A Flexible Network Access Scheme in Heterogeneous Cell Networks with H2H and M2M Coexistence
-
摘要:
针对人与人(H2H)和物到物(M2M)业务共存的异构无线网络,该文设计了一种根据业务特性的代理节点的网络选择策略,用博弈论对以保障两类业务服务质量(QoS)需求和网络负载均衡为目标的代理节点网络选择问题进行建模,并分析了该博弈模型纳什均衡(NE)的存在性和可行性;同时,提出了基于学习自动机的分布式网络-信道选择算法(DNCSALA),求得该博弈的纳什均衡。仿真结果表明,所提算法能够获得与穷举搜索算法相近的性能,可满足共存场景中不同类型业务的QoS需求并提高网络资源利用率。
Abstract:Considering the problem of agents’ network selection for Human-to-Human(H2H) and Machine-to-Machine (M2M) traffic in heterogeneous wireless networks, an agents’ network selection scheme based on the characteristic of traffic is designed. Game theory is adopted to solve the problem of network selection to satisfy difference in traffic’s Quality of Service (QoS) requirements. The existence and feasibility of the Nash Equilibrium (NE) of the proposed game are also analyzed. Then, a Distributed Network-Channe Selection Algorithm based on Learning Automata (DNCSALA) is presented to obtain the NE of the proposed game. In simulations, the proposed algorithm can achieve a near optimal performance compared to the exhaustive search, satisfy the QoS requirements of different types of traffic, and improves the efficiency of network resources.
-
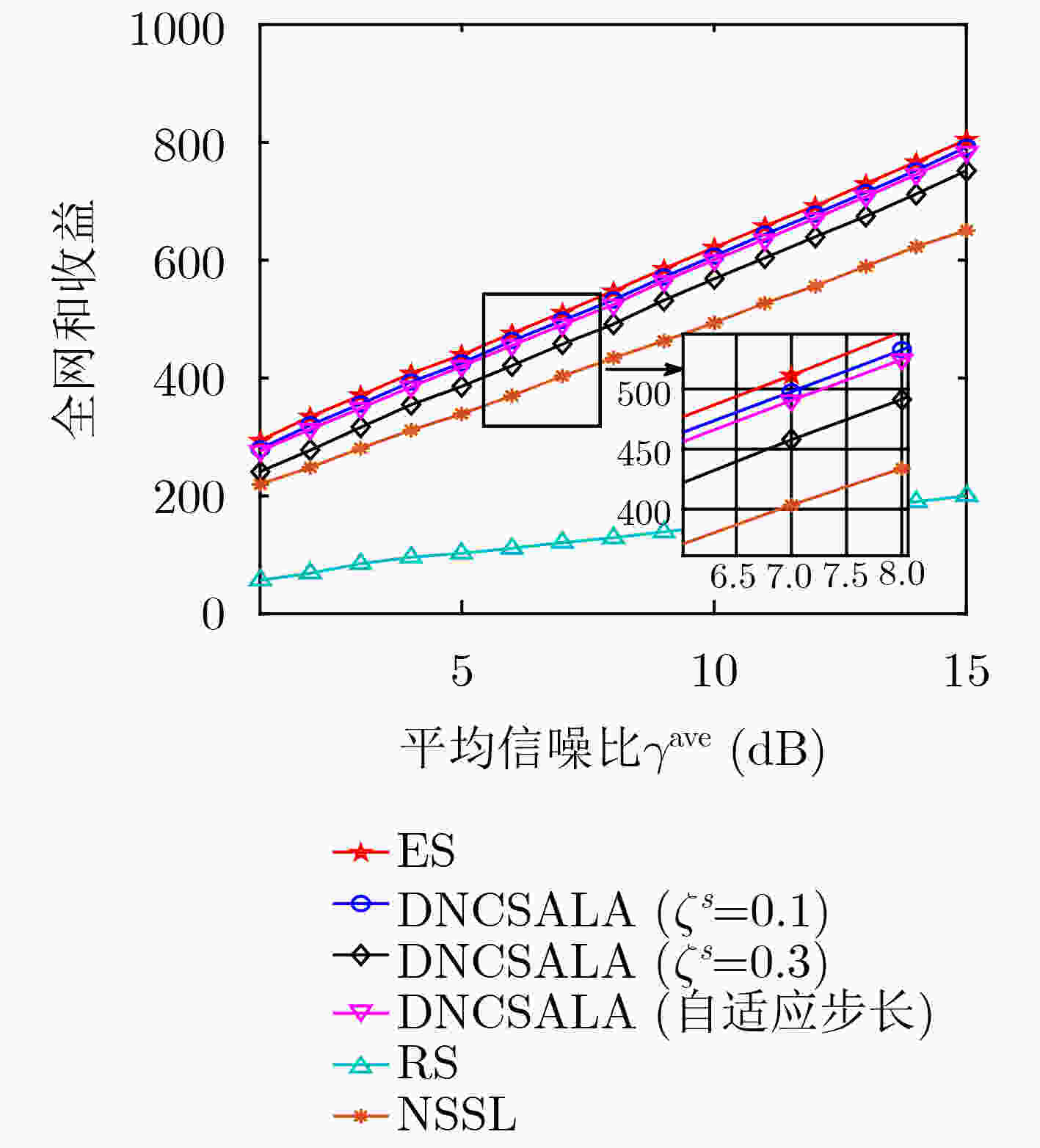
图 3 不同算法下全网和收益随SNR变化曲线图(仿真参数同图2)
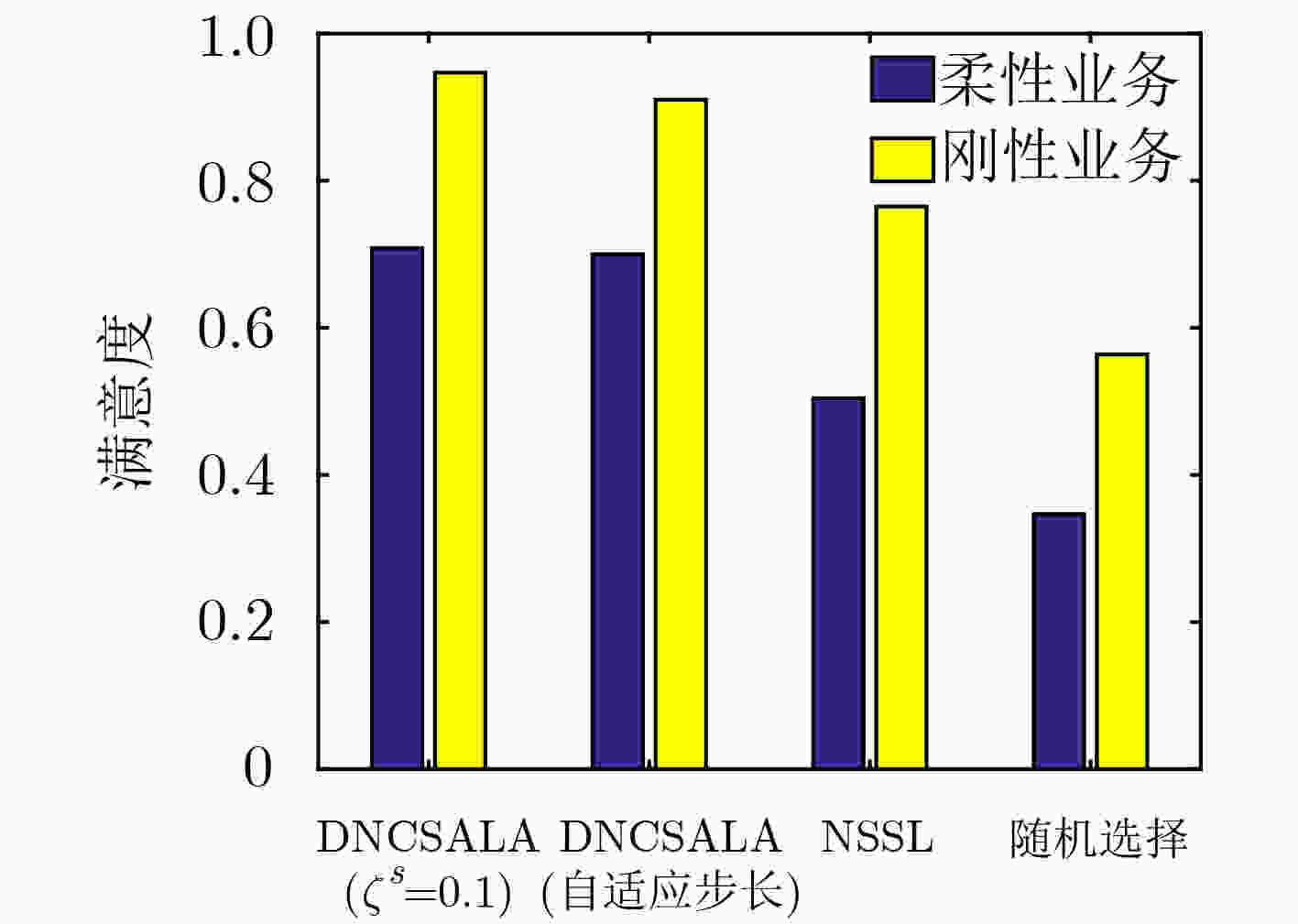
图 4 不同算法的满意度性能对比柱状图(仿真参数同图2)
图 5 不同算法的负载均衡指数对比柱状图(仿真参数同图2)
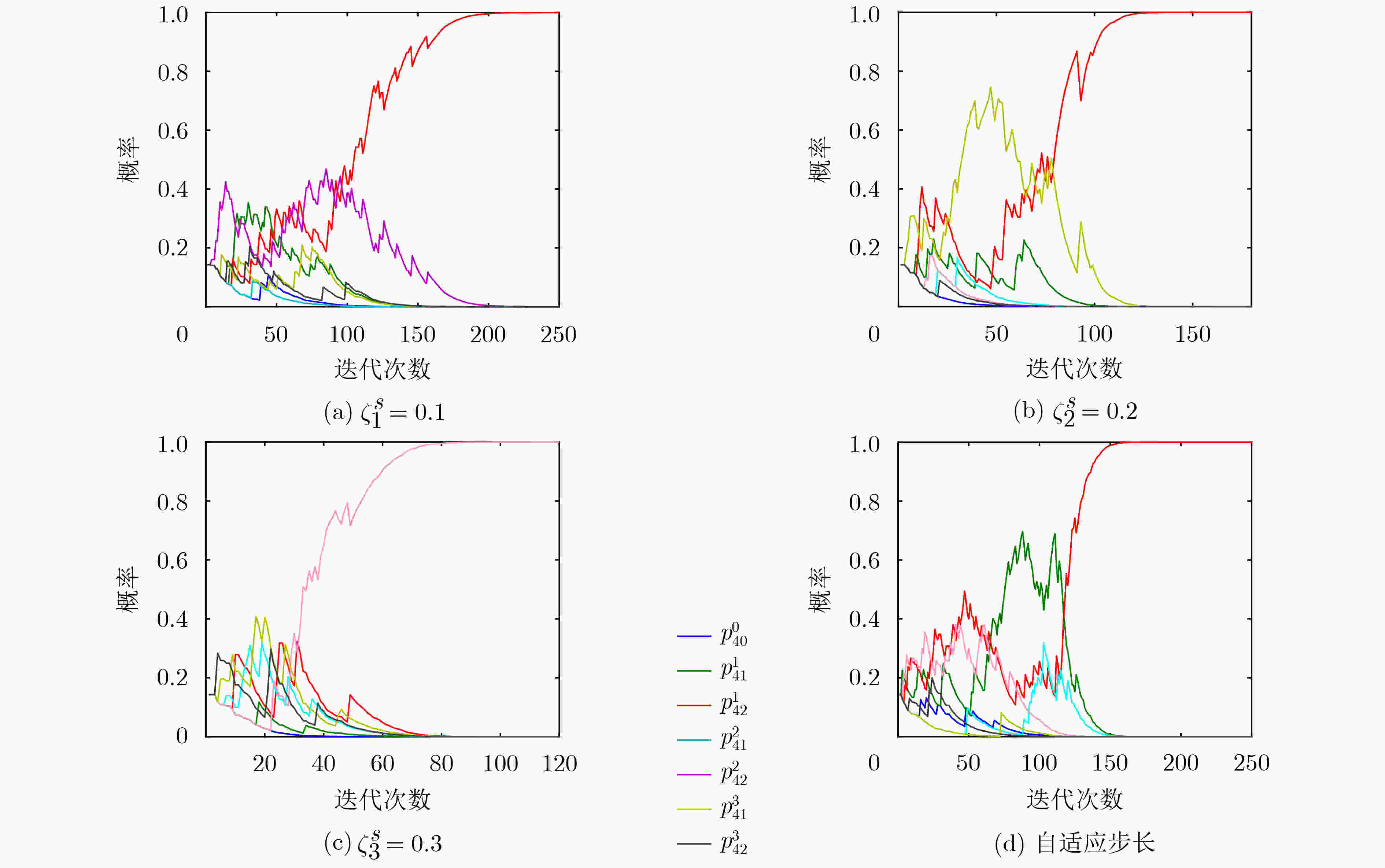
表 1 基于学习自动机的分布式网络选择算法(DNCSALA)
(1) 首先,初始化每个代理节点第0时刻的行为概率分布${ {{p} }_i}(0)$为$p_{ik}^j(0) = {1 / {\left(1 + \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{j \in {\cal{N}}} {{K_j}} \right)}}$, $\forall i \in {\cal M},j \in {\cal N}$。每一个代理节点根据自 己的行为概率分布${ {{p} }_i}(0)$选择一个行为②; (2) 在每一个时刻$t > 0$,每一个代理节点都根据当前时刻的概率分布${ {{p} }_i}(0)$选择一个行为(${s_i}(t)$); (3) 基站根据所有代理节点的行为,计算出收益,并将其广播给所有代理节点; (4) 在获得反应函数之后,每一个代理节点根据式(16),更新自己的行为概率分布, 其中$0 < {\zeta ^s} < 1$表示步长参数;
$\left. \begin{aligned} & {p_{ik}^j(t + 1) = p_{ik}^j(t) - {\zeta ^s}{\gamma _i}(t)p_{ik}^j(t),\quad \quad \quad\quad {s_i}(t) \ne {\rm{CH} }_{ik}^j} \\ & {p_{ik}^j(t + 1) = p_{ik}^j(t) + {\zeta ^s}{\gamma _i}(t)(1 - p_{ik}^j(t)),\quad \;\,{s_i}(t) = {\rm{CH} }_{ik}^j} \end{aligned} \right\}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\qquad\qquad (16)$(5) 如果对于任意$i \in {\cal M}$, 其行为概率分布存在一个元素接近1,确切地说等于0.99,那么算法停止。否则,跳转到步骤(2)。 -
AGIWAL M, ROY A, and SAXENA N. Next generation 5G wireless networks: A comprehensive survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2016, 18(3): 1617–1655. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2016.2532458 AKPAKWU G A, SILVA B J, HANCKE G P, et al. A survey on 5G networks for the Internet of Things: Communication technologies and challenges[J]. IEEE Access, 2018(6): 3619–3647. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2779844 WANG Hai and ABRAHAM O F. A survey of enabling technologies of low power and long range Machine-to-Machine communications[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(4): 2621–2639. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2721379 XIA Nian, CHEN H H, and YANG C S. Radio resource management in Machine-to-Machine communications-a survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(1): 791–828. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2765344 李宁, 林家儒. CDMA/OFDMA异构网络中最小化中断概率的网络选择方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(12): 2965–2970. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00387LI Ning and LIN Jiaru. Network selection strategy for minimizing outage probability in CDMA/OFDMA heterogeneous networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2011, 33(12): 2965–2970. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00387 KUMAR A, MALLIK R K, and SCHOBER R. A probabilistic approach to modeling users’ network selection in the presence of heterogeneous wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2014, 63(7): 3331–3341. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2013.2297437 DU Zhiyong, WU Qihui, and YANG Panlong. Dynamic user demand driven online network selection[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2014, 18(3): 419–422. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2014.011214.132617 杜白, 李红艳, 龙彦. 最小最大剩余服务时间的异构网络选择算法[J]. 通信学报, 2015, 36(8): 104–109. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2015231DU Bai, LI Hongyan, and LONG Yan. Network selection algorithm in heterogeneous wireless networks to minimize the maximum residual service time[J]. Journal on Communications, 2015, 36(8): 104–109. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2015231 TSENG L C, CHIEN F T, ZHANG Daqiang, et al. Network selection in cognitive heterogeneous networks using stochastic learning[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2013, 17(12): 2304–2307. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2013.102113.131876 KWON T and CHOI J W. Multi-group random access resource allocation for M2M devices in multicell systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2012, 16(6): 834–837. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2012.041112.112568 LIU Dantong, CHEN Yue, CHAI K K, et al. Opportunistic user association for multi-service HetNets using Nash bargaining solution[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2014, 18(3): 463–466. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2014.012314.140090 LIU Yi, YUEN C, CAO Xianghui, et al. Design of a scalable hybrid MAC protocol for heterogeneous M2M networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2014, 1(1): 99–111. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2014.2310425 HUANG Yao, TIAN Hui, ZHANG Jie, et al. Rate allocation scheme for Machine-to-Machine service based on 3GPP in heterogeneous wireless networks[J]. China Communications, 2013, 10(9): 65–71. doi: 10.1109/CC.2013.6623504 NESSA A, KADOCH M, and RONG Bo. Fountain coded cooperative communications for LTE-A connected heterogeneous M2M network[J]. IEEE Access, 2016(4): 5280–5292. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2601031 SHAFIQ M Z, JI Lusheng, LIU A X, et al. Large-scale measurement and characterization of cellular Machine-to-Machine traffic[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2013, 21(6): 1960–1973. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2013.2256431 YE Qiaoyang, RONG Beiyu, CHEN Yudong, et al. User association for load balancing in heterogeneous cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2013, 12(6): 2706–2716. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2013.040413.120676 钟卫. 有限反馈认知无线电动态频谱共享技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 上海交通大学, 2011.ZHONG Wei. Limited feedback dynamic spectrum sharing in cognitive radio systems[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2011. MONDERER D and SHAPLEY L S. Potential games[J]. Games and Economic Behavior, 1996, 14(1): 124–143. doi: 10.1006/game.1996.0044 SASTRY P S, PHANSALKAR V V, and THATHACHAR M A L. Decentralized learning of Nash equilibria in multi-person stochastic games with incomplete information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1994, 24(5): 769–777. doi: 10.1109/21.293490 -





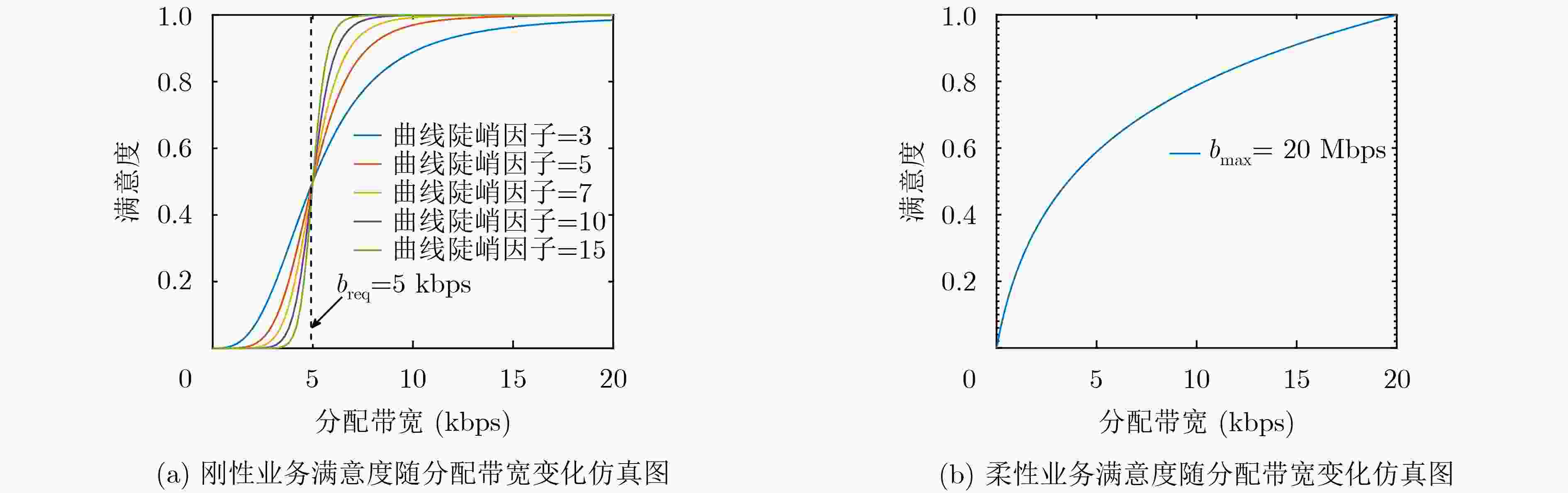
 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:
