Hysteretic Noisy Chaotic Neural Networks Based Pilot Assignment
-
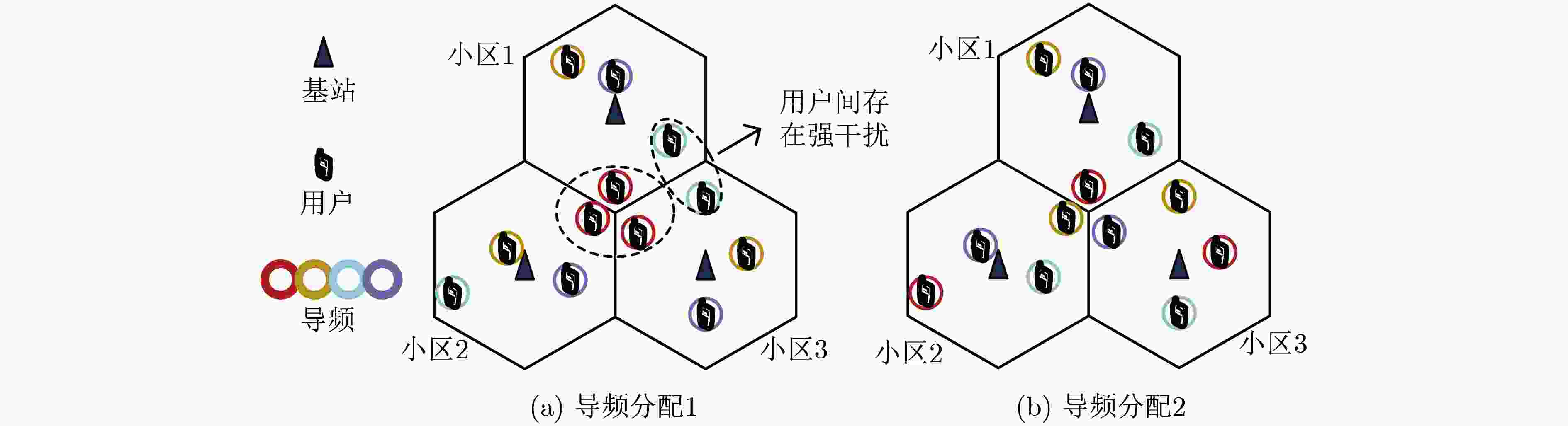
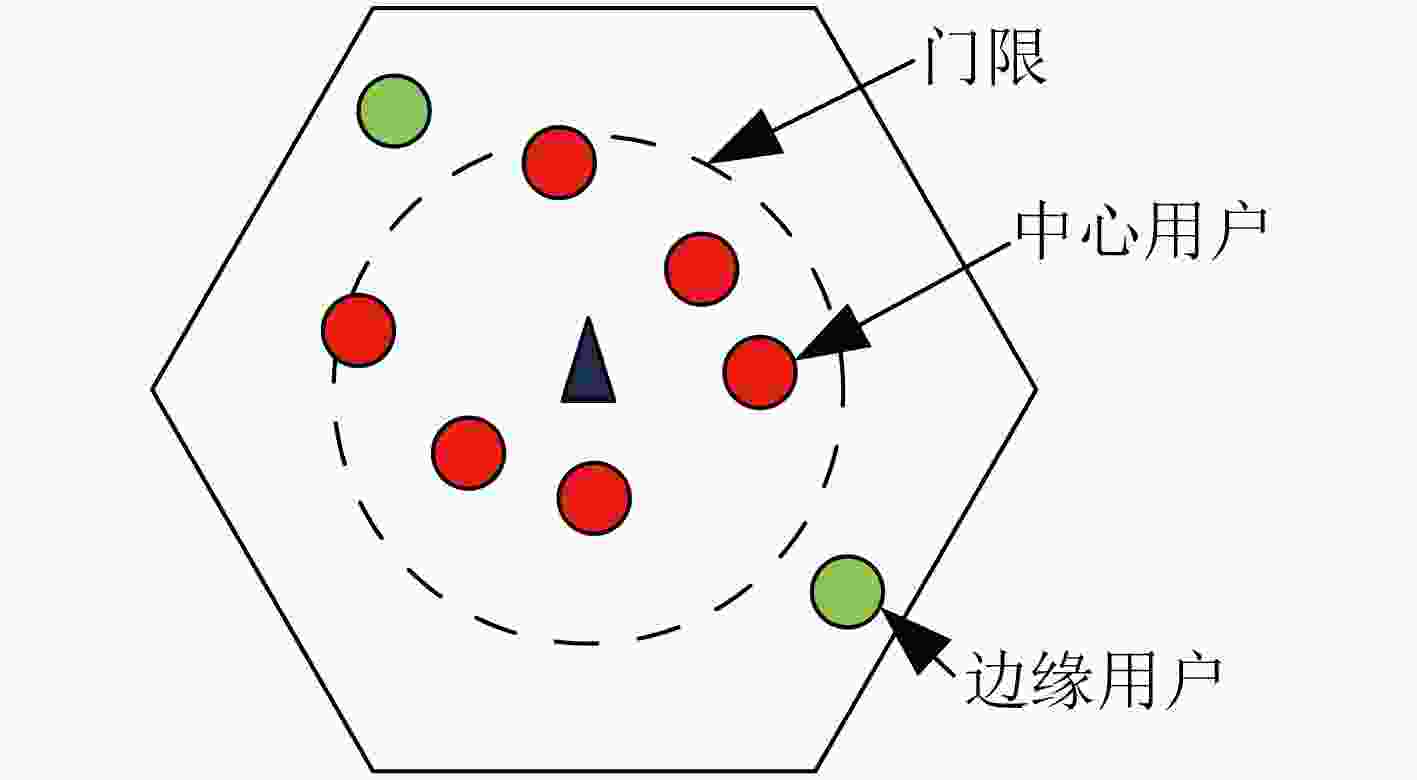
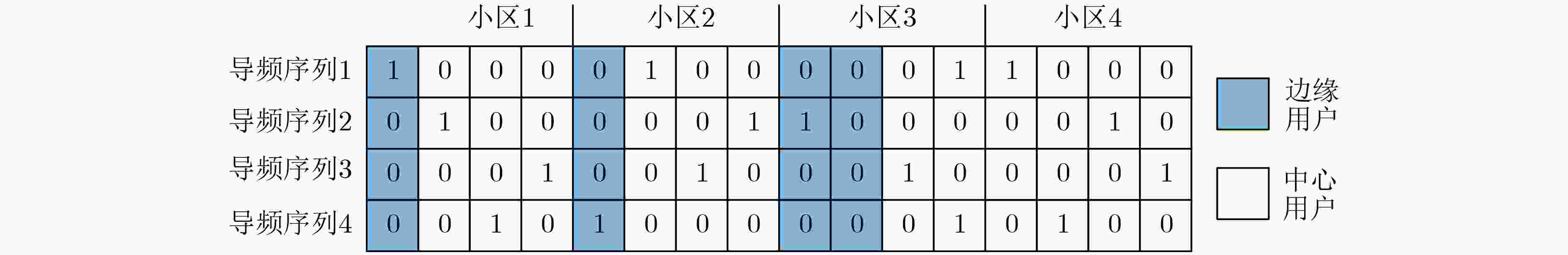
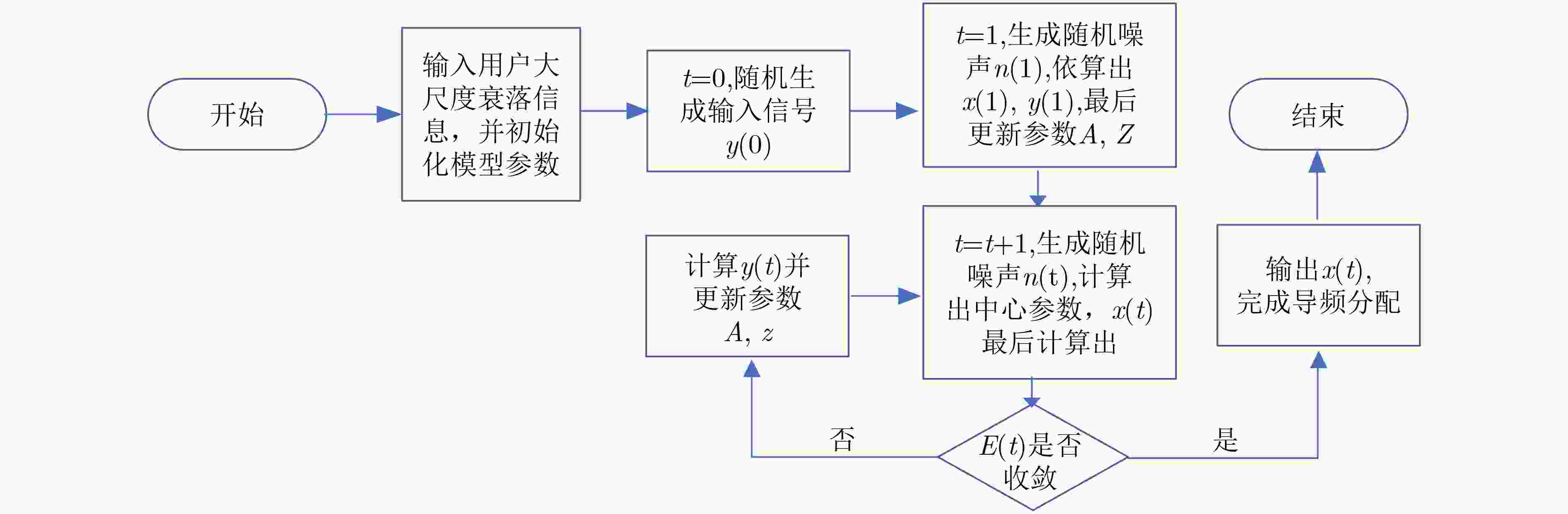
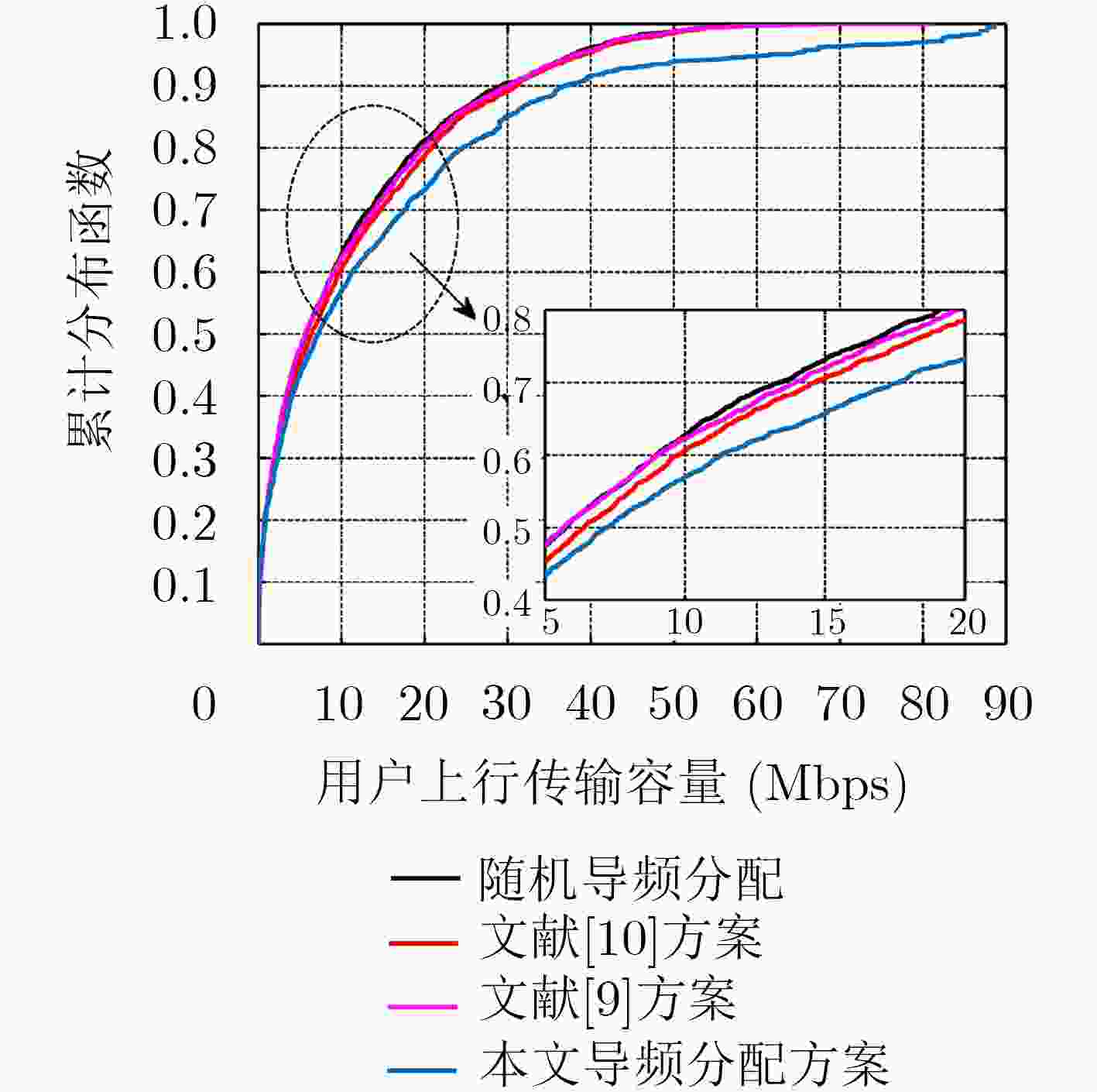
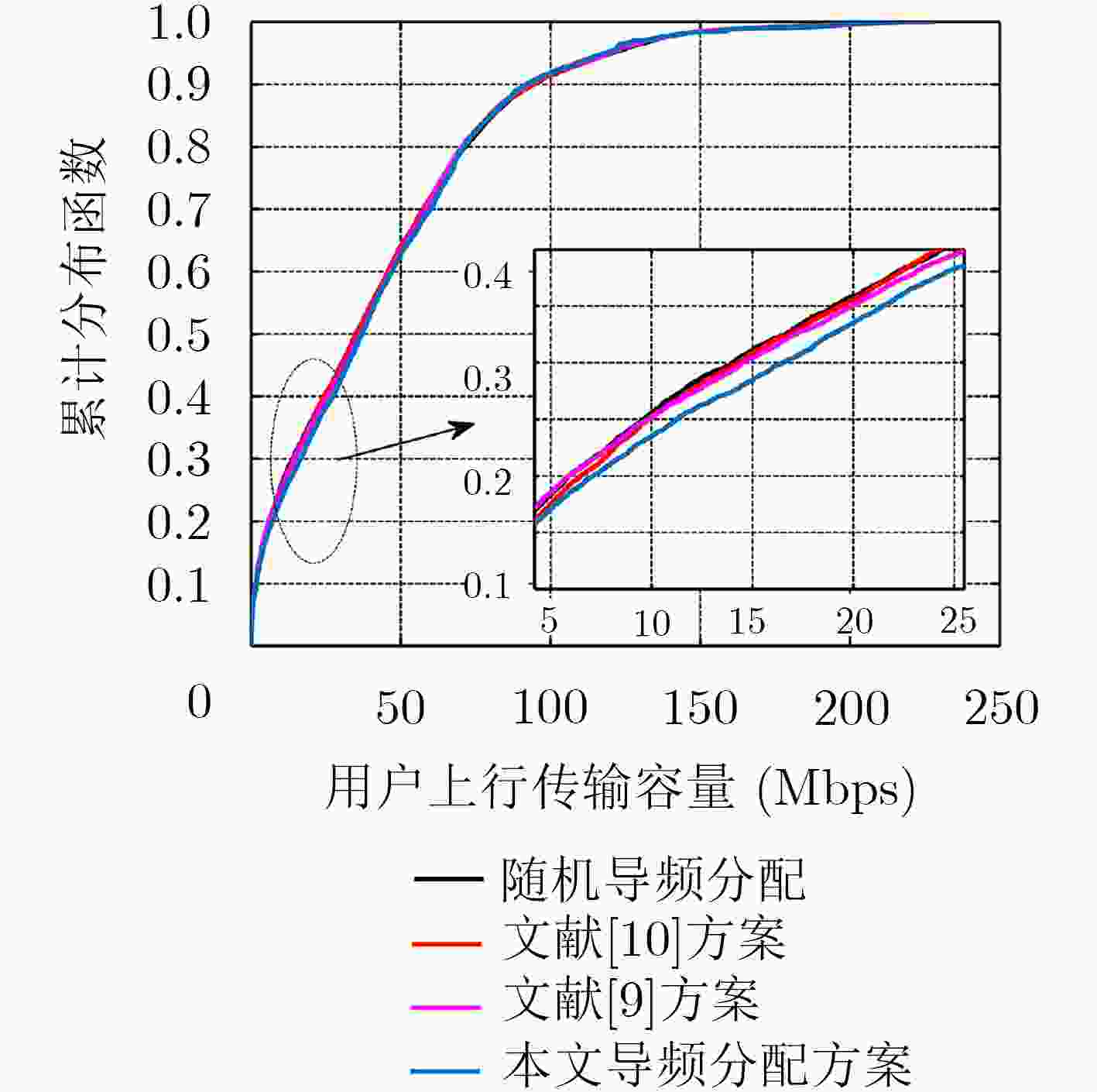
摘要: 在多小区大规模多输入多输出(MIMO)系统中,导频污染已经成为制约整个系统的瓶颈。合理地使用导频资源能减轻导频污染的影响,为了寻找使边缘用户和容量最大的导频分配方式,该文首次提出了基于迟滞噪声混沌神经网络(HNCNN)的导频分配方案。迟滞噪声混沌神经网络作为良好的优化工具,其优化能力与所设计的能量函数相关。该方案结合导频资源使用的特点以及最大化边缘用户和容量的计算方式,设计了新的能量函数。仿真结果表明,网络能在一定迭代次数后收敛到较优的导频分配方式。与其它文献方案相比,采用以HNCNN为框架求取导频分配方式,可以更有效减轻导频污染的影响,使系统性能得到改善。
-
关键词:
- 大规模多输入多输出 /
- 导频污染 /
- 导频分配 /
- 迟滞噪声混沌神经网络
Abstract: In multi-cell massive Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) systems, pilot contamination has become the bottleneck which restricts the performance of the whole system, so the reasonable usage of pilot resources can mitigate the pilot contamination of the system. In order to find the pilot allocation method that maximizes the total transmission capacity of edge users, a pilot allocation scheme based on Hysteretic Noise Chaotic Neural Network (HNCNN) is proposed for the first time. HNCNN is a famous optimization tool, and its optimization ability is related to the designed energy function. This scheme combines the characteristics of pilot resource usage and the calculation method of maximizing the total transmission capacity of edge users to design a new energy function. The simulation results show that the proposed network can converge to a better pilot allocation mode after a certain number of iterations. Compared with other literature pilot allocation solution, the pilot allocation method based on HNCNN can further reduce the influence of pilot contamination and improve the system performance. -
表 1 大规模MIMO参数
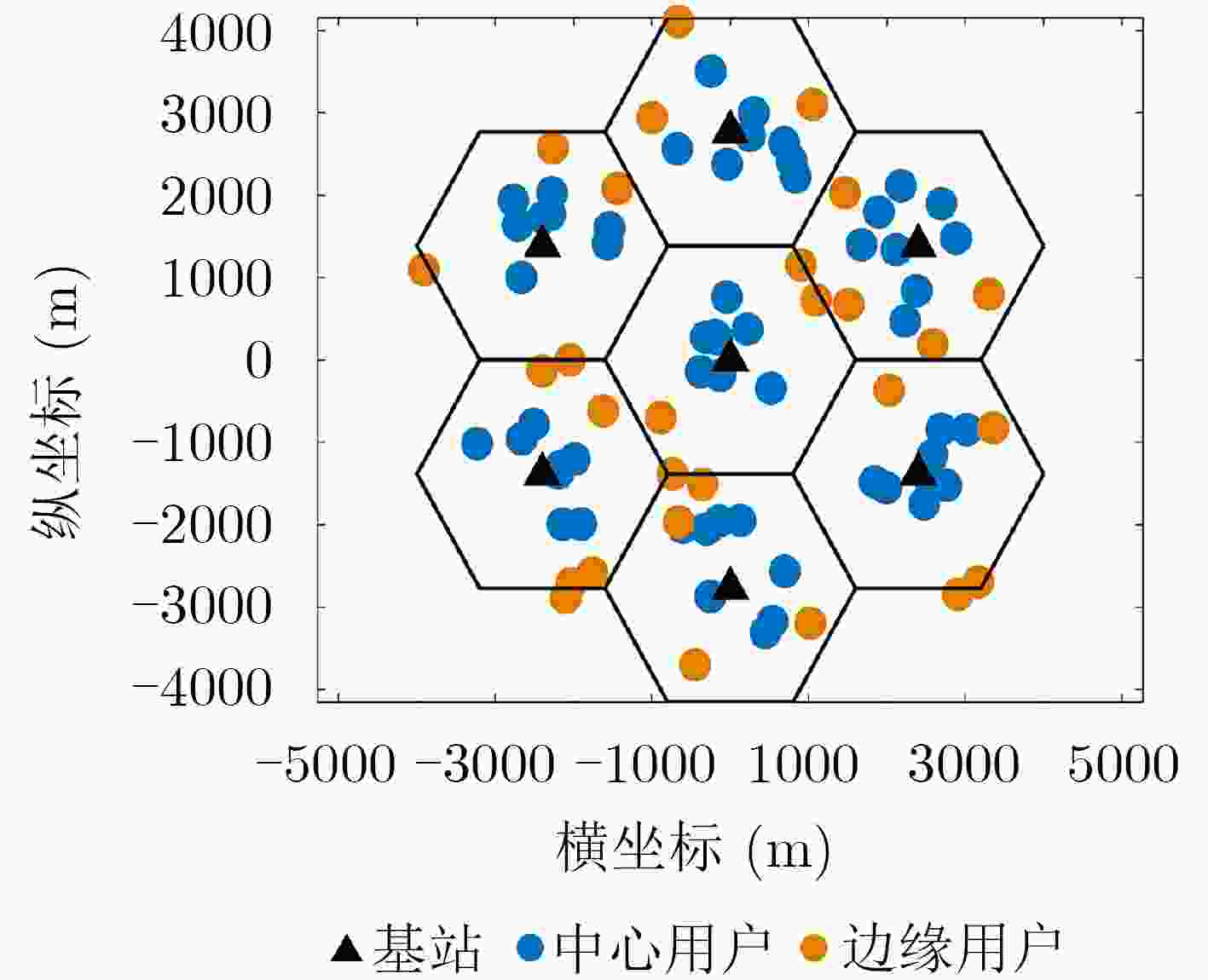
参数 取值 小区数$L$ 7 每小区天线数 256 小区半径 1.6 km 小区服务数 12 上下行发射功率 15 dBm, 43 dBm 路径衰落指数$\alpha $ 3.8 用户分组门限F 0.33 对数阴影衰落 8 dB 表 2 HNCNN仿真分析
场景 随机平均$\Sigma $ 算法 有效次数 平均$\varSigma$ 提升比例(%) 1 58.38 HNCNN-C 981/1000 78.73 34.86 HNCNN-A 1000/1000 79.90 36.86 2 65.43 HNCNN-C 982/1000 84.98 29.88 HNCNN-A 990/1000 85.86 31.22 3 78.26 HNCNN-C 964/1000 97.07 24.04 HNCNN-A 982/1000 97.49 24.57 4 54.47 HNCNN-C 982/1000 65.65 20.53 HNCNN-A 1000/1000 67.13 23.24 5 59.04 HNCNN-C 946/1000 82.20 39.23 HNCNN-A 958/1000 83.66 41.70 6 62.81 HNCNN-C 984/1000 73.14 16.45 HNCNN-A 993/1000 74.80 19.09 -
NGO H Q, LARSSON E G, and MARZETTA T L. Energy and spectral efficiency of very large multiuser MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2013, 61(4): 1436–1449. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2013.020413.110848 RUSEK R, PERSSON D, LAU B K, et al. Scaling up MIMO: Opportunities and challenges with very large arrays[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2013, 30(1): 40–60. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2011.2178495 LEE T, PARK S, KIM H S, et al. Sounding resource management for QoS support in massive MIMO systems[J]. Computer Networks, 2014, 70: 142–153. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2014.05.001 MUPPIRISETTY L S, CHARALAMBOUS T, KAROUT J, et al. Location-aided pilot contamination avoidance for massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(4): 2662–2674. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2800038 ZHOU Zhichao, WANG Dong, and Wang Zhenchao. Asynchronous pilots scheduling in massive MIMO systems[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Paris, France, 2017: 1–6. 方昕, 张建锋, 曹海燕, 等. 大规模MIMO系统中动态导频分配[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(8): 1901–1907. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151091FANG Xin, ZHANG Jianfeng, CAO Haiyan, et al. Dynamic pilot allocation in massive MIMO system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(8): 1901–1907. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151091 XU Yaohua and WU Yong. An approach of pilot contamination reduction based on power control and orthogonal identification[C]. The 3rd IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing and Big Data Analysis (ICCCBDA), Chengdu, China, 2018: 476–480. ZHANG Xiaoqing, LIU Ju, WU Shangbin, et al. Uplink pilot power control with genetic algorithm for massive MIMO networks[C]. The 9th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP), Nanjing, China, 2017: 1–6. 李梦婉, 景小荣, 莫林琳. 多小区大规模MIMO系统中基于部分导频交替复用的导频污染减轻方法[J]. 信号处理, 2017, 33(8): 1104–1114. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2017.08.011LI Mengwan, JING Xiaorong, and MO Linlin. Pilot contamination reduction method with alternately fractional pilot reuse for multi-cell massive MIMO Systems[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2017, 33(8): 1104–1114. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2017.08.011 ZHU Xudong, DAI Linglong, WANG Zhaocheng, et al. Weighted-Graph-Coloring-Based pilot decontamination for multicell massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(3): 2829–2834. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2572203 AHN C W, RAMAKRISHNA R S, KANG C G, et al. Shortest path routing algorithm using Hopfield neural network[J]. Electronics Letters, 2001, 37(19): 1176–1178. doi: 10.1049/el:20010800 SUN Ming, ZHAO Lin, CAO Wei, et al. Novel hysteretic noisy chaotic neural network for broadcast scheduling problems in packet radio networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2010, 21(9): 1422–1433. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2010.2059041 SUN Ming, LEE K Y, XU Yaoqun, et al. Hysteretic noisy chaotic neural networks for resource allocation in OFDMA system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(2): 273–285. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2618898 MARZETTA T L. Noncooperative cellular wireless with unlimited numbers of base station antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2010, 9(11): 3590–3600. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2010.092810.091092 周鹏, 赵春明, 盛彬. MIMO-OFDM系统中基于导频辅助的信道估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(1): 133–137.ZHOU Peng, ZHAO Chunming, and SHENG Bin. Channel estimation based on pilot-assisted for MIMO-OFDM systems[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2007, 29(1): 133–137. -







 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
