A Link Prediction Method in Directed Networks Via Linear Programming
-
摘要: 大多数有向网络链路预测方法在计算节点相似性时没有充分考虑有向网络的结构特点,未区分不同有向邻居对连边形成具有的贡献差异,导致预测性能受到局限。鉴于此,该文提出一种基于线性规划的有向网络链路预测方法。该方法对3种有向邻居的信息贡献进行量化分析,结合结构特点建立线性规划模型,进而通过求解贡献矩阵的最优解构建相似性指标。9个真实有向网络中的实验结果表明,所提方法相比于9种现有方法在两种衡量标准下表现出较高的预测性能与良好的鲁棒性。Abstract: Most existing link prediction methods in directed networks fail to consider the structural properties of directed networks when calculating node similarity, nor do they differentiate the contributions of directed neighbors on link formation, resulting in the limitation on prediction performance. To solve these problems, a novel link prediction method in directed networks based on linear programming is proposed. The contributions of three types of directed neighbors are quantified, then the linear programming problem is established based on network topological property. The similarity index is deduced by solving the optimal solution of the linear programming problem. Experimental results on nine real-world directed networks show that the proposed method outperforms nine benchmarks on both accuracy and robustness under two evaluation metrics.
-
Key words:
- Directed network /
- Link prediction /
- Node similarity /
- Linear programming
-
表 1 网络数据基本统计参数
序号 名称 类型 $N$ $M$ $\left\langle k \right\rangle $ $\rho $(%) $C$ $\left\langle d \right\rangle $ $\gamma $ $\kappa $ (1) ADO 社交网络 2,539 12,969 10.22 38.8 14.2 5.30 0.251 8.25 (2) HIG 社交网络 70 366 10.46 50.3 40.4 3.51 0.083 4.38 (3) RES 社交网络 217 2,672 24.63 62.4 30.4 2.79 0.096 6.32 (4) EMA 信息网络 1,005 25,571 50.89 71.1 25.7 3.01 –0.014 2.80 (5) USA 交通网络 1,574 28,236 35.88 78.1 38.4 3.85 –0.113 1.85 (6) OF 交通网络 2,939 30,501 20.76 97.2 25.5 5.19 0.051 1.74 (7) CELE 生物网络 453 4,596 20.29 16.8 12.4 3.03 –0.226 2.62 (8) FWFD 生态网络 128 2,137 33.39 2.9 31.4 1.88 –0.104 5.02 (9) LAK 生态网络 183 2,494 27.26 4.09 33.2 2.65 –0.266 2.99 表 2 AUC结果对比
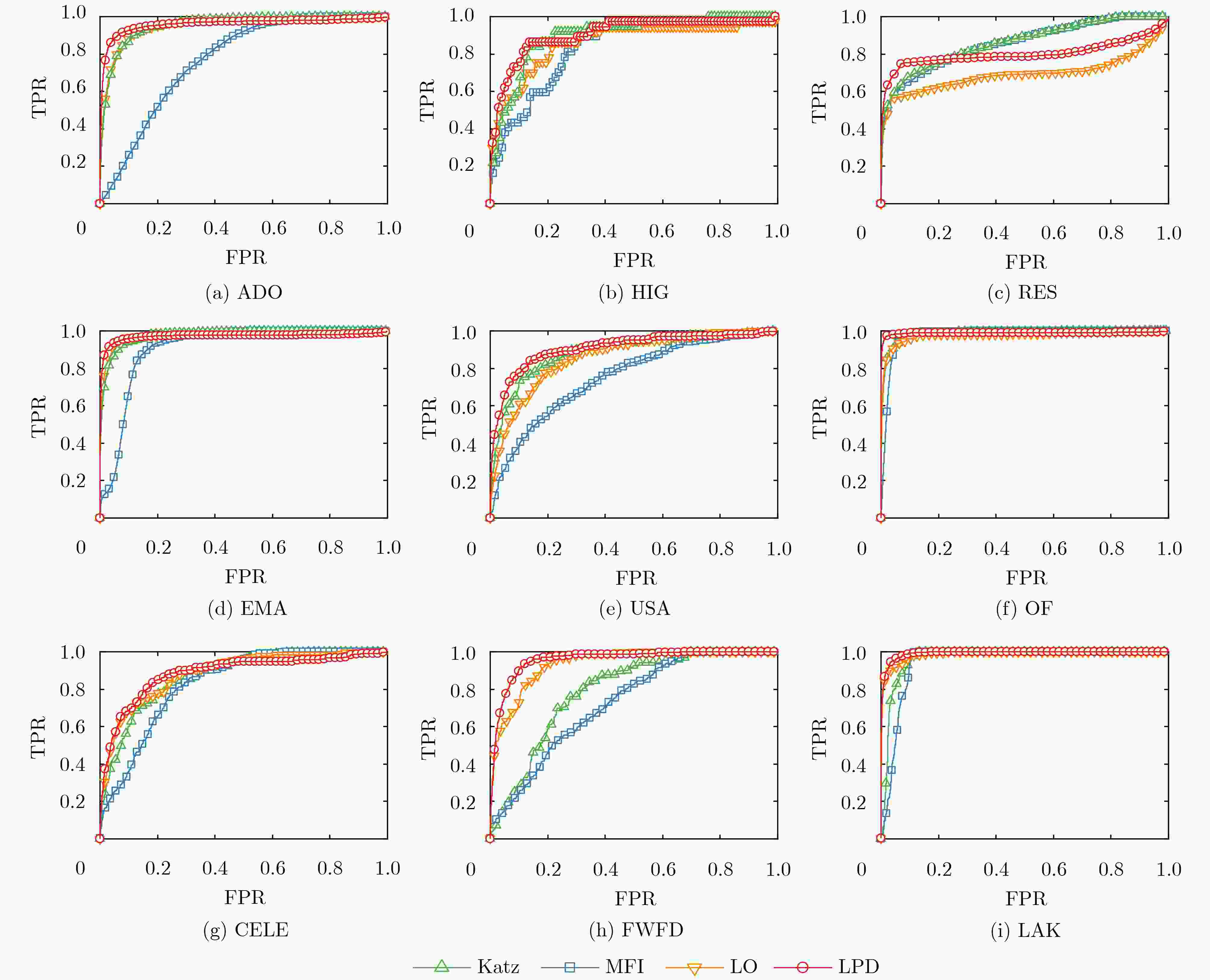
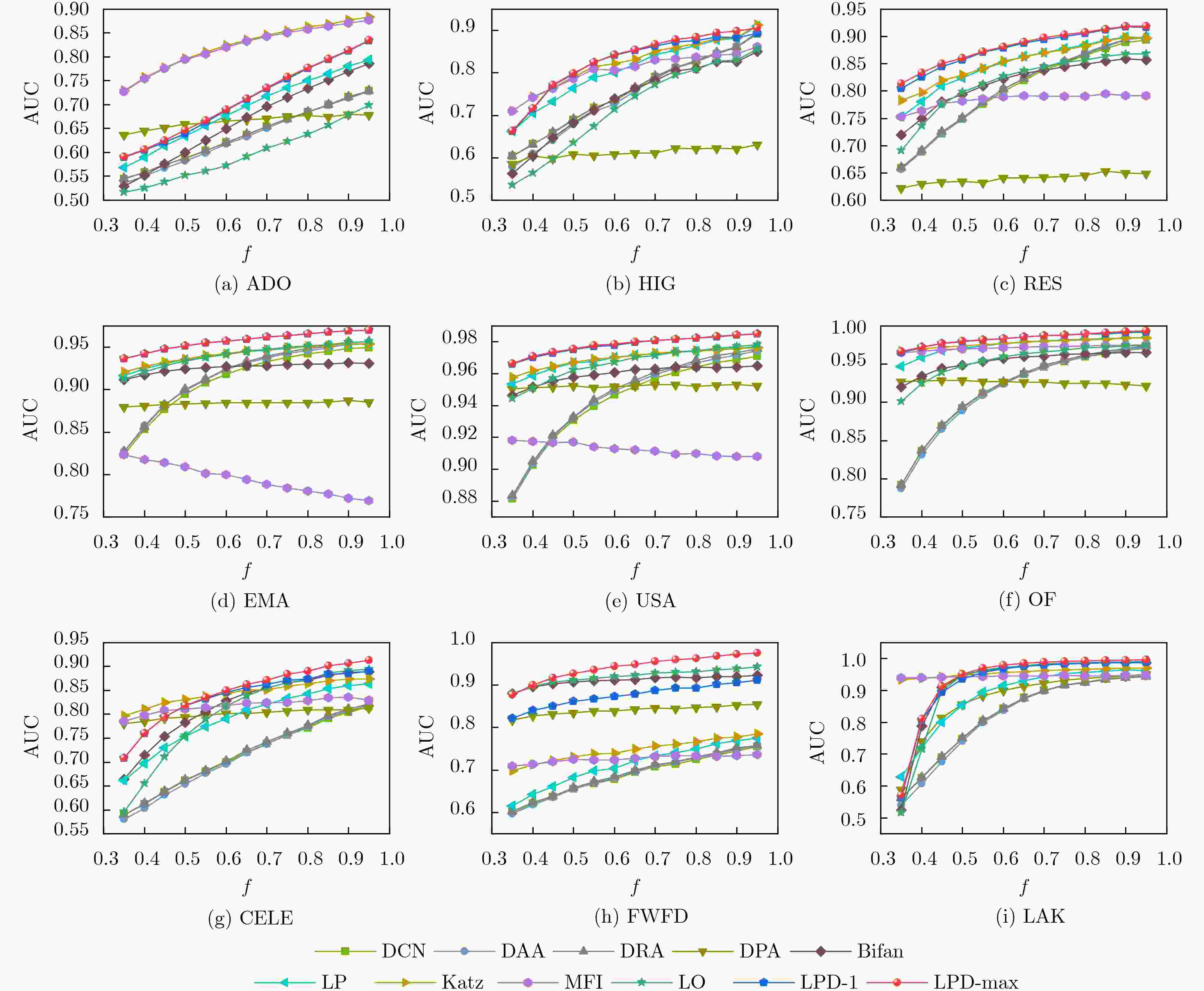
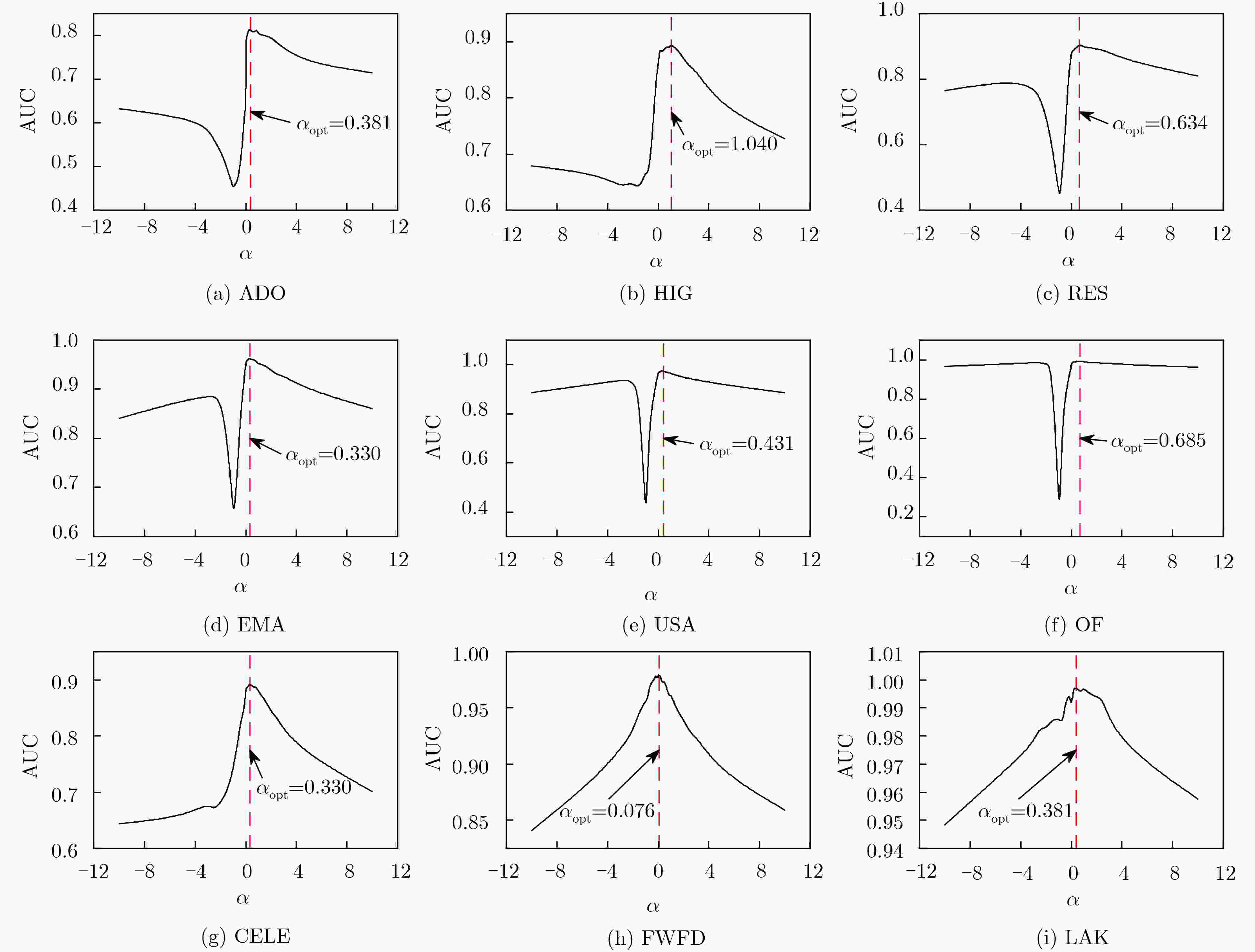
预测指标 ADO HIG RES EMA USA OF CELE FWFD LAK DCN 0.716 0.860 0.889 0.949 0.969 0.968 0.804 0.745 0.942 DAA 0.714 0.862 0.895 0.953 0.972 0.969 0.807 0.749 0.940 DRA 0.716 0.861 0.895 0.956 0.973 0.971 0.811 0.752 0.939 DPA 0.680 0.621 0.650 0.887 0.953 0.924 0.810 0.854 0.946 Bifan 0.770 0.826 0.859 0.932 0.964 0.965 0.888 0.920 0.988 LP-0.001 0.781 0.882 0.899 0.954 0.976 0.984 0.860 0.769 0.964 Katz-0.001 0.877 0.883 0.898 0.954 0.976 0.984 0.874 0.778 0.970 MFI 0.872 0.845 0.792 0.772 0.908 0.975 0.836 0.734 0.947 LO-0.01 0.678 0.830 0.888 0.949 0.967 0.971 0.889 0.972 0.995 LO-0.001 0.679 0.830 0.868 0.956 0.977 0.974 0.892 0.934 0.990 LPD-0.01-1 0.803 0.898 0.917 0.956 0.984 0.991 0.899 0.956 0.994 LPD-0.001-1 0.812 0.883 0.902 0.969 0.968 0.990 0.886 0.907 0.988 LPD-max 0.814 0.898 0.919 0.969 0.984 0.993 0.907 0.973 0.996 -
REN Zhuoming, ZENG An, and ZHANG Yicheng. Structure-oriented prediction in complex networks[J]. Physics Reports, 2018, 750: 1–51. doi: 10.1016/J.PHYSREP.2018.05.002 LÜ Linyuan and ZHOU Tao. Link prediction in complex networks: A survey[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2011, 390(6): 1150–1170. doi: 10.1016/J.PHYSA.2010.11.027 王凯, 李星, 兰巨龙, 等. 一种基于资源传输路径拓扑有效性的链路预测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(3): 653–660. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190333WANG Kai, LI Xing, LAN Julong, et al. A new link prediction method for complex networks based on topological effectiveness of resource transmission paths[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(3): 653–660. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190333 LIU Shuxin, JI Xinsheng, LIU Caixia, et al. Similarity indices based on link weight assignment for link prediction of unweighted complex networks[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics B, 2017, 31(2): 1650254. doi: 10.1142/S0217979216502544 AGHABOZORGI F and KHAYYAMBASHI M R. A new similarity measure for link prediction based on local structures in social networks[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2018, 501: 12–23. doi: 10.1016/J.PHYSA.2018.02.010 LIU Shuxin, JI Xinsheng, LIU Caixia, et al. Extended resource allocation index for link prediction of complex network[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2017, 479: 174–183. doi: 10.1016/J.PHYSA.2017.02.078 王凯, 刘树新, 陈鸿昶, 等. 一种基于节点间资源承载度的链路预测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1225–1234. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180553WANG Kai, LIU Shuxin, CHEN Hongchang, et al. A new link prediction method for complex networks based on resources carrying capacity between nodes[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1225–1234. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180553 KATZ L. A new status index derived from sociometric analysis[J]. Psychometrika, 1953, 18(1): 39–43. doi: 10.1007/BF02289026 CHEBOTAREV P and SHAMIS E. The matrix-forest theorem and measuring relations in small social groups[J]. Automation and Remote Control, 1997, 58(9): 1505–1514. ZHOU Tao, LÜ Linyuan, and ZHANG Yicheng. Predicting missing links via local information[J]. The European Physical Journal B, 2009, 71(4): 623–630. doi: 10.1140/EPJB/E2009-00335-8 LI Jinsong, PENG Jianhua, LIU Shuxin, et al. Link prediction in directed networks utilizing the role of reciprocal links[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 28668–28680. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2972072 ZHANG Xue, ZHAO Chengli, WANG Xiaojie, et al. Identifying missing and spurious interactions in directed networks[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2015, 11(9): 507386. doi: 10.1155/2015/507386 WANG Xiaojie, ZHANG Xue, ZHAO Chengli, et al. Predicting link directions using local directed path[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2015, 419: 260–267. doi: 10.1016/J.PHYSA.2014.10.007 BÜTÜN E and KAYA M. A pattern based supervised link prediction in directed complex networks[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2019, 525: 1136–1145. doi: 10.1016/J.PHYSA.2019.04.015 SALHA G, LIMNIOS S, HENNEQUIN R, et al. Gravity-inspired graph autoencoders for directed link prediction[C]. The 28th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Beijing, China, 2019: 589–598. doi: 10.1145/3357384.3358023. GUNDALA L A and SPEZZANO F. Estimating node indirect interaction duration to enhance link prediction[J]. Social Network Analysis and Mining, 2019, 9(1): 17. doi: 10.1007/s13278-019-0561-2 PECH R, HAO D, LEE Y L, et al. Link prediction via linear optimization[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2019, 528: e121319. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.121319 ZHANG Qianming, LÜ Linyuan, WANG Wenqiang, et al. Potential theory for directed networks[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2): e55437. doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0055437 KUNEGIS J. KONECT network dataset[EB/OL]. http://konect.uni-koblenz.de/networks/, 2017. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
