Optimal Task Offloading Scheme Based on Network Delay and Resource Management in Joint Blockchain and Fog Computing System
-
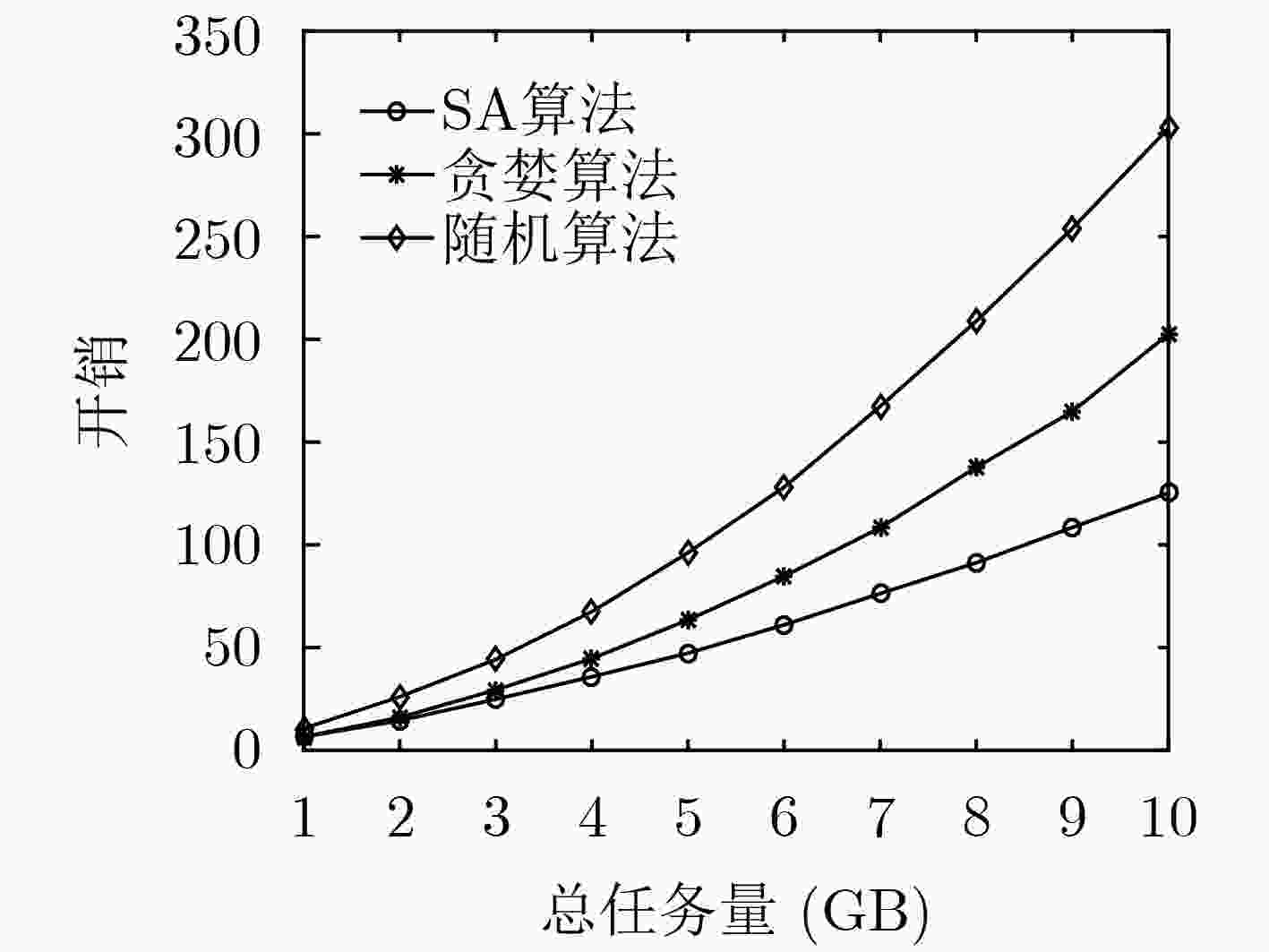
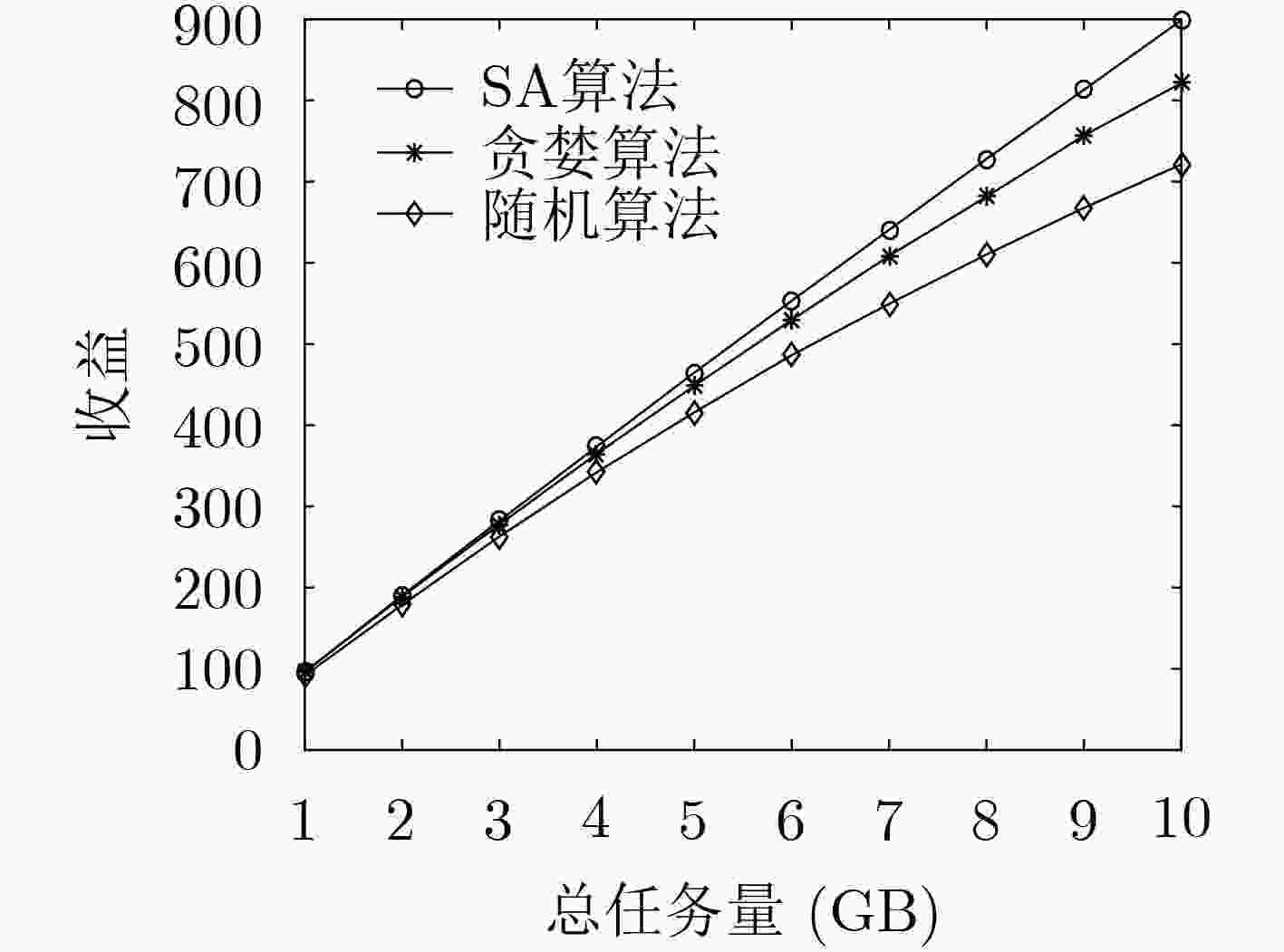
摘要: 针对如何基于有限的系统剩余资源进行任务优化卸载以增加移动终端的数字货币收益问题,该文在融合区块链与雾计算系统中提出一种基于节点剩余资源、网络时延的任务卸载方案。为了实现任务的优化卸载,首先基于任务量对移动终端的预期收益进行了分析,其次基于网络节点剩余计算资源、存储资源、功率资源、网络时延联合分析了移动终端的支出。此后以最大化移动终端的数字货币收益为优化目标建立了数学优化模型,并利用模拟退火(SA)算法对优化模型进行求解。仿真结果证明上述方案的有效性。Abstract: To solve the problem of increasing the digital currency of mobile terminals based on limited residual resources of the system, a task offloading scheme is proposed based on node residual resources and network delay in the joint blockchain and fog computing system. In order to offload the task in an optimal way, the expected revenue of mobile terminals is firstly analyzed based on the amount of tasks. Secondly, based on the remaining computing resources, storage resources, power resources and network delays, the expenditure of mobile terminal is analyzed. Then, a mathematical optimization model is established to maximize the digital currency income of the mobile terminal. The Simulated Annealing (SA) algorithm is employed to deal with the suboptimal model, respectively. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme.
-
Key words:
- Blockchain /
- Fog computing /
- Network delay /
- Resource management
-
表 1 求解优化模型的模拟退火算法流程
输入:${Q_{\rm{n}}}$, $\varphi $, ${T_{\max }}$, ${T_{\min }}$, $L$, $\nu $; 输出:优化解$\pi^* = \{ \alpha^*,\beta^*\}$; (1) 初始化${Q_{\rm{n}}}$, 最高温度${T_{\max }}$和最低温度${T_{\min }}$,降温速度$\nu $,迭代
次数$L$;(2) for m=1:L do; (3) 求解状态${\pi _m} = \{ {\alpha _m},{\beta _m}\}$, 并计算当前$E_{{\rm{n}}m}^{\rm{T}}$,将
${\pi _m} = \{ {\alpha _m},{\beta _m}\}$赋值给最佳解$\pi^* = \{ \alpha^*,\beta^*\}$;(4) 计算下一状态解${\pi '} = \{ {\alpha '},{\beta '}\}$,并计算对应的$E_{{\rm{n}}(m + 1)}^{\rm{T}}$; (5) 计算增量$\Delta E_{{\rm{n}}m}^{\rm{T}} = E_{{\rm{n}}(m + 1)}^{\rm{T}} - E_{{\rm{n}}m}^{\rm{T}}$; (6) if $\Delta E_{{\rm{n}}m}^{\rm{T}} < 0$ then; (7) 接受当前解为最佳解,并将${\pi _m} = \{ {\alpha _m},{\beta _m}\} $赋值给最佳解
$\pi^* = \{ \alpha^*,\beta^*\}$;(8) else; (9) 以metropolis准则中的概率${p_{{\rm{sol}}}}$接受${\pi _m} = \{ {\alpha _m},{\beta _m}\}$作为当
前最佳解;(10) End if; (11) if m≠L; (12) 返回(2); (13) else; (14) end for; (15) $T(k + 1) = \nu T(k)$; (16) if $T(k + 1) > {T_{\min }}$; (17) 返回(2); (18) else; (19) end for 表 2 各种节点的总资源和剩余资源量及其权重的设置
节点类型 资源类型 总资源 剩余资源 权重 BN 存储资源(GB) 1024 [600, 800] 0.33 计算资源(MCPS) 1000 [600, 800] 0.33 功率资源(W) 400 [280, 350] 0.34 FN 存储资源(GB) 512 [256, 300] 0.33 计算资源(MCPS) 400 [280, 350] 0.33 功率资源(W) 40 [28, 30] 0.34 MN 存储资源(GB) 128 [16, 32] 0.33 计算资源(MCPS) 200 [100, 160] 0.33 功率资源(W) 2 [1.2, 1.6] 0.34 -
BACCARELLI E, NARANJO P G V, SCARPINITI M, et al. Fog of everything: Energy-efficient networked computing architectures, research challenges, and a case study[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 9882–9910. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2702013 张海波, 李虎, 陈善学, 等. 超密集网络中基于移动边缘计算的任务卸载和资源优化[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1194–1201. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180592ZHANG Haibo, LI Hu, CHEN Shanxue, et al. Computing offloading and resource optimization in ultra-dense networks with mobile edge computation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1194–1201. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180592 CHEN Lixing, ZHOU Pan, GAO Liang, et al. Adaptive fog configuration for the industrial internet of things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(10): 4656–4664. doi: 10.1109/TⅡ.2018.2846549 SHIRAZI S N, GOUGLIDIS A, FARSHAD A, et al. The extended cloud: review and analysis of mobile edge computing and fog from a security and resilience perspective[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2017, 35(11): 2586–2595. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2017.2760478 YU Yong, LI Yannan, TIAN Junfeng, et al. Blockchain-based solutions to security and privacy issues in the internet of things[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2018, 25(6): 12–18. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2017.1800116 CHO H. ASIC-resistance of multi-hash proof-of-work mechanisms for blockchain consensus protocols[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 66210–66222. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2878895 CONTI M, KUMAR E S, LAL C, et al. A survey on security and privacy issues of bitcoin[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(4): 3416–3452. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2018.2842460 TSCORSCH F and SCHEUERMANN B. Bitcoin and Beyond: A technical survey on decentralized digital currencies[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2016, 18(3): 2084–2123. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2016.2535718 JANG H and LEE J. An empirical study on modeling and prediction of bitcoin prices with bayesian neural networks based on blockchain information[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 5427–5437. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2779181 VAN DER HORST L, CHOO K K R, and LE-KHAC N A. Process memory investigation of the bitcoin clients electrum and bitcoin core[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 22385–22398. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2759766 LIU Mengting, YU F R, TENG Yinglei, et al. Computation offloading and content caching in wireless blockchain networks with mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(11): 11008–11021. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2866365 XIONG Zehui, ZHANG Yang, NIYATO D, et al. When mobile blockchain meets edge computing[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2018, 56(8): 33–39. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1701095 YAO Haipeng, MAI Tianle, WANG Jingjing, et al. Resource trading in blockchain-based industrial internet of things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(6): 3602–3609. doi: 10.1109/TⅡ.2019.2902563 WANG Xiaojie, NING Zhaolong, and WANG Lei. Offloading in internet of vehicles: A fog-enabled real-time traffic management system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(10): 4568–4578. doi: 10.1109/TⅡ.2018.2816590 -





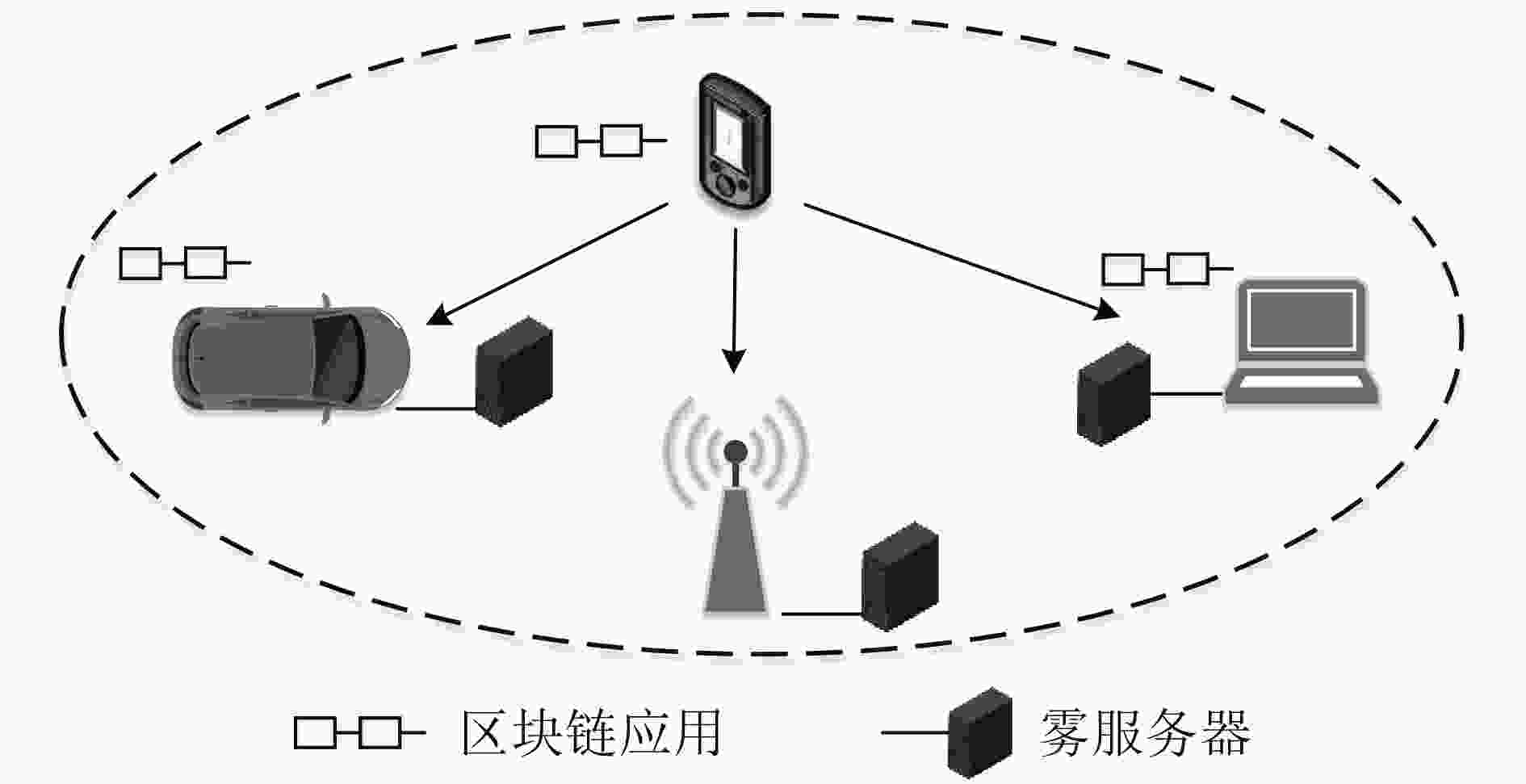
 下载:
下载:
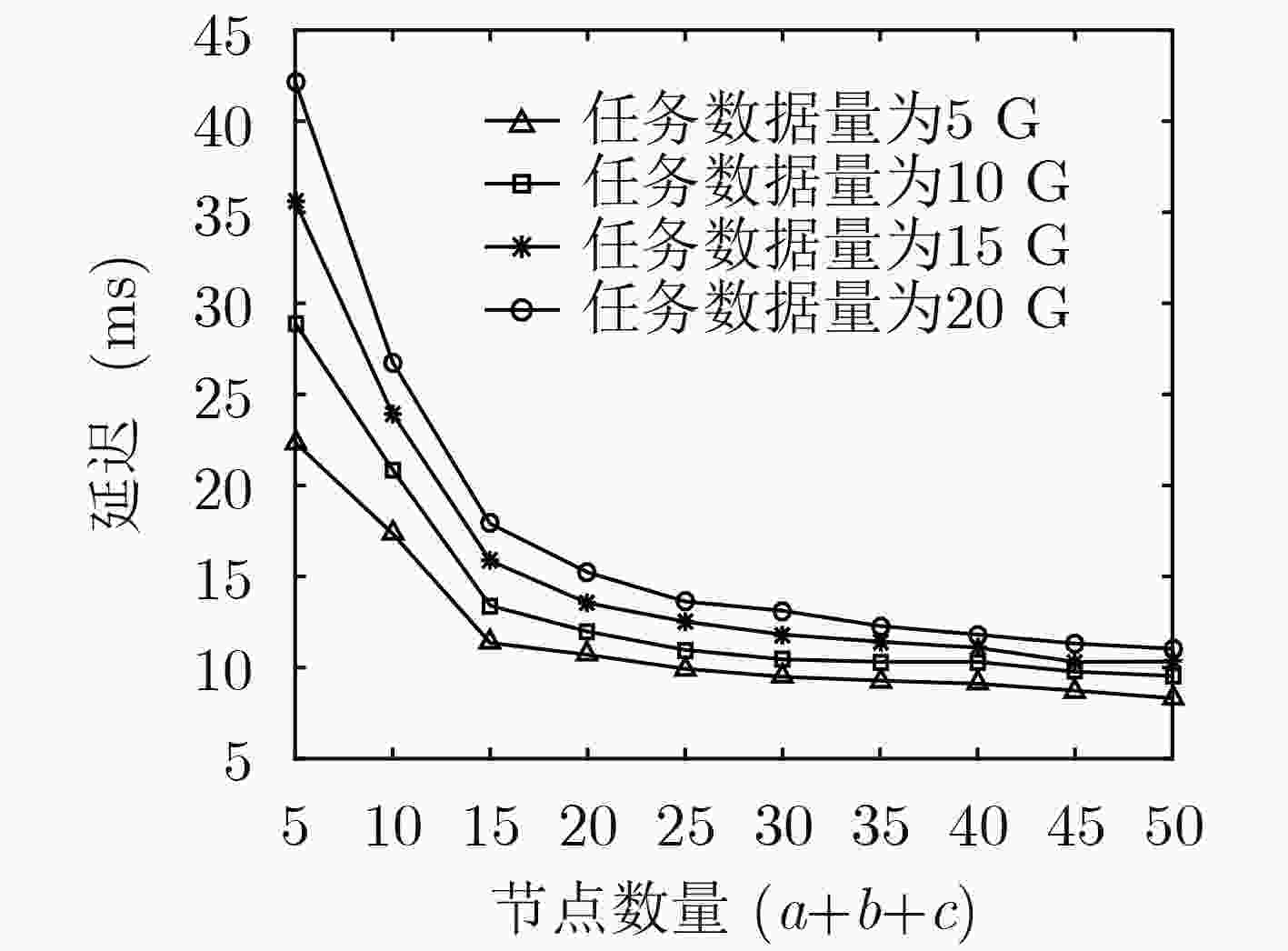
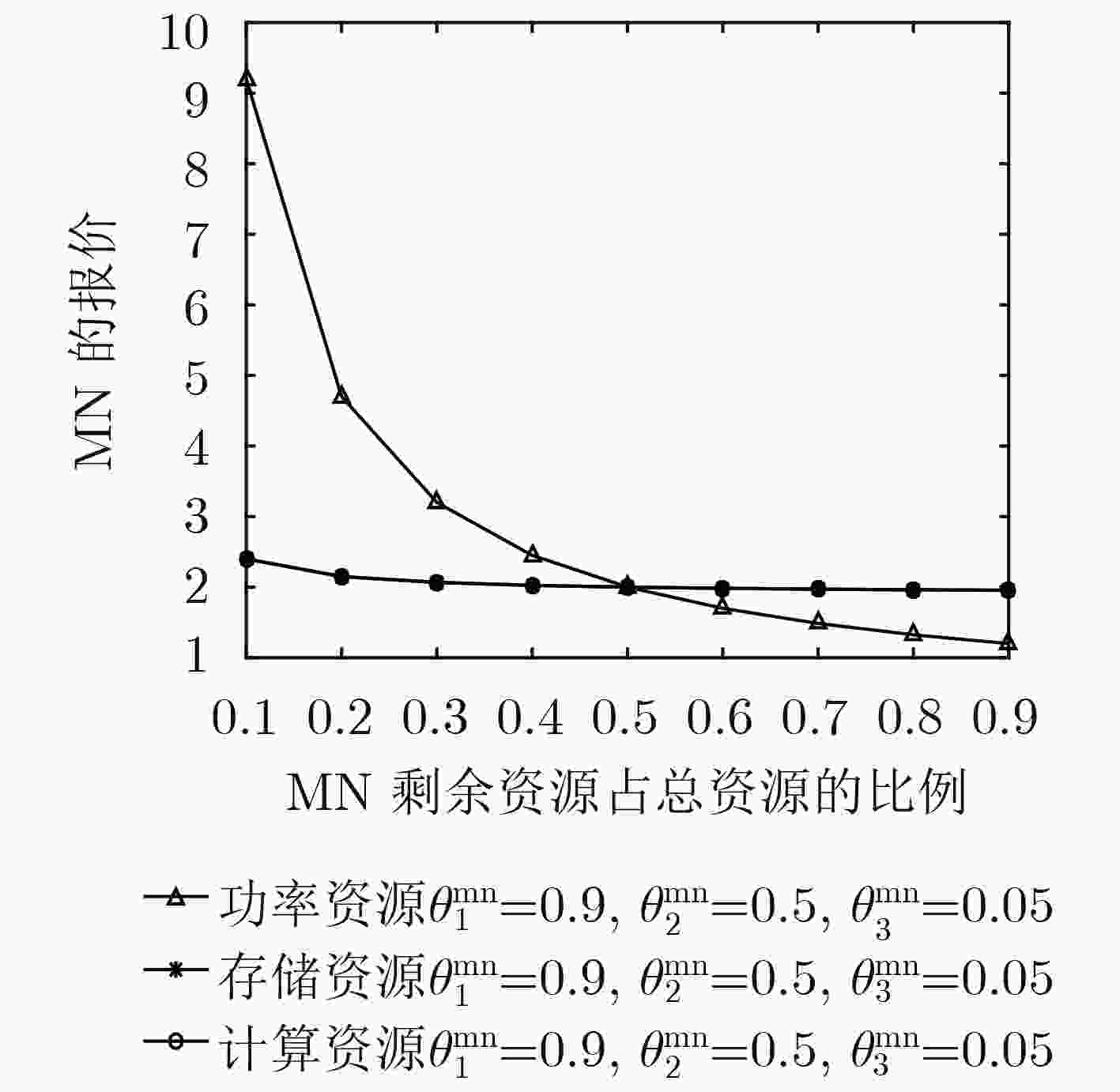
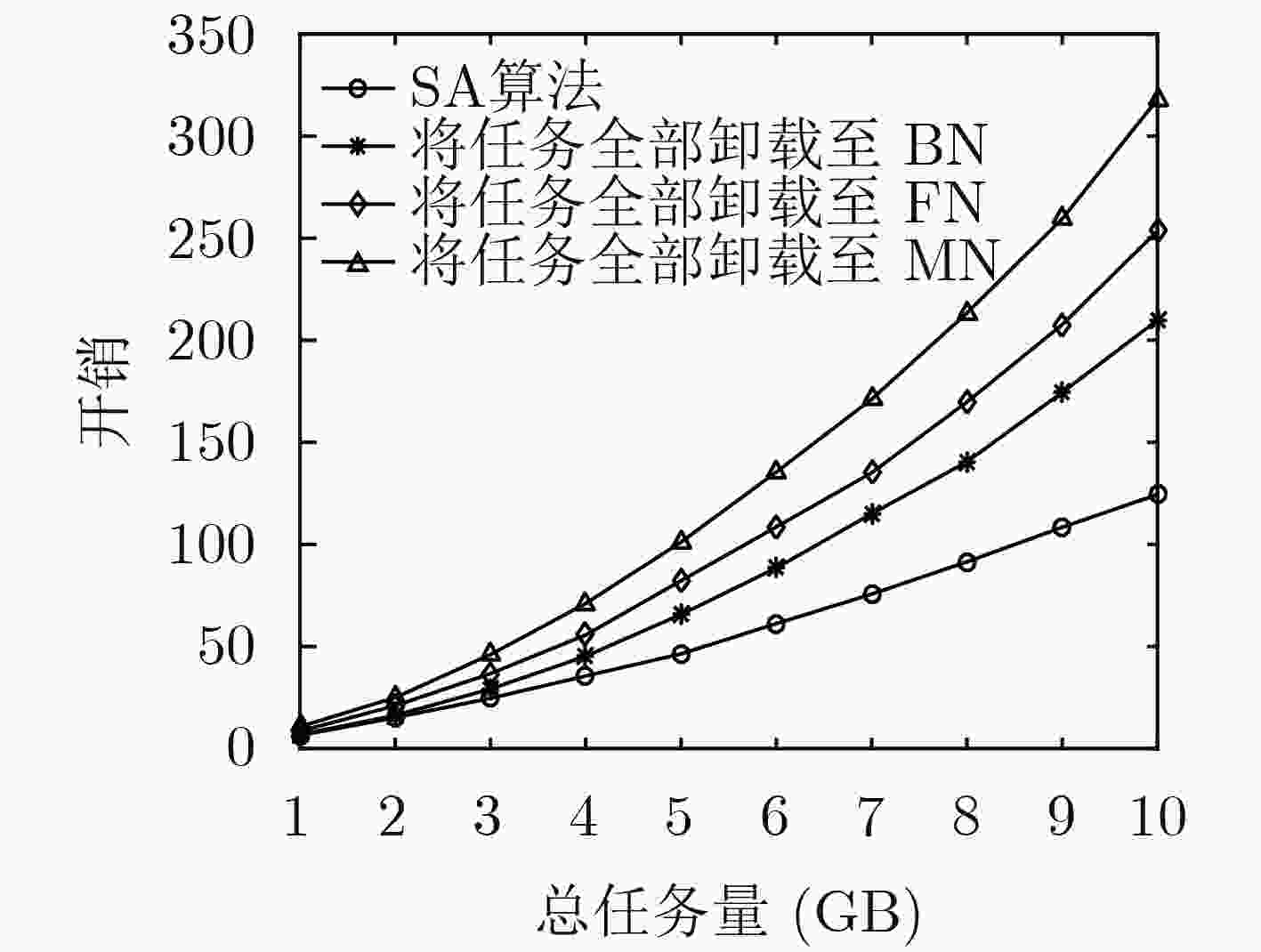



 下载:
下载:
