A Survey on Personality in Cyberspace Security
-
摘要: 网络空间是所有信息系统的集合,是人类赖以生存的信息环境。网络空间安全已经从物理域、信息域安全扩展到以人为中心的认知域和社会域安全,对人的安全研究已经成为了网络空间安全的必然趋势。人是复杂多变的综合体,而人格作为人的稳定的心理特征,成为了人的安全相关研究的切入点。该文梳理当前网络空间安全中的人格研究,介绍了网络空间安全和人格的基本概念,提出了网络空间安全中人格的研究框架,涵盖理论研究、技术研究和技术应用3个层次;其中技术研究主要包括人格测量、人格的安全脆弱性和针对人的安全防护3部分;详细探讨了当前人格安全研究现状和存在的问题,最后讨论了未来的研究方向和发展趋势。Abstract: Cyberspace is a collection of all information systems, which refers to the information environment for human survival. Cyberspace security has expanded from physical and information domain security to human-centered social and cognitive domain security. The research on human security has become an inevitable trend of Cyberspace security. The characteristics of human are complex and changeable. The personality, as a stable psychological characteristic, is an appropriate breakthrough point for human security research. This paper investigates and untangles relevant personality research in Cyberspace security. The concepts of Cyberspace security and personality are introduced concisely. A research framework of personality in Cyberspace security is proposed, including theoretical research, technological research and technological application. The technological research mainly includes three parts: personality measurement, personality vulnerability and protection methods in Cyber security. Additionally, this paper discusses the current research status and problems of personality in Cyber security in detail. Finally, the future research directions and development trends of personality in Cyber security are explored.
-
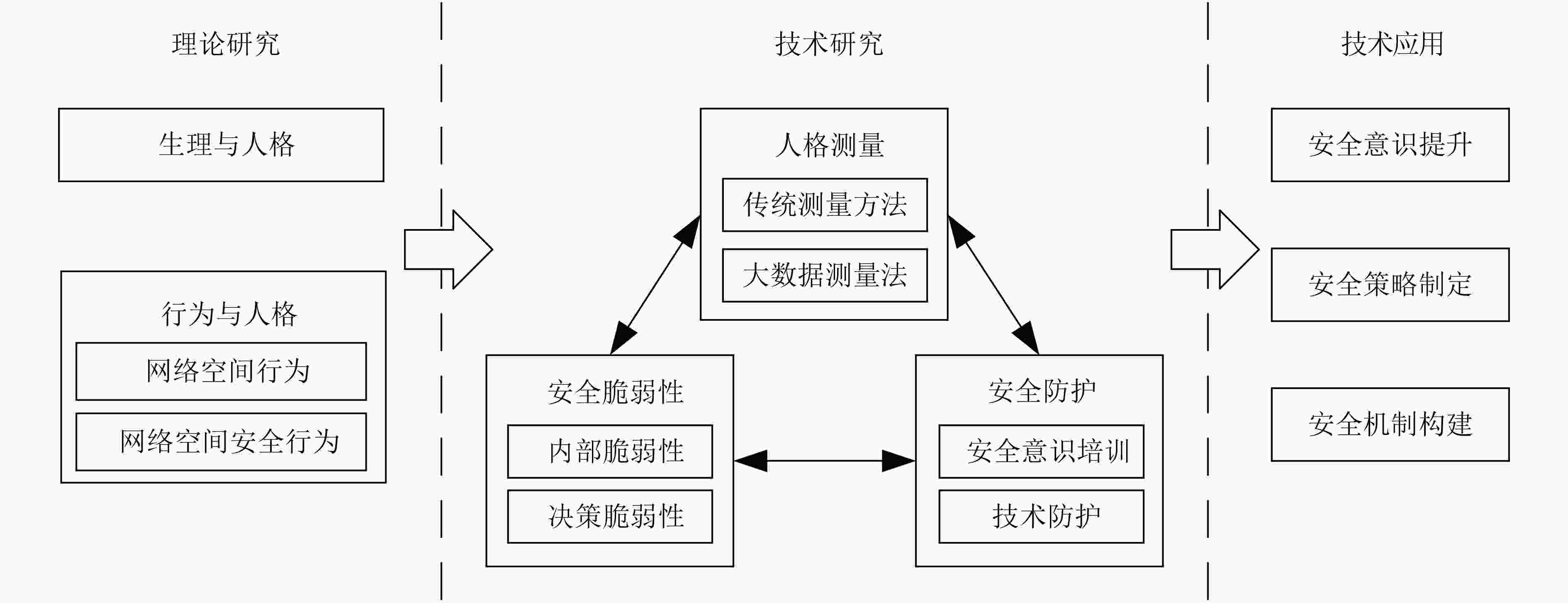
图 2 安全意识评估模型[59]
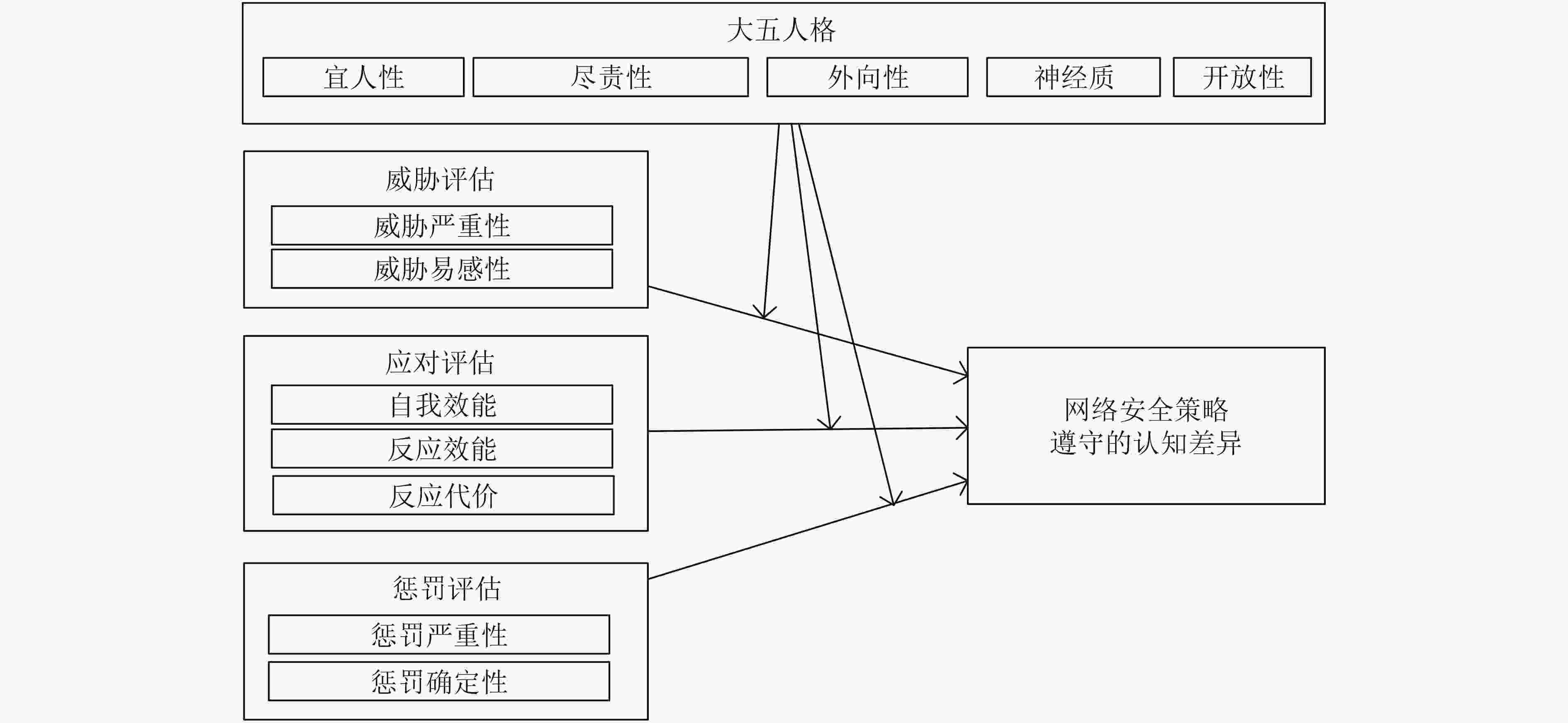
图 3 人格与意识、行为关联模型[63]
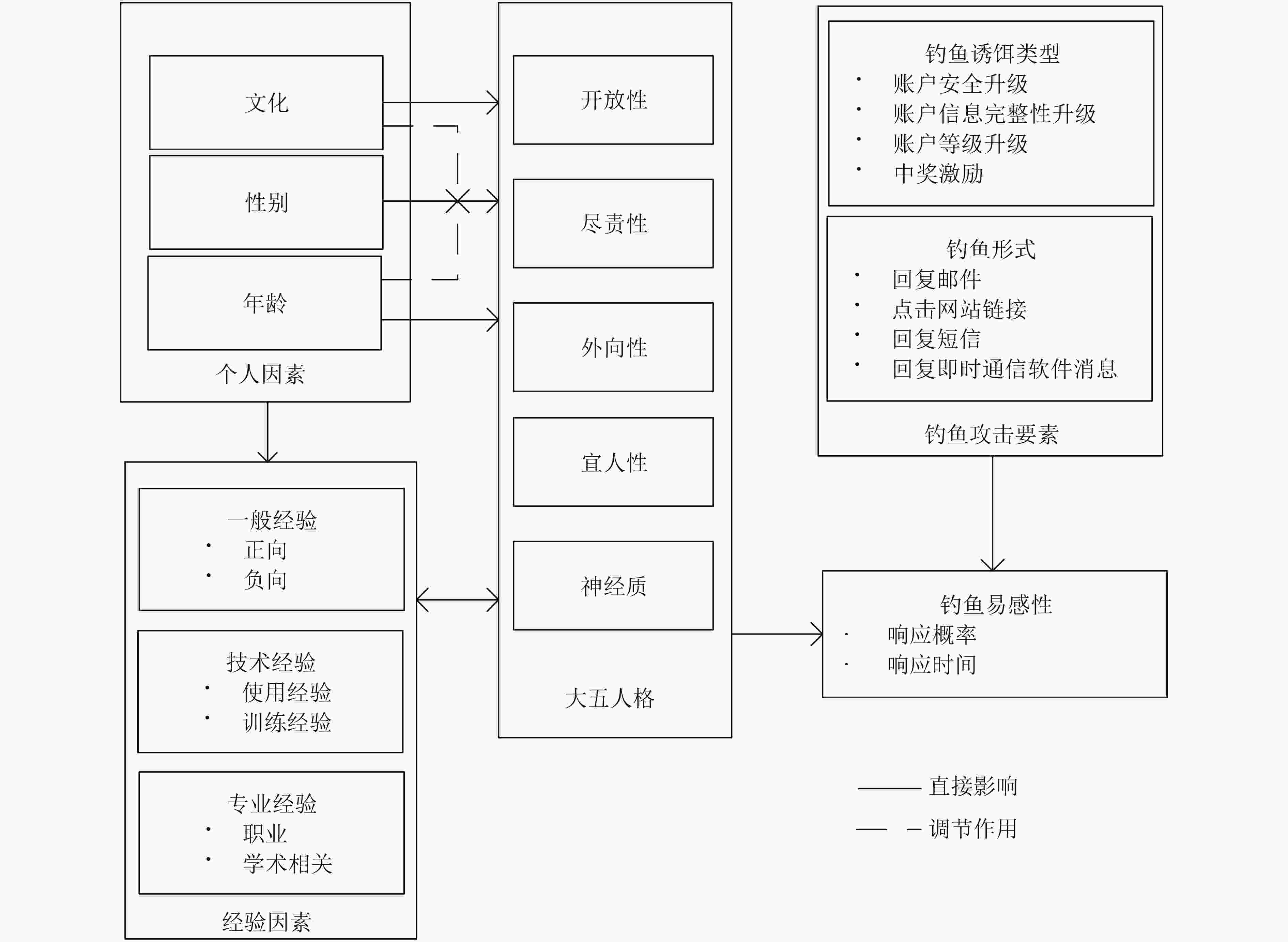
图 4 以大五人格理论为核心的钓鱼易感性研究框架[69]
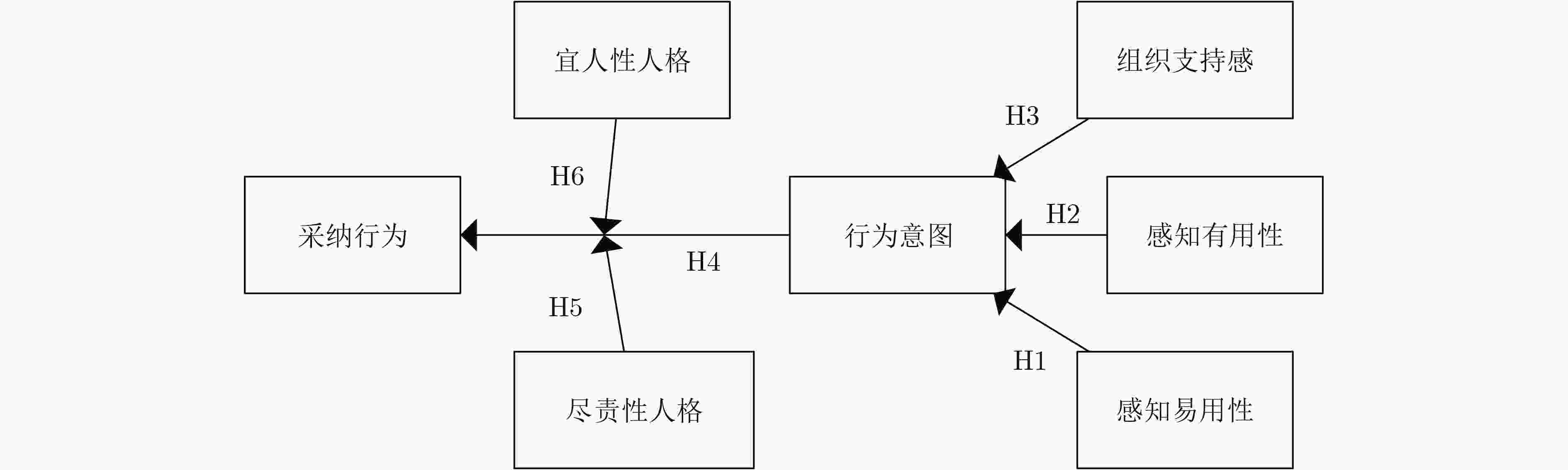
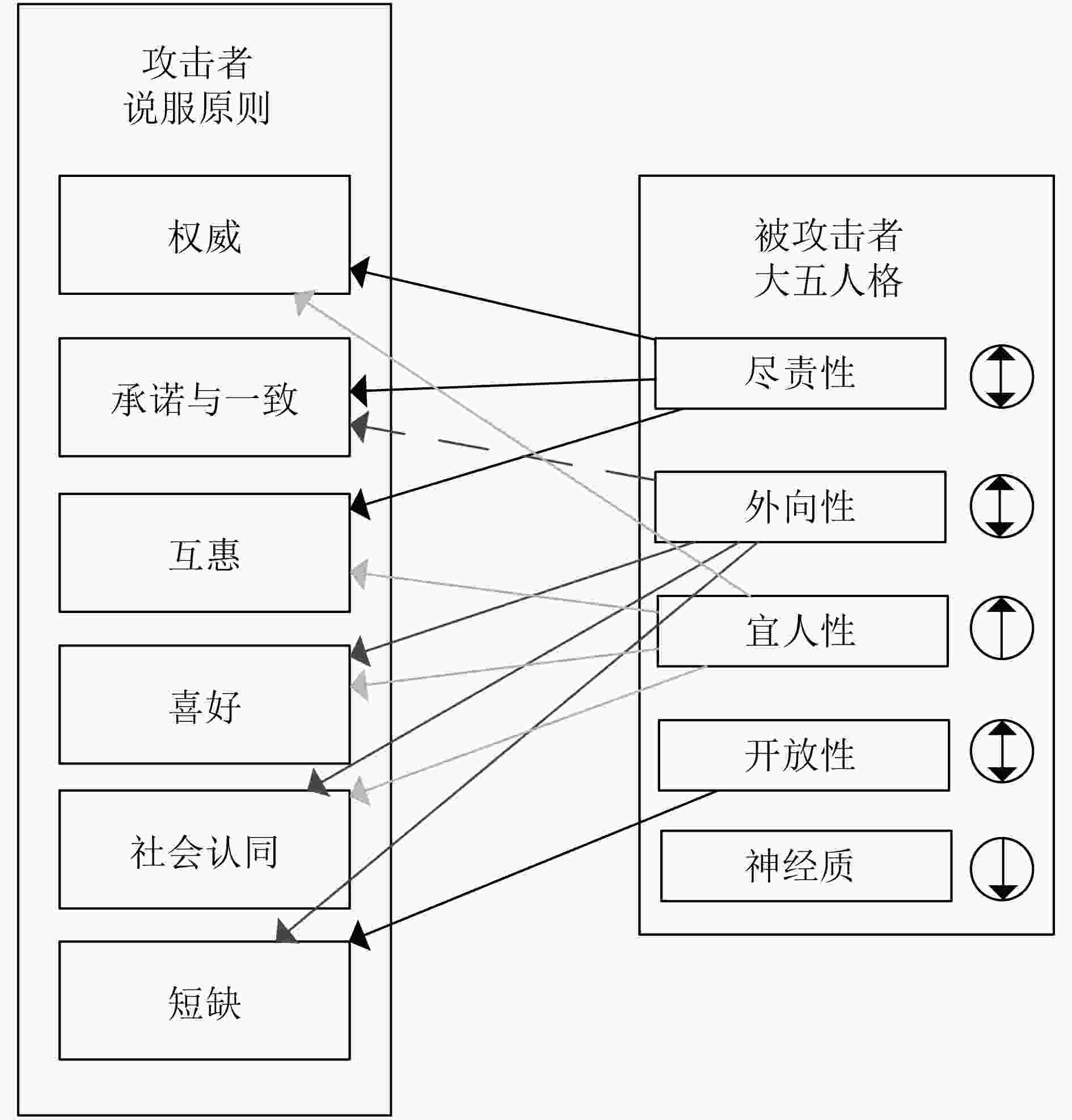
图 5 社会工程学-人格框架[70]
表 1 大五人格模型
特质因素 特征 神经质 烦恼对平静
不安全感对安全感
自怜对自我满意外向性 好交际对不好交际
爱娱乐对严肃
感情丰富对含蓄开放性 富于想象对务实
寻求变化对遵守惯例
自主对顺从宜人性 热心对无情
信赖对怀疑
乐于助人对不合作尽责性 有序对无序
谨慎细心对粗心大意
自律对意志薄弱 -
GIBSON W. Burning Chrome[M]. New York: EOS/HarperCollins Publishers, 2003: 1–5. 张焕国, 韩文报, 来学嘉, 等. 网络空间安全综述[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2015, 58(1): 1–43.ZHANG Huanguo, HAN Wenbao, LAI Xuejia, et al. Survey on cyberspace security[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2015, 58(1): 1–43. OTTIS R and LORENTS P. Cyberspace: Definition and implications[C]. The 5th International Conference on Information Warfare and Security, Dayton, 2010: 267. MITNICK K D and SIMON W L. The Art of Deception: Controlling the Human Element of Security[M]. Indianapolis: John Wiley & Sons, 2002: 1–10. STEWART JR J H. Social engineering deception susceptibility: Modification of personality traits susceptible to social engineering manipulation to acquire information through attack and exploitation[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Colorado Technical University, 2015. BULLER D B, BURGOON J K, BUSLIG A, et al. Testing interpersonal deception theory: The Language of interpersonal deception[J]. Communication Theory, 1996, 6(3): 268–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2885.1996.tb00129.x DEPAULO B M, LINDSAY J J, MALONE B E, et al. Cues to deception[J]. Psychological Bulletin, 2003, 129(1): 74–118. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.129.1.74 IRANI D, BALDUZZI M, BALZAROTTI D, et al. Reverse Social engineering attacks in online social networks[C]. The 8th International Conference on Detection of Intrusions and Malware, and Vulnerability Assessment, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011: 55–74. BURGER J M. Personality[M]. California: Thomson Learning, 2007: 5–7. 彭聃龄. 普通心理学[M]. 北京: 北京师范大学出版社, 2012: 203–210.PENG Danling. Common Psychology[M]. Beijing: Beijing Normal University Press, 2012: 203–210. ALMLUND M, DUCKWORTH A L, HECKMAN J, et al. Personality psychology and economics[J]. Handbook of the Economics of Education, 2011, 4: 1–181. HOGAN R, JOHNSON J, and BRIGGS S R. Handbook of Personality Psychology[M]. San Diego: Academic Press, 1997: 750–751. GERRIG R J and ZIMBARDO P G. Psychology and Life[M]. New York: Pearson, 2012. GOLDBERG L R, JOHNSON J A, Eber H W, et al. The international personality item pool and the future of public-domain personality measures[J]. Journal of Research in Personality, 2006, 40(1): 84–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2005.08.007 郑敬华, 郭世泽, 高梁, 等. 基于多任务学习的大五人格预测[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2018, 35(4): 550–560. doi: 10.7523/j.issn.2095-6134.2018.04.019ZHENG Jinghua, GUO Shize, GAO Liang, et al. Microblog users’ Big-Five personality prediction based on multi-task learning[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 35(4): 550–560. doi: 10.7523/j.issn.2095-6134.2018.04.019 KOSINSKI M, BACHRACH Y, KOHLI P, et al. Manifestations of user personality in website choice and behaviour on online social networks[J]. Machine Learning, 2014, 95(3): 357–380. doi: 10.1007/s10994-013-5415-y HU Jian, ZENG Huajun, LI Hua, et al. Demographic prediction based on user’s browsing behavior[C]. The 16th International Conference on World Wide Web, Banff, Canada, 2007: 151–160. doi: 10.1145/1242572.1242594. RENTFROW P J and GOSLING S D. The do re mi’s of everyday life: The structure and personality correlates of music preferences[J]. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 2003, 84(6): 1236–1256. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.84.6.1236 郑日昌, 蔡永红, 周益群. 心理测量学[M]. 北京: 人民教育出版社, 1999: 155–170.ZHENG Richang, CAI Yonghong, and ZHOU Yiqun. Psychological Testing[M]. Beijing: People Education Press, 1999: 155–170. GREGORY R J. Psychological Testing: History, Principles, and Applications[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2013: 25. KUHN M H and MCPARTLAND T S. An empirical investigation of self-attitudes[J]. American Sociological Review, 1954, 19(1): 68–76. doi: 10.2307/2088175 朱廷劭, 李昂, 宁悦, 等. 网络社会中个体人格特征及其行为关系[J]. 兰州大学学报: 社会科学版, 2011, 39(5): 44–51.ZHU Tingshao, LI Ang, NING Yue, et al. Individual personality and its behavior in the cyber society[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University:Social Sciences, 2011, 39(5): 44–51. WEINER I B. The Corsini Encyclopedia of Psychology[M]. 4th ed. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2010. MORGAN C D and MURRAY H A. A method for investigating fantasies: The thematic apperception test[J]. Archives of Neurology & Psychiatry, 1935, 34(2): 289–306. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1935.02250200049005 MURRAY H A and DAN M A. Explorations in personality[J]. Journal of Projective Techniques & Personality Assessment, 1938(2): 283–285. MURRAY H A. Explorations in personality: A clinical and experimental study of fifty men of college age[J]. American Journal of Sociology, 1938, 4(4): 576–583. MCCRAE R R and WEISS A. Observer Ratings of Personality[M]. ROBINS R W, FRALEY R C, and KRUEGER R F. Handbook of Research Methods in Personality Psychology. New York: The Guilford Press, 2007: 259–272. VINCIARELLI A and MOHAMMADI G. A survey of personality computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2014, 5(3): 273–291. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2014.2330816 ARGAMON S, DHAWLE S, KOPPEL M, et al. Lexical predictors of personality type[C]. 2005 Joint Annual Meeting of the Interface and the Classification Society of North America, 2005. MAIRESSE F, WALKER M A, MEHL M R, et al. Using linguistic cues for the automatic recognition of personality in conversation and text[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2007, 30(1): 457–500. doi: 10.1613/jair.2349 TAUSCZIK Y R and PENNEBAKER J W. The psychological meaning of words: LIWC and computerized text analysis methods[J]. Journal of Language and Social Psychology, 2010, 29(1): 24–54. doi: 10.1177/0261927x09351676 OBERLANDER J and NOWSON S. Whose thumb is it anyway?: Classifying author personality from weblog text[C]. The COLING/ACL on Main Conference Poster Sessions, Sydney, Australia, 2006: 627–634. NOWSON S and OBERLANDER J. Identifying more bloggers: Towards large scale personality classification of personal weblogs[C]. The International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, Boulder, USA, 2007: 115–127. MINAMIKAWA A and YOKOYAMA H. Blog tells what kind of personality you have: Egogram estimation from Japanese weblog[C]. 2011 ACM Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work, Hangzhou, China, 2011: 217–220. doi: 10.1145/1958824.1958856. MINAMIKAWA A and YOKOYAMA H. Personality estimation based on Weblog text classification[C]. The 24th International Conference on Industrial Engineering and other Applications of Applied Intelligent Systems Conference on Modern Approaches in Applied Intelligence, Syracuse, USA, 2011: 89–97. GILL A J, NOWSON S, and OBERLANDER J. What are they blogging about? Personality, topic and motivation in Blogs[C]. The 3rd International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, San Jose, USA, 2009: 18–25. HAMBURGER Y A and BEN-ARTZI E. The relationship between extraversion and neuroticism and the different uses of the Internet[J]. Computers in Human Behavior, 2000, 16(4): 441–449. doi: 10.1016/S0747-5632(00)00017-0 PARK G, SCHWARTZ H A, EICHSTAEDT J C, et al. Automatic personality assessment through social media language[J]. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 2015, 108(6): 934–952. doi: 10.1037/pspp0000020 WEI Xiangyu, XU Guangquan, WANG Hao, et al. Sensing users’ emotional intelligence in social networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2020, 7(1): 103–112. doi: 10.1109/TCSS.2019.2944687 LUYCKX K and DAELEMANS W. Using syntactic features to predict author personality from text[C]. Digital Humanities 2008, Oulu, Finland, 2008: 146–149. MAO Yu, ZHANG Dongmei, WU Chunhua, et al. Feature analysis and optimisation for computational personality recognition[C]. The IEEE 4th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 2018: 2410–2414, doi: 10.1109/CompComm.2018.8780801. WOLFRADT U and DOLL J. Motives of adolescents to use the Internet as a function of personality traits, personal and social factors[J]. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 2001, 24(1): 13–27. doi: 10.2190/ANPM-LN97-AUT2-D2EJ ROSS C, ORR E S, SISIC M, et al. Personality and motivations associated with Facebook use[J]. Computers in Human Behavior, 2009, 25(2): 578–586. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2008.12.024 AMICHAI-HAMBURGER Y and VINITZKY G. Social network use and personality[J]. Computers in Human Behavior, 2010, 26(6): 1289–1295. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2010.03.018 LI Lin, LI Ang, HAO Bibo, et al. Predicting active users’ personality based on micro-Blogging behaviors[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(1): e84997. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084997 SWICKERT R J, ROSENTRETER C J, HITTNER J B, et al. Extraversion, social support processes, and stress[J]. Personality and Individual Differences, 2002, 32(5): 877–891. doi: 10.1016/s0191-8869(01)00093-9 FRIGGERI A, LAMBIOTTE R, KOSINSKI M, et al. Psychological aspects of social communities[C]. 2012 International Conference on Privacy, Security, Risk and Trust and 2012 International Conference on Social Computing, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2012: 195–202. doi: 10.1109/SocialCom-PASSAT.2012.104. LAMBIOTTE R and KOSINSKI M. Tracking the digital footprints of personality[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2014, 102(12): 1934–1939. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2014.2359054 University of Cambridge. MyPersonality project[EB/OL]. http://mypersonality.org/wiki/doku.php, 2010. RIFE S C, CATE K L, KOSINSKI M, et al. Participant recruitment and data collection through Facebook: The role of personality factors[J]. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 2016, 19(1): 69–83. doi: 10.1080/13645579.2014.957069 KOSINSKI M, STILLWELL D, and GRAEPEL T. Private traits and attributes are predictable from digital records of human behavior[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(15): 5802–5805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218772110 OLGUÍN D O, GLOOR P A, and PENTLAND A. Capturing individual and group behavior with wearable sensors[C]. 2009 AAAI Spring Symposium on Human Behavior Modeling, Stanford, USA, 2009: 68–74. CHITTARANJAN G, BLOM J, and GATICA-PEREZ D. Who’s who with big-five: Analyzing and classifying personality traits with smartphones[C]. The 15th Annual International Symposium on Wearable Computers, San Francisco, USA, 2011: 29–36. doi: 10.1109/ISWC.2011.29. CHITTARANJAN G, BLOOM J, and GATICA-PEREZ D. Mining large-scale smartphone data for personality studies[J]. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, 2013, 17(3): 433–450. doi: 10.1007/s00779-011-0490-1 STAIANO J, LEPRI B, AHARONY N, et al. Friends don’t lie: Inferring personality traits from social network structure[C]. 2012 ACM Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Pennsylvania, USA, 2012: 321–330. doi: 10.1145/2370216.2370266. BIEL J I, TEIJEIRO-MOSQUERA L, and GATICA-PEREZ D. FaceTube: Predicting personality from facial expressions of emotion in online conversational video[C]. The 14th ACM international conference on Multimodal Interaction, Santa Monica, USA, 2012: 53–56. doi: 10.1145/2388676.2388689. SKOWRON M, TKALČIČ M, FERWERDA B, et al. Fusing social media cues: Personality prediction from twitter and instagram[C]. The 25th International Conference Companion on World Wide Web, Montréal Québec, Canada, 2016: 107–108. doi: 10.1145/2872518.2889368. FERWERDA B, SCHEDL M, and TKALCIC M. Using instagram picture features to predict users’ personality[C]. The 22nd International Conference on Multimedia Modeling, Miami, USA, 2016: 850–861. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-27671-7_71. WARKENTIN M, MCBRIDE M, CARTER L, et al. The role of individual characteristics on insider abuse intentions[C]. The 18th Americas Conference on Information Systems, Seattle, USA, 2012: 4833–4842. KORZAAN M L and BOSWELL K T. The influence of personality traits and information privacy concerns on behavioral intentions[J]. Journal of Computer Information Systems, 2008, 48(4): 15–24. UFFEN J and BREITNER M H. Management of technical security measures: An empirical examination of personality traits and behavioral intentions[C]. The 46th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Wailea, USA, 2013: 4551–4560. doi: 10.1109/HICSS.2013.388. BRECHT F, FABIAN B, KUNZ S, et al. Communication anonymizers: Personality, internet privacy literacy and their influence on technology acceptance[C]. The 20th European Conference on Information Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2012: 214. SHROPSHIRE J, WARKENTIN M, and SHARMA S. Personality, attitudes, and intentions: Predicting initial adoption of information security behavior[J]. Computers & Security, 2015, 49: 177–191. doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2015.01.002 MODIC D and LEA S E G. How neurotic are scam victims, really? The Big Five and internet scams[EB/OL]. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2448130, 2014. PATTINSON M, JERRAM C, PARSONS K, et al. Why do some people manage phishing e-mails better than others?[J]. Information Management & Computer Security, 2012, 20(1): 18–28. doi: 10.1108/09685221211219173 DARWISH A, EL ZARKA A, and ALOUL F. Towards understanding phishing victims’ profile[C]. 2012 International Conference on Computer Systems and Industrial Informatics, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2012: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICCSII.2012.6454454. ENOS F, BENUS S, CAUTIN R L, et al. Personality factors in human deception detection: Comparing human to machine performance[C]. The 9th International Conference on Spoken Language Processing, Pittsburgh, USA, 2006: 813–816. HALEVI T, LEWIS J, and MEMON N. Phishing, personality traits and facebook[J]. 2013, arXiv: 1301.7643. PARRISH JR J L, BAILEY J L, and COURTNEY J F. A personality based model for determining susceptibility to phishing attacks[R]. University of Arkansas at Little Rock Technique Report, Arkansas, USA, 2009: 285–296. CHO J H, CAM H, and OLTRAMARI A. Effect of personality traits on trust and risk to phishing vulnerability: Modeling and analysis[C]. 2016 IEEE International Multi-disciplinary Conference on Cognitive Methods in Situation Awareness and Decision Support (CogSIMA), San Diego, USA, 2016: 7–13. doi: 10.1109/COGSIMA.2016.7497779. JENSEN-CAMPBELL L A, KNACK J M, and GOMEZ H L. The psychology of nice people[J]. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 2010, 4(11): 1042–1056. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-9004.2010.00307.x JOHN O P, NAUMANN L P, and Soto C J. Paradigm Shift to the Integrative Big Five Trait Taxonomy: History, Measurement and Conceptual Issues[M]. JOHN O P, ROBINS R W, and PERVIN L A. Handbook of Personality: Theory and Research. 3rd ed. New York, NY: Guilford, 2008. CROSSLER R E, JOHNSTON A C, LOWRY P B, et al. Future directions for behavioral information security research[J]. Computers & Security, 2013, 32: 90–101. doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2012.09.010 PFLEEGER S L, PREDD J B, HUNKER J, et al. Insiders behaving badly: Addressing bad actors and their actions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2010, 5(1): 169–179. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2009.2039591 DOWNS J S, HOLBROOK M, and CRANOR L F. Behavioral response to phishing risk[C]. The Anti-Phishing Working Groups 2nd annual eCrime Researchers Summit, Pittsburgh, USA, 2007: 37–44. doi: 10.1145/1299015.1299019. HALEVI T, LEWIS J, and MEMON N. A pilot study of cyber security and privacy related behavior and personality traits[C]. The 22nd International Conference on World Wide Web, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2013: 737–744. doi: 10.1145/2487788.2488034. 冯登国, 张敏, 叶宇桐. 基于差分隐私模型的位置轨迹发布技术研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 74–88. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190632FENG Dengguo, ZHANG Min, and YE Yutong. Research on differentially private trajectory data publishing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 74–88. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190632 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
