An Anti-cheat Method of Game Based on Windows Kernel Events
-
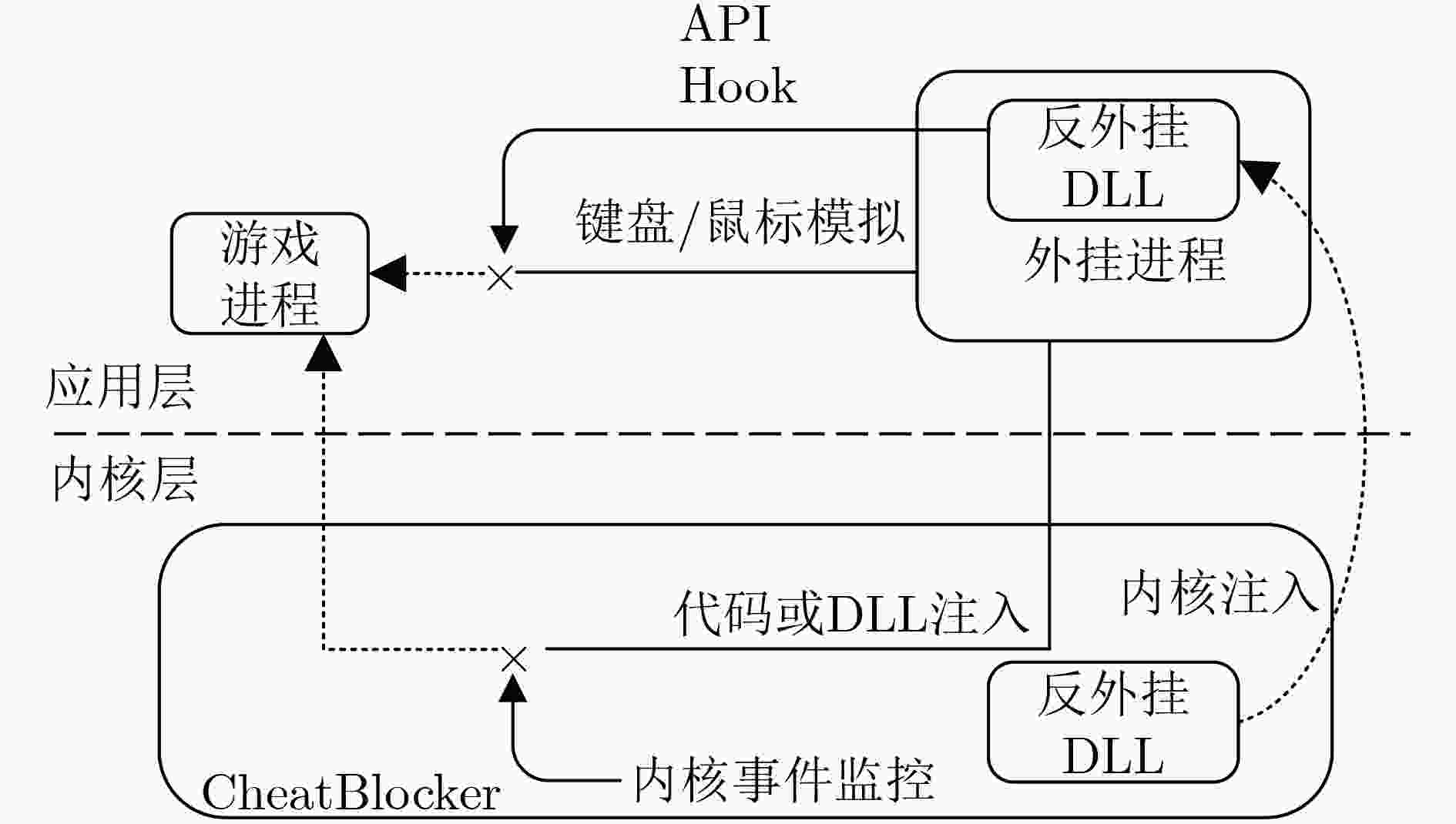
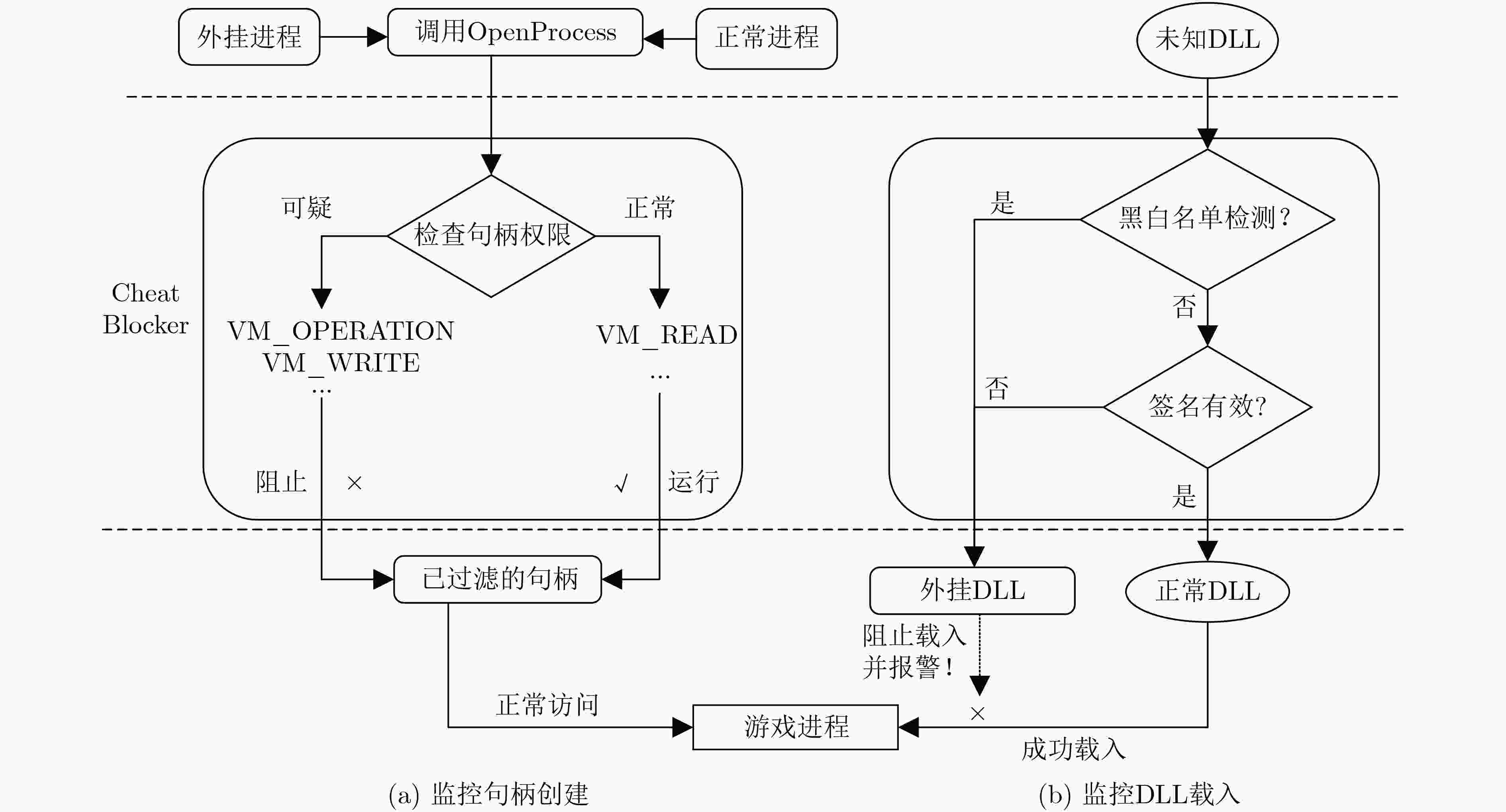
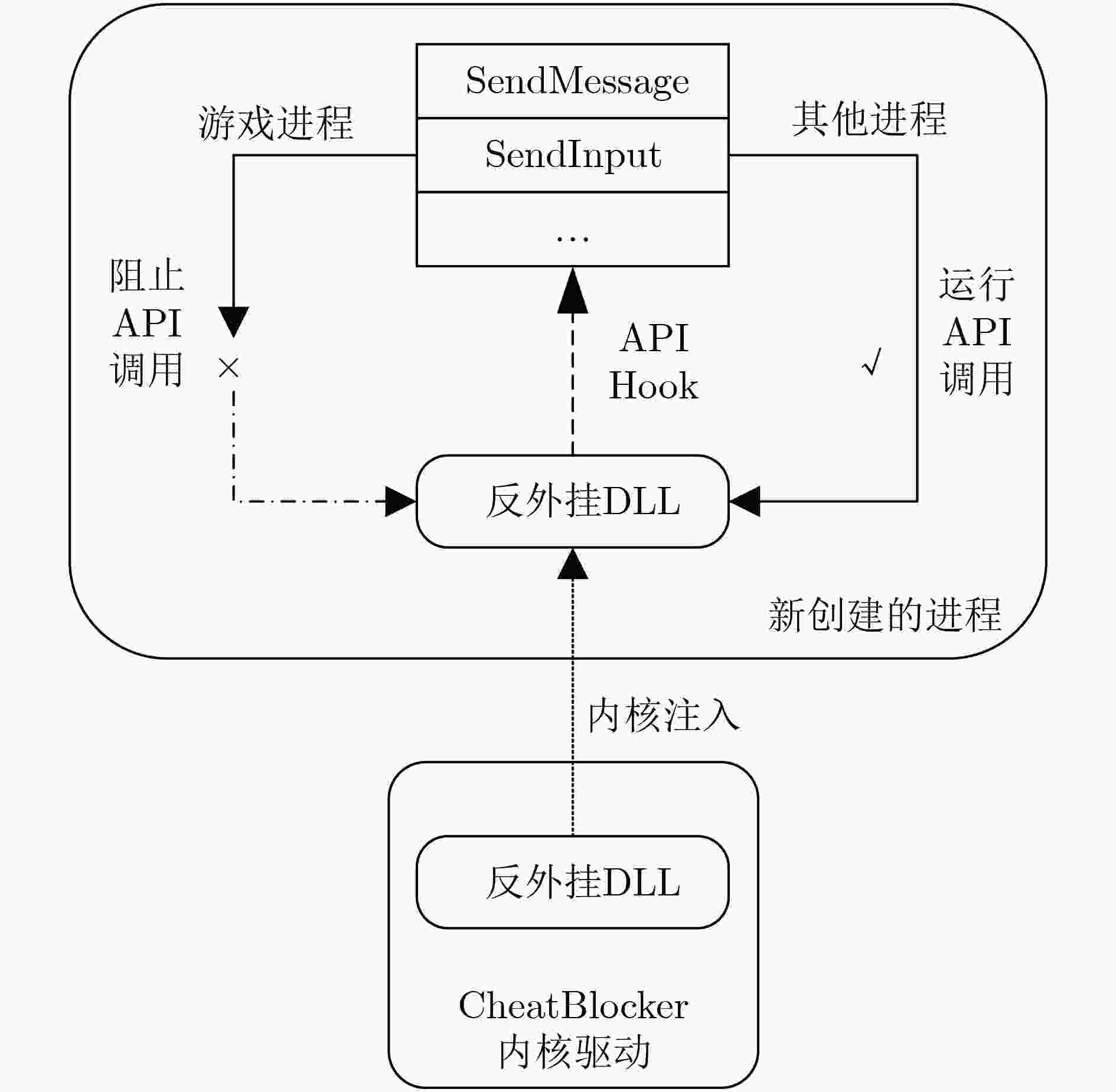
摘要: 针对目前客户端反外挂方法的诸多局限,该文提出一种基于内核事件的网络游戏反外挂方法,并实现了反外挂系统CheatBlocker。该方法通过监控Windows系统中的内核事件监视和拦截进程间的异常访问及异常模块注入,同时从内核注入反外挂动态加载库(DLL)用以阻断鼠标键盘的模拟。实验结果表明,CheatBlocker可防御进程模块注入外挂和用户输入模拟类外挂,且具有较低的性能开销。而且,CheatBlocker无需修改内核数据或代码,相比于目前的反外挂系统具有更好的通用性与兼容性。Abstract: In view of many limitations of current client anti plug-in methods, an anti-cheat method based on kernel events is proposed, and the network game anti-cheat system called CheatBlocker is implemented. This method uses the kernel event monitoring provided by Windows to intercept the abnormal access between processes and the injection of abnormal modules. At the same time, the anti-cheat Dynamic Loaded Library (DLL) injected from the kernel can block the simulation of the mouse keyboard. The experimental results show that CheatBlocker can defend against process module injection cheating and user input simulation cheating, and has low performance overhead. Moreover, CheatBlocker does not need to modify the kernel data or code which ensures the integrity of the kernel and is more compatible than the current anti-cheat systems.
-
Key words:
- Game cheating /
- Anti-cheating /
- Module injection /
- Kernel event
-
表 1 反外挂DLL Hook函数
模拟类型 相关API API 描述 WindowSimulation SendMessage 直接向指定窗口发送消息 PostMessage 将消息至于指定窗口的消息队列上 RtlUserSendMessage SendMessage内部调用API RtlUserPostMessage PostMessage内部调用API GlobalSimulation SendInput 直接模拟鼠标或键盘操作 mouse_event 模拟鼠标 keyboard_event 模拟键盘 表 2 实验环境
VM CPU 内存 操作系统 VM1 2 cores 1 GB Win7 SP1 (64 bit) VM2 2 cores 1 GB Win7 SP1 (32 bit) 表 3 外挂测试样本
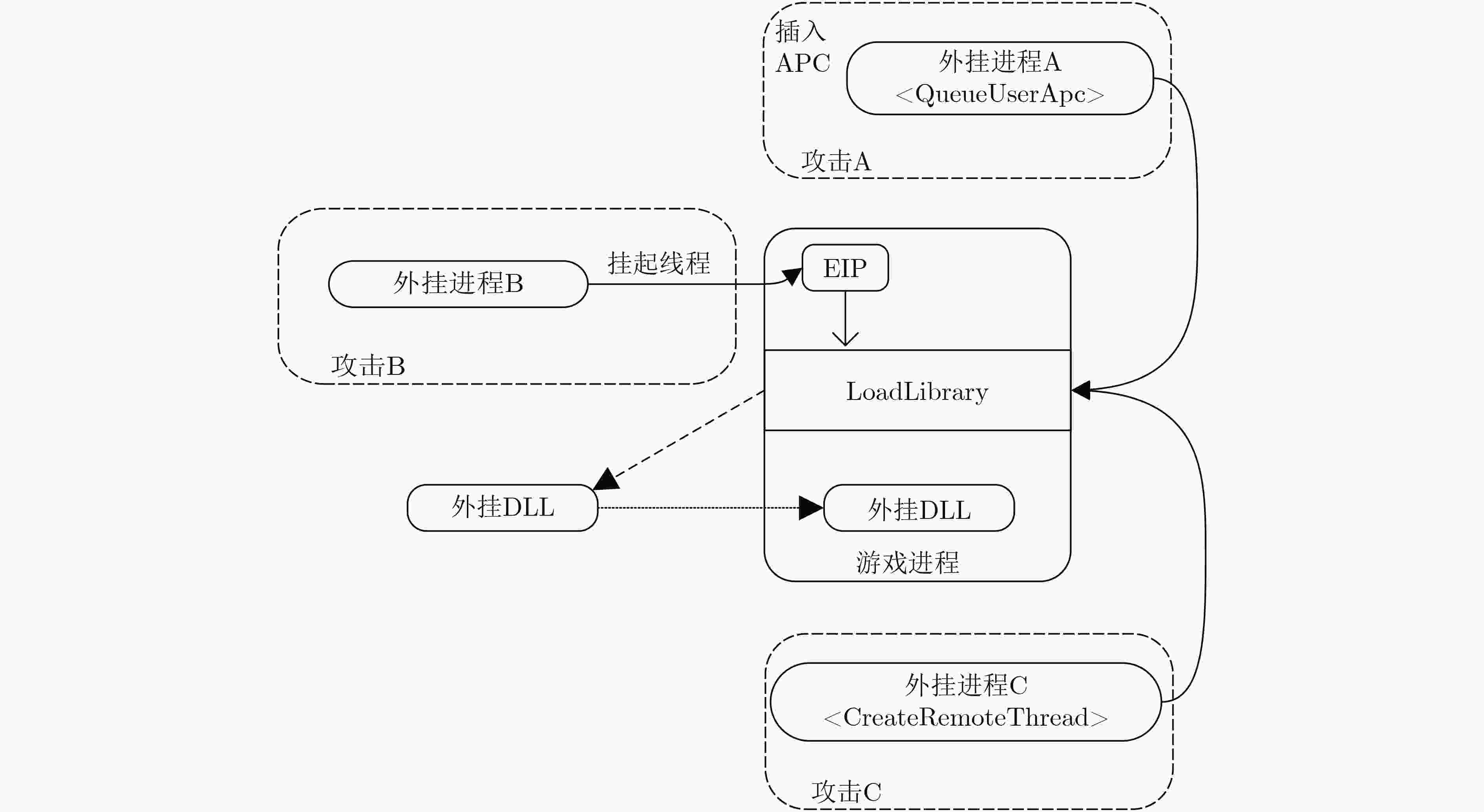
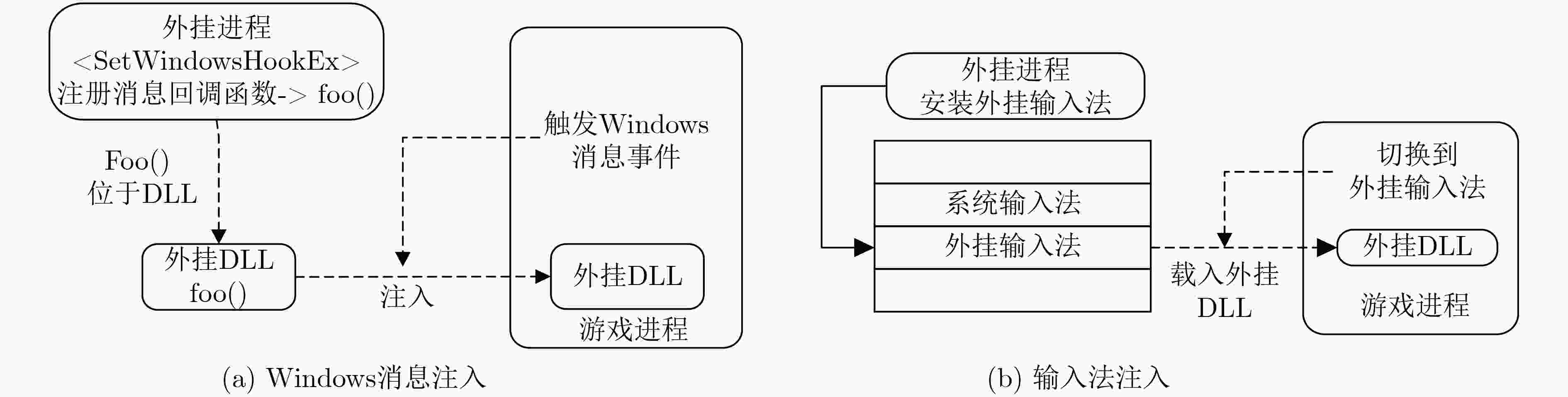
外挂工具 相关外挂技术 外挂行为描述 FIFA 10 FIFA Cheater 0.5 CreateRemoteThread 注入 内存修改 Mr.Anti.Fun Cheat CreateRemoteThread 注入 内存修改 CPY FIFA Cheater QueueUserApc 注入 代码注入 FIFA Auto Runner 窗口模拟 挂机脚本 CROSS FIRE Sniper Rifle 1.0 CreateRemoteThread 注入 内存修改 LOCK Health Cheater QueueUserApc 注入 内存修改 Ice Modz 6041 Rc1 Hook Windows 消息注入 内存修改 Crossfire Hacker 线程劫持注入 代码注入 Remote Dll Injector 所有注入技术 DLL注入 Assassin Wall Cf 窗口模拟 挂机脚本 Auto-Shooter 输入法注入/全局模拟 挂机脚本 Antifun GOLD Getter 线程劫持注入/窗口模拟 挂机脚本 表 4 反外挂系统防御效果对比
外挂技术 反外挂系统 CheatBlocker Nprotect Xray Warden GameGuard EasyAntiCheat 创建远程线程注入 √ √ √ √ √ √ 插入APC注入 √ √ × × √ √ 线程劫持注入 √ √ × √ √ √ Hook Windows消息注入 √ × √ × √ √ 输入法注入 √ × × × √ √ 全局模拟 √ × × × √ × 窗口模拟 √ × × × √ × 是否支持64位系统 √ √ √ √ × √ 表 5 反外挂系统系统开销对比
系统开销 No Anti-Cheat CheatBlocker Nprotect Xray Warden GameGuard EasyAntiCheat 平均CPU占用 (%) 23.5 28.7 25.8 26.4 23.3 30.8 29.4 平均内存占用(%) 35.3 35.8 34.7 37.5 36.5 36.7 35.8 平局启动时间(s) 20.1 24.6 23.4 22.8 22.3 28.9 25.7 -
腾讯游戏研发部游戏安全中心. 游戏安全: 手游安全技术入门[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2016.Game Security Center of Tencent Game R & D Department. Game Security: Introduction to Mobile Security Technology[M]. Beijing: Electronic Industry Press, 2016. YAN J J and CHOI H J. Security issues in online games[J]. The Electronic Library, 2002, 20(2): 125–133. doi: 10.1108/02640470210424455 YAN J and RANDELL B. A systematic classification of cheating in online games[C]. The 4th ACM SIGCOMM Workshop on Network and System Support for Games, New York, USA, 2005: 1–9. doi: 10.1145/1103599.1103606. KABUS P, TERPSTRA W W, CILIA M, et al. Addressing cheating in distributed MMOGs[C]. The 4th ACM SIGCOMM Workshop on Network and System Support for Games, New York, USA, 2005: 1–6. doi: 10.1145/1103599.1103607. CHOI Y, CHANG S J, KIM Y, et al. Detecting and monitoring game bots based on large-scale user-behavior log data analysis in multiplayer online games[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2016, 72(9): 3572–3587. doi: 10.1007/s11227-015-1545-2 罗平, 徐倩华. 网络游戏外挂技术及检测[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2007, 28(6): 1273–1276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7024.2007.06.011LUO Ping and XU Qianhua. Hack technology and detection of online games[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2007, 28(6): 1273–1276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7024.2007.06.011 杨英杰, 冷强, 常德显, 等. 基于属性攻击图的网络动态威胁分析技术研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(8): 1838–1846. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181025YANG Yingjie, LENG Qiang, CHANG Dexian, et al. Research on network dynamic threat analysis technology based on attribute attack graph[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(8): 1838–1846. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181025 CHANG H and ATALLAH M J. Protecting software code by guards[C]. ACM CCS-8 Workshop DRM on Security and Privacy in Digital Rights Management, Berlin, Germany, 2001: 160–175. doi: 10.1007/3-540-47870-1_10. THE L B and KHANH V N. GameGuard: A windows-based software architecture for protecting online games against hackers[C]. The Symposium on Information and Communication Technology, Hanoi, Vietnam, 2010: 171–178. doi: 10.1145/1852611.1852643. 梁光辉, 庞建民, 单征. 基于代码进化的恶意代码沙箱规避检测技术研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(2): 341–347. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180257LIANG Guanghui, PANG Jianmin, and SHAN Zheng. Malware sandbox evasion detection based on code evolution[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(2): 341–347. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180257 WOO J, KANG A R, and KIM H K. The contagion of malicious behaviors in online games[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2013, 43(4): 543–544. doi: 10.1145/2534169.2491712 AHMAD M A, KEEGAN B, SRIVASTAVA J, et al. Mining for gold farmers: Automatic detection of deviant players in mmogs[C]. 2009 International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering, Vancouver, Canada, 2009: 340–345. doi: 10.1109/cse.2009.307. KWON H, MOHAISEN A, WOO J, et al. Crime scene reconstruction: Online gold farming network analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2017, 12(3): 544–556. doi: 10.1109/tifs.2016.2623586 CHUNG Y, PARK C Y, KIM N R, et al. Game bot detection approach based on behavior analysis and consideration of various play styles[J]. ETRI Journal, 2013, 35(6): 1058–1067. doi: 10.4218/etrij.13.2013.0049 DUH H B L and CHEN V H. Cheating behaviors in online gaming[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Online Communities and Social Computing, Berlin, Germany, 2009: 567–573. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-02774-1_61. 傅建明, 彭碧琛, 杜浩. 一种组件加载漏洞的动态检测[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2012, 52(10): 1356–1363, 1369. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2012.10.007FU Jianming, PENG Bichen, and DU Hao. Dynamic detection of component loading vulnerability[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University:Science and Technology, 2012, 52(10): 1356–1363, 1369. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2012.10.007 HOGLUND G and MCGRAW G. Exploiting Online Games: Cheating Massively Distributed Systems[M]. New York, USA: Addison-Wesley Professional, 2007: 119–125. WEBB S D and SOH S. Cheating in networked computer games: A review[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Digital Interactive Media in Entertainment and Arts, Perth, Australia, 2007: 105–112. doi: 10.1145/1306813.1306839. LIU H I and LO Y T. DaCAP-a distributed Anti-Cheating peer to peer architecture for massive multiplayer on-line role playing game[C]. The 8th IEEE International Symposium on Cluster Computing and the Grid (CCGRID), Lyon, France, 2008: 584–589. doi: 10.1109/ccgrid.2008.49. SEBASTIO S, AMORETTI M, MURGA J R, et al. Honest vs Cheating Bots in PATROL-based Real-time Strategy MMOGs[M]. CAGNONI S, MIROLLI M, and VILLANI M. Evolution, Complexity and Artificial Life. Heidelberg: Germaay, Springer, 2014: 225–238. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-37577-4_15. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
