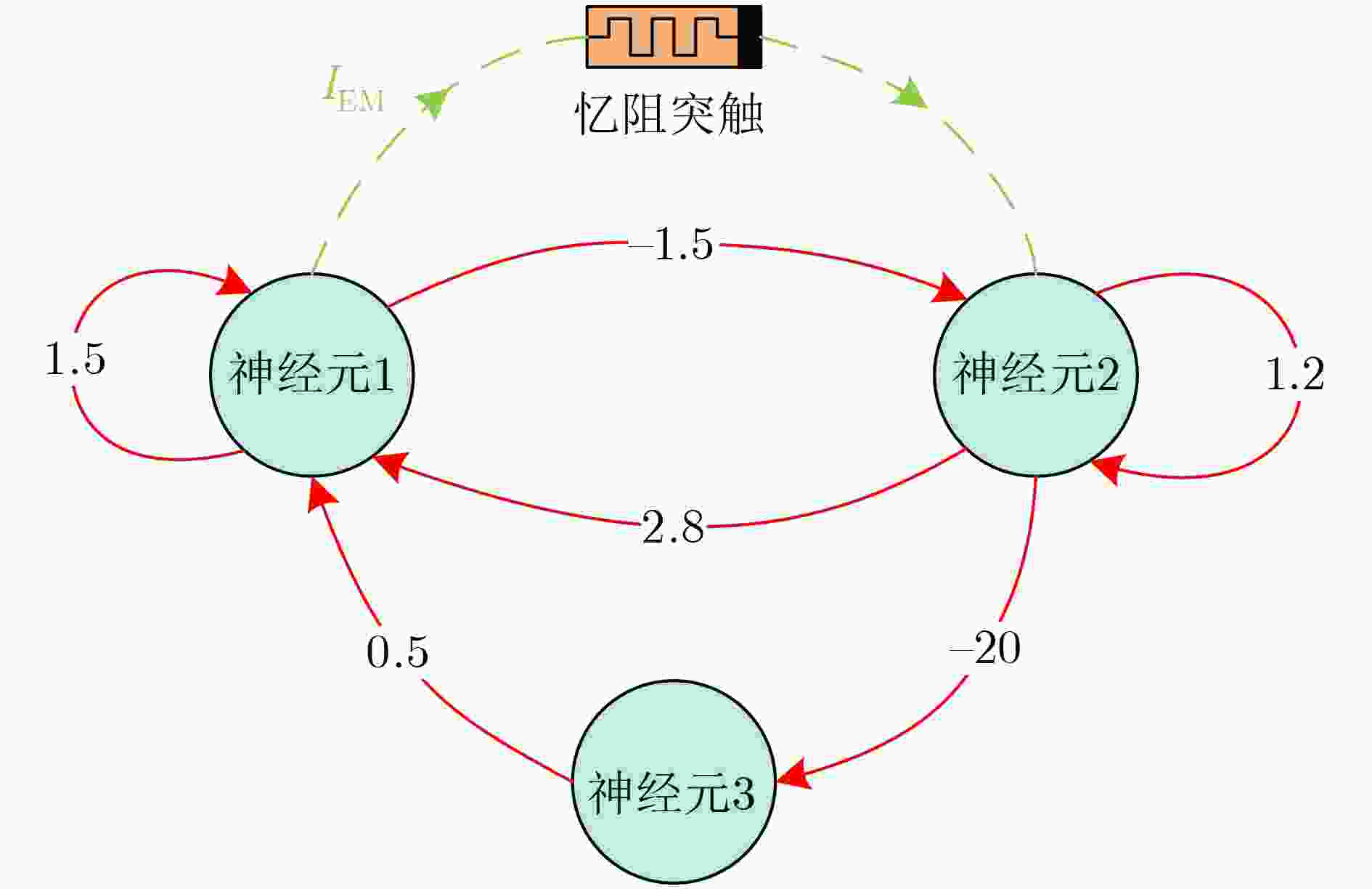
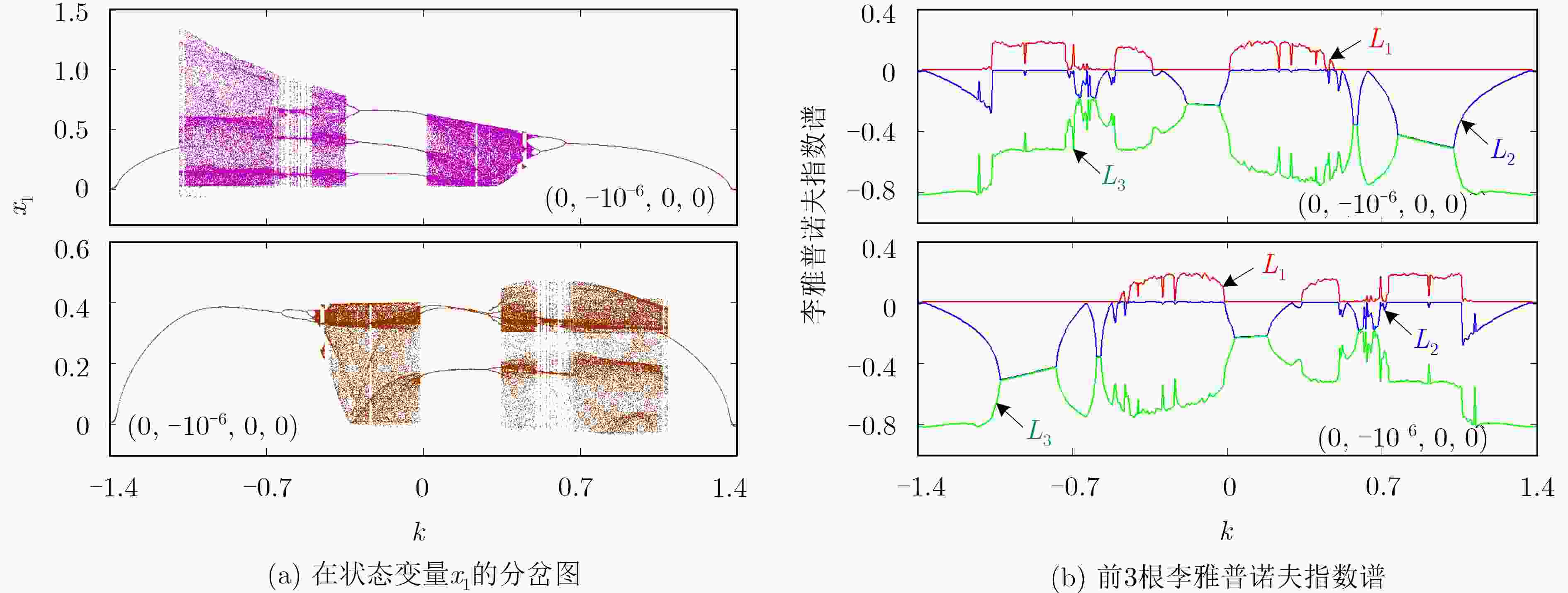
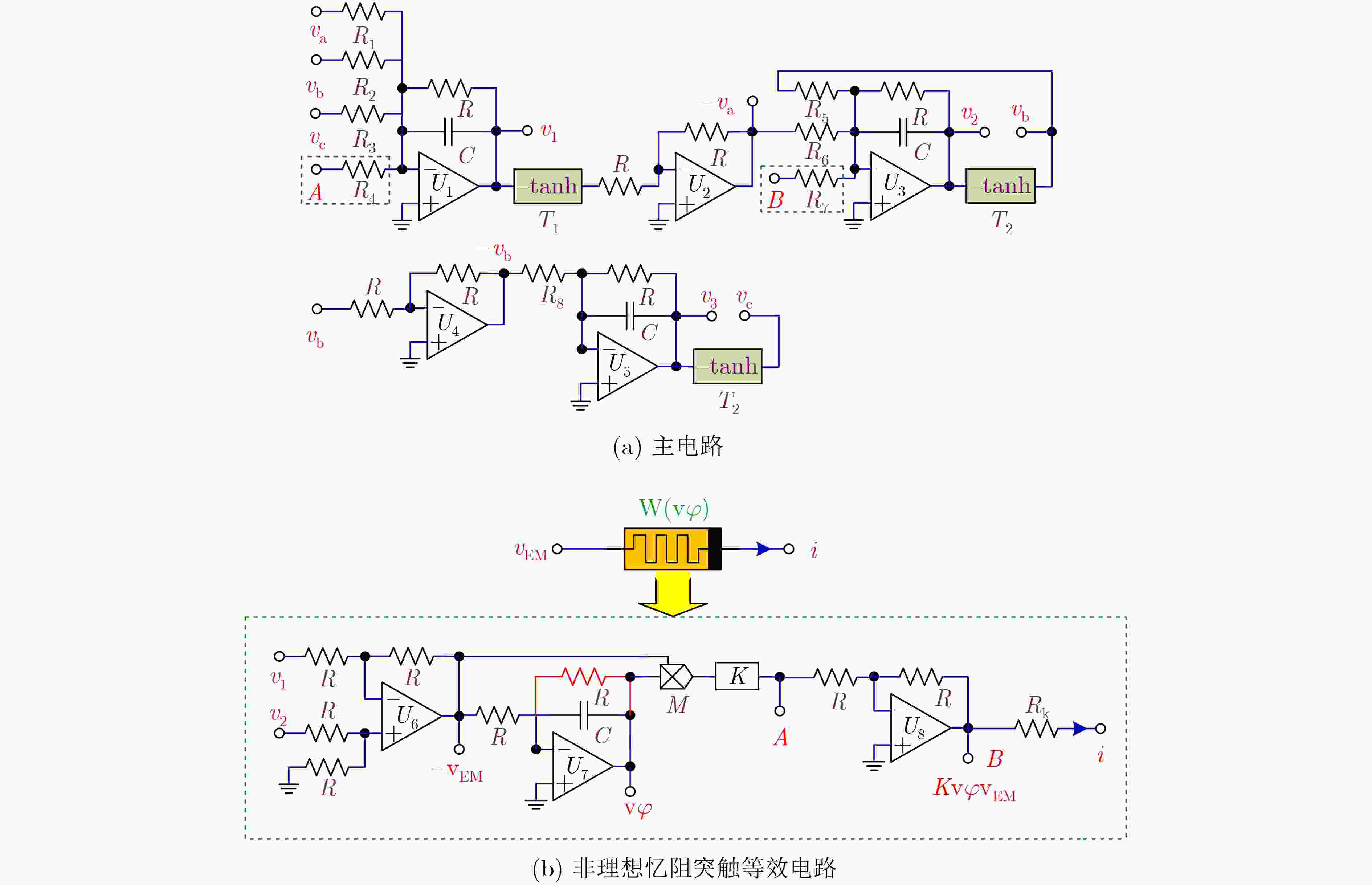
摘要: 该文报道了3神经元Hopfield神经网络(HNN)在电磁感应电流作用下的初值敏感动力学。利用非理想忆阻突触,模拟由两个相邻神经元膜电位之差引起的电磁感应电流,构建了一种简单的4维忆阻Hopfield神经网络模型。借助理论分析和数值仿真,分析了不同忆阻突触耦合强度下的复杂动力学行为,揭示了与状态初值密切相关的特殊动力学行为。最后,设计了该忆阻HNN的模拟等效实现电路,并由PSIM电路仿真验证了MATLAB数值仿真的正确性。
-
关键词:
- 非理想忆阻突触 /
- Hopfield神经网络 /
- 状态初值 /
- 数值仿真
Abstract: The initial sensitive dynamics in a Hopfield Neural Network (HNN) with three neurons under the action of electromagnetic induction current is reported. A simple 4-D memristive HNN is constructed by using a non-ideal memristor synapse to imitate the electromagnetic induction current caused by membrane potential difference between two adjacent neurons. By means of theoretical analyses and numerical simulations, the complex dynamical behaviors under different coupling strengths of the memristor synapse are researched, and special phenomena closely related to the initial values are revealed. Finally, the analog equivalent realization circuit of the memristive HNN model is designed, and the correctness of MATLAB numerical simulation is verified by PSIM circuit simulations. -
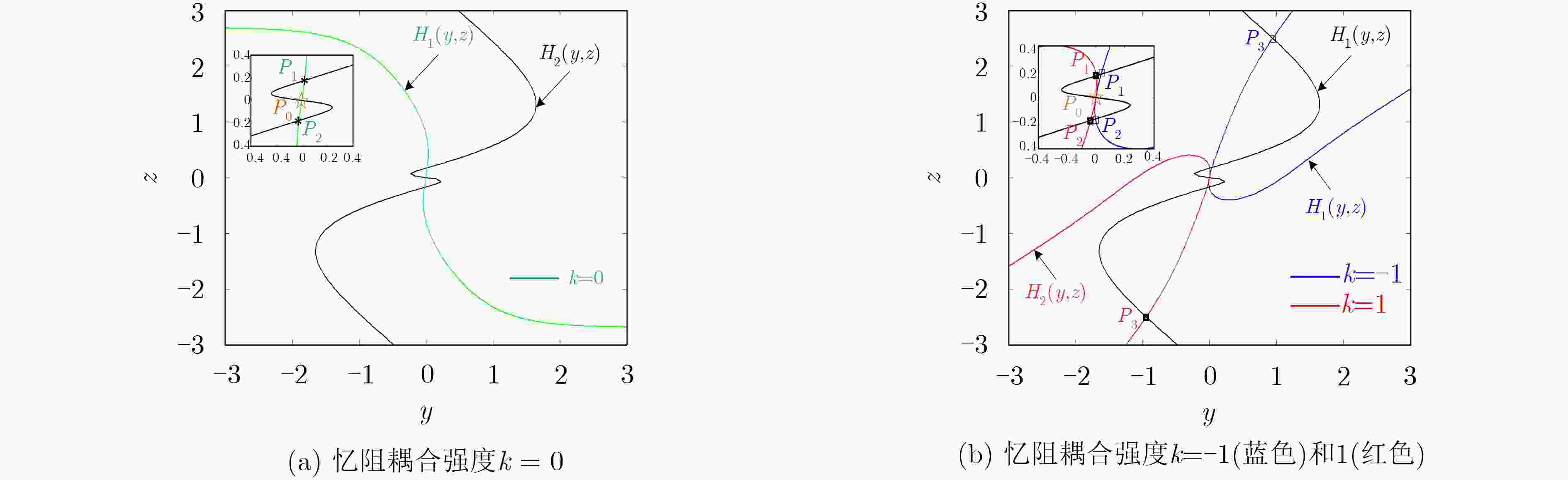
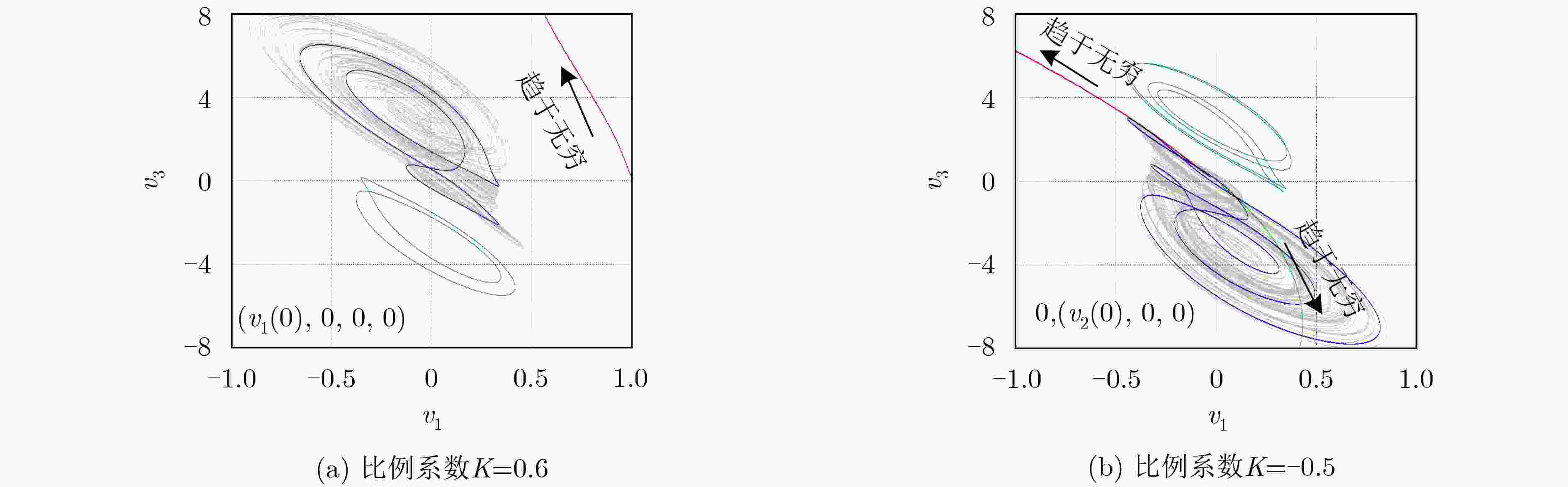
表 1 k=–1, 0和1时的平衡点及其特征值和稳定性
k 平衡点 特征值 稳定性 –1 P0: (0, 0, 0, 0) 1.6062, –0.9531±j2.3986, –1 不稳定指数1鞍焦 P1: (–0.0019, –0.1689, 3.3462, 0.1670) 0.0981±j2.0026, –0.8763, –0.9875 不稳定指数2鞍焦 P2: (0.0369, 0.1814, –3.5887, –0.1445) 0.5146±j2.0051, –0.9923, –1.0882 不稳定指数2鞍焦 P3: (0.9448, 2.5018, –19.7332, –1.5570) 3.4659, –0.9464, –1, –1.6894 不稳定鞍点 0 P0: (0, 0, 0, 0) 1.6062, –0.9531±j2.3986, –1 不稳定指数1鞍焦 P1: (0.0220, 0.1761, –3.4860, –0.1541) 0.3267±j2.0074, –0.9906, –1 不稳定指数2鞍焦 P2: (–0.0220, –0.1761, 3.4860, 0.1541) 0.3267±j2.0074, –0.9906, –1 不稳定指数2鞍焦 1 P0: (0, 0, 0, 0) 1.6062, –0.9531±j2.3986, –1 不稳定指数1鞍焦 P1: (–0.9448, –2.5018, 19.7332, 1.5570) 3.4659, –0.9464, –1, –1.6894 不稳定鞍点 P2: (–0.0369, –0.1814, 3.5887, 0.1445) 0.5146±j2.0051, –0.9923, –1.0882 不稳定指数2鞍焦 P3: (0.0019, 0.1689, –3.3462, –0.1670) 0.0981±j2.0026, –0.8763, –0.9875 不稳定指数2鞍焦 表 2 图7中不同颜色吸引子对应的初值及吸引子类型
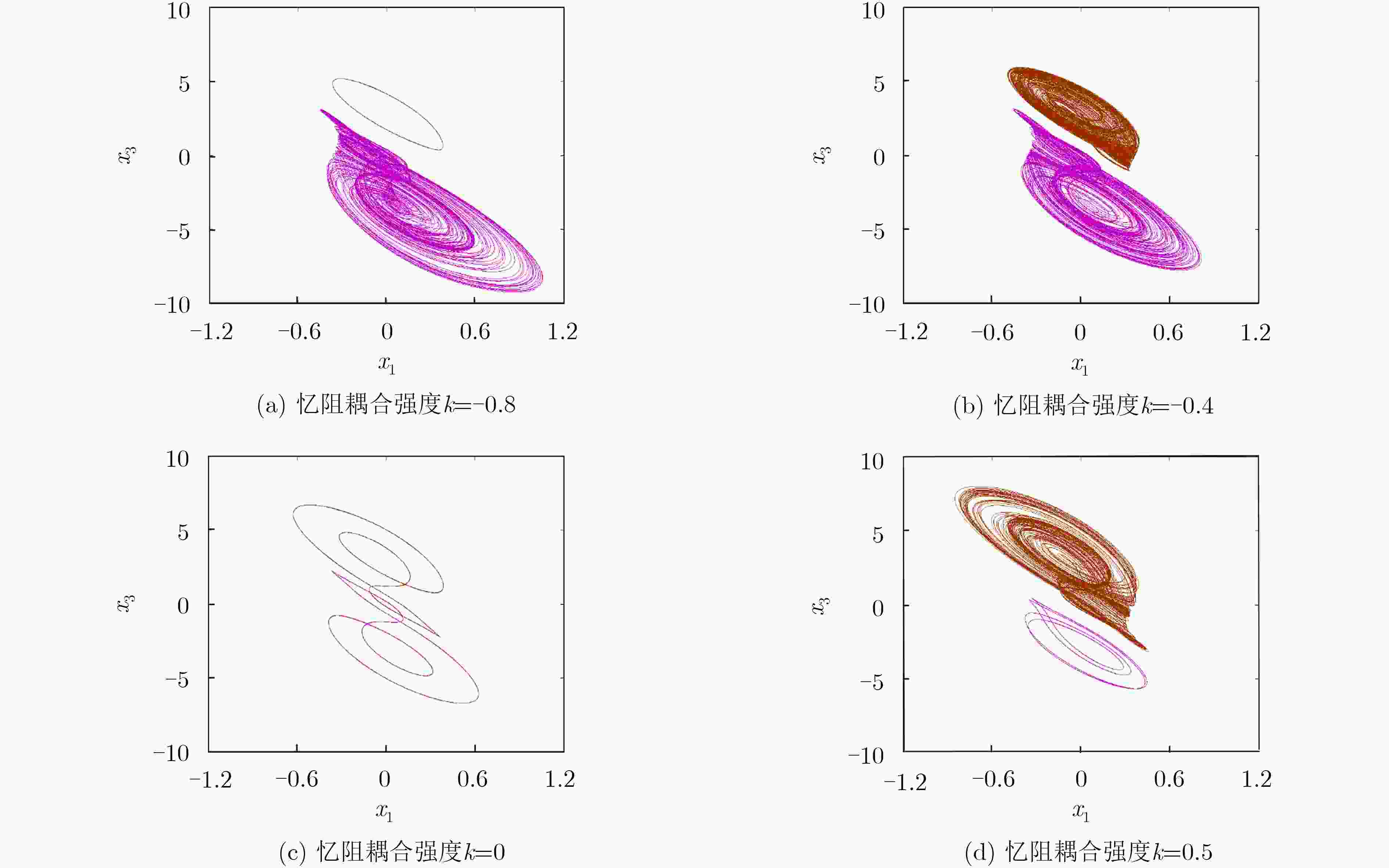
颜色 k=0.6 k=–0.5 吸引子类型 
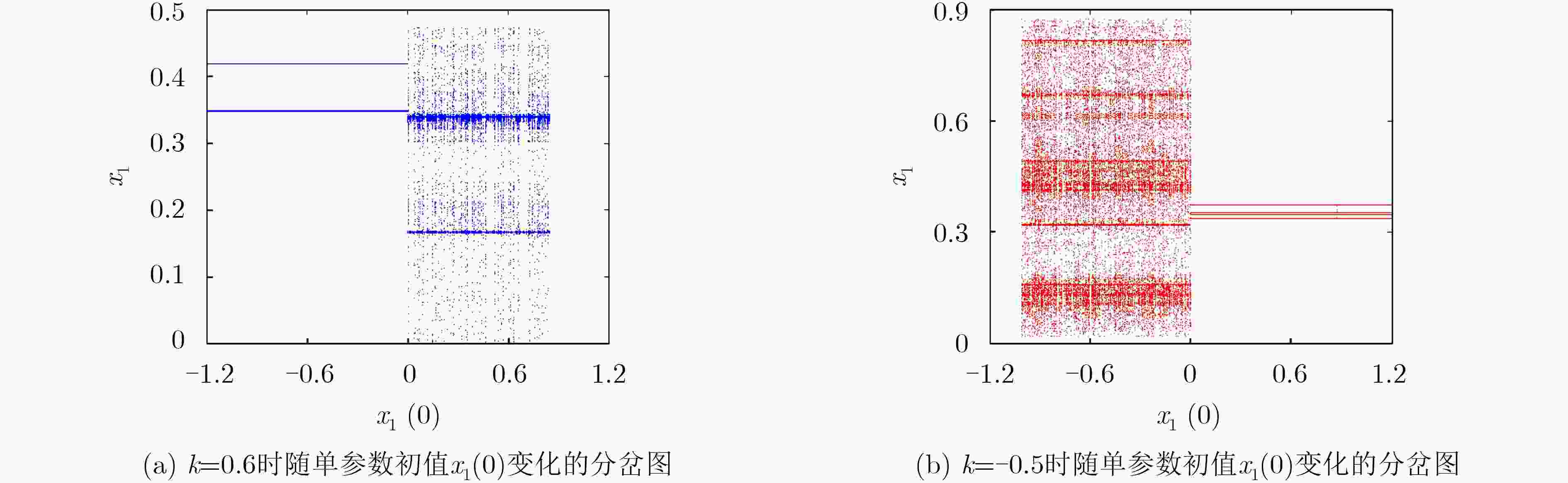
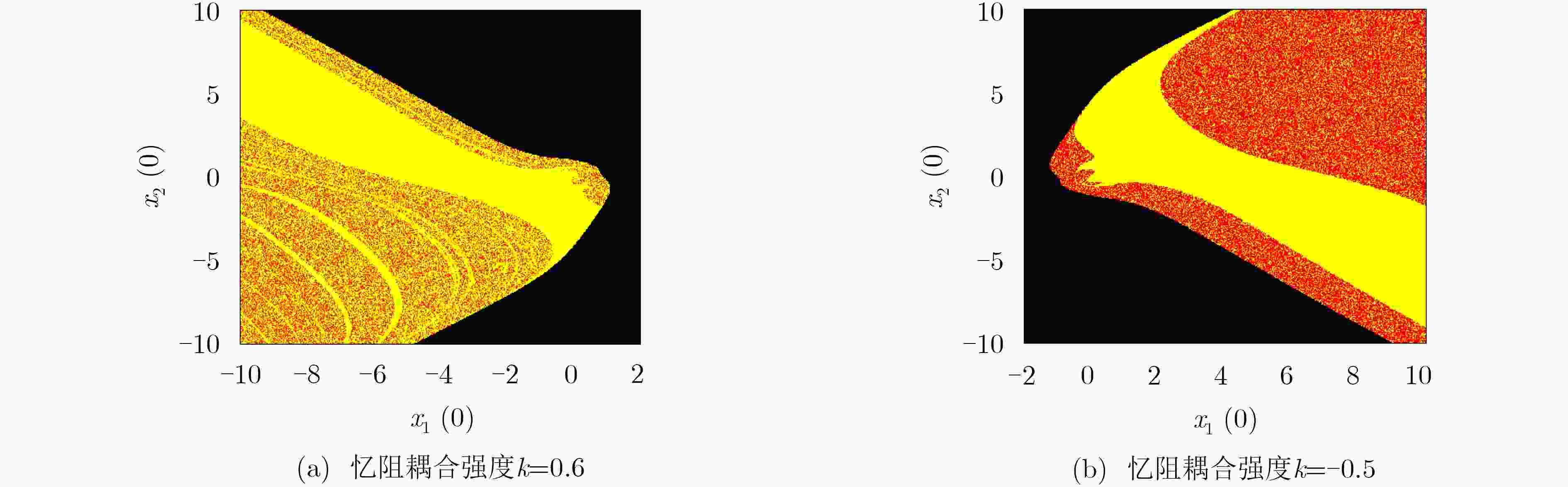
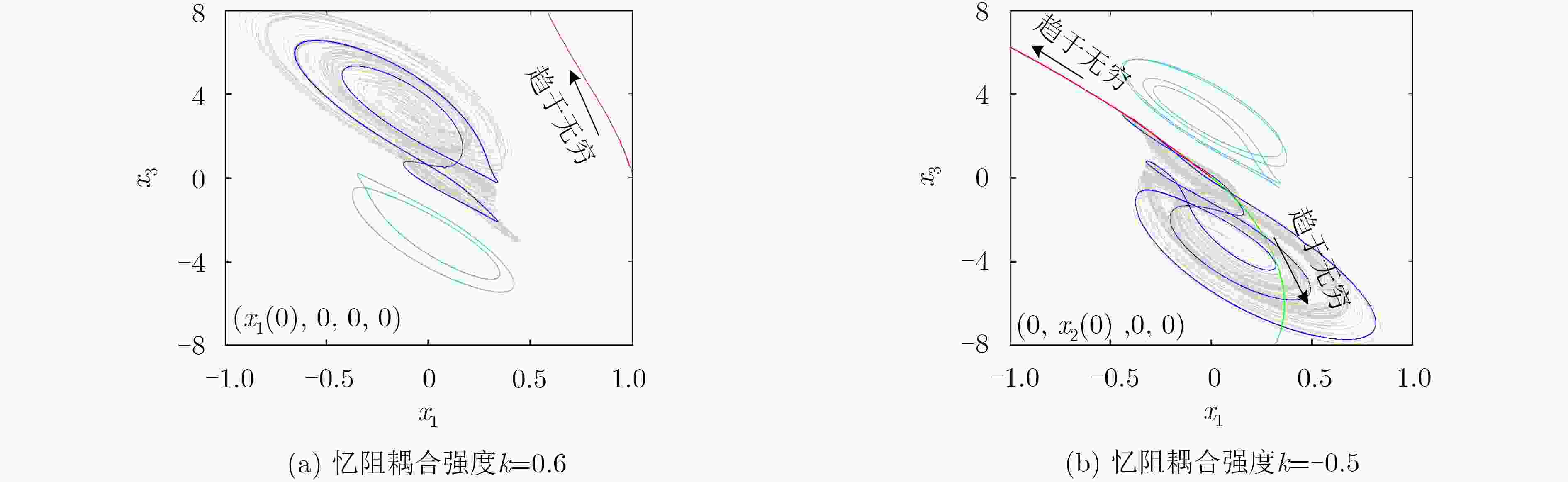
(–10–6, 0, 0, 0) (0, –10–9, 0, 0) 周期吸引子 
(10–6, 0, 0, 0) (0, 10–9, 0, 0) 多周期吸引子 
(10–5, 0, 0, 0) (0, 10–7, 0, 0) 混沌吸引子 
(1, 0, 0, 0) (0, –2, 0, 0) 发散 
– (0, 5, 0, 0) 发散 -
HOPFIELD J J. Neurons with graded response have collective computational properties like those of two-state neurons[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1984, 81(10): 3088–3092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3088 KORN H and FAURE P. Is there chaos in the brain? II. Experimental evidence and related models[J]. Comptes Rendus Biologies, 2003, 326(9): 787–840. doi: 10.1016/j.crvi.2003.09.011 MA Jun and TANG Jun. A review for dynamics in neuron and neuronal network[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2017, 89(3): 1569–1578. doi: 10.1007/s11071-017-3565-3 阮秀凯, 张志涌. 基于连续Hopfield型神经网络的QAM信号盲检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(7): 1600–1605. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01271RUAN Xiukai and ZHANG Zhiyong. Blind detection of QAM signals using continuous Hopfield-type neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2011, 33(7): 1600–1605. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01271 HILLAR C J and TRAN N M. Robust exponential memory in Hopfield networks[J]. The Journal of Mathematical Neuroscience, 2018, 8: 1–20. doi: 10.1186/s13408-017-0056-2 王春华, 蔺海荣, 孙晶如, 等. 基于忆阻器的混沌、存储器及神经网络电路研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 795–810. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190821WANG Chunhua, LIN Hairong, SUN Jingru, et al. Research progress on chaos, memory and neural network circuits based on memristor[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 795–810. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190821 NJITACKE Z T and KENGNE J. Complex dynamics of a 4D Hopfield Neural Networks (HNNs) with a nonlinear synaptic weight: Coexistence of multiple attractors and remerging Feigenbaum trees[J]. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2018, 93: 242–252. doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2018.06.025 DANCA M F and KUZNETSOV N. Hidden chaotic sets in a Hopfield neural system[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2017, 103: 144–150. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2017.06.002 RAJAGOPAL K, MUNOZ-PACHECO J M, PHAM V T, et al. A Hopfield neural network with multiple attractors and its FPGA design[J]. The European Physical Journal Special Topics, 2018, 227(7/9): 811–820. doi: 10.1140/epjst/e2018-800018-7 BAO Bocheng, CHEN Chengjie, BAO Han, et al. Dynamical effects of neuron activation gradient on Hopfield neural network: Numerical analyses and hardware experiments[J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2019, 29(4): 1930010. doi: 10.1142/S0218127419300106 NJITACKE Z T, KENGNE J, FOZIN T F, et al. Dynamical analysis of a novel 4-neurons based Hopfield neural network: emergences of antimonotonicity and coexistence of multiple stable states[J]. International Journal of Dynamics and Control, 2019, 7(3): 823–841. doi: 10.1007/s40435-019-00509-w 刘益春, 林亚, 王中强, 等. 氧化物基忆阻型神经突触器件[J]. 物理学报, 2019, 68(16): 168504. doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20191262LIU Yichun, LIN Ya, WANG Zhongqiang, et al. Oxide-based memristive neuromorphic synaptic devices[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2019, 68(16): 168504. doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20191262 PHAM V T, JAFARI S, VAIDYANATHAN S, et al. A novel memristive neural network with hidden attractors and its circuitry implementation[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2016, 59(3): 358–363. doi: 10.1007/s11431-015-5981-2 BAO Bocheng, QIAN Hui, XU Quan, et al. Coexisting behaviors of asymmetric attractors in hyperbolic-type memristor based Hopfield neural network[J]. Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience, 2017, 11: No. 81, 1–14. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2017.00081 HU Xiaoyu, LIU Chongxin, LIU Ling, et al. Chaotic dynamics in a neural network under electromagnetic radiation[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2018, 91(3): 1541–1554. doi: 10.1007/s11071-017-3963-6 LIN Hairong and WANG Chunhua. Influences of electromagnetic radiation distribution on chaotic dynamics of a neural network[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2020, 369: 124840. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2019.124840 BAO Han, HU Aihuang, LIU Wenbo, et al. Hidden bursting firings and bifurcation mechanisms in memristive neuron model with threshold electromagnetic induction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(2): 502–511. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2905137 XU Fei, ZHANG Jiqian, JIN Meng, et al. Chimera states and synchronization behavior in multilayer memristive neural networks[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2018, 94(2): 775–783. doi: 10.1007/s11071-018-4393-9 BAO Han, LIU Wenbo, and HU Aihuang. Coexisting multiple firing patterns in two adjacent neurons coupled by memristive electromagnetic induction[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2019, 95(1): 43–56. doi: 10.1007/s11071-018-4549-7 CHEN Chengjie, CHEN Jingqi, BAO Han, et al. Coexisting multi-stable patterns in memristor synapse-coupled Hopfield neural network with two neurons[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2019, 95(4): 3385–3399. doi: 10.1007/s11071-019-04762-8 CHEN Chengjie, BAO Han, CHEN Mo, et al. Non-ideal memristor synapse-coupled bi-neuron Hopfield neural network: Numerical simulations and breadboard experiments[J]. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2019, 111: 152894. doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2019.152894 BREAKSPEAR M. Dynamic models of large-scale brain activity[J]. Nature Neuroscience, 2017, 20(3): 340–352. doi: 10.1038/nn.4497 WANG Guangyi, YUAN Fang, CHEN Guanrong, et al. Coexisting multiple attractors and riddled basins of a memristive system[J]. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2018, 28(1): 013125. doi: 10.1063/1.5004001 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
