Adaptive-Rate Compressive Sensing Using Energy Matching for Monitoring Video
-
摘要: 获取信号稀疏度对压缩感知(CS)性能的提升有重大意义,但在采样端不进行完整信号数字化采集和存储的情况下,对信号稀疏度进行估计比较困难。现有方法在稀疏度估计性能和计算复杂度方面难以取得较好的平衡。针对采样端对信号特性未知的监控视频应用,该文提出一种新的使用能量匹配的自适应速率压缩感知方法(ARCS-EM),通过观测一个恒定低速率的压缩感知观测结果来对当前帧实际稀疏度进行估计,然后根据估计结果决定当前帧应执行的压缩感知测量数,再进行补充测量得到当前帧的优化压缩感知采样结果。实验结果表明,该方法可以较好地适应视频中前景稀疏度的变化,为每帧图像分配适当的压缩感知测量速率,在不显著提高采样端计算复杂度的前提下,有效提高重建视频的质量。Abstract: Signal sparsity is of great significance for the improvement of Compressive Sensing (CS) performance. However, it is difficult to estimate the sparsity when the whole signal is not captured and stored at the sampling side. Few existing mothed can achieve good balance in terms of the sparsity estimation performance and the computational complexity. For the monitoring video applications where the signal characteristics is unknown for sampling devices, a new Adaptive-Rate CS using Energy Matching (ARCS-EM) method is proposed. By observing the measurement results of a low-rate compressive sensing, the actual sparsity of the current frame is estimated and then the rate of measurement for the current frame is determined. Finally, supplementary measurements are performed to obtain the optimized compressive sensing result for the current frame. Experiment results show that the proposed method could allocate suitable measurement rate for each frame to adapt to the variation of sparsity in different frames. The quality of reconstructed videos is effectively improved without noticeably increasing computational complexity in the sampling side.
-
表 1 实验参数
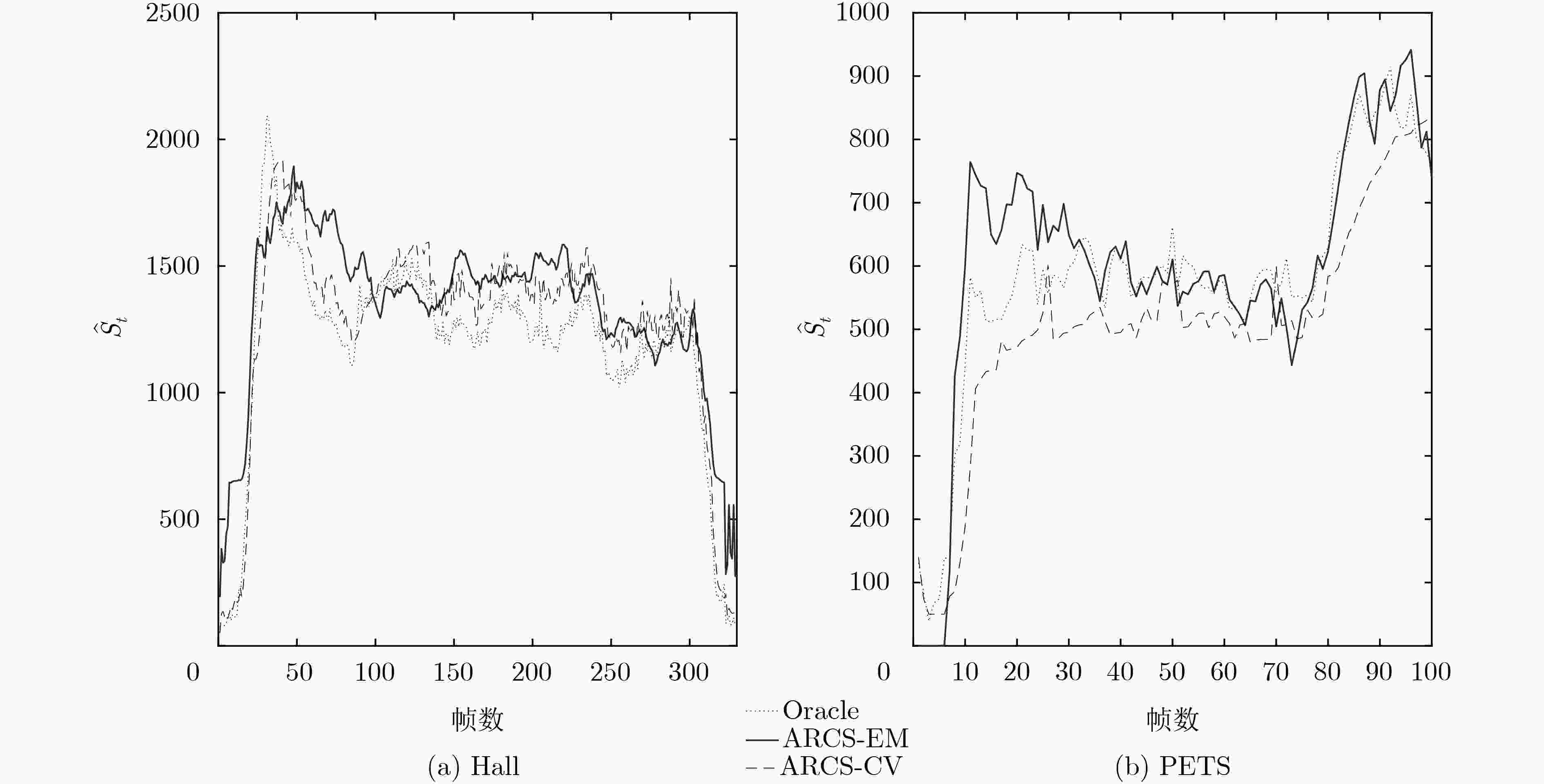
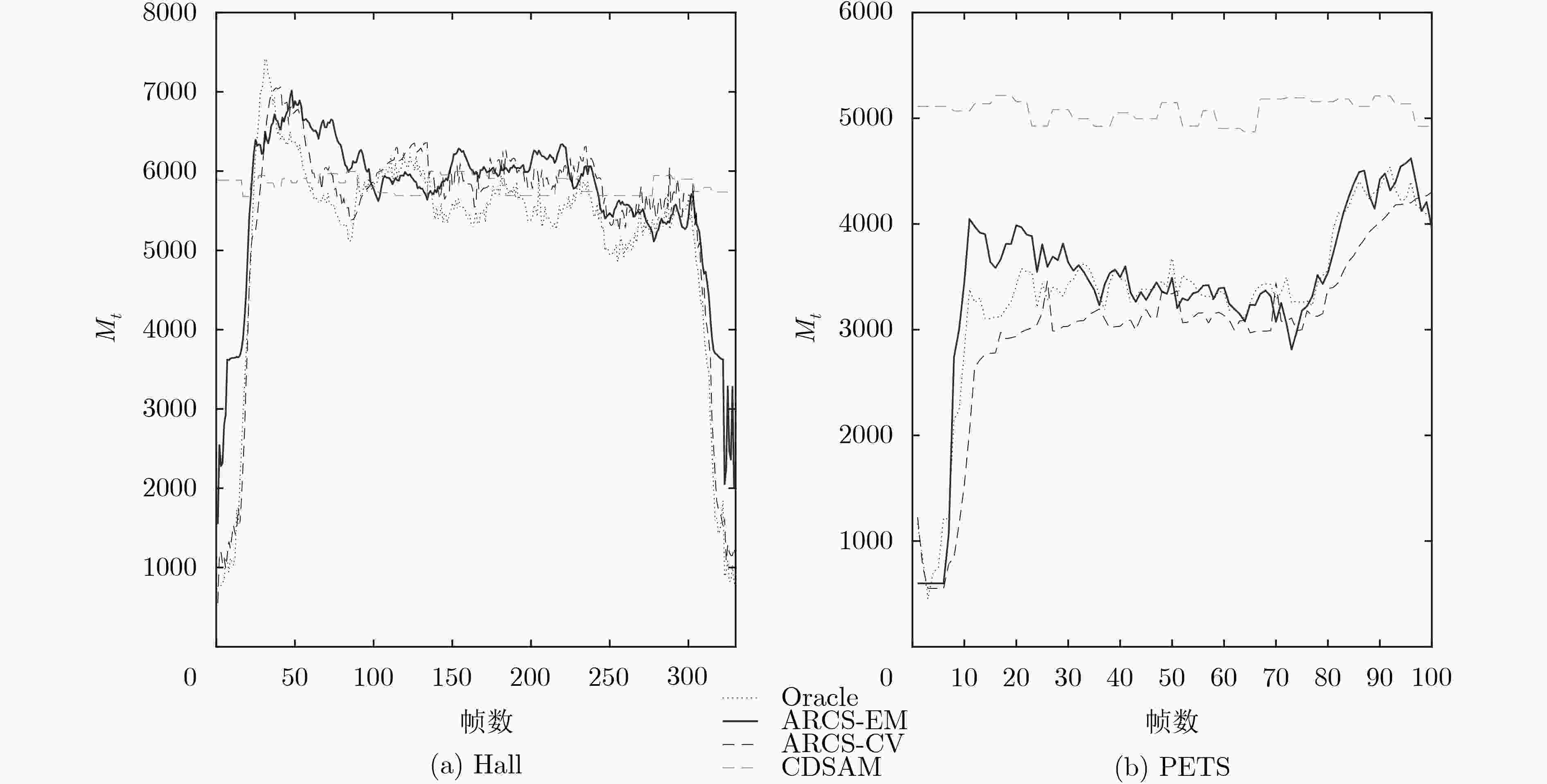
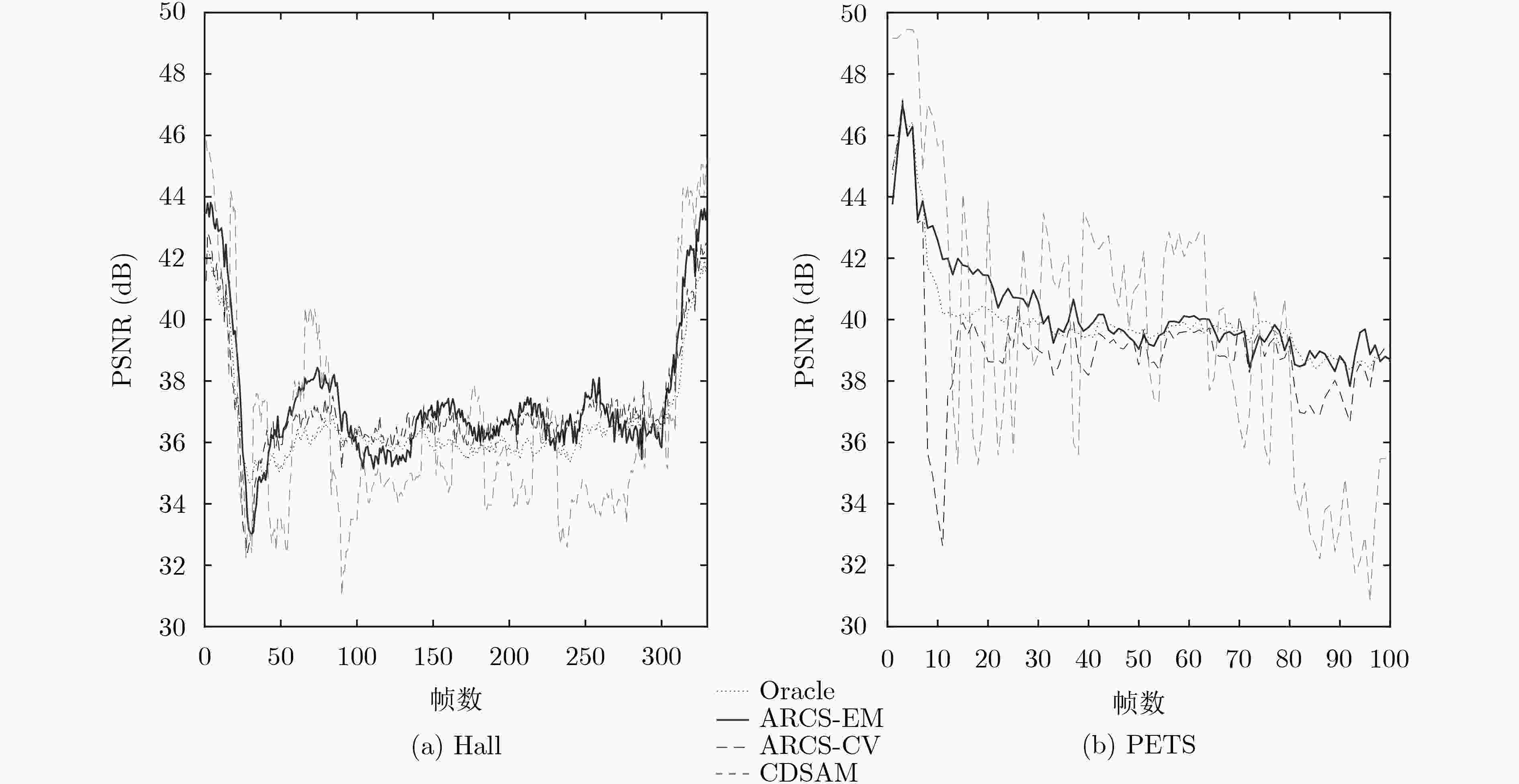
参数 $\varSigma $ $a$ $b$ $\tau $ $r$ 视频序列Hall 2.65 16 128 8 600 视频序列PETS 2.45 16 128 8 600 表 2 不同方法的自适压缩感知平均性能对比
实验结果 Hall视频平均压缩
感知采样率Hall视频平均峰值
信噪比(dB)PETS视频平均压缩
感知采样率PETS视频平均峰值
信噪比(dB)Oracle 0.2040 36.59 0.1317 40.02 CDSAM方法 0.2297 36.34 0.2001 39.53 ARCS-CV方法 0.2137 37.03 0.1191 39.07 ARCS-EM方法 0.2232 37.26 0.1350 40.26 表 3 采样运行时间对照表(ms)
运行时间 Hall视频T1 Hall视频T2 Hall视频T3 Hall视频T PETS视频T1 PETS视频T2 PETS视频T3 PETS视频T CDSAM方法 7.48 104.18 0 111.66 6.76 94.93 0 101.69 ARCS-CV方法 957.26 0.14 2.99×105 3.00×105 526.56 0.11 1.44×105 1.45×105 ARCS-EM方法 800.87 0.42 0 801.29 498.75 0.51 0 499.26 -
CANDÈS E J, ROMBERG J, and TAO T. Robust uncertainty principles: Exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(2): 489–509. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2005.862083 DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 CANDÈS E J. The restricted isometry property and its implications for compressed sensing[J]. Comptes Rendus Mathematique, 2008, 346(9/10): 589–592. doi: 10.1016/j.crma.2008.03.014 王钢, 周若飞, 邹昳琨. 基于压缩感知理论的图像优化技术[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 222–233. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190669WANG Gang, ZHOU Ruofei, and ZOU Yikun. Research on image optimization technology based on Compressed Sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 222–233. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190669 杨森林, 万国宾. 联合结构预测和运动补偿的视频自适应压缩感知[J]. 西北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 49(6): 909–917. doi: 10.16152/j.cnki.xdxbzr.2019-06-010YANG Senlin and WAN Guobin. Adaptive compressed sensing of video by combining structural predictions and motion compensation[J]. Journal of Northwest University:Natural Science Edition, 2019, 49(6): 909–917. doi: 10.16152/j.cnki.xdxbzr.2019-06-010 SHAHRASBI B and RAHNAVARD N. Model-based nonuniform Compressive Sampling and recovery of natural images utilizing a Wavelet-domain universal hidden Markov model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(1): 95–104. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2614654 LAKSHMI T C S, GNANADURAI D, and MUTHULAKSHMI I. Energy conserving texture-based adaptable Compressive Sensing scheme for WVSN[J]. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 2019: e5178. doi: 10.1002/cpe.5178 ZHANG Xufan, WANG Yong, WANG Dianhong, et al. Adaptive image compression based on compressive sensing for video sensor nodes[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2018, 77(11): 13679–13699. doi: 10.1007/s11042-017-4981-6 DUARTE M F, DAVENPORT M A, TAKHAR D, et al. Single-pixel imaging via compressive sampling[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(2): 83–91. doi: 10.1109/msp.2007.914730 范剑英, 马明阳, 赵首博. 基于压缩感知高反光成像技术研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 1013–1020. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190512FAN Jianying, MA Mingyang, and ZHAO Shoubo. Research on high reflective imaging technology based on compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 1013–1020. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190512 吴新杰, 闫诗雨, 徐攀峰, 等. 基于稀疏度自适应压缩感知的电容层析成像图像重建算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(5): 1250–1257. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170794WU Xinjie, YAN Shiyu, XU Panfeng, et al. Image reconstruction algorithm for electrical capacitance tomography based on sparsity adaptive Compressed Sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(5): 1250–1257. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170794 SHANGGUAN Wentao, YAN Qiurong, WANG Hui, et al. Adaptive single photon compressed imaging based on constructing a smart threshold matrix[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(10): 3449. doi: 10.3390/s18103449 YUAN Xin, YANG Jianbo, LLULL P, et al. Adaptive temporal compressive sensing for video[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Melbourne, Australia, 2013: 14–18. doi: 10.1109/ICIP.2013.6738004. WANG Yeru, TANG Chaoying, CHEN Yueting, et al. Adaptive temporal Compressive Sensing for video with motion estimation[J]. Optical Review, 2018, 25(2): 215–226. doi: 10.1007/s10043-018-0408-5 练秋生, 田天, 陈书贞, 等. 基于变采样率的多假设预测分块视频压缩感知[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(1): 203–208. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00590LIAN Qiusheng, TIAN Tian, CHEN Shuzhen, et al. Block compressed sensing of video based on variable sampling rates and multihypothesis predictions[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(1): 203–208. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00590 LI Honggui. Compressive domain spatial–temporal difference saliency-based realtime adaptive measurement method for video recovery[J]. IET Image Processing, 2019, 13(11): 2008–2017. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2019.0116 WARNELL G, BHATTACHARYA S, CHELLAPPA R, et al. Adaptive-rate compressive sensing using side information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 3846–3857. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2456425 DUARTE-CARVAJALINO J M, YU Guoshen, CARIN L, et al. Task-driven adaptive statistical compressive sensing of Gaussian mixture models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(3): 585–600. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2225054 VAN DER BERG E and FRIEDLANDER M P. Probing the Pareto Frontier for basis pursuit solutions[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2009, 31(2): 890–912. doi: 10.1137/080714488 DONOHO D L and TANNER J. Precise undersampling theorems[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2010, 98(6): 913–924. doi: 10.1109/jproc.2010.2045630 CEVHER V, SANKARANARAYANAN A, DUARTE M F, et al. Compressive sensing for background subtraction[C]. The 10th European Conference on Computer Vision, France, Marseille, 2008: 155–168. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-88688-4_12. WARD R. Compressed sensing with cross validation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2009, 55(12): 5773–5782. doi: 10.1109/tit.2009.2032712 JOHNSON W B and LINDENSTRAUSS J. Extensions of Lipschitz mappings into a Hilbert space[J]. Contemporary Mathematics, 1984, 26(12): 189–206. doi: 10.1090/conm/026/737400 -
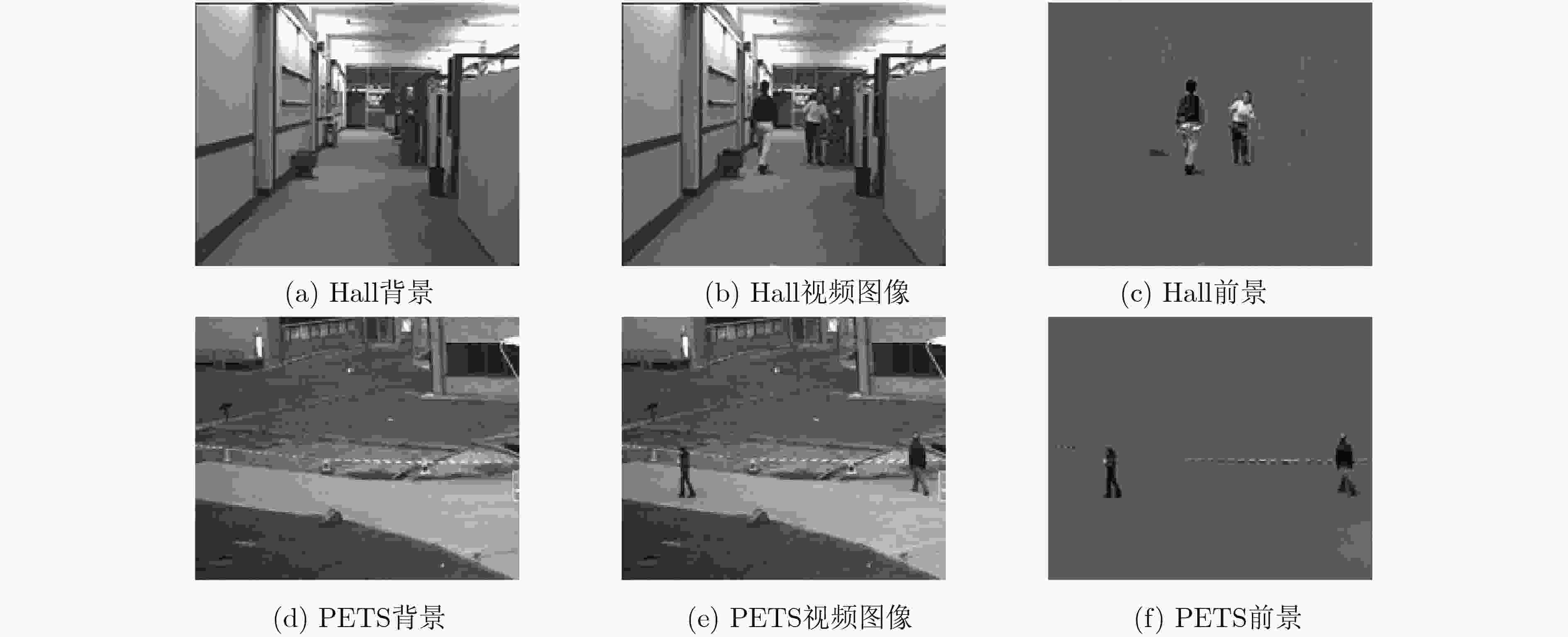






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
