Arrhythmia Classification Based on Convolutional Long Short Term Memory Network
-
摘要:
心律失常等慢性心血管疾病严重影响人类健康,采用心电信号(ECG)实现心律失常自动分类可有效提高该类疾病的诊断效率,降低人工成本。为此,该文基于1维心电信号,提出一种改进的长短时记忆网络(LSTM)方法实现心律失常自动分类。该方法首先设计深层卷积神经网络(CNN)对心电信号进行深度编码,提取心电信号形态特征。其次,搭建长短时记忆分类网络实现基于心电信号特征的心律失常自动分类。基于MIT-BIH心律失常数据库进行的实验结果表明,该方法显著缩短分类时间,并获得超过99.2%的分类准确率,灵敏度等评价参数均得到不同程度的提高,满足心电信号自动分类实时高效的要求。
Abstract:Chronic cardiovascular diseases such as arrhythmia seriously affect human health. The automatic classification of ElectroCardioGram(ECG) signals can effectively improve the diagnostic efficiency of such diseases and reduce labor costs. To tackle this problem, an improved Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM) method is proposed to achieve automatic classification of one dimensional ECG signals. Firstly, deep Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is designed to deeply encode the ECG signal, and ECG signal morphological features are extracted. Secondly, the LSTM classification network is used to realize automatic classification of arrhythmia of ECG signal features. Experimental studies based on the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database show that the training duration is significantly shortened and more than 99.2% classification accuracy is obtained. Sensitivity and other evaluation parameters are improved to meet the real-time and efficient requirements for automatic classification of ECG signals.
-
表 1 CNN模型的细节和参数
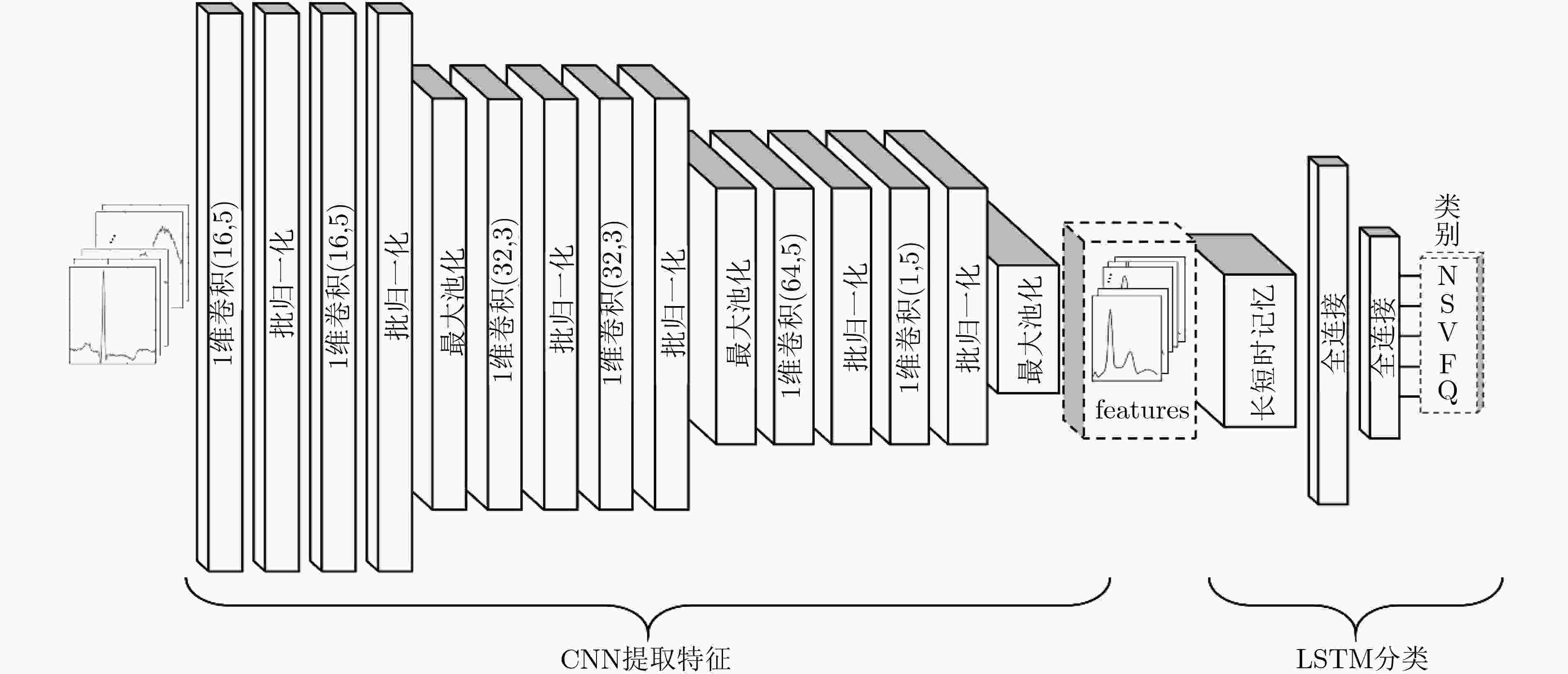
层数 层名称 卷积核大小 卷积核个数 激活函数 步长 参数 输出大小 0 输入 – – – – 300×1 1 1维卷积 5×1 16 ReLU 1 96 300×16 2 批归一化 – – – – 128 300×16 3 1维卷积 5×1 16 ReLU 1 1424 300×16 4 批归一化 – – – – 1456 300×16 5 最大池化 2 16 – 2 32 150×16 6 1维卷积 3×1 32 ReLU 1 3024 150×32 7 批归一化 – – – – 3088 150×32 8 1维卷积 3×1 32 ReLU 1 6192 150×32 9 批归一化 – – – – 6256 150×32 10 最大池化 2 32 – 2 64 75×32 11 1维卷积 5×1 64 ReLU 1 16560 75×64 12 批归一化 – – – – 16688 75×64 13 1维卷积 5×1 1 ReLU 1 28800 75×1 14 批归一化 – – – – 28928 75×1 15 最大池化 2 1 – 2 2 38×1 表 2 LSTM模型的细节和参数
层名称 隐含单元 激活函数 参数 长短时记忆层 32 – 12 全连接 256 ReLU 9996 全连接 5 Softmax 11024 表 3 AAMI标准在心电信号分类中描述
AAMI类别 类别数量 MIT-BIH心跳节拍类别 Normal(N) 89972 正常(NOR) 左束支传导阻塞(LBBB) 右束支传导阻塞(RBBB) 房性逸搏(AE) 结性逸搏(NE) Supraventricular(S) 2758 房性早搏(AP) 异常房性早搏(aAP) 交界性早搏(NP) 室上性早搏(SP) Ventricular(V) 7140 室性早搏(PVC) 室性逸搏(VE) Fusion(F) 800 心室融合心跳(fVN) Unknown(Q) 30 起搏心跳(P) 起搏融合心跳(fPN) 未分类心跳(U) 表 4 LSTM网络和C-LSTM网络测试集的相关评价参数(%)
网络 评价参数 模型类别 N S V F Q LSTM Acc 99.54 99.62 99.44 99.71 99.97 Sen 99.87 91.06 95.66 80.19 0 Spe 96.91 99.86 99.76 99.58 99.99 PPV 99.61 95.09 97.00 78.70 0.00 C-LSTM Acc 99.52 99.61 99.51 99.84 99.97 Sen 99.78 92.11 96.63 88.52 0 Spe 98.36 99.83 99.73 99.93 99.99 PPV 99.68 94.08 96.45 91.53 0.00 表 5 自动检测心律失常分类结果性能比较
研究 类型 分类器 信号长度 性能(%) Acc Sen Spe PPV 文献[19] 4 FFNN 250 samples (0.69 s) 96.94 97.78 96.31 – 文献[17] 17 KNN 360 samples (1.00 s) 97.00 97.10 96.90 – 文献[18] 5 SVM+RBF 200 samples (0.56 s) 98.91 98.91 97.85 – 文献[4] 14 NPE+SVM 300 samples (0.83 s) 98.51 98.51 – 98.51 文献[11] 5 CNN 360 samples (1.00 s) 94.03 96.71 91.54 97.86 文献[20] 4 SVM 8×1071 98.39 96.86 98.92 96.85 文献[12] 5 CNN 73×73 98.42 72.06 97.83 65.91 文献[15] 5 FCMDBN 200 samples (0.56 s) 96.54 94.55 93.31 93.91 文献[14] 2 CNN+RNN 211×24 95.76 87.85 87.85 94.99 本文方法 5 LSTM 300 sample (0.83 s) 99.14 91.70 99.22 92.60 C-LSTM 300 →38 samples(0.83 s)→(0.12 s) 99.23 94.26 99.57 95.44 -
World Health Organization. Cardiovascular diseases[EB/OL]. https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases/#tab=tab_1, 2017. YE Can, KUMAR B V K V, and COIMBRA M T. Heartbeat classification using morphological and dynamic features of ECG signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2012, 59(10): 2930–2941. doi: 10.1109/tbme.2012.2213253 YILDIRIM Ö. ECG beat detection and classification system using wavelet transform and online sequential ELM[J]. Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology, 2019, 19(1): 1940008. doi: 10.1142/S0219519419400086 高兴姣, 李智, 陈珊珊, 等. 基于近邻保持嵌入算法的心律失常心拍分类[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2017, 34(1): 1–6. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.201605045GAO Xingjiao, LI Zhi, CHEN Shanshan, et al. Arrhythmia heartbeats classification based on neighborhood preserving embedding algorithm[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 34(1): 1–6. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.201605045 AHMED R and ARAFAT S. Cardiac arrhythmia classification using hierarchical classification model[C]. The 6th International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology (CSIT), Amman, Jordan, 2014: 203–207. doi: 10.1109/CSIT.2014.6806001. BALOUCHESTANI M, SUGAVANESWARAN L, and KRISHNAN S. Advanced K-means clustering algorithm for large ECG data sets based on K-SVD approach[C]. The 9th International Symposium on Communication Systems, Networks & Digital Sign (CSNDSP), Manchester, UK, 2014: 177–182. doi: 10.1109/CSNDSP.2014.6923820. LI Duan, ZHANG Hongxin, and ZHANG Mingming. Wavelet de-noising and genetic algorithm-based least squares twin SVM for classification of arrhythmias[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2017, 36(7): 2828–2846. doi: 10.1007/s00034-016-0439-8 YIN Xi and LIU Xiaoming. Multi-task convolutional neural network for pose-invariant face recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(2): 964–975. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2765830 王斐, 吴仕超, 刘少林, 等. 基于脑电信号深度迁移学习的驾驶疲劳检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(9): 2264–2272. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180900WANG Fei, WU Shichao, LIU Shaolin, et al. Driver fatigue detection through deep transfer learning in an electroencephalogram-based system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(9): 2264–2272. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180900 MENG Huanhuan and ZHANG Yue. Classification of electrocardiogram signals with deep belief networks[C]. The 17th International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering, Chengdu, China, 2014: 7–12. doi: 10.1109/CSE.2014.36. ACHARYA U R, OH S L, HAGIWARA Y, et al. A deep convolutional neural network model to classify heartbeats[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2017, 89: 389–396. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.08.022 ZHAI Xiaolong and TIN C. Automated ECG classification using dual heartbeat coupling based on convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 27465–27472. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2833841 CHENG Maowei, SORI W J, JIANG Feng, et al. Recurrent neural network based classification of ecg signal features for obstruction of sleep apnea detection[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering (CSE) and IEEE International Conference on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing (EUC), Guangzhou, China, 2017, 199–202. doi: 10.1109/CSE-EUC.2017.220. TAN J H, HAGIWARA Y, PANG W, et al. Application of stacked convolutional and long short-term memory network for accurate identification of CAD ECG signals[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2018, 94: 19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.12.023 吴志勇, 丁香乾, 许晓伟, 等. 基于深度学习和模糊C均值的心电信号分类方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(10): 1913–1920. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170417WU Zhiyong, DING Xiangqian, XU Xiaowei, et al. A method for ECG classification using deep learning and fuzzy C-means[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(10): 1913–1920. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170417 HANNUN A Y, RAJPURKAR P, HAGHPANAHI M, et al. Cardiologist-level arrhythmia detection and classification in ambulatory electrocardiograms using a deep neural network[J]. Nature Medicine, 2019, 25(1): 65–69. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0268-3 PARK J, LEE K, and KANG K. Arrhythmia detection from heartbeat using k-nearest neighbor classifier[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine, Shanghai, China, 2013: 15–22. doi: 10.1109/BIBM.2013.6732594. ELHAJ F A, SALIM N, HARRIS A R, et al. Arrhythmia recognition and classification using combined linear and nonlinear features of ECG signals[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2016, 127: 52–63. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2015.12.024 GÜLER I and ÜBEYLI E D. ECG beat classifier designed by combined neural network model[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2005, 38(2): 199–208. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2004.06.009 SAHOO S, KANUNGO B, BEHERA S, et al. Multiresolution wavelet transform based feature extraction and ECG classification to detect cardiac abnormalities[J]. Measurement, 2017, 108: 55–66. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2017.05.022 -





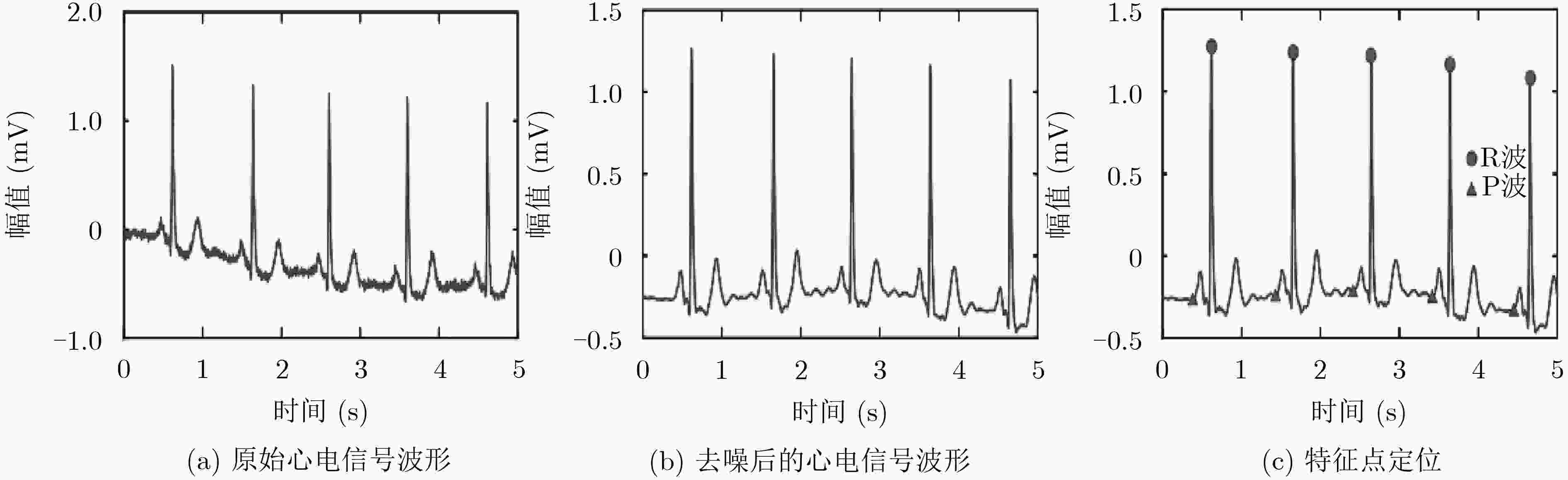
 下载:
下载:
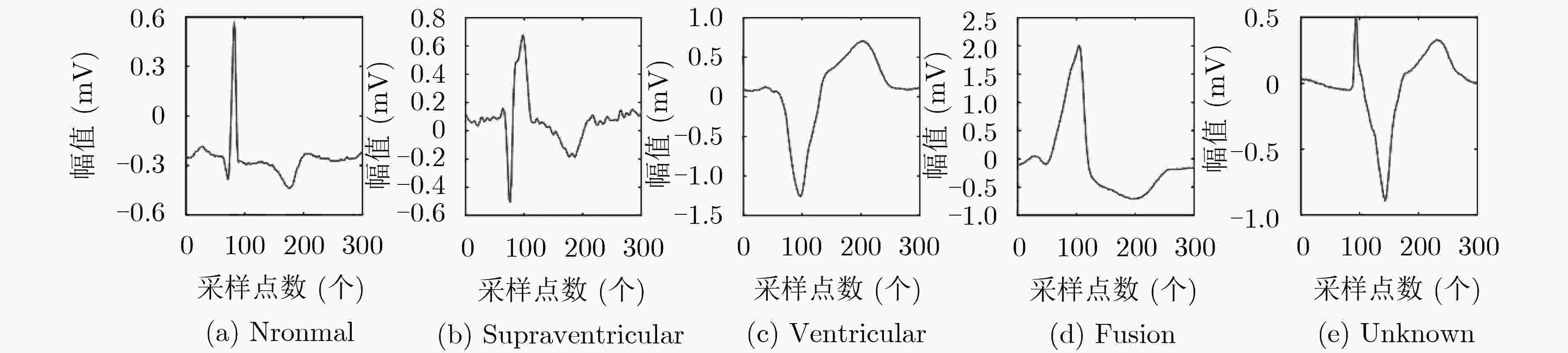
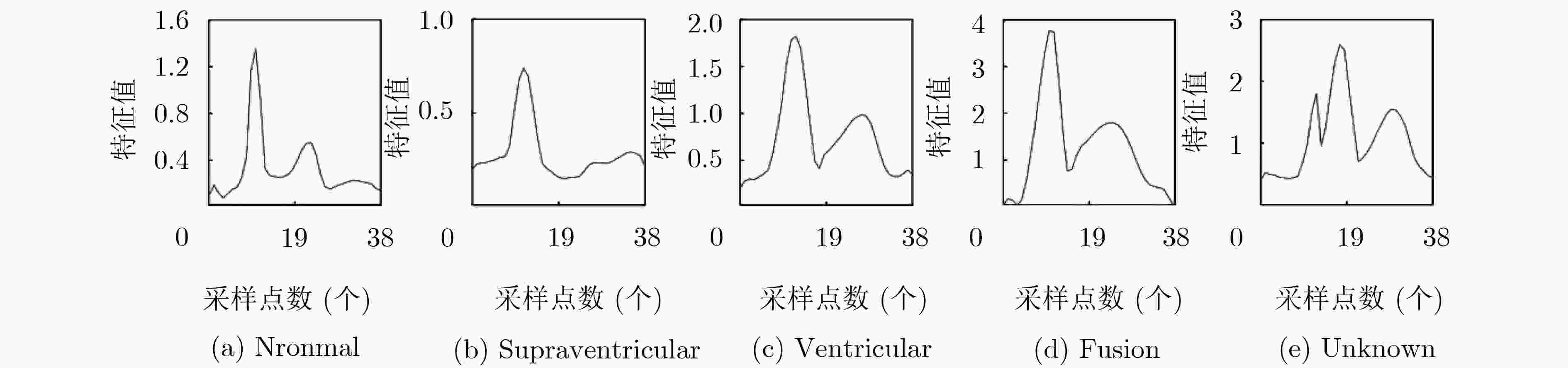
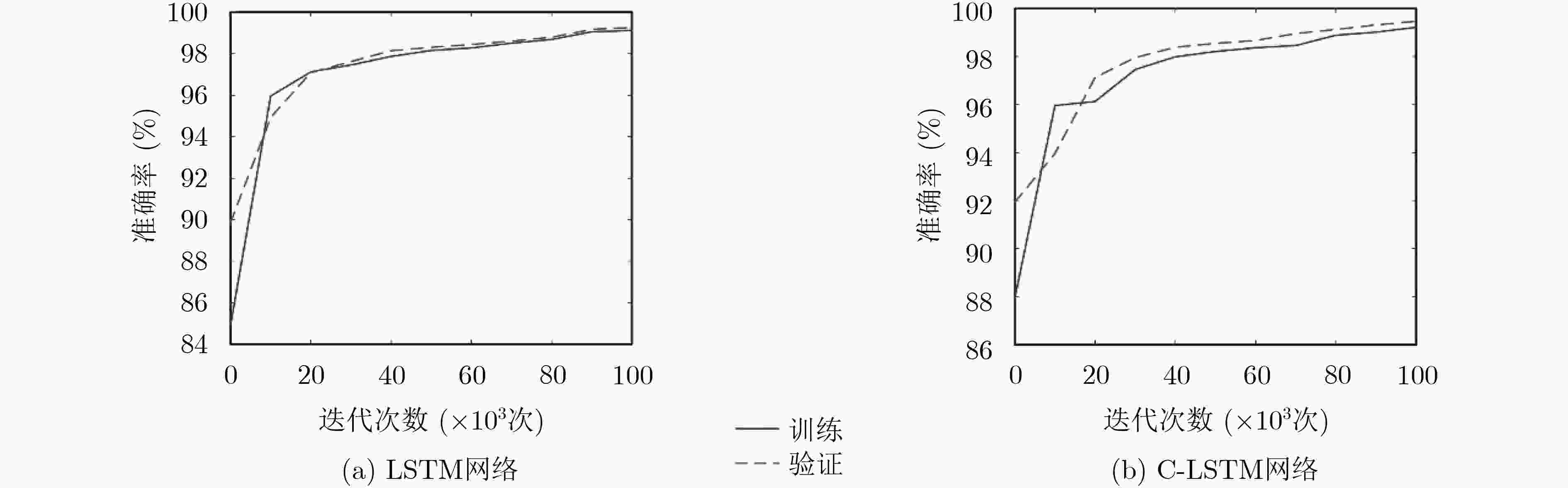



 下载:
下载:
