Airborne Distributed Coherent Aperture Radar Synchronization Error Calibration Method Based on Prominent Points
-
摘要:
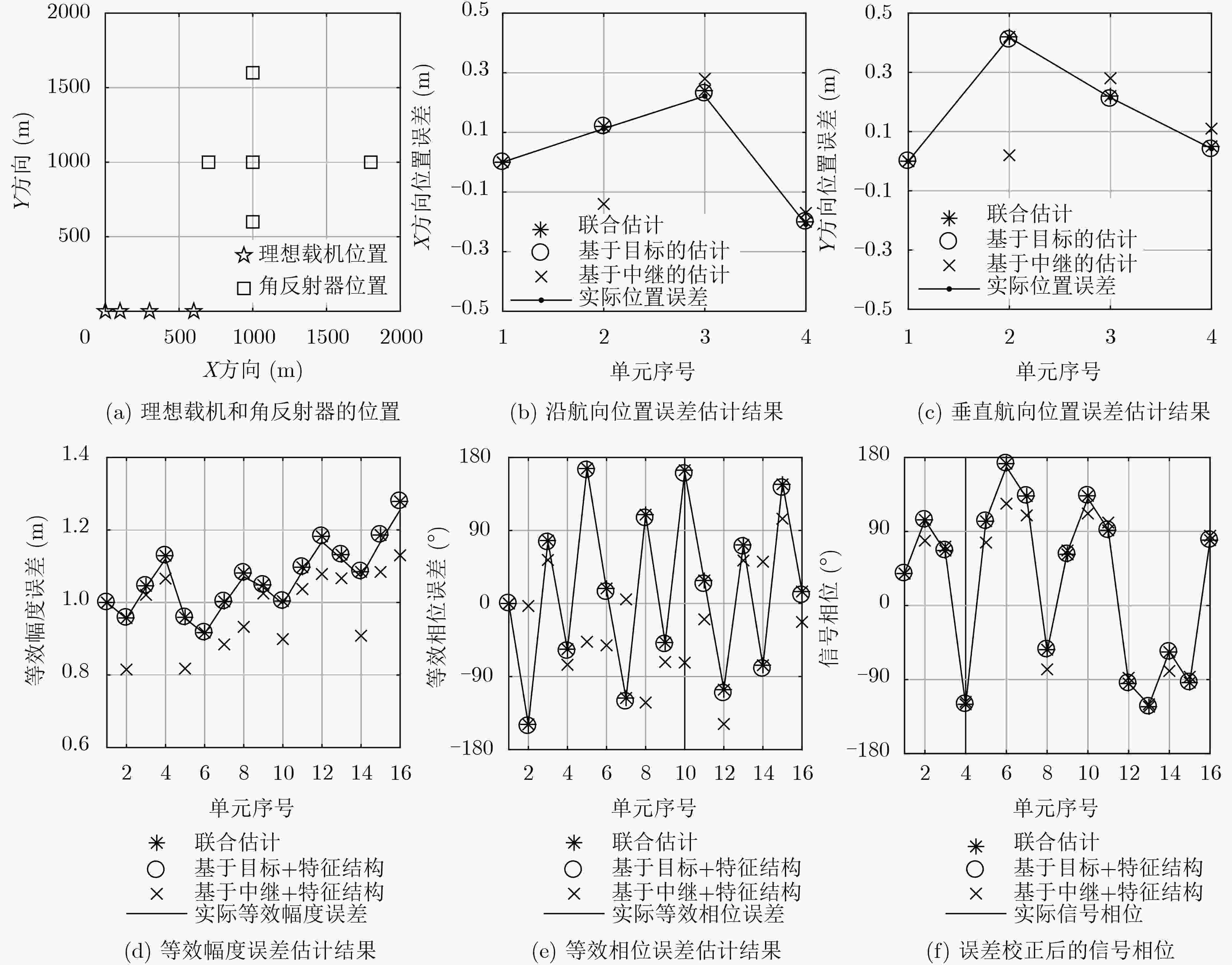
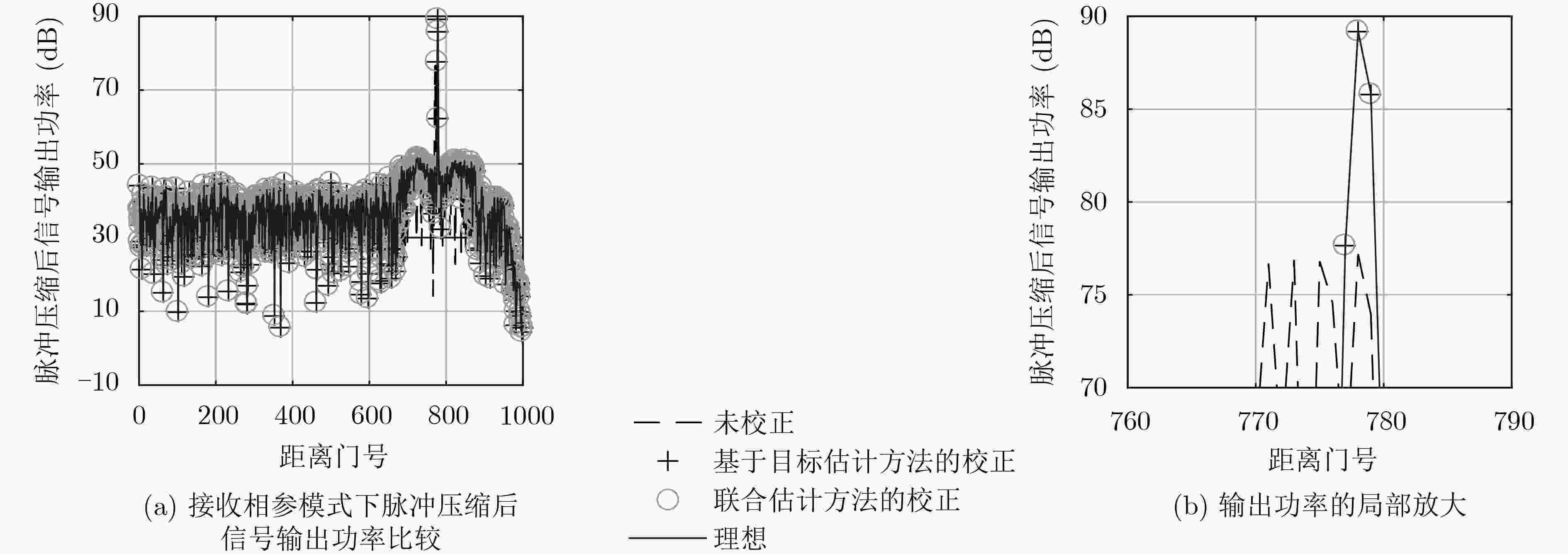
机载分布式相参雷达(DCAR)相比较于地基DCAR具有探测距离远、机动性高和部署灵活等优势,然而,载机平台运动使得机载DCAR面临更加严格的时间、空间和相位同步要求。为此,该文建立了基于慢时间码分多址(ST-CDMA)波形的机载DCAR信号模型及其矩阵表示形式,分析了时间、空间和相位同步误差对目标相参合成的影响,并提出一种基于特显点的机载DCAR同步误差校正方法。该方法首先采用目标参数搜索的方式消除滤波器网格失配误差;接着,利用基于目标的估计方法或者基于中继的估计方法完成单元位置误差校正;最后,利用特征结构方法校正等效幅相误差。仿真实验验证了所提方法的有效性。
Abstract:Airborne Distributed Coherent Aperture Radar (DCAR) has the advantages of wide observation range, high maneuverability and flexible deployment. However, airborne DCAR is confronted with more stringent time, space and phase synchronization requirements. Therefore, an airborne DCAR signal model and its matrix representation based on Slow-Time Code Division Multiple Access (ST-CDMA) waveform are established successively. Moreover, the influence on target coherence synthesis resulted from time, space and phase synchronization errors is analyzed in detail, and a novel airborne DCAR synchronization error calibration method based on prominent points is proposed. This method utilizes the target parameter search strategy to eliminate the grid mismatch filtering firstly. Then, with the utilization of estimation approaches based on target model or repeater station model, the unit platform position error is calibrated. Finally, equivalent amplitude and phase errors are calibrated by Eigen structure methods. The validity of the proposed method to calibrate the airborne DCAR synchronization error is demonstrated by simulation experiments.
-
表 1 算法时间复杂度比较
算法 时间复杂度 基于目标+特征结构 $O(MPW){\rm{ + }}O(2{M^6})$ 基于中继+特征结构 $O\left(\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{\tilde m{\rm{ = } }1}^M { { {\tilde m}^2}PW} \right){\rm{ + } }O(2{M^6})$ 联合估计方法 $O(MPW) + O\left(\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{\tilde m{\rm{ = } }1}^M { { {\tilde m}^2}PW} \right){\rm{ + } }O(4{M^6})$ 表 2 不同方法估计的时间同步误差比较 (μs)
单元雷达序号 2 3 4 实际时间同步误差 2.0368 2.2645 0.3175 基于目标的方法的估计误差 2.0350 2.2650 0.3175 联合方法的估计误差 2.0350 2.2650 0.3175 -
AHLGREN G W. Next generation radar concept definition team final report[R]. 2003. KEVIN M, SCOTT D, JEFFREY C, et al. Wideband aperture coherence processing for next generation radar(NexGen)[R]. Tehnical Report ESC-TR200087, 2004. FLETCHER A S and ROBEY F C. Performance bounds for adaptive coherence of sparse array radar[C]. The 11th Conference Adaptive Sensors Array Processing, Lexington, USA, 2003: 290–293. ZENG Tao, YIN Pilei, and LIU Quanhua. Wideband distributed coherent aperture radar based on stepped frequency signal: Theory and experimental results[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(4): 672–688. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0221 LIU Xinghua, XU Zhenhai, and XIAO Shunping. Performance gain bounds of coherently combining multiple radars in a target-based calibration manner[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 30(2): 278–287. doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2019.02.07 宋靖, 张剑云. 分布式全相参雷达相参性能分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(1): 9–14. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140202SONG Jing and ZHANG Jianyun. Coherence performance analysis for distributed aperture coherent radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(1): 9–14. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140202 王俊, 向洪, 魏少明, 等. 快拍数据的分布式二维阵列测角方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(6): 1375–1382. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170856WANG Jun, XIANG Hong, WEI Shaoming, et al. 2-D DOA estimation of distributed array with single snapshot[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(6): 1375–1382. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170856 刘兴华, 徐振海, 肖顺平. 分布式相参雷达几何布置约束条件[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2017, 39(8): 1723–1731. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.08.09LIU Xinghua, XU Zhenhai, and XIAO Shunping. Geometric arrangement constraints of distributed coherent aperture radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(8): 1723–1731. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.08.09 陆潞, 高梅国. 分布式阵列雷达基线位置和相位误差的卫星标校方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(12): 2896–2902. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181152LU Lu and GAO Meiguo. A satellite calibration method for the baseline coordinate and phase difference of distributed radar array[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(12): 2896–2902. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181152 陈金铭, 王彤, 吴建新, 等. 基于滤波器网格失配的分布式相参雷达目标参数估计方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(11): 2460–2470. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.11.09CHEN Jinming, WANG Tong, WU Jianxin, et al. Target parameter estimation method for distributed coherent aperture radar based on grid mismatch filtering[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(11): 2460–2470. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.11.09 YANG Xiaopeng, YIN Pilei, and ZENG Tao. Time and phase synchronization for wideband distributed coherent aperture radar[C]. IET International Radar Conference 2013, Xi’an, China, 2013: 1–5. doi: 10.1049/cp.2013.0241. CHATTERJEE P and NANZER J A. Effects of time alignment errors in coherent distributed radar[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference, Oklahoma City, USA, 2018: 727–731. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2018.8378649. GINI F, DE MAIO A, and PATTON L. Waveform Design and Diversity for Advanced Radar Systems[M]. London: The Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2012: 89–117. RABIDEAU D J. MIMO radar waveforms and cancellation ratio[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(2): 1167–1178. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6178055. WEISS A J and FRIEDLANDER B. Eigenstructure methods for direction finding with sensor gain and phase uncertainties[J]. Circuits, Systems and Signal Processing, 1990, 9(3): 271–300. doi: 10.1007/BF01201215 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
