Primary Signal Suppression Based on Synchrosqueezed Wavelet Transform
-
摘要:
在辐射源个体识别(SEI)技术中,能量较高的主信号往往导致微弱个体特征稳定性降低,进而影响最终的个体识别效果。为了解决该问题并提升辐射源个体识别性能,该文提出基于同步压缩小波变换的主信号抑制技术。首先,利用静态小波变换完成对带噪信号的去噪预处理;然后,利用同步压缩小波变换完成对主信号的检测和抑制,并以均方根误差和皮尔逊相关系数为数值指标,验证算法的有效性;最后,在主信号抑制的基础上,利用分形理论中盒维数完成对信号的特征提取,并利用单核支持向量机验证个体识别性能。实验结果表明,与主信号抑制之前相比,主信号抑制算法下个体识别率提升了10%左右,验证了同步压缩小波变换的主信号抑制算法对辐射源个体识别率提升的有效性。
Abstract:In Specific Emitter Identification (SEI), the stability of individual features and final correct identification rate are always declined due to the influence of the primary signal with high energy on the individual features. To solve the problem above, a primary signal suppression algorithm based on synchrosqueezed wavelet transform is exploited for specific emitter identification in this paper. Firstly, a denoising method based on stationary wavelet transform is applied to preprocess the noised signal; Then, the detection and suppression of the primary signal from time-frequency distribution are developed, where root mean square error and Pearson correlation coefficient are used as numerical indicators to measure the effectiveness of the proposed primary signal suppression algorithm; Finally, a feature extraction based on box-counting dimension and a classification based on support vector machine are exploited to verify the identification performance. The simulation results show that the correct identification rate of SEI using the proposed primary signal suppression outperforms the conventional SEI with 10%, which proves the practical improvement of the proposed primary signal suppression algorithm on specific emitter identification.
-
表 1 加性相位噪声参数
辐射源个体 与频偏对应的相位噪声幅度(信相噪比(dB)) f1=±2.75 MHz f2=±2.80 MHz f3=±3.10 MHz E1 11.9897 12.7815 15.7918 E2 10.4845 11.6722 16.1877 f21=±2.8 MHz f22=±2.9 MHz f23=±3.15 MHz E3 12.7815 14.0308 16.1394 -
WANG Xuebao, HUANG Gaoming, ZHOU Zhiwen, et al. Radar emitter recognition based on the short time fourier transform and convolutional neural networks[C]. The 10th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics, Shanghai, China, 2017: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/CISP-BMEI.2017.8302111. LIANG Kaiqiang, HUANG Zhen, HU Dexiu, et al. An individual emitter recognition method combining bispectrum with wavelet entropy[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Progress in Informatics and Computing, Nanjing, China, 2015: 206–210. doi: 10.1109/PIC.2015.7489838. GUO Haizhao, ZHANG Xiaonu, YANG Libo, et al. Improved fisher linear discriminant analysis for feature extraction of unintentional modulation on pulse by combining ambiguity function with wavelet transform[C]. IET International Radar Conference 2015, Hangzhou, China, 2015: 1–4. doi: 10.1049/cp.2015.1108. LI Yibing, GE Juan, LIN Yun, et al. Radar emitter signal recognition based on multi-scale wavelet entropy and feature weighting[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21(11): 4254–4260. doi: 10.1007/s11771-014-2422-5 曹银萍, 郭璐. 基于MATLAB的小波分析在信号去噪中的应用[J]. 信息记录材料, 2018, 19(7): 85–87. doi: 10.16009/j.cnki.cn13-1295/tq.2018.07.056CAO Yinping and GUO Lu. Application of wavelet analysis based on MATLAB in signal denoising[J]. Information Recording Materials, 2018, 19(7): 85–87. doi: 10.16009/j.cnki.cn13-1295/tq.2018.07.056 DUDCZYK J and KAWALEC A. Fractal features of specific emitter identification[J]. Acta Physica Polonica A, 2013, 124(2): 406–409. doi: 10.12693/APhysPolA.124.406 DUDCZYK J and KAWALEC A. Identification of emitter sources in the aspect of their fractal features[J]. Bulletin of the Polish Academy of Sciences: Technical Sciences, 2013, 61(3): 623–628. doi: 10.2478/bpasts-2013-0065 WU Xiaopo, SHI Yangming, MENG Weibo, et al. Specific emitter identification for satellite communication using probabilistic neural networks[J]. International Journal of Satellite Communications and Networking, 2019, 37(3): 283–291. doi: 10.1002/sat.1286 王欢欢, 张涛, 孟凡玉. 基于时频域细微特征的辐射源个体识别[J]. 信息工程大学学报, 2018, 19(1): 23–29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0673.2018.01.006WANG Huanhuan, ZHANG Tao, and MENG Fanyu. Specific emitter identification based on time-frequency domain characteristic[J]. Journal of Information Engineering University, 2018, 19(1): 23–29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0673.2018.01.006 WANG Huanhuan and ZHNAG Tao. Specific emitter identification based on fractal and wavelet theories[C]. The 2nd IEEE Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, Chongqing, China, 2017: 1613–1617. doi: 10.1109/IAEAC.2017.8054286. WANG Wei, LIU Hui, YANG Jun’an, et al. Specific emitter identification using decomposed hierarchical feature extraction methods[C]. The 13th International Conference on Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, Guilin, China, 2017: 1639–1643. doi: 10.1109/FSKD.2017.8393011. HE Boxiang, WANG Fanggang, LIU Yu, et al. Specific emitter identification via multiple distorted receivers[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops, Shanghai, China, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICCW.2019.8757066. 潘一苇, 彭华, 李天昀, 等. 一种新的时分多址信号射频特征及其在特定辐射源识别中的应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(11): 2661–2668. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190163PAN Yiwei, PENG Hua, LI Tianyun, et al. A novel radiometric signature of time-division multiple access signals and its application to specific emitter identification[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(11): 2661–2668. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190163 潘一苇, 杨司韩, 彭华, 等. 基于矢量图的特定辐射源识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 941–949. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190329PAN Yiwei, YANG Sihan, PENG Hua, et al. Specific emitter identification using signal trajectory image[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 941–949. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190329 LI Suyi, LIU Guangda, and LIN Zhenbao. Comparisons of wavelet packet, lifting wavelet and stationary wavelet transform for de-noising ECG[C]. The 2009 2nd IEEE International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology, Beijing, China, 2009: 491–494. doi: 10.1109/ICCSIT.2009.5234650. 王勇, 邹辉, 饶勤菲, 等. 结合空域噪声信息的小波脊提取算法[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2018, 47(4): 613–620. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.04.022WANG Yong, ZOU Hui, RAO Qinfei, et al. A wavelet ridge extraction algorithm combined with spatial noise information[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2018, 47(4): 613–620. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.04.022 唐智灵. 通信辐射源非线性个体识别方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2013.TANG Zhiling. A study of nonlinear method for specific communications emitter identification[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2013. WU Longwen, ZHAO Yaqin, WANG Zhao, et al. Specific emitter identification using fractal features based on box-counting dimension and variance dimension[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology, Bilbao, Spain, 2017: 226–231. doi: 10.1109/ISSPIT.2017.8388646. BIHL T J, BAUER K W, and TEMPLE M A. Feature selection for RF fingerprinting with multiple discriminant analysis and using ZigBee device emissions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2016, 11(8): 1862–1874. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2016.2561902 WU Longwen, ZHAO Yaqin, FENG Mengfei, et al. Specific emitter identification using IMF-DNA with a joint feature selection algorithm[J]. Electronics, 2019, 8(9): 934. doi: 10.3390/electronics8090934 CHEN Taowei, JIN Weidong, and LI Jie. Feature extraction using surrounding-line integral bispectrum for radar emitter signal[C]. 2008 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Hong Kong, China, 2008: 294–298. doi: 10.1109/IJCNN.2008.4633806. -





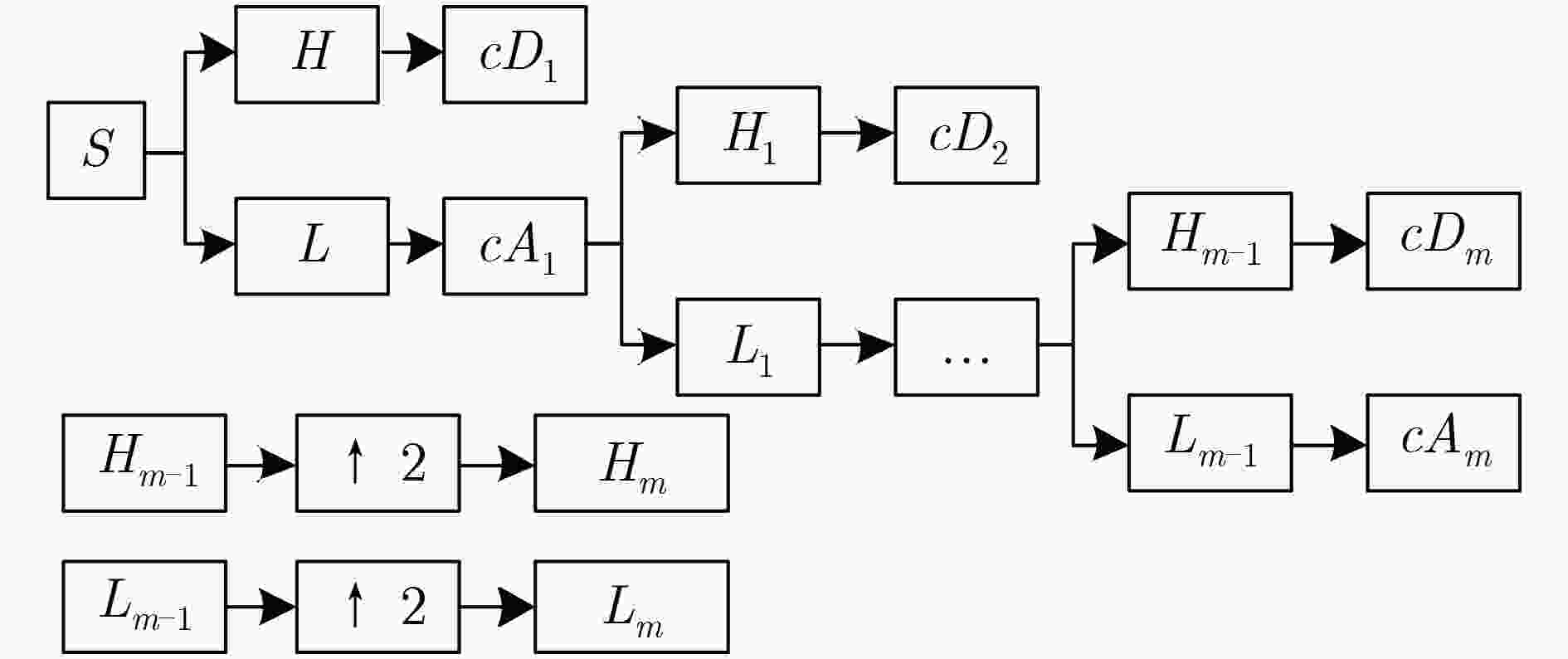
 下载:
下载:
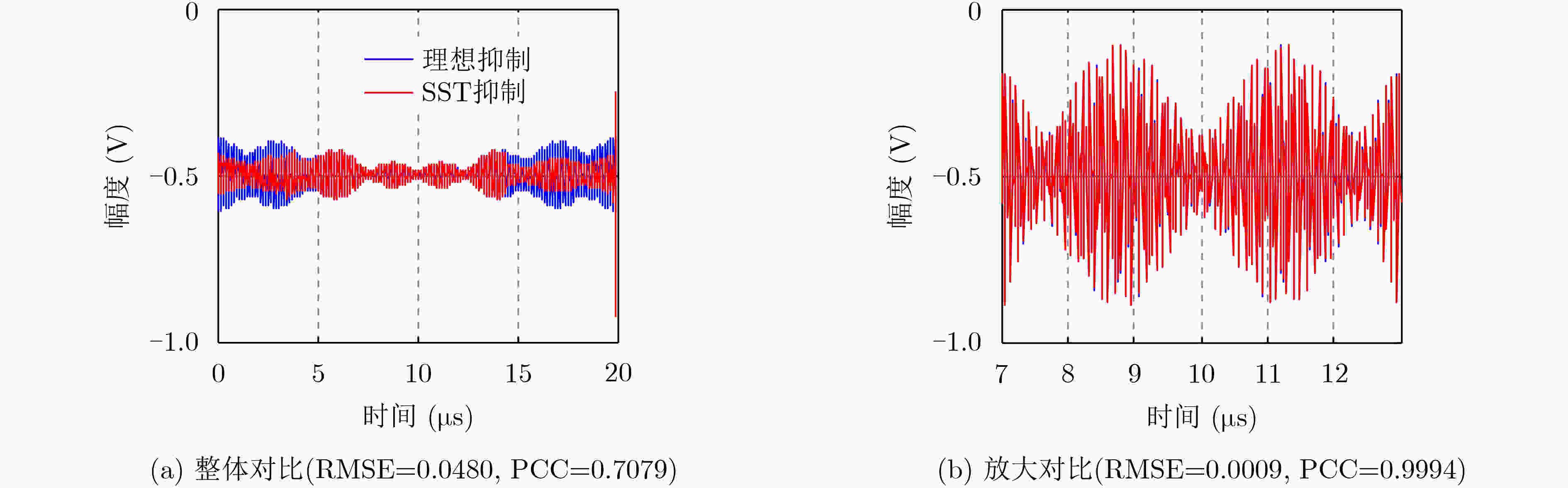
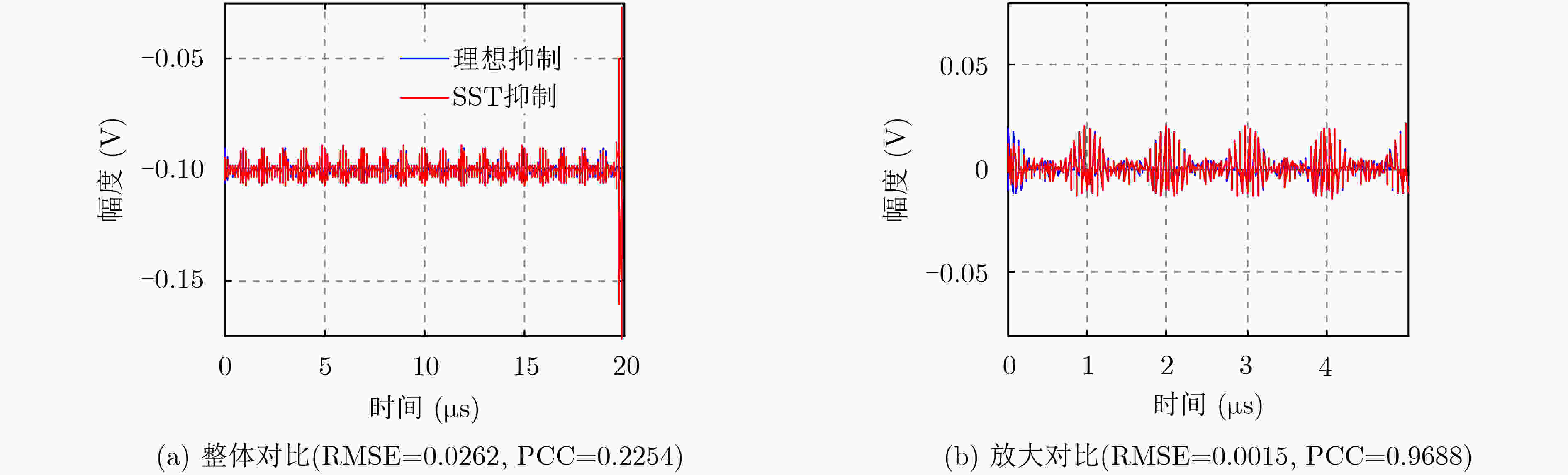
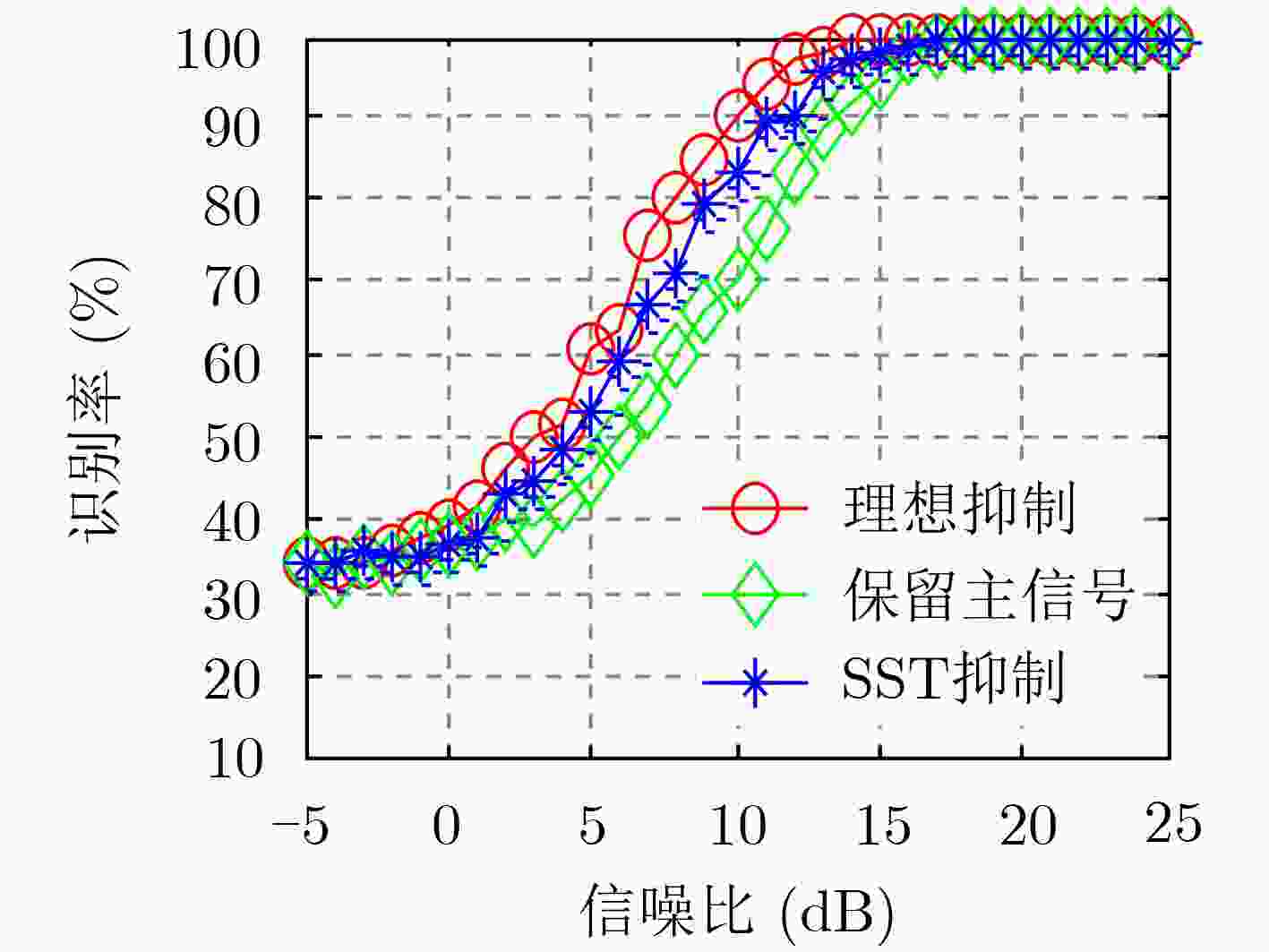



 下载:
下载:
