Review of Research on Biomedical Image Processing Based on Pattern Recognition
-
摘要:
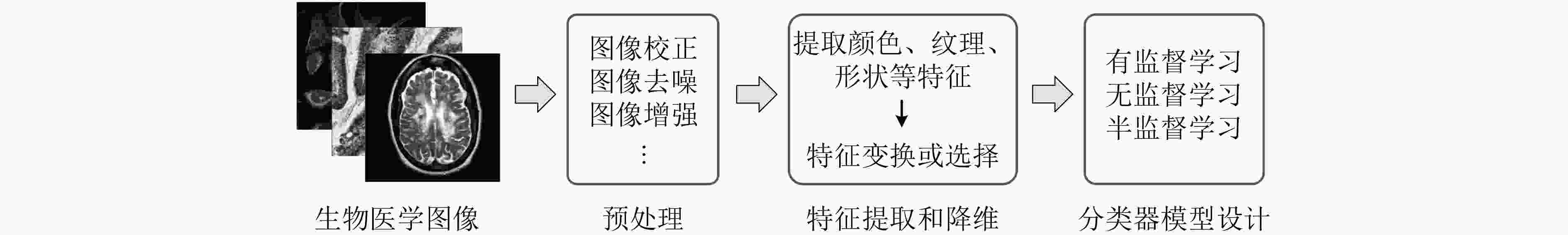
海量的生物医学图像蕴含着丰富的信息,模式识别算法能够从中挖掘规律并指导生物医学基础研究和临床应用。近年来,模式识别和机器学习理论和实践不断完善,尤其是深度学习的广泛研究和应用,促使人工智能、模式识别与生物医学的交叉研究成为了当前的前沿热点,相关的生物医学图像研究有了突破式的进展。该文首先简述模式识别的常用算法,然后总结了这些算法应用于荧光显微图像、组织病理图像、医疗影像等多种图像中的挑战性和国内外研究现状,最后对几个潜在研究方向进行了分析和展望。
Abstract:Pattern recognition algorithms can discover valuable information from mass data of biomedical images as guide for basic research and clinical application. In recent years, with improvement of the theory and practice of pattern recognition and machine learning, especially the appearance and application of deep learning, the crossing researches among artificial intelligence, pattern recognition, and biomedicine become a hotspot, and achieve many breakthrough successes in related fields. This review introduces briefly the common framework and algorithms of image pattern recognition, summarizes the applications of these algorithms to biomedical image analysis including fluorescence microscopic images, histopathological images, and medical radiological images, and finally analyzes and prospect several potential research directions.
-
Key words:
- Image processing /
- Biomedical images /
- Pattern recognition /
- Deep learning
-
表 1 常用的生物图像数据集
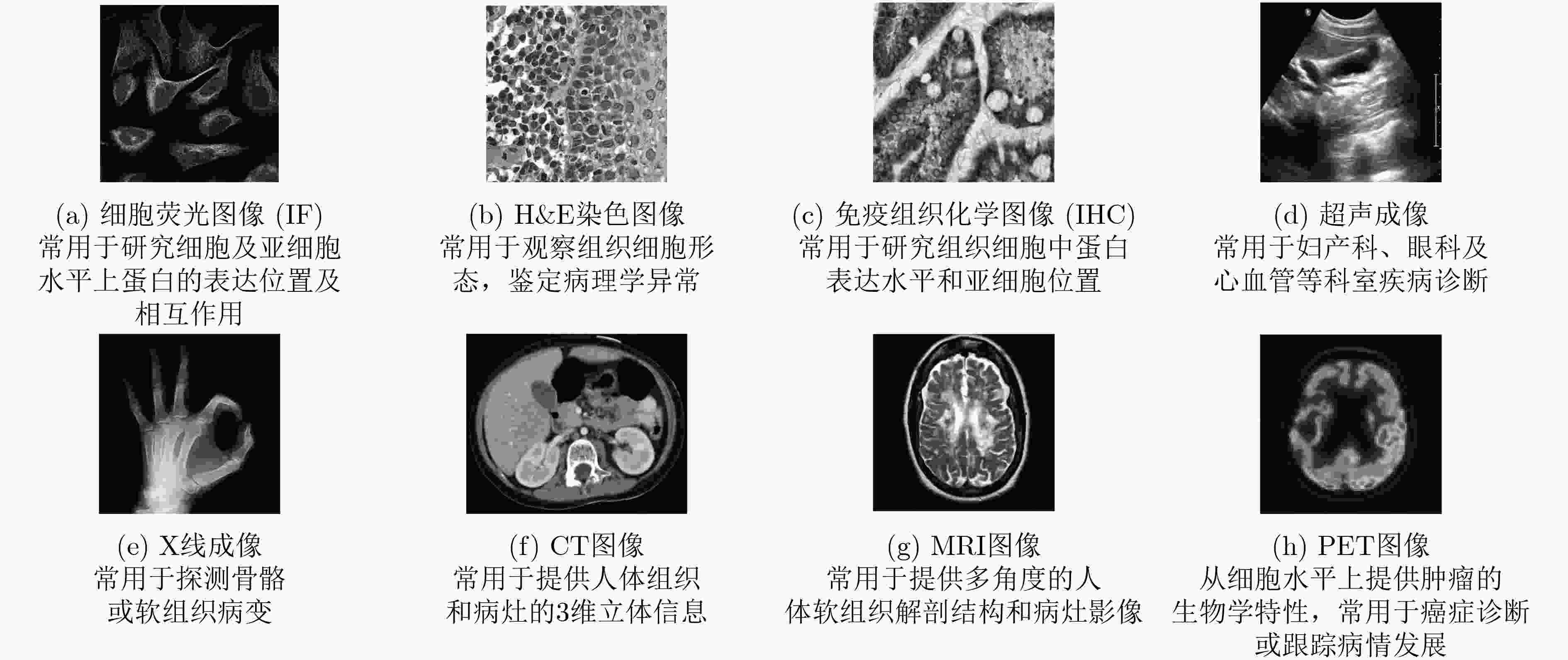
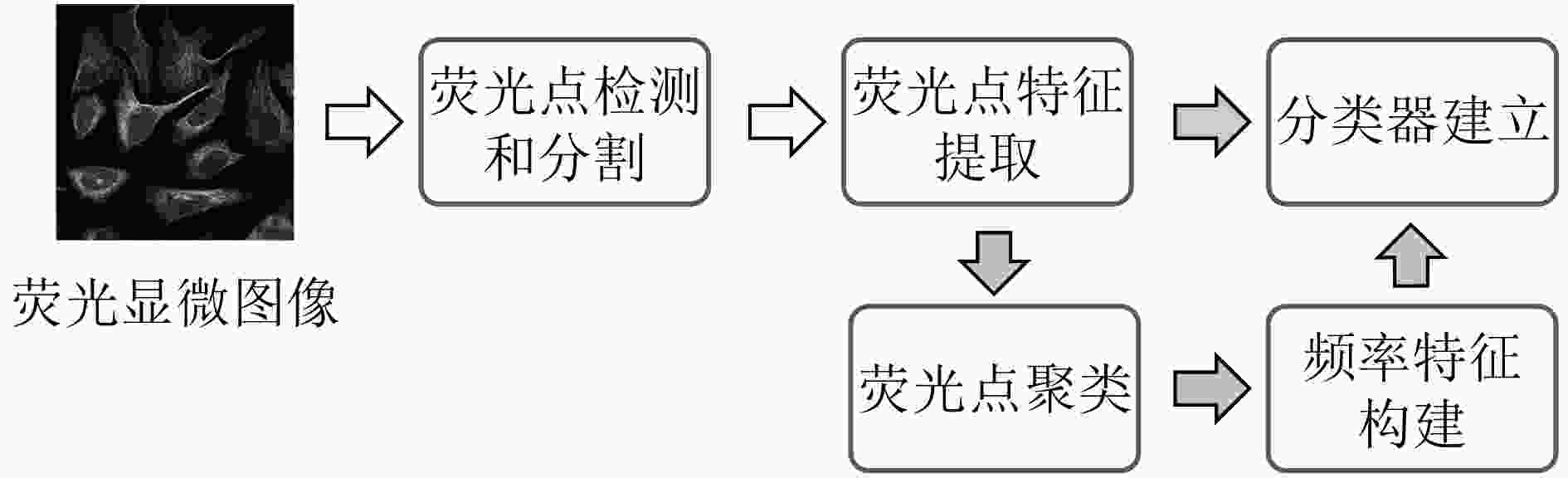
类型 数据集 数据量 特点 荧光显微图像 CYCLoPs[23] 超3×105幅蛋白荧光图像 标注酵母细胞中蛋白质16类亚细胞位置及表达量 HPA IF[24] 2.2×105幅IF图像 20余个细胞系的蛋白图像,标注34类亚细胞位置 2D HeLa[25] 862幅荧光显微图像 HeLa宫颈癌细胞系,标注10个标志蛋白的表达模式 2D CHO[26] 327幅荧光显微图像 中国仓鼠卵巢细胞图像,标注5个标志蛋白的表达模式 组织病理图像 BreakHis[27] 7909幅H&E图像 乳腺良性和恶性肿瘤图像,共8类病理状态 TCGA[28] 18462幅H&E图像 记录36类癌症的病理检查及治疗数据, TMAD[29] 3726幅IHC图像 对蛋白质着色的评分,分为4个等级 HPA IHC[30] 约106幅IHC图像 人体正常和癌症组织的蛋白图像,标注3类亚细胞位置 医疗影像图像 BRATS[31] 65幅MRI图像 经专家人工分割的脑胶质瘤患者的多对比度MR扫描图像,两组癌症分级 ADNI[32] 2000余名志愿者的MRI、PET图像 阿尔茨海默病患者和健康组对照 ISLES[33] 103位病人的MRI图像 缺血性中风病人图像,由专家人工分割出损伤的脑组织 DeepLesion[34] 32735幅CT图像 肾脏病变、骨病变、肺结节、淋巴结肿大等多种病理诊断 表 2 常用的生物图像处理工具
类型 处理工具 作用 通用 ImageJ[36] 对多种生物医学图像做如缩放、旋转、平滑、区域分割、像素统计等多种处理分析 CellProfiler[37] 分割荧光点或细胞,提取细胞的统计学特征 荧光显微图像 Squassh[38] 分割和定量亚细胞结构 DeepLoc[39] 基于荧光图像预测蛋白质的亚细胞位置 CellOrganizer[40] 对多种细胞亚结构建立生成式模型,产生新的细胞图像或视频 OMERO.searcher[41] 图像匹配和检索 组织病理图像 HistomicsML[42] 交互式机器学习系统,训练基于病理图像的分类器 IHC Profiler[43] IHC图像统计学特征提取,着色评分 iLocator[44-46] 基于IHC图像的蛋白质亚细胞位置预测系统 医疗影像图像 RayPlus[47] 在线的云端的智能医学影像平台,集成3维影像重建、专科影像分析等功能 Mimics[48] 一套高度整合而且易用的3D图像生成及编辑处理软件 ANTS[49] 提供了高级的工具用于大脑图像配准映射,在解释和可视化多维数据方面有优势 FSL[50] 用于分析fMRI,MRI和DTI大脑成像数据的综合软件库 -
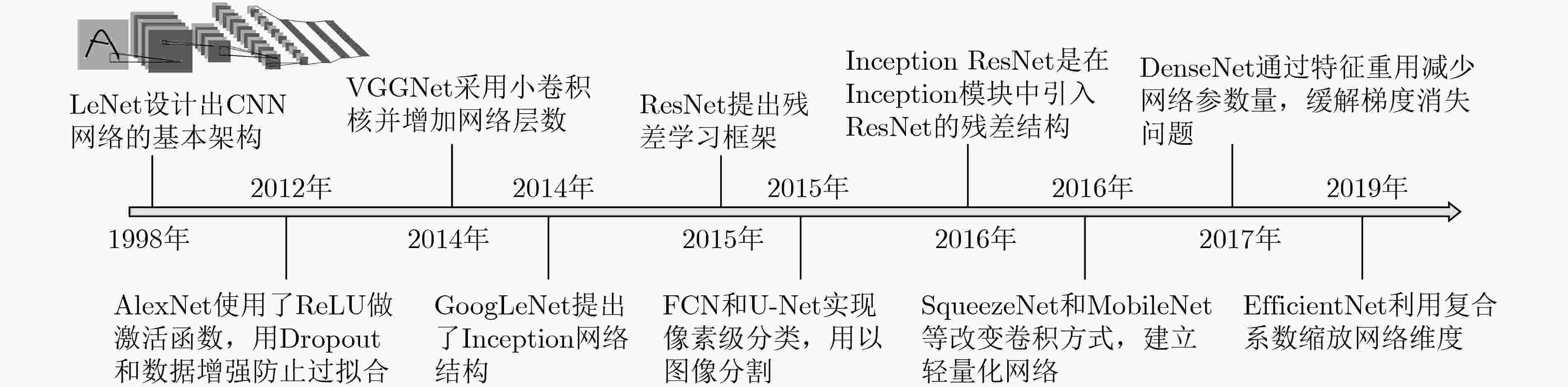
MEIJERING E, CARPENTER A E, PENG Hanchuan, et al. Imagining the future of bioimage analysis[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2016, 34(12): 1250–1255. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3722 江贵平, 秦文健, 周寿军, 等. 医学图像分割及其发展现状[J]. 计算机学报, 2015, 38(6): 1222–1242. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2015.01222JIANG Guiping, QIN Wenjian, ZHOU Shoujun, et al. State-of-the-Art in medical image segmentation[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2015, 38(6): 1222–1242. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2015.01222 廖苗, 赵于前, 曾业战, 等. 基于图割和边缘行进的肝脏CT序列图像分割[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(6): 1552–1556. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151005LIAO Miao, ZHAO Yuqian, ZENG Yezhan, et al. Liver segmentation from abdominal CT volumes based on graph cuts and border marching[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(6): 1552–1556. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151005 文登伟, 张东波, 汤红忠, 等. 融合纹理与形状特征的HEp-2细胞分类[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(7): 1599–1605. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161090WEN Dengwei, ZHANG Dongbo, TANG Hongzhong, et al. HEp-2 cell classification by fusing texture and shape features[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(7): 1599–1605. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161090 田娟秀, 刘国才, 谷珊珊, 等. 医学图像分析深度学习方法研究与挑战[J]. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(3): 401–424. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170153TIAN Juanxiu, LIU Guocai, GU Shanshan, et al. Deep learning in medical image analysis and its challenges[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(3): 401–424. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170153 DE MATOS J, DE SOUZA BRITTO JR A, OLIVEIRA L E S, et al. Histopathologic image processing: A review[J]. arXiv: 1904.07900, 2019. XU Yingying, YAO Lixiu, and SHEN Hongbin. Bioimage-based protein subcellular location prediction: A comprehensive review[J]. Frontiers of Computer Science, 2018, 12(1): 26–39. doi: 10.1007/s11704-016-6309-5 LITJENS G, KOOI T, BEJNORDI B E, et al. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2017, 42: 60–88. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2017.07.005 KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Taboe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. AWAD A I and HASSABALLAH M. Image Feature Detectors and Descriptors: Foundations and Applications[M]. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-28854-3. LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014. SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1–9. HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. LONG J, SHELHAMER E, and DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]. 2015 IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3431–3440. SZEGEDY C, IOFFE S, VANHOUCKE V, et al. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]. The 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, 2017: 4278–4284. HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. The 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4700–4708. IANDOLA F N, HAN Song, MOSKEWICZ M W, et al. Squeezenet: Alexnet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5 MB model size[J]. arXiv: 1602.07360, 2016. HOWARD A G, ZHU Menglong, CHEN Bo, et al. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[J]. arXiv: 1704.04861, 2017. TAN Mingxing and LE Q V. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[J]. arXiv: 1905.11946, 2019. CIOMPI F, DE HOOP B, VAN RIEL S J, et al. Automatic classification of pulmonary peri-fissural nodules in computed tomography using an ensemble of 2D views and a convolutional neural network out-of-the-box[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2015, 26(1): 195–202. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2015.08.001 KHOSRAVI P, KAZEMI E, IMIELINSKI M, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks enable discrimination of heterogeneous digital pathology images[J]. EBioMedicine, 2018, 27: 317–328. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.12.026 KOH J L Y, CHONG Y T, FRIESEN H, et al. Cyclops: A comprehensive database constructed from automated analysis of protein abundance and subcellular localization patterns in saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics, 2015, 5(6): 1223–1232. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.017830 THUL P J, ÅKESSON L, WIKING M, et al. A subcellular map of the human proteome[J]. Science, 2017, 356(6340): eaal3321. doi: 10.1126/science.aal3321 BOLAND M V and MURPHY R F. A neural network classifier capable of recognizing the patterns of all major subcellular structures in fluorescence microscope images of hela cells[J]. Bioinformatics, 2001, 17(12): 1213–1223. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/17.12.1213 彭佳林, 揭萍. 基于序列间先验约束和多视角信息融合的肝脏CT图像分割[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(4): 971–978. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170933PENG Jialin and JIE Ping. Liver segmentation from CT image based on sequential constraint and multi-view information fusion[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(4): 971–978. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170933 SPANHOL F A, OLIVEIRA L S, PETITJEAN C, et al. A dataset for breast cancer histopathological image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 63(7): 1455–1462. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2015.2496264 The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, WEINSTEIN J N, COLLISSON E A, et al. The cancer genome atlas pan-cancer analysis project[J]. Nature Genetics, 2015, 45(10): 1113–1120. doi: 10.1038/ng.2764 MARINELLI R J, MONTGOMERY K, LIU C L, et al. The stanford tissue microarray database[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2008, 36(S1): D871–D877. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm861 UHLÉN M, FAGERBERG L, HALLSTRÖM B M, et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome[J]. Science, 2015, 347(6220): 1260419. doi: 10.1126/science.1260419 MENZE B H, JAKAB A, BAUER S, et al. The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (brats)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2015, 34(10): 1993–2024. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2014.2377694 IWATSUBO T. Alzheimer's disease neuroimaging initiative (ADNI)[J]. Nihon Rinsho Japanese Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2011, 69(S8): 570–574. MAIER O, MENZE B H, VON DER GABLENTZ J, et al. ISLES 2015 - a public evaluation benchmark for ischemic stroke lesion segmentation from multispectral mri[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2017, 35: 250–269. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2016.07.009 YAN Ke, WANG Xiaosong, LU Le, et al. Deeplesion: Automated mining of large-scale lesion annotations and universal lesion detection with deep learning[J]. Journal of Medical Imaging, 2018, 5(3): 036501. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.5.3.036501 RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. The 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. SCHINDELIN J, RUEDEN C T, HINER M C, et al. The imagej ecosystem: An open platform for biomedical image analysis[J]. Molecular Reproduction & Development, 2015, 82(7/8): 518–529. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22489 CARPENTER A E, JONES T R, LAMPRECHT M R, et al. Cellprofiler: Image analysis software for identifying and quantifying cell phenotypes[J]. Genome Biology, 2006, 7(10): R100. doi: 10.1186/gb-2006-7-10-r100 RIZK A, PAUL G, INCARDONA P, et al. Segmentation and quantification of subcellular structures in fluorescence microscopy images using squassh[J]. Nature Protocols, 2014, 9(3): 586–596. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2014.037 KRAUS O Z, GRYS B T, BA J, et al. Automated analysis of high-content microscopy data with deep learning[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2017, 13(4): 924. doi: 10.15252/msb.20177551 MURPHY R F. Cellorganizer: Image-derived models of subcellular organization and protein distribution[J]. Methods in Cell Biology, 2012, 110: 179–193. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-388403-9.00007-2 CHO B H, CAO-BERG I, BAKAL J A, et al. OMERO.searcher: Content-based image search for microscope images[J]. Nature Methods, 2012, 9(7): 633–634. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2086 NALISNIK M, AMGAD M, LEE S, et al. Interactive phenotyping of large-scale histology imaging data with HistomicsML[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 14588. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15092-3 VARGHESE F, BUKHARI A B, MALHOTRA R, et al. Ihc profiler: An open source plugin for the quantitative evaluation and automated scoring of immunohistochemistry images of human tissue samples[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(5): e96801. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096801 XU Yingying, YANG Fan, and SHEN Hongbin. Incorporating organelle correlations into semi-supervised learning for protein subcellular localization prediction[J]. Bioinformatics, 2016, 32(14): 2184–2192. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw219 XU Yingying, YANG Fan, ZHANG Yang, et al. An image-based multi-label human protein subcellular localization predictor (ilocator) reveals protein mislocalizations in cancer tissues[J]. Bioinformatics, 2013, 29(16): 2032–2040. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt320 XU Yingying, YANG Fan, ZHANG Yang, et al. Bioimaging-based detection of mislocalized proteins in human cancers by semi-supervised learning[J]. Bioinformatics, 2015, 31(7): 1111–1119. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu772 YUAN Rong, LUO Ming, SUN Zhi, et al. Rayplus: A web-based platform for medical image processing[J]. Journal of Digital Imaging, 2017, 30(2): 197–203. doi: 10.1007/s10278-016-9920-y MIMICS.[M/OL]. Https: //www.Materialise.Com/en/medical/software/mimics, 2019. AVANTS B B, TUSTISON N, and SONG Gang. Advanced normalization tools (ANTS)[R]. Pennsylvania: University of Pennsylvania, 2011: 1–35. SMITH S M, JENKINSON M, WOOLRICH M W, et al. Advances in functional and structural mr image analysis and implementation as fsl[J]. Neuroimage, 2004, 23(S1): S208–S219. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.051 LOO L H, LAKSAMEETHANASAN D, and TUNG Y L. Quantitative protein localization signatures reveal an association between spatial and functional divergences of proteins[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2014, 10(3): e1003504. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003504 LU A X, CHONG Y T, HSU I S, et al. Integrating images from multiple microscopy screens reveals diverse patterns of change in the subcellular localization of proteins[J]. eLife, 2018, 7: e31872. doi: 10.7554/eLife.31872 LI Jieyue, SHARIFF A, WIKING M, et al. Estimating microtubule distributions from 2d immunofluorescence microscopy images reveals differences among human cultured cell lines[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(11): e50292. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050292 NANNI L and MELUCCI M. Combination of projectors, standard texture descriptors and bag of features for classifying images[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 173: 1602–1614. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.09.032 COELHO L P, KANGAS J D, NAIK A W, et al. Determining the subcellular location of new proteins from microscope images using local features[J]. Bioinformatics, 2013, 29(18): 2343–2349. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt392 PÄRNAMAA T and PARTS L. Accurate classification of protein subcellular localization from high-throughput microscopy images using deep learning[J]. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics, 2017, 7(5): 1385–1392. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.033654 SULLIVAN D P, WINSNES C F, ÅKESSON L, et al. Deep learning is combined with massive-scale citizen science to improve large-scale image classification[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(9): 820–828. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4225 RUMETSHOFER E, HOFMARCHER M, RÖHRL C, et al. Human-level protein localization with convolutional neural networks[C]. The ICLR 2019, Las Cruces, USA, 2019: 1–18. CHEN Jiamei, QU Aiping, WANG Linwei, et al. New breast cancer prognostic factors identified by computer-aided image analysis of he stained histopathology images[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 10690. doi: 10.1038/srep10690 SANTAMARIA-PANG A, RITTSCHER J, GERDES M, et al. Cell segmentation and classification by hierarchical supervised shape ranking[C]. The 12th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, New York, USA, 2015: 1296–1299. GEESSINK O G F, BAIDOSHVILI A, FRELING G, et al. Toward automatic segmentation and quantification of tumor and stroma in whole-slide images of h and e stained rectal carcinomas[J]. SPIE, 2015, 9420: 94200F. doi: 10.1117/12.2081665. ARTETA C, LEMPITSKY V, NOBLE J A, et al. Learning to detect cells using non-overlapping extremal regions[C]. The 15th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Nice, France, 2012: 348–356. QU Aiping, CHEN Jiamei, WANG Linwei, et al. Two-step segmentation of hematoxylin-eosin stained histopathological images for prognosis of breast cancer[C]. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine, Belfast, UK, 2014: 218–223. BEJNORDI B E, LIN J, GLASS B, et al. Deep learning-based assessment of tumor-associated stroma for diagnosing breast cancer in histopathology images[C]. The 14th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Melbourne, Australia, 2017: 929–932. doi: 10.1109/ISBI.2017.7950668. SIRINUKUNWATTANA K, SNEAD D R J, and RAJPOOT N M. A stochastic polygons model for glandular structures in colon histology images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2015, 34(11): 2366–2378. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2015.2433900 XU Yan, LI Yang, WANG Yipei, et al. Gland instance segmentation using deep multichannel neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 64(12): 2901–2912. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2017.2686418 XU Yan, JIA Zhipeng, WANG Liangbo, et al. Large scale tissue histopathology image classification, segmentation, and visualization via deep convolutional activation features[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2017, 18(1): 281. doi: 10.1186/s12859-017-1685-x BARKER J, HOOGI A, DEPEURSINGE A, et al. Automated classification of brain tumor type in whole-slide digital pathology images using local representative tiles[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2016, 30: 60–71. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2015.12.002 BENTAIEB A, LI-CHANG H, HUNTSMAN D, et al. A structured latent model for ovarian carcinoma subtyping from histopathology slides[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2017, 39: 194–205. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2017.04.008 YU K H, ZHANG Ce, BERRY G J, et al. Predicting non-small cell lung cancer prognosis by fully automated microscopic pathology image features[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7(1): 12474. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12474 CHENG Jun, ZHANG Jie, HAN Yatong, et al. Integrative analysis of histopathological images and genomic data predicts clear cell renal cell carcinoma prognosis[J]. Cancer Research, 2017, 77(21): e91–e100. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0313 SHARMA H, ZERBE N, KLEMPERT I, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks for automatic classification of gastric carcinoma using whole slide images in digital histopathology[J]. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 2017, 61: 2–13. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2017.06.001 BENTAIEB A, LI-CHANG H, HUNTSMAN D, et al. Automatic diagnosis of ovarian carcinomas via sparse multiresolution tissue representation[C]. The 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 629–636. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24553-9_77. WANG Chaofeng, SHI Jun, ZHANG Qi, et al. Histopathological image classification with bilinear convolutional neural networks[C]. The 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Seogwipo, South Korea, 2017: 4050–4053. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2017.8037745. CIOMPI F, GEESSINK O, BEJNORDI B E, et al. The importance of stain normalization in colorectal tissue classification with convolutional networks[C]. The 14th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Melbourne, Australia, 2017: 160–163. doi: 10.1109/ISBI.2017.7950492. SHEIKHZADEH F, WARD R K, VAN NIEKERK D, et al. Automatic labeling of molecular biomarkers of immunohistochemistry images using fully convolutional networks[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(1): e0190783. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190783 COUDRAY N, OCAMPO P S, SAKELLAROPOULOS T, et al. Classification and mutation prediction from non–small cell lung cancer histopathology images using deep learning[J]. Nature Medicine, 2018, 24(10): 1559–1567. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0177-5 KWAK J T and HEWITT S M. Nuclear architecture analysis of prostate cancer via convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 18526–18533. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2747838 OIKAWA K, SAITO A, KIYUNA T, et al. Pathological diagnosis of gastric cancers with a novel computerized analysis system[J]. Journal of Pathology Informatics, 2017, 8(1): 5. doi: 10.4103/2153-3539.201114 QAISER T, MUKHERJEE A, REDDY P B C, et al. Her2 challenge contest: A detailed assessment of automated her2 scoring algorithms in whole slide images of breast cancer tissues[J]. Histopathology, 2018, 72(2): 227–238. doi: 10.1111/his.13333 NEWBERG J and MURPHY R F. A framework for the automated analysis of subcellular patterns in human protein atlas images[J]. Journal of Proteome Research, 2008, 7(6): 2300–2308. doi: 10.1021/pr7007626 KUMAR A, RAO A, BHAVANI S, et al. Automated analysis of immunohistochemistry images identifies candidate location biomarkers for cancers[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(51): 18249–18254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1415120112 KONDO S, TAKAGI K, NISHIDA M, et al. Computer-aided diagnosis of focal liver lesions using contrast-enhanced ultrasonography with perflubutane microbubbles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2017, 36(7): 1427–1437. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2017.2659734 KUPPILI V, BISWAS M, SREEKUMAR A, et al. Extreme learning machine framework for risk stratification of fatty liver disease using ultrasound tissue characterization[J]. Journal of Medical Systems, 2017, 41(10): 152. doi: 10.1007/s10916-017-0862-9 SERAG A, WILKINSON A G, TELFORD E J, et al. Segma: An automatic segmentation approach for human brain mri using sliding window and random forests[J]. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 2017, 11: 2. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2017.00002 KHAN S A, NAZIR M, KHAN M A, et al. Lungs nodule detection framework from computed tomography images using support vector machine[J]. Microscopy Research & Technique, 2019, 82(8): 1256–1266. doi: 10.1002/jemt.23275 TIZHOOSH H R and BABAIE M. Representing medical images with encoded local projections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 65(10): 2267–2277. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2018.2791567 GAO X W, HUI Rui, and TIAN Zengmin. Classification of ct brain images based on deep learning networks[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2017, 138: 49–56. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.10.007 VAN TULDER G and DE BRUIJNE M. Combining generative and discriminative representation learning for lung ct analysis with convolutional restricted boltzmann machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2016, 35(5): 1262–1272. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2016.2526687 TERAMOTO A, FUJITA H, YAMAMURO O, et al. Automated detection of pulmonary nodules in pet/ct images: Ensemble false-positive reduction using a convolutional neural network technique[J]. Medical Physics, 2016, 43(6): 2821–2827. doi: 10.1118/1.4948498 CHEN Hao, WU Lingyun, DOU Qi, et al. Ultrasound standard plane detection using a composite neural network framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(6): 1576–1586. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2685080 AREVALO J, GONZÁLEZ F A, RAMOS-POLLÁN R, et al. Representation learning for mammography mass lesion classification with convolutional neural networks[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2016, 127: 248–257. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2015.12.014 CUI Zhipeng, YANG Jie, and QIAO Yu. Brain MRI segmentation with patch-based CNN approach[C]. The 35th Chinese Control Conference, Chengdu, China, 2016: 7026–7031. RAJPURKAR P, IRVIN J, ZHU K, et al. Chexnet: Radiologist-level pneumonia detection on chest x-rays with deep learning[J]. arXiv: 1711.05225, 2017. CHRISTIANSEN E M, YANG S J, ANDO D M, et al. In silico labeling: Predicting fluorescent labels in unlabeled images[J]. Cell, 2018, 173(3): 792–803. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.040 BRENT R and BOUCHERON L E. Deep learning to predict microscope images[J]. Nature Methods, 2018, 15(11): 868–870. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0194-9 RIVENSON Y, WANG Hongda, WEI Zhensong, et al. Virtual histological staining of unlabelled tissue-autofluorescence images via deep learning[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2019, 3(6): 466–477. doi: 10.1038/s41551-019-0362-y ZHANG Zizhao, CHEN Pingjun, MCGOUGH M, et al. Pathologist-level interpretable whole-slide cancer diagnosis with deep learning[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2019, 1(5): 236–245. doi: 10.1038/s42256-019-0052-1 VAKOC B J, LANNING R M, TYRRELL J A, et al. Three-dimensional microscopy of the tumor microenvironment in vivo using optical frequency domain imaging[J]. Nature Medicine, 2009, 15(10): 1219–1223. doi: 10.1038/nm.1971 JONES S A, SHIM S, HE Jiang, et al. Fast, three-dimensional super-resolution imaging of live cells[J]. Nature Methods, 2011, 8(6): 499–505. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1605 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
