A Review of Target Detection Algorithm for GPR B-scan Processing
-
摘要:
利用无损探测技术来获取地下目标的信息是当前研究的热点,探地雷达(GPR)作为一种重要的无损工具,已被广泛用于检测,定位和特征化地下目标。然而,从GPR成像中探测掩埋物体并评估其位置既费时又费力。因此,实现地下目标的自动化探测对实际应用是必要的。为此,该文在综合分析地下目标回波特征的基础上,讨论了使用GPR评估目标位置的可行性,并回顾了国内外学者在GPR成像中对双曲线特征自动化检测的研究进展。该文还在国内外典型实例剖析的基础上,总结并比较了目标检测的处理方法。最后指出,未来的研究应集中于开发新的深度学习检测框架,用以自动检测和估计真实场景中的地下特征。
Abstract:Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR), as a non-destructive technology, has been widely used to detect, locate, and characterize subsurface objects. Example applications include underground utility mapping and bridge deck deterioration assessment. However, manually interpreting the GPR scans to detect buried objects and estimate their positions is time-consuming and labor-intensive. Hence, the automatic detection of targets is necessary for practical application. To this end, this paper discusses the feasibility of using GPR to estimate target positions, and reviews the progress made by domestic and international scholars on automatic hyperbolic signature detection in GPR scans. Thereafter, this paper summarizes and compares the processing methods for target detection. It is concluded that future research should focus on developing deep-learning based method to automatically detect and estimate subsurface features for on-site applications.
-
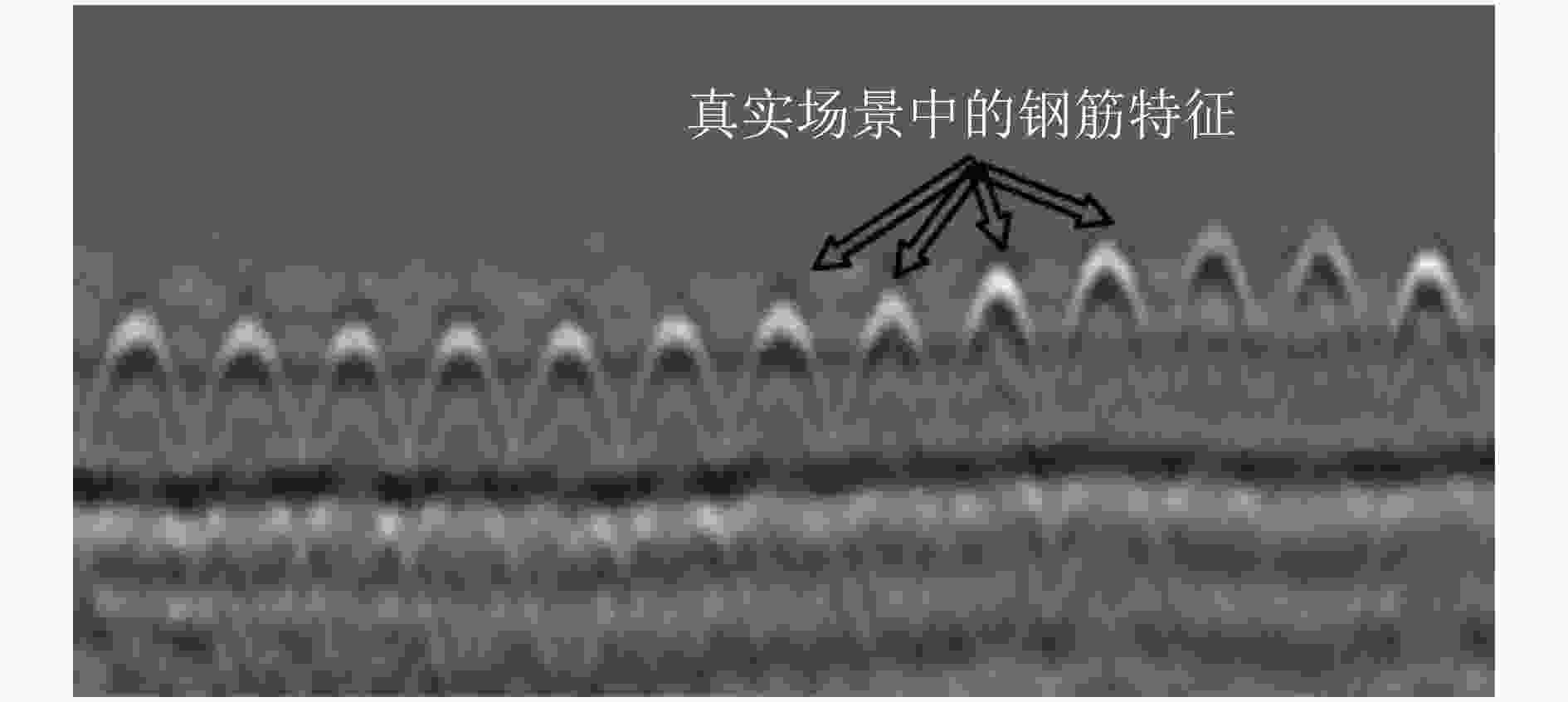
图 2 在文献[28]中解决的一些复杂情况示例
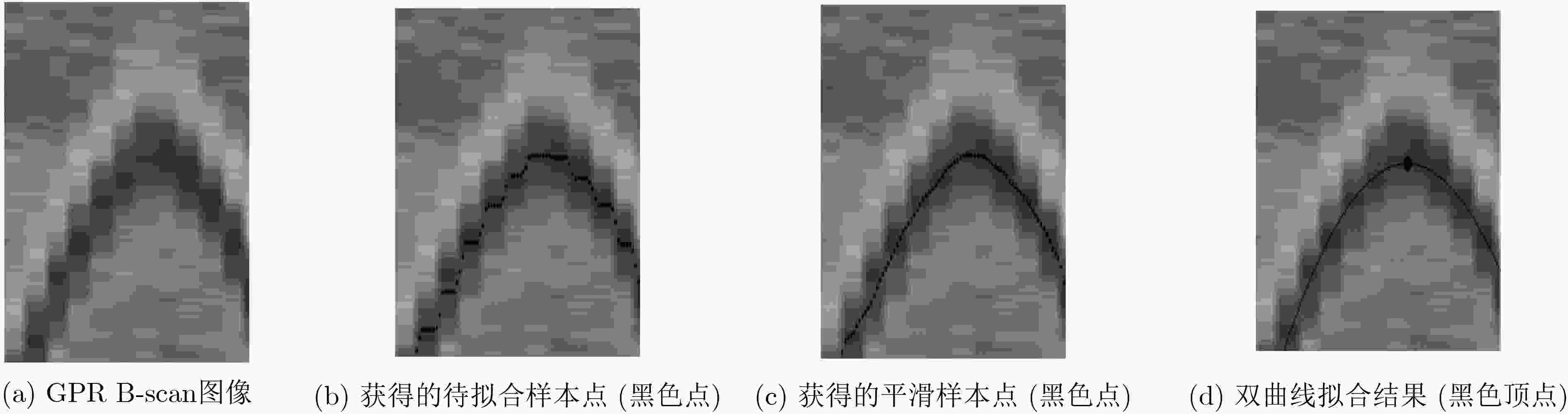
表 1 GPR目标检测的经典算法总结
序号 参考文献 时间 GPR目标 客观评价 1 Borgioli et al. [17] 2008 地埋管道 在Hough变换中引入加权因子,解决了管道靠近时双曲线重叠的问题;但是需要预备模型,计算成本相对较高。 2 Maas et al. [23] 2013 双曲线反射 使用Viola-Jones算法标记目标候选区域,它避免了模板匹配并缩小了后续搜索区域;然而,应用特征需手动识别,分类结果取决于特征的质量,难度随着数据量的增加。 3 Besaw et al. [2] 2016 地埋爆炸物 应用CNN从GPR B-scan中提取有意义的特征并对目标进行分类。交叉验证,网络权重正则化和“dropout”用于防止过度训练。 4 Besaw[3] 2016 地埋爆炸物 在CNN基础上增加了额外的Data Augmentation技术,用于增加可用训练数据的数量和可变性。 5 文献[4,5] 2017 地埋爆炸物 研究了预训练CNN的初始化步骤,以解决GPR数据标记样本不足的问题;但是输入网络中真实图像的大小和数量通常是有限的,仅实现分类步骤。 6 Pham et al. [27] 2018 双曲线反射 首次采用Faster RCNN来检测GPR B-scan中的反射双曲线。该技术在真实测试集上的性能要超过使用HOG或Haar-like特征的检测器,但缺少定量的评估。 7 Lei et al. [28] 2019 地埋钢筋 在文献[27]基础上,采用了DA手段增加真实GPR数据集和仿真数据集;提出DCSE算法以识别双曲线特征,完善了文献[30]中提出的OSCA算法;提出CTFP算法自动提取拟合点。所提出方案的有效性在仿真和真实数据集上得到了验证。 8 Dou et al. [29] 2016 双曲线反射 提出了C3算法分割交叉双曲线,并将其送入神经网络进行分类。C3算法水平扫描B-scan图像中的每个像素以进行聚类。然而,双曲线是垂直向下打开的,C3算法没有考虑这个重要特征。 9 Zhou et al. [30] 2018 金属管道
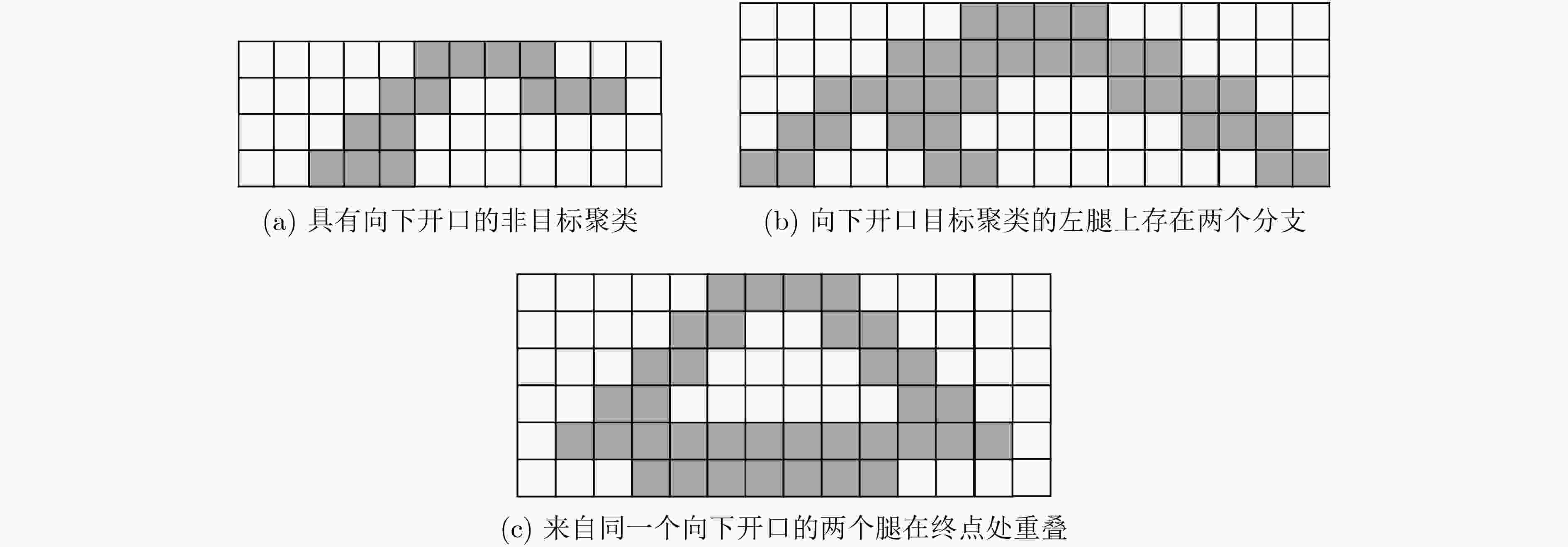
水泥管道提出OSCA算法解决了文献[29]中的难题,可以识别具有向下开口特征的聚类。然而,在整个图像上进行OSCA算法是不合适的,因为难以处理包含太多非平稳噪声的大型现场数据集,导致后续处理复杂化。 -
JOL H M. 雷文太, 童孝忠, 周旸, 译. 探地雷达理论与应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2011.JOL H M. LEI Wentai, TONG Xiaozhong, ZHOU Yang, translation. Ground Penetrating Radar: Theory and Applications[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2011. BESAW L E and STIMAC P J. Deep convolutional neural networks for classifying GPR B-Scans[J]. SPIE, 2015, 9454: 945413. BESAW L E. Detecting buried explosive hazards with handheld GPR and deep learning[J]. SPIE, 2016, 9823: 98230N. doi: 10.1117/12.2223797 BRALICH J, REICHMAN D, COLLINS L M, et al. Improving convolutional neural networks for buried target detection in ground penetrating radar using transfer learning via pretraining[J]. SPIE, 2017: 10182. REICHMAN D, COLLINS L M, and MALOF J M. Some good practices for applying convolutional neural networks to buried threat detection in Ground Penetrating Radar[C]. The 9th International Workshop on Advanced Ground Penetrating Radar, Edinburgh, UK, 2017: 1–5. LAMERI S, LOMBARDI F, BESTAGINI P, et al. Landmine detection from GPR data using convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th European Signal Processing Conference, Kos, Greece, 2017: 508–512. BENEDETTO A, BENEDETTO F, DE BLASⅡS M R, et al. Reliability of radar inspection for detection of pavement damage[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2004, 5(1): 93–110. doi: 10.1080/14680629.2004.9689964 LEI Wentai, SHI Ronghua, DONG Jian, et al. A multi-scale weighted back projection imaging technique for ground penetrating radar applications[J]. Remote Sensing, 2014, 6(6): 5151–5163. doi: 10.3390/rs6065151 LEI Wentai, ZENG Sheng, ZHAO Jian, et al. An improved back projection imaging algorithm for subsurface target detection[J]. Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences, 2013, 21(6): 1820–1826. BENEDETTO F and TOSTI F. GPR spectral analysis for clay content evaluation by the frequency shift method[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2013, 97: 89–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2013.03.012 KAUR P, DANA K J, ROMERO F A, et al. Automated GPR rebar analysis for robotic bridge deck evaluation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(10): 2265–2276. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2474747 DINH K, GUCUNSKI N, and DUONG T H. An algorithm for automatic localization and detection of rebars from GPR data of concrete bridge decks[J]. Automation in Construction, 2018, 89: 292–298. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2018.02.017 YUAN Chenxi, LI Shuai, CAI Hubo, et al. GPR signature detection and decomposition for mapping buried utilities with complex spatial configuration[J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2018, 32(4): 04018026. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CP.1943-5487.0000764 LI Shuai, CAI Hubo, and KAMAT V R. Uncertainty-aware geospatial system for mapping and visualizing underground utilities[J]. Automation in Construction, 2015, 53: 105–119. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2015.03.011 LI Shuai, CAI Hubo, ABRAHAM D M, et al. Estimating features of underground utilities: Hybrid GPR/GPS approach[J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2016, 30(1): 04014108. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CP.1943-5487.0000443 ILLINGWORTH J and KITTLER J. A survey of the Hough transform[J]. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, 1988, 43(2): 280. BORGIOLI G, CAPINERI L, FALORNI P, et al. The detection of buried pipes from time-of-flight radar data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(8): 2254–2266. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2008.917211 WINDSOR C G, CAPINERI L, and FALORNI P. A data pair-labeled generalized Hough transform for radar location of buried objects[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(1): 124–127. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2248119 BOOKSTEIN F L. Fitting conic sections to scattered data[J]. Computer Graphics and Image Processing, 1979, 9(1): 56–71. doi: 10.1016/0146-664x(79)90082-0 AKIMA H. A method of bivariate interpolation and smooth surface fitting for irregularly distributed data points[J]. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 1978, 4(2): 148–159. doi: 10.1145/355780.355786 PORRILL J. Fitting ellipses and predicting confidence envelopes using a bias corrected Kalman filter[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 1990, 8(1): 37–41. doi: 10.1016/0262-8856(90)90054-9 YOUN H S and CHEN C C. Automatic GPR target detection and clutter reduction using neural network[J]. SPIE, 2002, 4758: 579–582. doi: 10.1117/12.462229. MAAS C and SCHMALZL J. Using pattern recognition to automatically localize reflection hyperbolas in data from ground penetrating radar[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2013, 58: 116–125. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2013.04.012 VIOLA P and JONES M J. Robust real-time face detection[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 57(2): 137–154. doi: 10.1023/b:visi.0000013087.49260.fb KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84–90. doi: 10.1145/3065386 WITTEN T R. Present state of the art in ground-penetrating radars for mine detection[J]. SPIE, 1998, 3392. PHAM M T and LEFÈVRE S. Buried object detection from B-scan ground penetrating radar data using Faster-RCNN[C]. 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 6804–6807. LEI Wentai, HOU Feifei, XI Jingchun, et al. Automatic hyperbola detection and fitting in GPR B-scan image[J]. Automation in Construction, 2019, 106: 102839. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2019.102839 DOU Qingxu, WEI Lijun, MAGEE D R, et al. Real-time hyperbola recognition and fitting in GPR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 51–62. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2016.2592679 ZHOU Xiren, CHEN Huanhuan, and LI Jinlong. An automatic GPR B-Scan image interpreting model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(6): 3398–3412. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2799586 TANOLI W A, SHARAFAT A, and PARK J, et al. Damage Prevention for underground utilities using machine guidance[J]. Automation in Construction, 2017, 107: 102893. YALÇINER C C, BANO M, KADIOGLU M, et al. New temple discovery at the archaeological site of Nysa (western Turkey) using GPR method[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2009, 36(8): 1680–1689. doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2008.12.016 CAPINERI L, GRANDE P, and TEMPLE J A G. Advanced image-processing technique for real-time interpretation of ground-penetrating radar images[J]. International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, 1998, 9(1): 51–59. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1098(1998)9:1<51::AID-IMA7>3.0.CO;2-Q PASOLLI E, MELGANI F, DONELLI M, et al. Automatic detection and classification of buried objects in GPR images using genetic algorithms and support vector machines[C]. 2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, USA, 2008: Ⅱ-525–Ⅱ-528. PASOLLI E, MELGANI F, and DONELLI M. Automatic analysis of GPR images: A pattern-recognition approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(7): 2206–2217. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2012701 MOLYNEAUX T C K, MILLARD S G, BUNGEY J H, et al. Radar assessment of structural concrete using neural networks[J]. NDT & E International, 1995, 28(5): 281–288. AL-NUAIMY W, HUANG Y, NAKHKASH M, et al. Automatic detection of buried utilities and solid objects with GPR using neural networks and pattern recognition[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2000, 43(2/4): 157–165. GAMBA P and LOSSANI S. Neural detection of pipe signatures in ground penetrating radar images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(2): 790–797. doi: 10.1109/36.842008 AL-NUAIMY W, HUANG Y, NAKHKASH M, et al. Neural network for the automatic detection of buried utilities and landmines[C]. 1998 Progress of Electromagnetic Research Symposium, Nantes, Frances, 1998: 141. SHIHAB S, AL-NUAIMY W, HUANG Y, et al. Automatic region-based shape discrimination of ground penetrating radar signatures[C]. 2003 Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Environmental and Engineering Problems SAGEEP 2003, San Antonio, USA, 2003. AL-NUAIMY W, LU Huihai, SHIHAB S, et al. Automatic mapping of linear structures in 3-dimensional space from ground-penetrating radar data[C]. 2001 IEEE/ISPRS Joint Workshop on Remote Sensing and Data Fusion over Urban Areas, Rome, Italy, 2001: 198–201. SHIHAB S, AL-NUAIMY W, and ERIKSEN A. Image processing and neural network techniques for automatic detection and interpretation of ground penetrating radar data[C]. The 6th WSEAS, Crete, 2002. AL-NUAIMY W, HUANG Yi, ERIKSEN A, et al. Automatic detection of hyperbolic signatures in ground-penetrating radar data[J]. SPIE, 2001, 4491: 327. SHAW M R, MOLYNEAUX T C K, MILLARD S G, et al. Assessing bar size of steel reinforcement in concrete using ground penetrating radar and neural networks[J]. Insight - Non-Destructive Testing and Condition Monitoring, 2003, 45(12): 813–816. doi: 10.1784/insi.45.12.813.52980 SHAW M R, MILLARD S G, MOLYNEAUX T C K, et al. Location of steel reinforcement in concrete using ground penetrating radar and neural networks[J]. NDT & E International, 2005, 38(3): 203–212. LAMERI S, LOMBARDI F, BESTAGINI P, et al. Landmine detection from GPR data using convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th European Signal Processing Conference, Kos, Greece, 2017. BENGIO Y. Learning deep architectures for AI[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2009, 2(1): 1–127. doi: 10.1561/2200000006 REICHMAN D, COLLINS L M, and MALOF J M. Some good practices for applying convolutional neural networks to buried threat detection in Ground Penetrating Radar[C]. The 9th International Workshop on Advanced Ground Penetrating Radar, Edinburgh, UK, 2017. WARREN C, GIANNOPOULOS A, and GIANNAKIS I. GprMax: Open source software to simulate electromagnetic wave propagation for Ground Penetrating Radar[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2016, 209: 163–170. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2016.08.020 KRIZHEVSKY A. Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images[R]. Technical Report TR-2009, 2009: 1–60. KANUNGO T, MOUNT D M, NETANYAHU N S, et al. An efficient k-means clustering algorithm: Analysis and implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(7): 881–892. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2002.1017616 NG R T and HAN Jiawei. Efficient and effective clustering methods for spatial data mining[C]. The 20th International Conference on Very Large Data Bases, Birmingham, USA, 1994: 144–155. ESTER M, KRIEGEL H P, SANDER J, et al. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters a density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Portland, Oregon, 1996: 226–231. ERTÖZ L, STEINBACH M, and KUMAR V. Finding clusters of different sizes, shapes, and densities in noisy, high dimensional data[C]. The 2nd SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, 2003. AHN S J, RAUH W, and WARNECKE H J. Least-squares orthogonal distances fitting of circle, sphere, ellipse, hyperbola, and parabola[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2001, 34(12): 2283–2303. doi: 10.1016/S0031-3203(00)00152-7 FITZGIBBON A, PILU M, and FISHER R B. Direct least square fitting of ellipses[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1999, 21(5): 476–480. doi: 10.1109/34.765658 GANDER W, GOLUB G H, and STREBEL R. Least-squares fitting of circles and ellipses[J]. BIT Numerical Mathematics, 1994, 34(4): 558–578. doi: 10.1007/BF01934268 PILU M, FITZGIBBON A W, and FISHER R B. Ellipse-specific direct least-square fitting[C]. The 3rd IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Lausanne, Switzerland, 1996: 599–602. CHEN Huanhuan and COHN A G. Probabilistic conic mixture model and its applications to mining spatial ground penetrating radar data[C]. The Workshops in SIAM Conference on Data Mining, 2010: 1–9. CHEN Huanhuan and COHN A G. Probabilistic robust hyperbola mixture model for interpreting ground penetrating radar data[C]. 2010 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Barcelona, Spain, 2010: 1–8. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
