A Dual-Channel Deep Convolutional Neural Network Model for Random-Valued Impulse Noise Removal
-
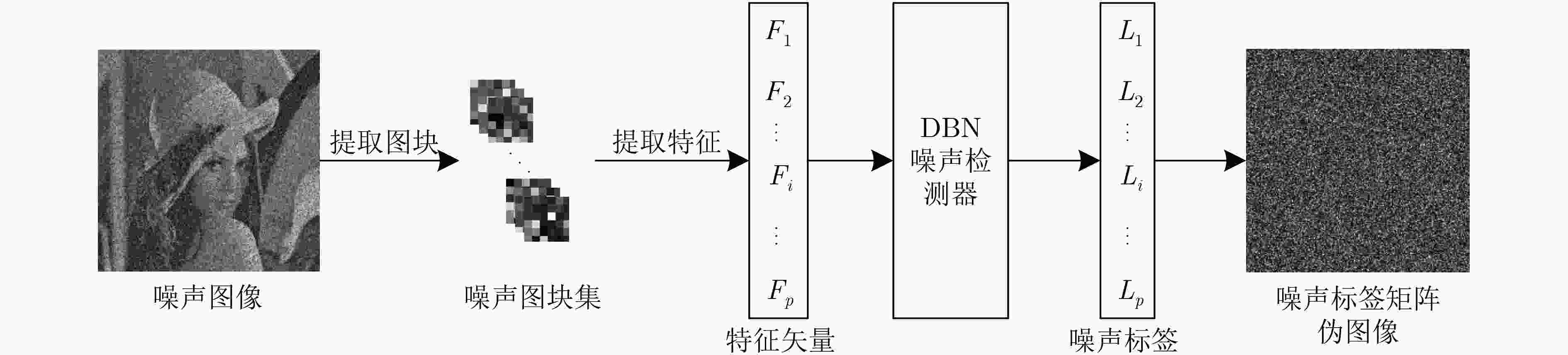
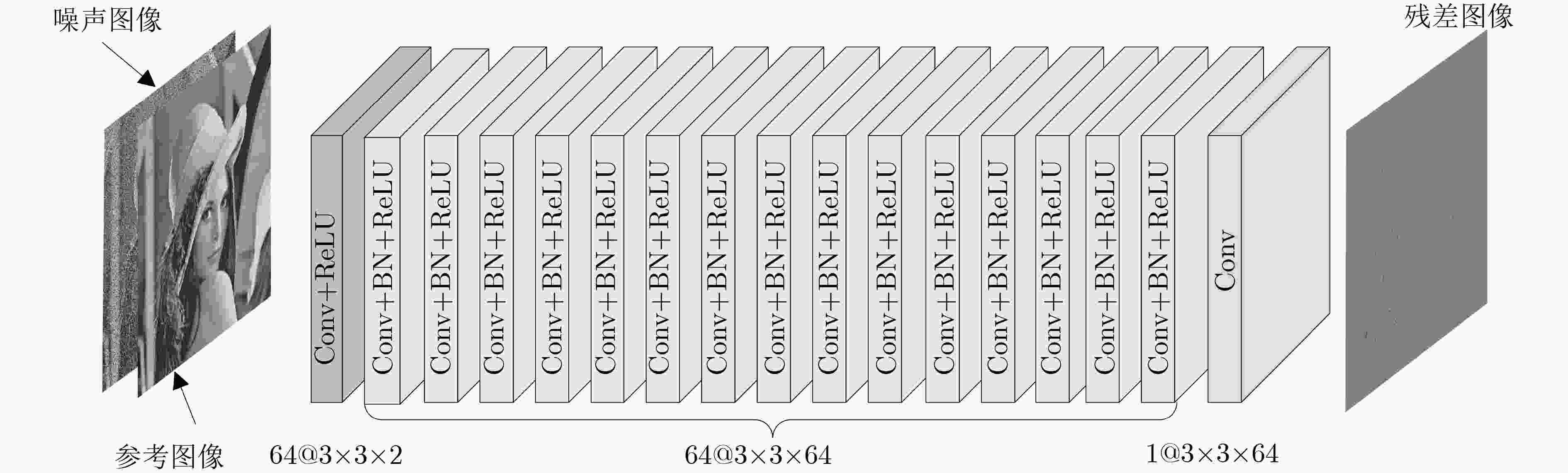
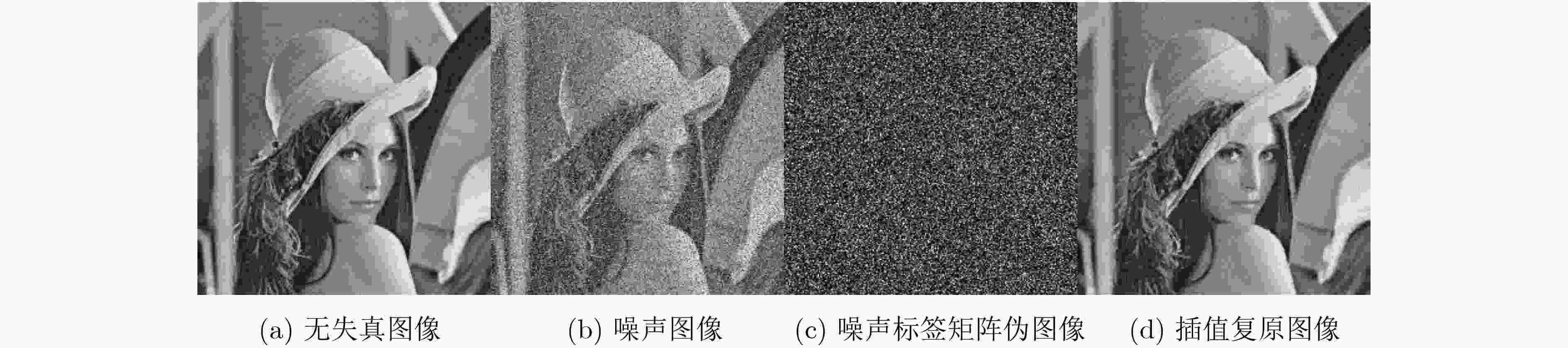
摘要: 为提高对随机脉冲噪声(RVIN)图像的降噪效果,该文提出一种被称为双通道降噪卷积神经网络(D-DnCNN)的RVIN深度降噪模型。首先,提取多个不同阶对数差值排序(ROLD)统计值及1个边缘特征统计值构成描述图块中心像素点是否为RVIN噪声的噪声感知特征矢量。其次,利用预先训练好的深度置信网络(DBN)预测模型实现特征矢量到噪声标签的映射,完成对噪声图像中噪声点的检测。再次,在噪声检测标签的指示下采用Delaunay三角剖分插值算法快速修复噪声像素点从而获得初步复原图像。最后,将初步复原图像作为参考图像与噪声图像联接(concatenate)后输入D-DnCNN模型后获得残差图像,将参考图像减去残差图像即可获得降噪后图像。实验数据表明:D-DnCNN模型在各个噪声比例下的降噪效果均显著超过了现有的经典开关型RVIN降噪算法,与普通的单通道RVIN深度降噪模型相比也有较大幅度提升。Abstract: A Dual-channel Denoising Convolutional Neural Network (D-DnCNN) model for the removal of Random-Valued Impulse Noise (RVIN) is proposed. To obtain the reference image quickly, several Rank-Ordered Logarithmic absolute Difference (ROLD) statistics and one edge feature statistic are first extracted from a local window to construct a RVIN-aware feature vector which can describe the central pixel of the patch is RVIN or not. Next, a noise detector based on Deep Belief Network (DBN) is trained to map the extracted feature vectors to their corresponding noise labels to detect all noise-like pixels in the observed image. Then, under the guidance of noise labels, the Delaunay triangulation-based interpolation algorithm is exploited to restore all detected noise-like pixels quickly and generate a preliminary restored image used as reference image. Finally, the reference image and the noisy image are simultaneously fed into the D-DnCNN model to output its corresponding residual image, and the final restored image can be obtained by subtracting the residual image from the noisy image. Extensive experimental results show that, the denoising effect of the proposed D-DnCNN denoising model outperforms the existing state-of-art switching ones across a range of noise ratios, and it also works better than the ordinary single-channel DnCNN model.
-
表 1 DBN网络在Set12测试集图像上的预测准确性
图像 20%噪声 40%噪声 60%噪声 检测正确率均值 False Miss Accuracy False Miss Accuracy False Miss Accuracy Cameraman 838 2257 0.9528 1914 3952 0.9105 3863 4062 0.8791 0.9141 House 209 1896 0.9679 911 3665 0.9302 2430 4123 0.9000 0.9327 Peppers 400 2524 0.9554 1254 4402 0.9137 3462 4489 0.8787 0.9159 Starfish 536 3217 0.9427 1594 5753 0.8879 5558 4647 0.8443 0.8916 Monarch 489 2776 0.9502 1773 4788 0.8999 4291 4313 0.8687 0.9063 Airplane 1108 2516 0.9447 1979 4514 0.9009 4286 4203 0.8705 0.9054 Parrot 588 2723 0.9495 1877 4465 0.9032 4374 4204 0.8691 0.9073 Lena 755 8303 0.9654 2342 15574 0.9317 9976 17336 0.8958 0.9310 Barbara 2219 12393 0.9443 8329 22147 0.8837 25515 18555 0.8319 0.8866 Boat 1758 10620 0.9564 5318 19001 0.9072 16137 18645 0.8673 0.9103 Man 1714 9717 0.9564 3976 17712 0.9173 13760 18459 0.8771 0.9169 Couple 2027 11049 0.9501 5553 19695 0.9037 16993 19032 0.8626 0.9055 表 2 不同噪声比例下各个降噪算法在BSD68测试图像集上所获得的PSNR均值 (dB)
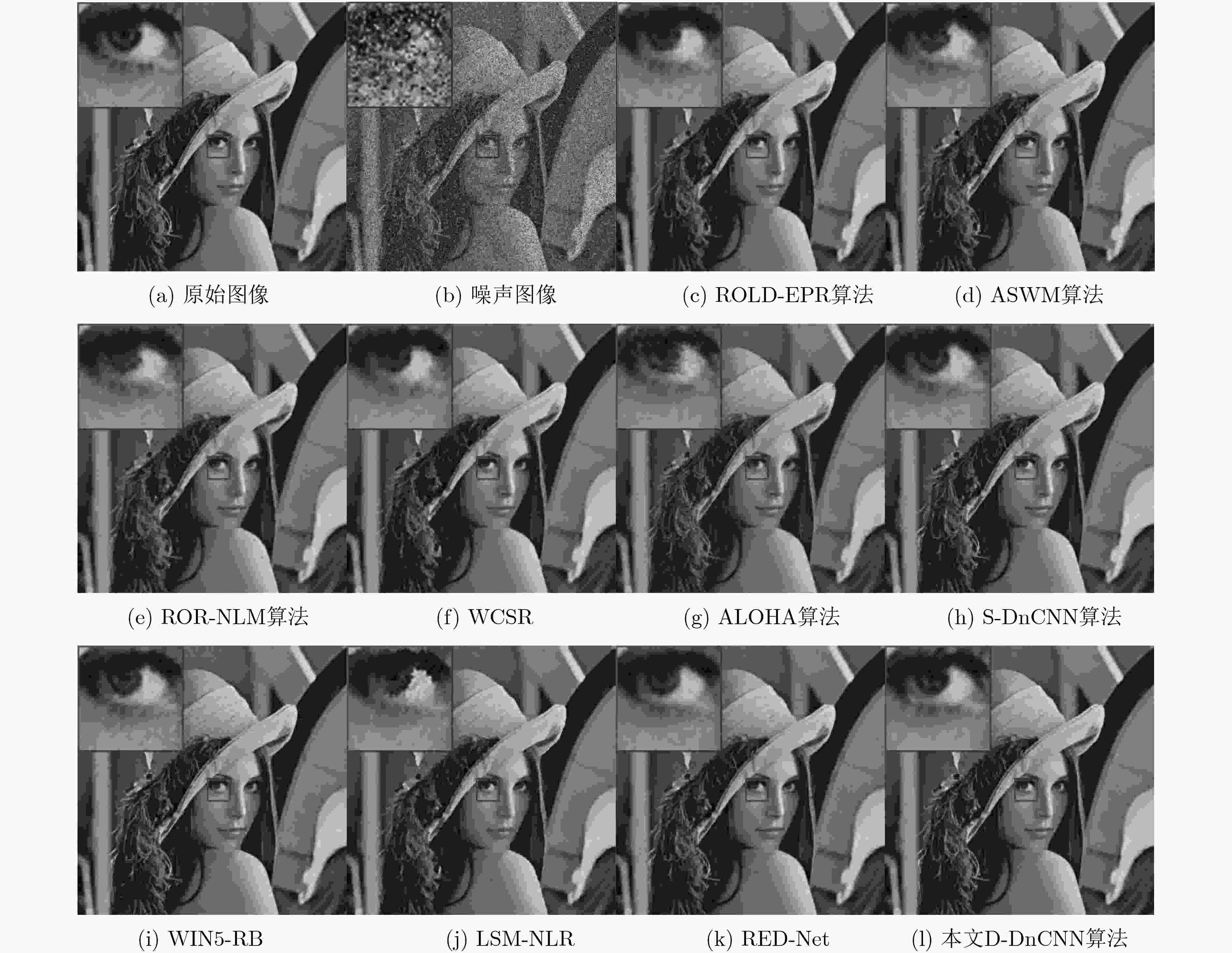
算法 噪声比例(%) 10 20 30 40 50 60 ROLD-EPR 30.24 28.26 26.97 25.96 25.04 23.98 ASWM 28.90 27.99 27.01 25.82 23.84 21.05 ROR-NLM 27.29 26.67 25.88 24.69 22.73 20.14 WCSR 30.11 27.93 26.55 25.51 24.52 23.49 ALOHA 31.75 29.04 25.13 23.74 21.81 18.79 WIN5-RB 34.67 31.46 29.02 27.11 25.46 23.68 RED-Net 33.11 30.68 28.87 27.29 25.81 24.37 LSM-NLR 28.86 26.85 25.59 24.63 23.76 22.86 S-DnCNN 35.76 32.41 30.10 27.79 26.15 24.20 本文D-DnCNN 35.71 32.72 30.56 28.62 26.76 25.31 表 3 D-DnCNN与S-DnCNN算法在真实噪声图像集上降噪效果PSNR对比(dB)
对比算法 图像编号 均值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 S-DnCNN 46.85 43.79 52.98 49.64 47.54 43.52 52.47 43.58 42.24 40.66 46.32 本文D-DnCNN 47.45 44.56 54.20 50.32 48.27 44.10 53.81 45.26 43.17 43.17 47.43 表 4 各算法执行时间的比较(s)
算法 执行时间 算法 执行时间 ROLD-EPR 5.6 WIN5RB 22.8 ASWM 86.3 LSM-NLR 257.2 ROR-NLM 43.1 RED-Net 5.3 WCSR 1085.1 S-DnCNN 4.1 ALOHA 1875.2 D-DnCNN 5.3 -
马济通, 邱天爽, 李蓉, 等. 脉冲噪声下基于Renyi熵的分数低阶双模盲均衡算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(2): 378–385. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170366MA Jitong, QIU Tianshuang, LI Rong, et al. Dual-mode blind equalization algorithm based on Renyi entropy and fractional lower order statistics under impulsive noise[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(2): 378–385. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170366 徐少平, 张贵珍, 李崇禧, 等. 基于深度置信网络的随机脉冲噪声快速检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1130–1136. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180558XU Shaoping, ZHANG Guizhen, LI Chongxi, et al. A fast random-valued impulse noise detection algorithm based on deep belief network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1130–1136. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180558 GARNETT R, HUEGERICH T, CHUI C, et al. A universal noise removal algorithm with an impulse detector[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2005, 14(11): 1747–1754. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2005.857261 DONG Yiqiu, CHAN R H, and XU Shufang. A detection statistic for random-valued impulse noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(4): 1112–1120. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2006.891348 ROY A, SINGHA J, DEVI S S, et al. Impulse noise removal using SVM classification based fuzzy filter from gray scale images[J]. Signal Processing, 2016, 128: 262–273. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.04.007 SOLEIMANY S and HAMGHALAM M. A novel random-valued impulse noise detector based on MLP neural network classifier[C]. 2017 Artificial Intelligence and Robotics, Qazvin, Iran, 2017: 165–169. doi: 10.1109/RIOS.2017.7956461. ZHANG Kai, ZUO Wangmeng, CHEN Yunjin, et al. Beyond a Gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7): 3142–3155. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2662206 ZHANG Kai, ZUO Wangmeng, and ZHANG Lei. FFDNet: Toward a fast and flexible solution for CNN-based image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(9): 4608–4622. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2839891 GUO Shi, YAN Zifei, ZHANG Kai, et al. Toward convolutional blind denoising of real photographs[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1712–1722. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00181. YU Hancheng, ZHAO Li, and WANG Haixian. An efficient procedure for removing random-valued impulse noise in images[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2008, 15: 922–925. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2008.2005051 SUN Jiande, LIU Xiaocui, WAN Wenbo, et al. Video hashing based on appearance and attention features fusion via DBN[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 213: 84–94. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.05.098 AKKOUL S, LEDEE R, LECONGE R, et al. A new adaptive switching median filter[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2010, 17(6): 587–590. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2010.2048646 XIONG Bo and YIN Zhouping. A universal denoising framework with a new impulse detector and nonlocal means[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(4): 1663–1675. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2172804 CHEN C L P, LIU Licheng, CHEN Long, et al. Weighted couple sparse representation with classified regularization for impulse noise removal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 4014–4026. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2456432 JIN K H and YE J C. Sparse and low-rank decomposition of a Hankel structured matrix for impulse noise removal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(3): 1448–1461. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2771471 LIU Peng and FANG Ruogu. Learning pixel-distribution prior with wider convolution for image denoising[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.09135, 2017. MAO Xiaojiao, SHEN Chunhua, and YANG Yubin. Image restoration using very deep convolutional encoder-decoder networks with symmetric skip connections[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 2810–2818. HUANG Tao, DONG Weisheng, XIE Xuemei, et al. Mixed noise removal via Laplacian scale mixture modeling and nonlocal low-rank approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7): 3171–3186. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2676466 ARBELÁEZ P, MAIRE M, FOWLKES C, et al. Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(5): 898–916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.161 YUE Zongsheng, YONG Hongwei, ZHAO Qian, et al. Variational denoising network: Toward blind noise modeling and removal[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.11314v1, 2019. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
