Multi-scale Pedestrian Detection in Infrared Images with Salient Background-awareness
-
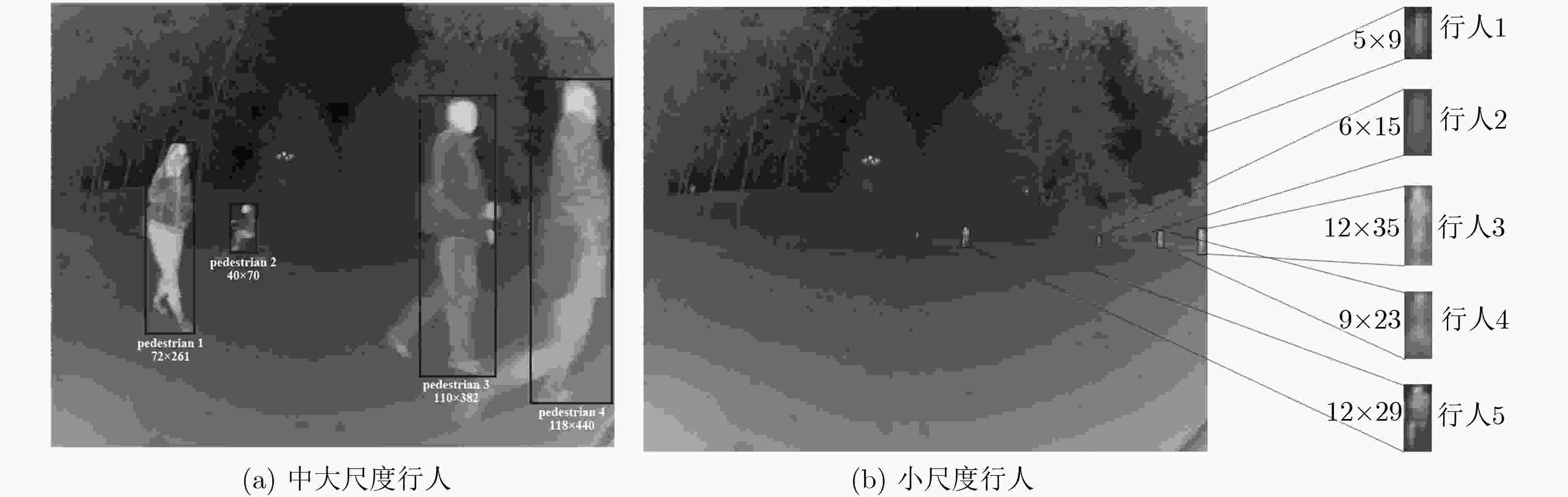
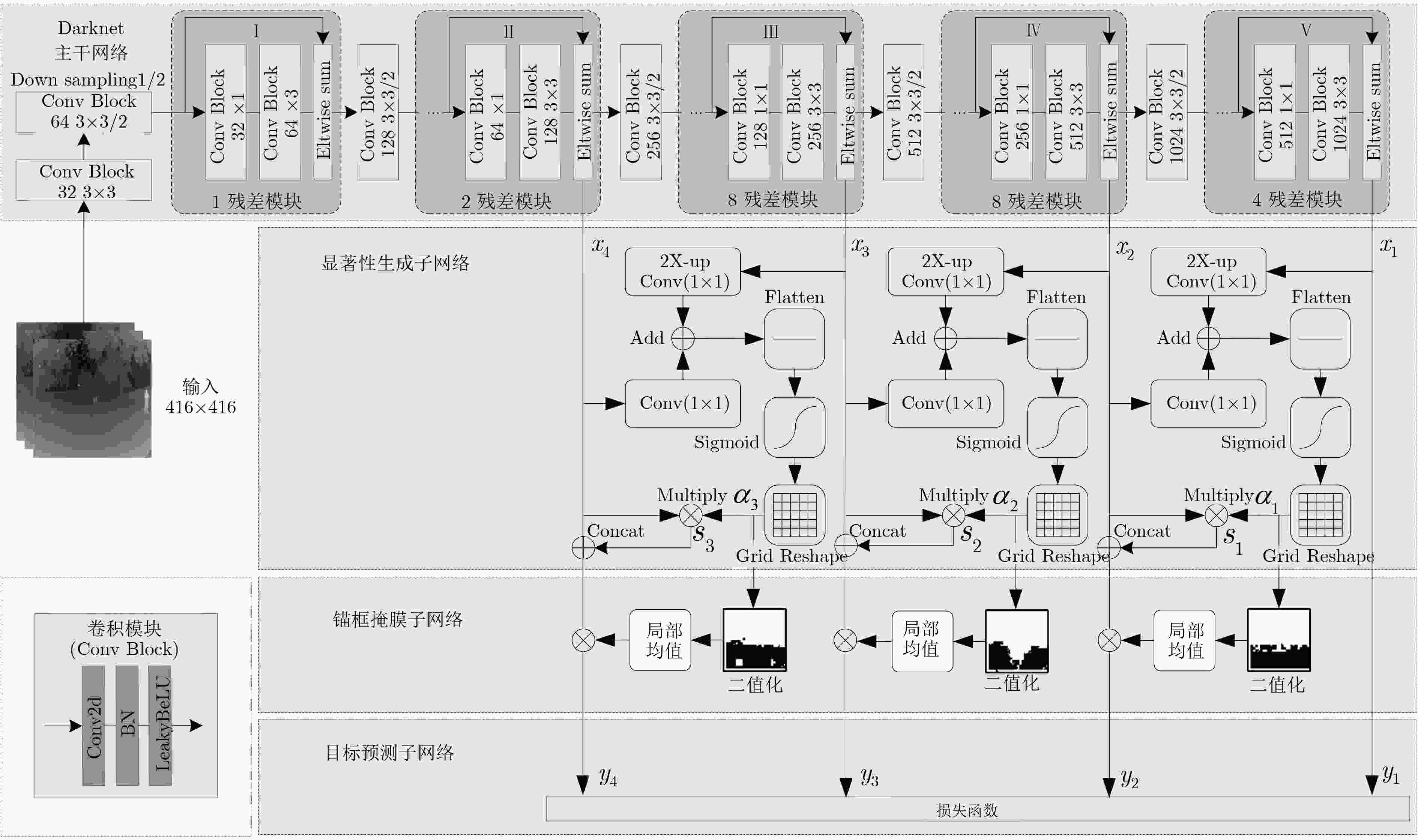
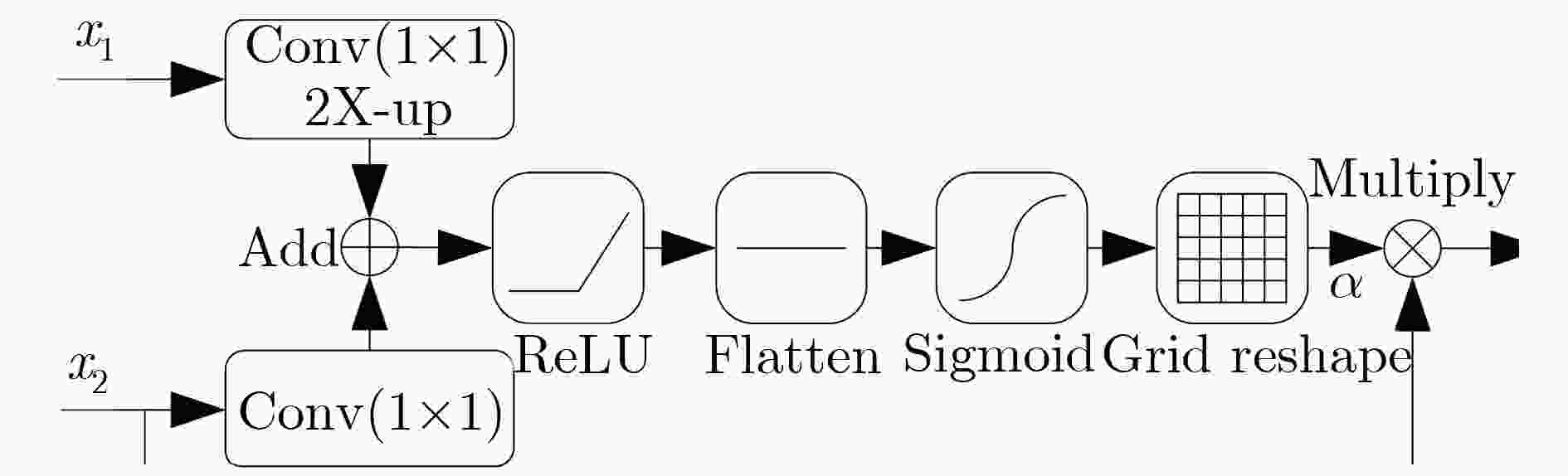
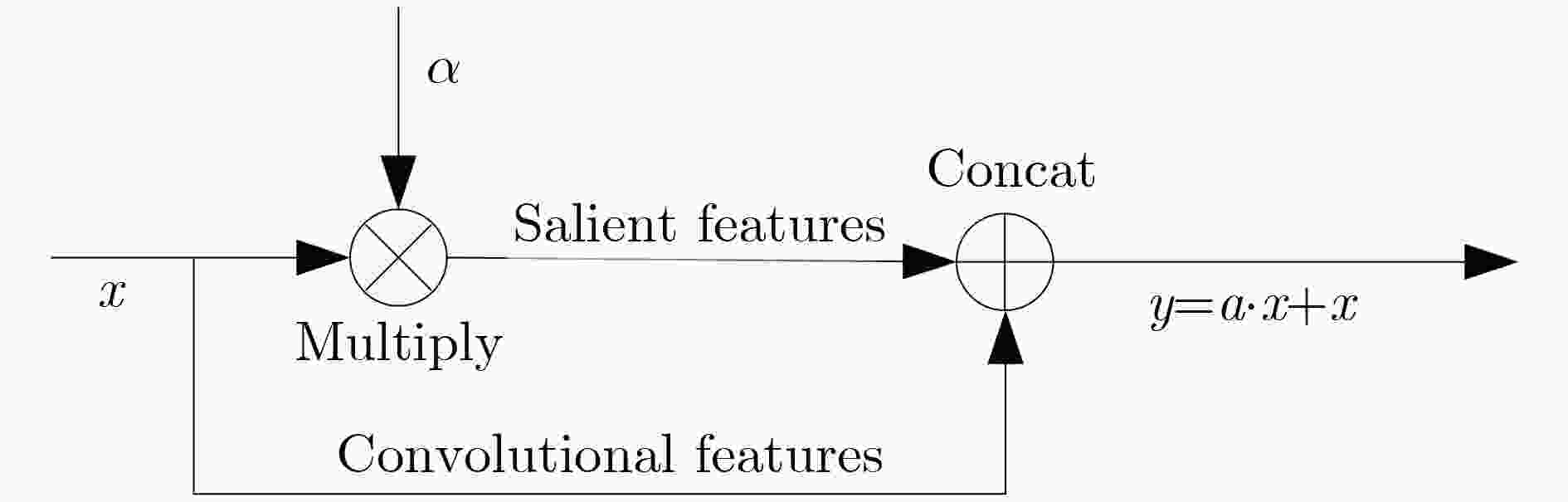
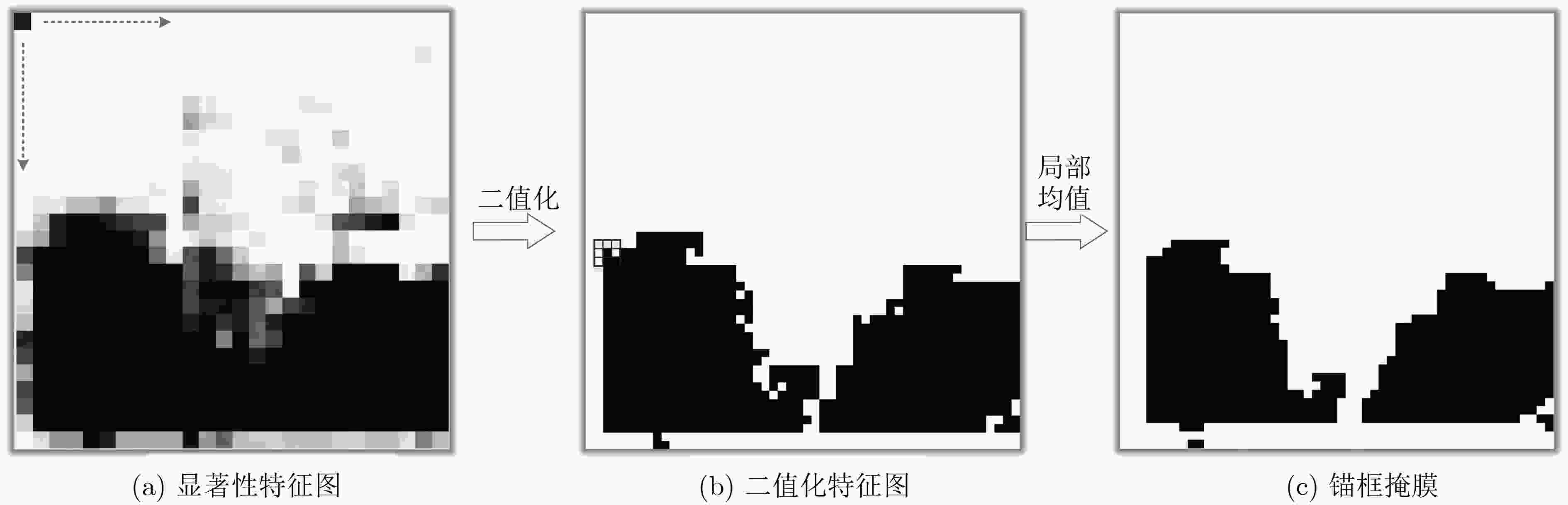
摘要: 超大视场(U-FOV)红外成像系统探测范围大、不受光照限制,但存在尺度多样、小目标丰富的特点。为此该文提出一种具备背景感知能力的多尺度红外行人检测方法,在提高小目标检测性能的同时,减少冗余计算。首先,构建了4尺度的特征金字塔网络分别独立预测目标,补充高分辨率细节特征。其次,在特征金字塔结构的横向连接中融入注意力模块,产生显著性特征,抑制不相关区域的特征响应、突出图像局部目标特征。最后,在显著性系数的基础上构建了锚框掩膜生成子网络,约束锚框位置,排除平坦背景,提高处理效率。实验结果表明,显著性生成子网络仅增加5.94%的处理时间,具备轻量特性;超大视场(U-FOV)红外行人数据集上的识别准确率达到了93.20%,比YOLOv3高了26.49%;锚框约束策略能节约处理时间18.05%。重构模型具有轻量性和高准确性,适合于检测超大视场中的多尺度红外目标。Abstract: The infrared imaging system of Ultrawide Field Of View (U-FOV) has large monitoring range and is not limited by illumination, but there are diverse scales and abundant small objects. For accurately detecting them, a multi-scale infrared pedestrian detection method is proposed with the ability of background-awareness, which can improve the detection performance of small objects and reduce the redundant computation. Firstly, a four scales feature pyramid network is constructed to predict object independently and supplement detail features with higher resolution. Secondly, attention module is integrated into the horizontal connection of feature pyramid structure to generate salient features, suppress feature response of irrelevant areas and enhance the object features. Finally, the anchor mask generation subnetwork is constructed on the basis of salient coefficient to the location of the anchors, to eliminate the flat background, and to improve the processing efficiency. The experimental results show that the salient generation subnetwork only increases the processing time by 5.94%, and has the lightweight characteristic. The Average-Precision is 93.20% on the U-FOV infrared pedestrian dataset, 26.49% higher than that of YOLOv3. Anchor box constraint strategy can save 18.05% of processing time. The proposed method is lightweight and accurate, which is suitable for detecting multi-scale infrared objects in the U-FOV camera.
-
表 1 不同IoU阈值下的行人检测平均准确率
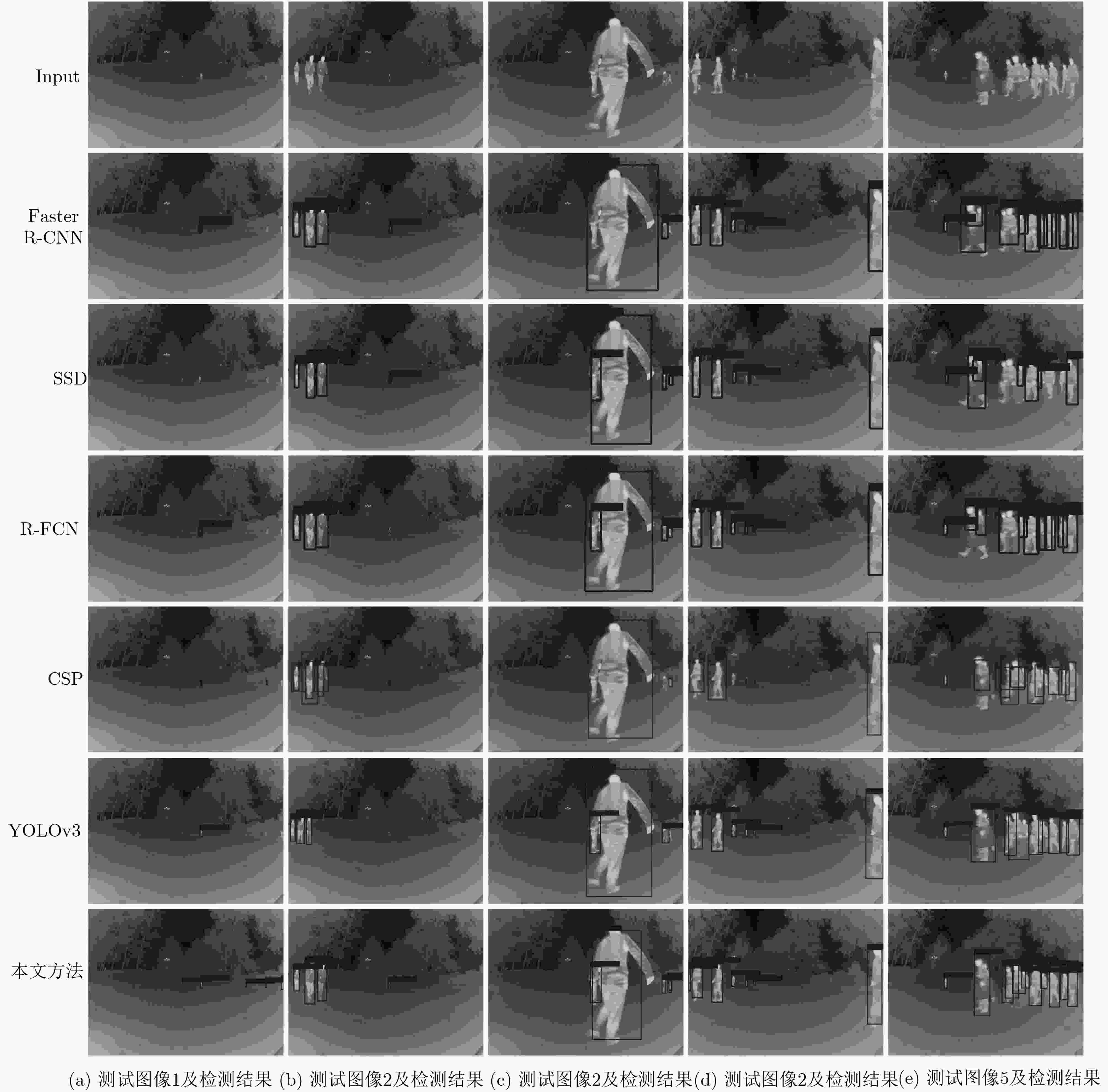
方法 主干网络 训练集 平均准确率(AP) IoU=0.3 IoU=0.45 IoU=0.5 IoU=0.7 Faster R-CNN ResNet101 U-FOV – – 0.5932 – SSD Mobilenet_v1 U-FOV – – 0.5584 – R-FCN ResNet101 U-FOV – – 0.6312 – CSP Resnet50 U-FOV – – 0.8414 – YOLOv3 Darknet53 U-FOV 0.6595 0.6671 0.6628 0.6461 YOLOv3+FS Darknet53 U-FOV 0.8880 0.8870 0.8828 0.8511 YOLOv3+FS Darknet53 Caltech+U-FOV 0.9057 0.9078 0.9084 0.8961 本文方法 Darknet53 Caltech+U-FOV 0.9201 0.9320 0.9315 0.9107 表 2 参数量对比
方法 总参数量 可训练参数量 不可训练参数量 YOLOv3 61576342 61523734 52608 本文方法 64861976 64806296 55680 表 3 U-FOV测试集图像总处理时间及处理帧速
方法 YOLOv3 YOLOv3+Attention FS+Attention 本文方法 总时间(s) 90.35 95.72 125.39 107.25 处理帧率 7.32 6.91 5.27 6.16 -
BLOISI D D, PREVITALI F, PENNISI A, et al. Enhancing automatic maritime surveillance systems with visual information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(4): 824–833. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2016.2591321 KANG J K, HONG H G, and PARK K R. Pedestrian detection based on adaptive selection of visible light or far-infrared light camera image by fuzzy inference system and convolutional neural network-based verification[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(7): 1598. doi: 10.3390/s17071598 KIM S, SONG W J, and KIM S H. Infrared variation optimized deep convolutional neural network for robust automatic ground target recognition[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 195–202. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2017.30. 王晨, 汤心溢, 高思莉. 基于人眼视觉的红外图像增强算法研究[J]. 激光与红外, 2017, 47(1): 114–118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2017.01.022WANG Chen, TANG Xinyi, and GAO Sili. Infrared image enhancement algorithm based on human vision[J]. Laser &Infrared, 2017, 47(1): 114–118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2017.01.022 MUNDER S, SCHNORR C, and GAVRILA D M. Pedestrian detection and tracking using a mixture of view-based shape-texture models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2008, 9(2): 333–343. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2008.922943 DALAL N and TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]. IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, USA, 2005: 886–893. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2005.177. ZHANG Shanshan, BAUCKHAGE C, and CREMERS A B. Informed haar-like features improve pedestrian detection[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 947–954. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2014.126. WATANABE T and ITO S. Two co-occurrence histogram features using gradient orientations and local binary patterns for pedestrian detection[C]. The 2nd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition, Naha, Japan, 2013: 415–419. doi: 10.1109/ACPR.2013.117. 余春艳, 徐小丹, 钟诗俊. 面向显著性目标检测的SSD改进模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(11): 2554–2561. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180118YU Chunyan, XU Xiaodan, and ZHONG Shijun. An improved SSD model for saliency object detection[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(11): 2554–2561. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180118 LIU Songtao, HUANG Di, and WANG Yunhong. Adaptive NMS: Refining pedestrian detection in a crowd[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6452–6461. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00662. LIU Wei, LIAO Shengcai, REN Weiqiang, et al. Center and scale prediction: A box-free approach for pedestrian and face detection[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Los Angeles, USA, 2019: 5187–5196. 车凯, 向郑涛, 陈宇峰, 等. 基于改进Fast R-CNN的红外图像行人检测研究[J]. 红外技术, 2018, 40(6): 578–584. doi: 10.11846/j.issn.1001_8891.201806010CHE Kai, XIANG Zhengtao, CHEN Yufeng, et al. Research on infrared image pedestrian detection based on improved fast R-CNN[J]. Infrared Technology, 2018, 40(6): 578–584. doi: 10.11846/j.issn.1001_8891.201806010 王殿伟, 何衍辉, 李大湘, 等. 改进的YOLOv3红外视频图像行人检测算法[J]. 西安邮电大学学报, 2018, 23(4): 48–52. doi: 10.13682/j.issn.2095-6533.2018.04.008WANG Dianwei, HE Yanhui, LI Daxiang, et al. An improved infrared video image pedestrian detection algorithm[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2018, 23(4): 48–52. doi: 10.13682/j.issn.2095-6533.2018.04.008 GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440–1448. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.169. REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1804.02767, 2018. 郭智, 宋萍, 张义, 等. 基于深度卷积神经网络的遥感图像飞机目标检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(11): 2684–2690. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180117GUO Zhi, SONG Ping, ZHANG Yi, et al. Aircraft detection method based on deep convolutional neural network for remote sensing images[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(11): 2684–2690. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180117 CHEN Long, ZHANG Hanwang, XIAO Jun, et al. SCA-CNN: Spatial and channel-wise attention in convolutional networks for image captioning[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6298–6306. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.667. WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1. DOLLÁR P, WOJEK C, SCHIELE B, et al. Pedestrian detection: An evaluation of the state of the art[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(4): 743–761. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.155 FU Chengyang, LIU Wei, RANGA A, et al. DSSD: Deconvolutional single shot detector[J]. arXiv, 2017, 1701.06659. HE Kaiming, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2980–2988. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.322. BERG A, AHLBERG J, and FELSBERG M. A thermal object tracking benchmark[C]. The 2015 12th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance, Karlsruhe, Germany, 2015: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/AVSS.2015.7301772. LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]. Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2. REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 DAI Jifeng, LI Yi, HE Kaiming, et al. R-FCN: Object detection via region-based fully convolutional networks[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 379–387. -






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
