Feature-Aware D2D Content Caching Strategy
-
摘要: 设备到设备通信(D2D)可以有效地卸载基站流量,在D2D网络中不仅需要共享大众化内容还需要个性化内容缓存。该文对缓存内容选择问题进行了深入研究,提出一种结合特征感知的内容社交价值预测(CSVP)方法。价值预测不仅可以降低时延也可以减少缓存替换次数降低缓存成本。首先结合用户特征和内容特征计算内容当前价值,然后通过用户社交关系计算未来价值。微基站根据内容的价值为用户提供个性化内容缓存服务,宏基站则在每个微基站的缓存内容中选择价值较大部分的内容。仿真结果表明,该文提出的缓存策略可以有效缓解基站流量,与其他方法相比降低时延约20%~40%。Abstract: Device to Device (D2D) communications can effectively offload base station traffic. In D2D networks, the popular content is not only needs to be shared, but also the individual content is needs to be cached. In this paper, the problem of cache content selection is researched. A Content Social Value Prediction(CSVP) method based on feature perception is proposed. Value prediction can not only reduce latency, but also reduce the number of cache replacements and reduce cache costs. Firstly, the current value of content is calculated by combining user features and content features, and then future value is calculated through user social relationships. The small base station provides the user with a personalized content caching service according to the value of the content, and the base station selects a content with a larger value in the individual cache content of each small base station as popular content. Simulation results show that the caching strategy based on the proposed method can alleviate the base station traffic effectively, and reduce the delay by about 20%~40%.
-
Key words:
- Edge network /
- D2D communication /
- Content caching /
- Exploration - exploitation /
- Value prediction
-
表 1 算法1 内容社交价值预测
输入:$T,r,\alpha ,\lambda ,{\lambda _1},{\lambda _2},{\beta _1},{\beta _2},\xi $ 输出:价值列表,观察用户请求情况 (1) 随机初始化参数$\widehat {{U}},\widehat {{C}},{{L}},{{W}}$ (2) For t=1, 2, ···, T do (3) 感知内容特征及用户特征 (4) For all k ∈C do (5) 如果内容是新内容: (6) 初始化参数:${{{A}}_k} \leftarrow {{{I}}_d}$, ${{{B}}_k} \leftarrow {0_{d*1}}$ (7) 结束 (8) 更新参数:${\theta _{t,k}} \leftarrow {{A}}_{t,k}^{ - 1}{{{B}}_{t,k}}$,
${P_{t,i,k}} \leftarrow {{X}}_{t,k}^{\rm{T}}{\theta _k} + \alpha \sqrt {{{X}}_{t,k}^{\rm{T}}{{A}}_{t,k}^{ - 1}{{X}}_{t,k}^{\rm{T}}} $,
${{{A}}_{t,k}} \leftarrow {{{A}}_{t,k}} + {{{X}}_{t,k}}{{X}}_{t,k}^{\rm{T}}$, ${{{B}}_{t,k}} \leftarrow {{{B}}_{t,k}} + {r_t}{{{X}}_{t,k}}$(9) 当式(29)的值没有收敛时: (10) 根据梯度更新参数 (11) 结束 (12) 计算未来价值 (13) 计算总价值 (14) 结束 (15) 按降序输出价值列表,观察用户请求情况 (16) 结束 表 2 仿真参数设置
参数 参数值 内容库数量 5000 内容包大小 20 MB SBS-UE延时 20 ms BS-UE延时 50 ms CDN-UE延时 100 ms D2D延时 10 ms -
Cisco. Cisco visual networking index: Global mobile data traffic forecast update, 2017–2022 white paper[EB/OL]. https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/service-provider/visual-networking-index-vni/white-paper-c11-738429.html, 2019. REBECCHI F, DE AMORIM M D, and CONAN V. Droid: Adapting to individual mobility pays off in mobile data offloading[C]. 2014 IFIP Networking Conference, Trondheim, Norway, 2014: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/IFIPNetworking.2014.6857087. FANG Chao, YAO Haipeng, WANG Zhuwei, et al. A survey of mobile information-centric networking: research issues and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(3): 2353–2371. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2018.2809670 TATAR A, DE AMORIM M D, FDIDA S, et al. A survey on predicting the popularity of web content[J]. Journal of Internet Services and Applications, 2014, 5(1): 8. doi: 10.1186/s13174-014-0008-y CHANDRASEKARAN G, WANG N, and TAFAZOLLI R. Caching on the move: Towards D2D-based information centric networking for mobile content distribution[C]. The 40th IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks, Clearwater Beach, USA, 2015: 312–320, doi: 10.1109/LCN.2015.7366325. KHAN F H and KHAN Z. Popularity-aware content caching for distributed wireless helper nodes[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2017, 42(8): 3375–3389. doi: 10.1007/s13369-017-2505-3 TAGHIZADEH M and BISWAS S. Community based cooperative content caching in social wireless networks[C]. The 14th ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing, Bangalore, India, 2013: 257–262. doi: 10.1145/2491288.2491318. 柴蓉, 王令, 陈明龙, 等. 基于时延优化的蜂窝D2D通信联合用户关联及内容部署算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(11): 2565–2570. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180408CHAI Rong, WANG Ling, CHEN Minglong, et al. Joint clustering and content deployment algorithm for cellular d2d communication based on delay optimization[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(11): 2565–2570. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180408 MEGIDDO N and MODHA D S. ARC: A self-tuning, low overhead replacement cache[C]. The 2nd USENIX Conference on File and Storage Technologies, San Francisco, USA, 2003: 115–130. MEGIDDO N and MODHA D S. Outperforming LRU with an adaptive replacement cache algorithm[J]. Computer, 2004, 37(4): 58–65. doi: 10.1109/MC.2004.1297303 XIANG Lin, Ng D W K, GE Xiaohu, et al. Cache-aided non-orthogonal multiple access: The two-user case[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2019, 13(3): 436–451. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2019.2907864 LI Lihong, CHU Wei, LANGFORD J, et al. A contextual-bandit approach to personalized news article recommendation[C]. The 19th International Conference on World Wide Web, Raleigh, USA, 2010: 661–670. doi: 10.1145/1772690.1772758. ZIPF G K. Selected studies of the principle of relative frequency in language[J]. Language, 1933, 9(1): 89–92. doi: 10.4159/harvard.9780674434929 JIANG Wei, FENG Gang, QIN Shuang, et al. Multi-agent reinforcement learning for efficient content caching in mobile D2D networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(3): 1610–1622. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2894403 WALSH T J, SZITA I, DIUK C, et al. Exploring compact reinforcement-learning representations with linear regression[C]. The 25th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, Canada, 2009, 591–598. MA Hao, ZHOU T C, LYU M R, et al. Improving recommender systems by incorporating social contextual information[J]. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 2011, 29(2): 1–23. doi: 10.1145/1961209.1961212 YANG Bo, LEI Yu, LIU Jiming, et al. Social collaborative filtering by trust[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(8): 1633–1647. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2605085 -





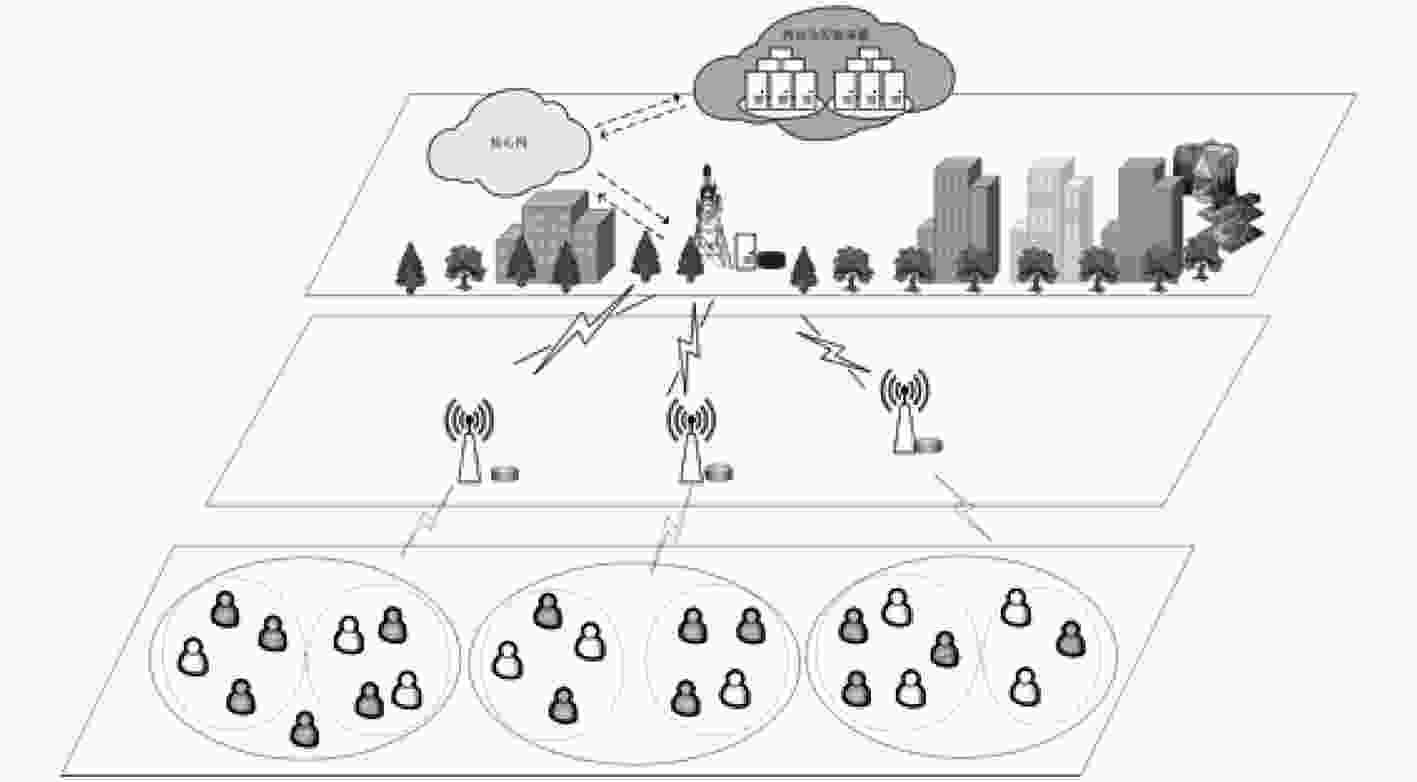
 下载:
下载:

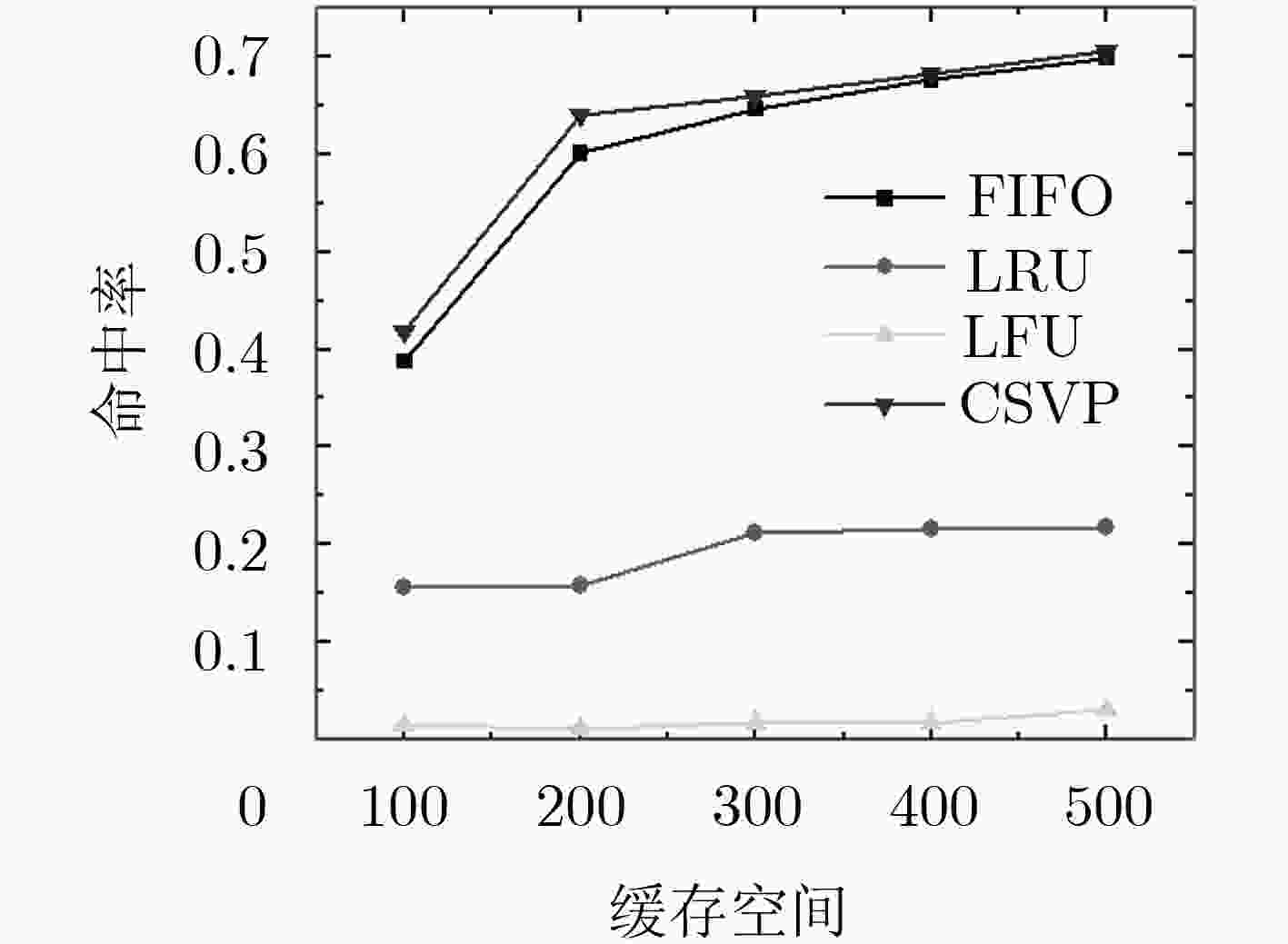
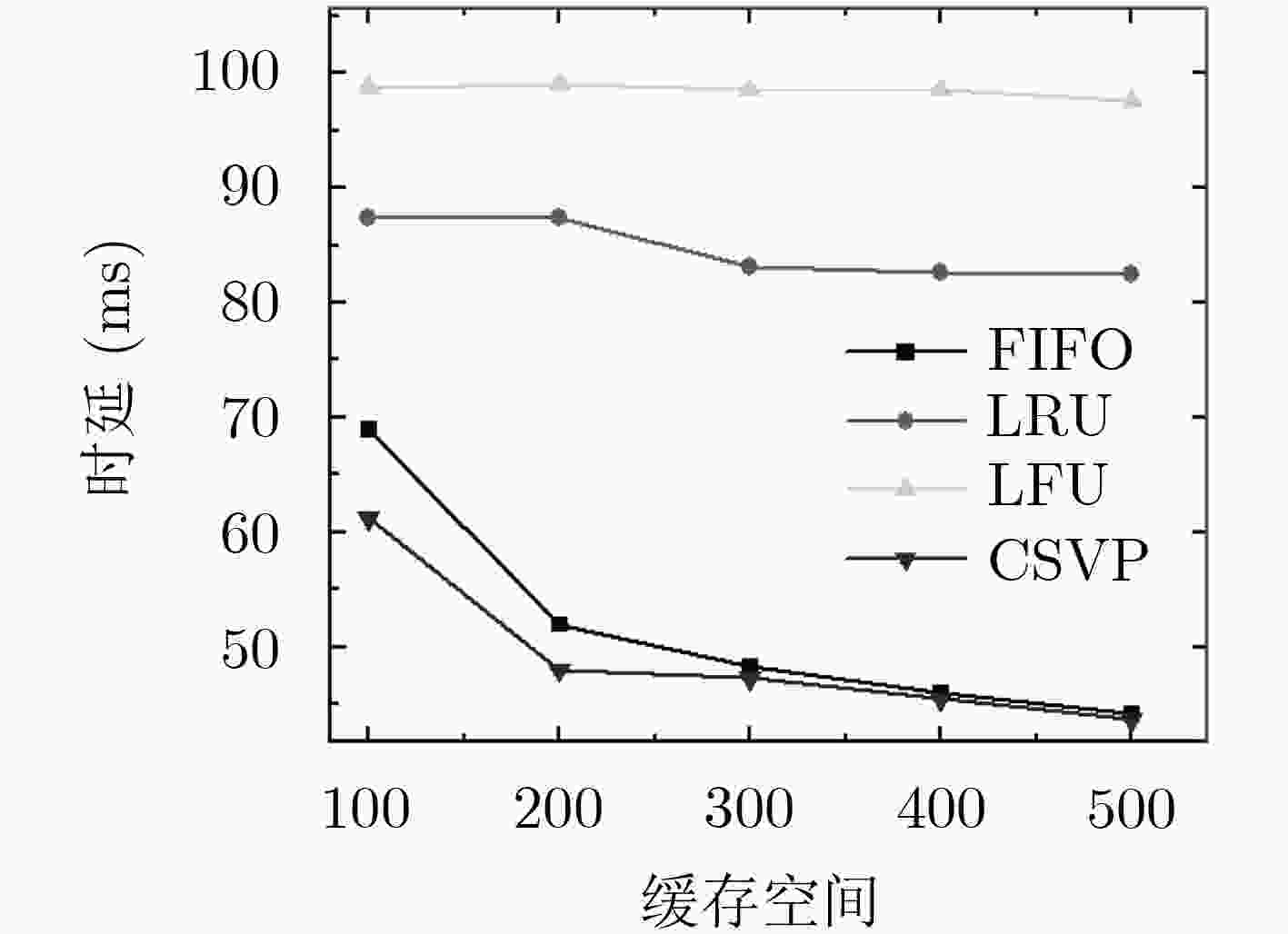
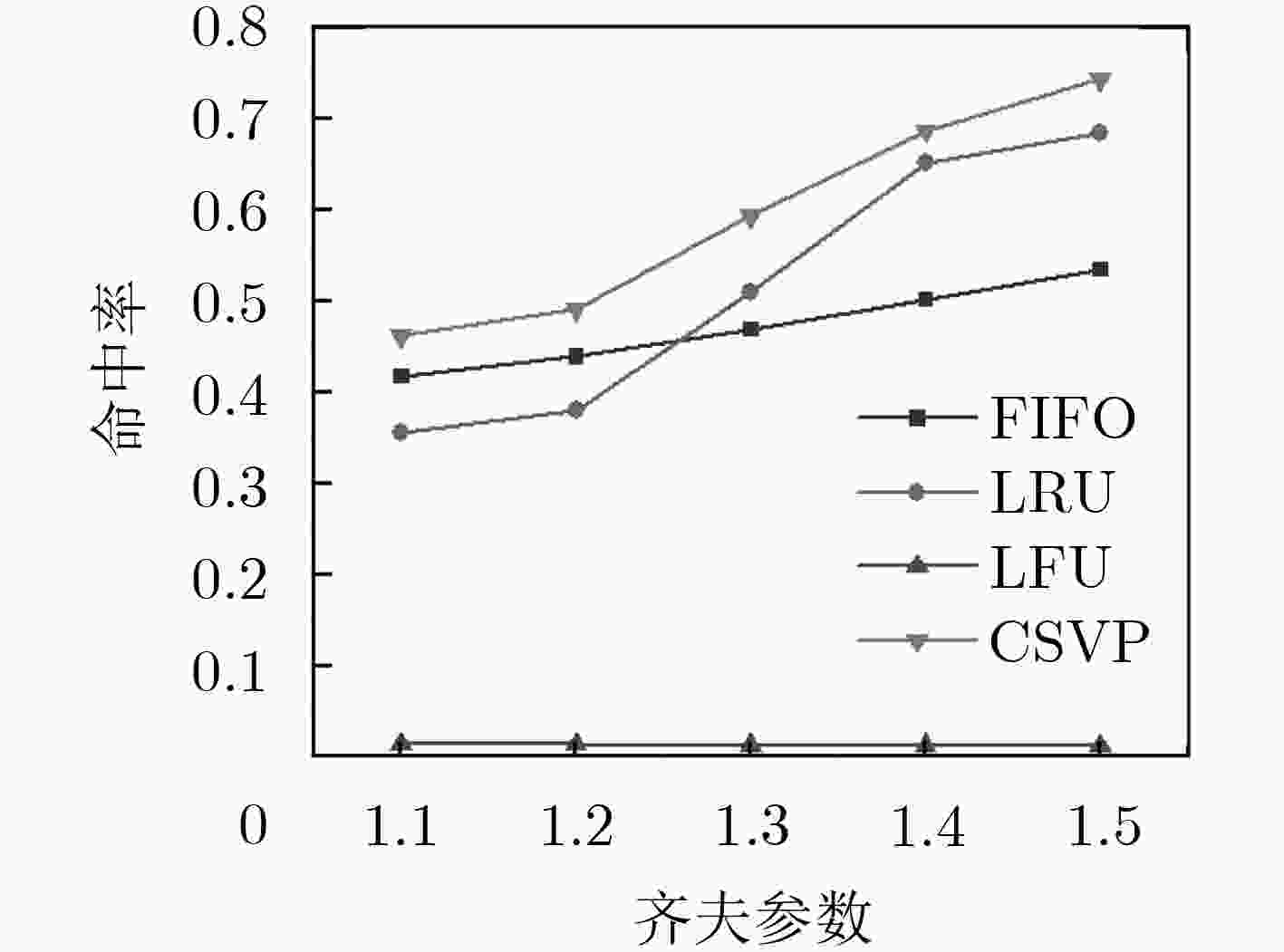
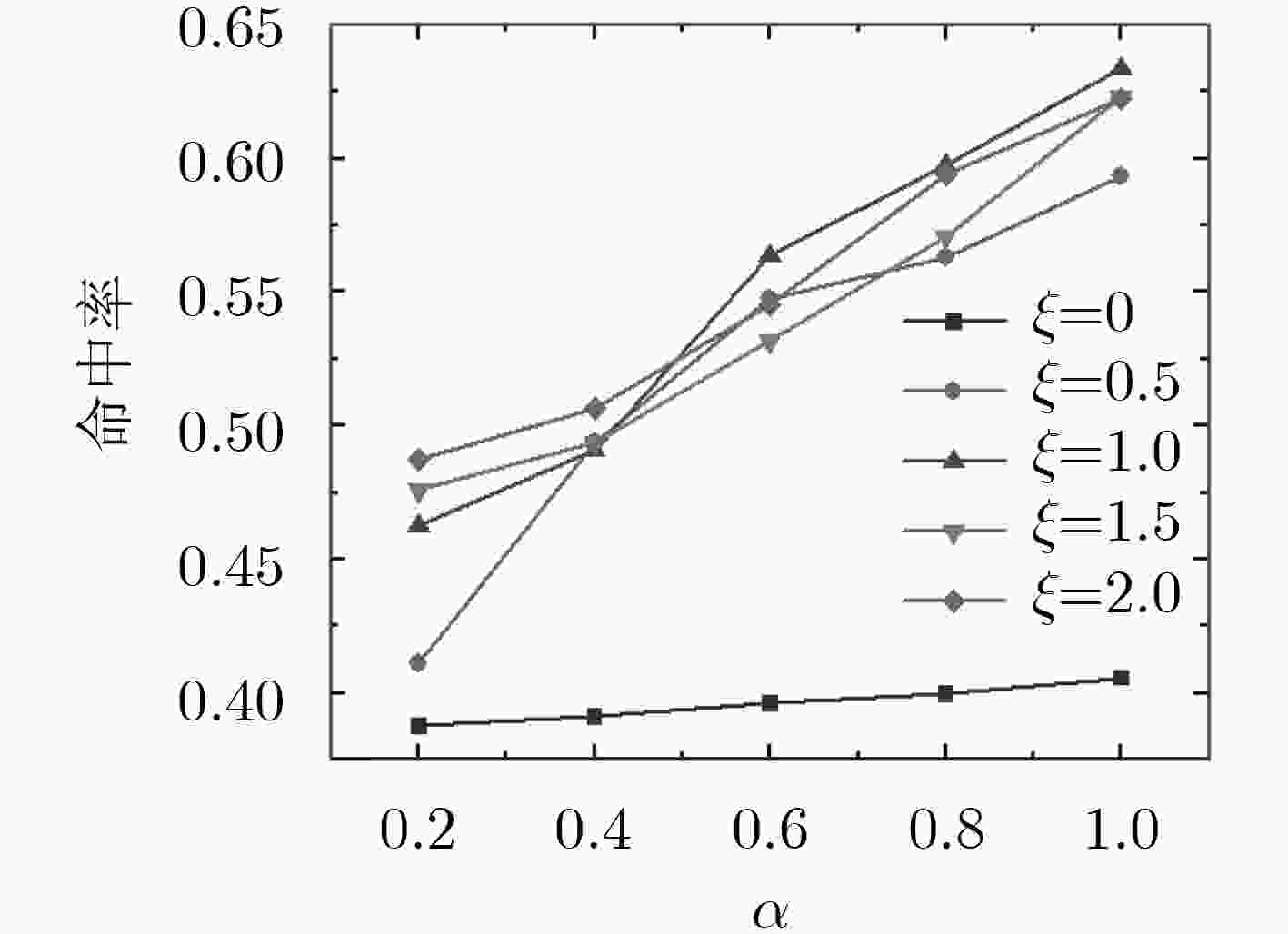


 下载:
下载:
