Occluded Pedestrian Detection Based on Joint Attention Mechanism of Channel-wise and Spatial Information
-
摘要:
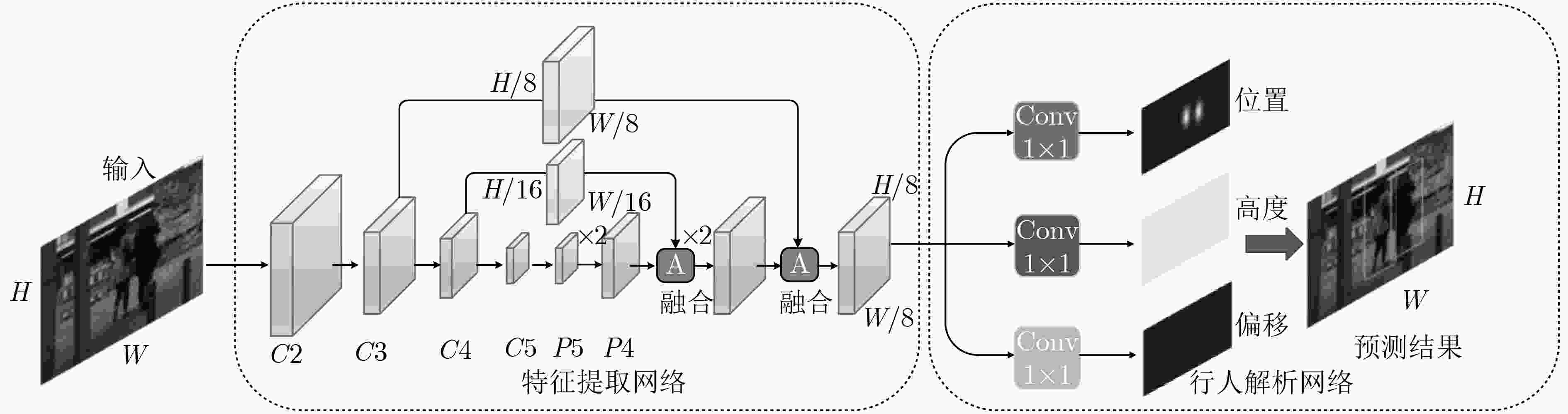
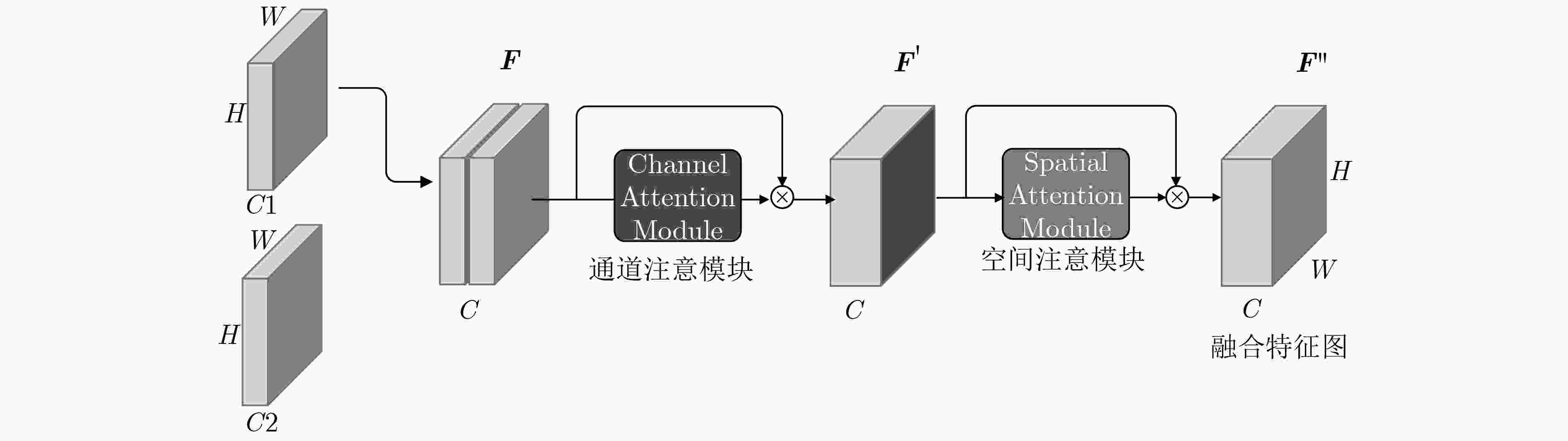
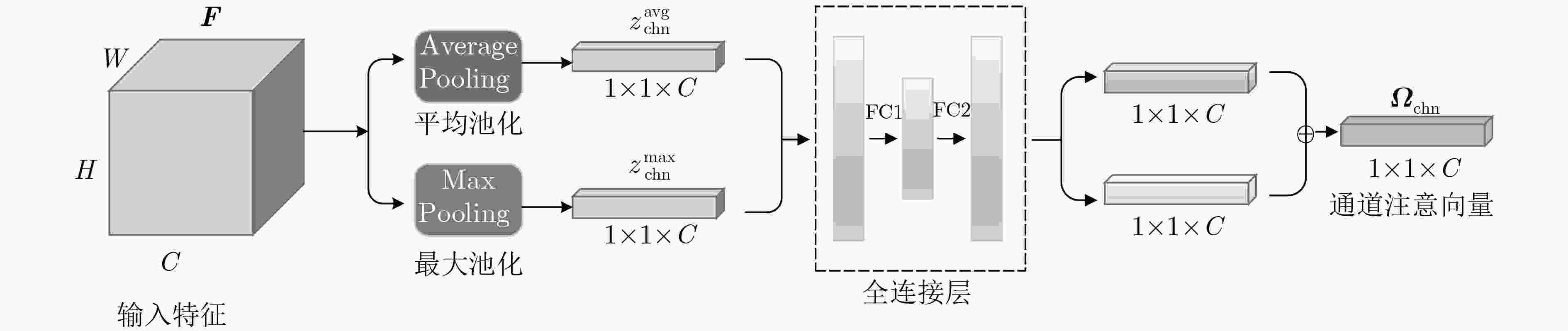
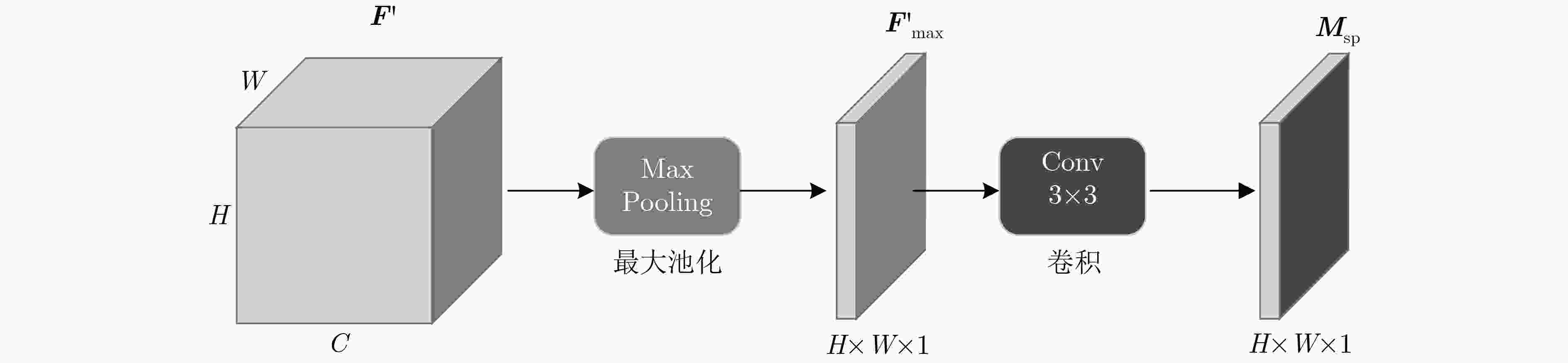
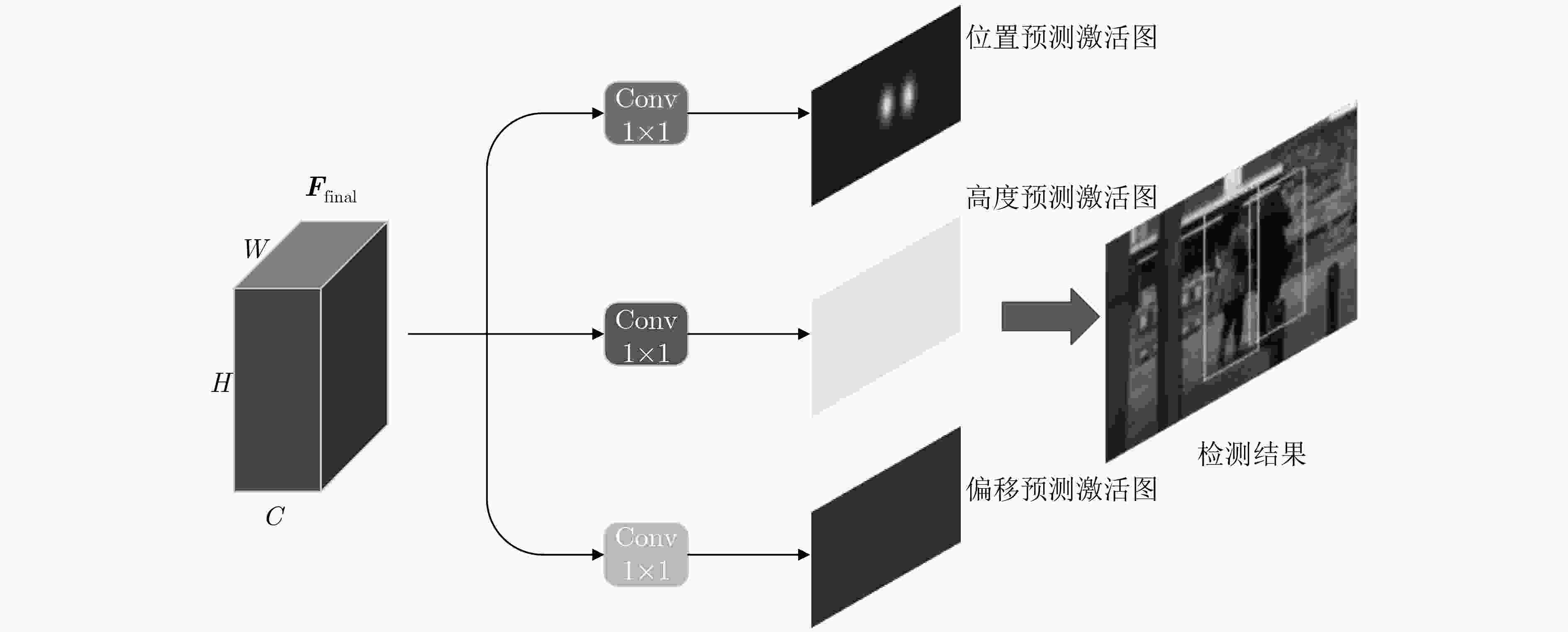
遮挡是行人检测任务中导致漏检发生的主要原因之一,对检测器性能造成了不利影响。为了增强检测器对于遮挡行人目标的检测能力,该文提出一种基于特征引导注意机制的单级行人检测方法。首先,设计一种特征引导注意模块,在保持特征通道间的关联性的同时保留了特征图的空间信息,引导模型关注遮挡目标可视区域;然后,通过注意模块融合浅层和深层特征,从而提取到行人的高层语义特征;最后,将行人检测作为一种高层语义特征检测问题,通过激活图的形式预测得到行人位置和尺度,并生成最终的预测边界框,避免了基于先验框的预测方式所带来的额外参数设置。所提方法在CityPersons数据集上进行了测试,并在Caltech数据集上进行了跨数据集实验。结果表明该方法对于遮挡目标检测准确度优于其他对比算法。同时该方法实现了较快的检测速度,取得了检测准确度和速度的平衡。
Abstract:Pedestrian detector performance is damaged because occlusion often leads to missed detection. In order to improve the detector's ability to detect pedestrian, a single-stage detector based on feature-guided attention mechanism is proposed. Firstly, a feature attention module is designed, which preserves the association between the feature channels while retaining spatial information, and guides the model to focus on visible region. Secondly, the attention module is used to fuse shallow and deep features, then high-level semantic features of pedestrians are extracted. Finally, pedestrian detection is treated as a high-level semantic feature detection problem. Pedestrian location and scale are obtained through heat map prediction, then the final prediction bounding box is generated. This way, the proposed method avoids the extra parameter settings of the traditional anchor-based method. Experiments show that the proposed method is superior to other comparison algorithms for the accuracy of occlusion target detection on CityPersons and Caltech pedestrian database. At the same time, the proposed method achieves a faster detection speed and a better balance between detection accuracy and speed.
-
表 1 验证实验条件设置
R (Reasonable) HO (Heavy Occlusion) R+HO (Reasonable+Heavy Occlusion) $v \in [0.65,\infty )$ $v \in [0.20,0.65]$ $v \in [0.20,\infty )$ 表 2 注意网络验证结果MR–2(%)
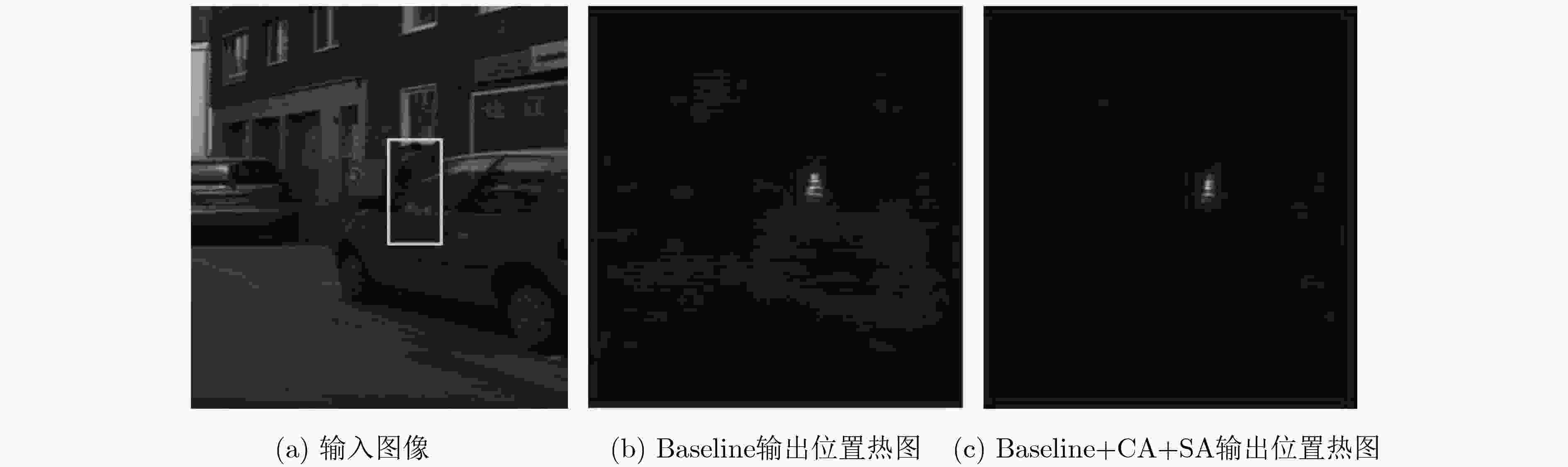
方法 R HO R+HO 文献[16] 16.0 56.7 38.2 Baseline 12.1 41.1 38.1 Baseline+CA 11.8 39.2 37.8 Baseline+CA+SA 11.6 38.5 37.3 表 3 CityPersons数据集测试结果MR-2(%)
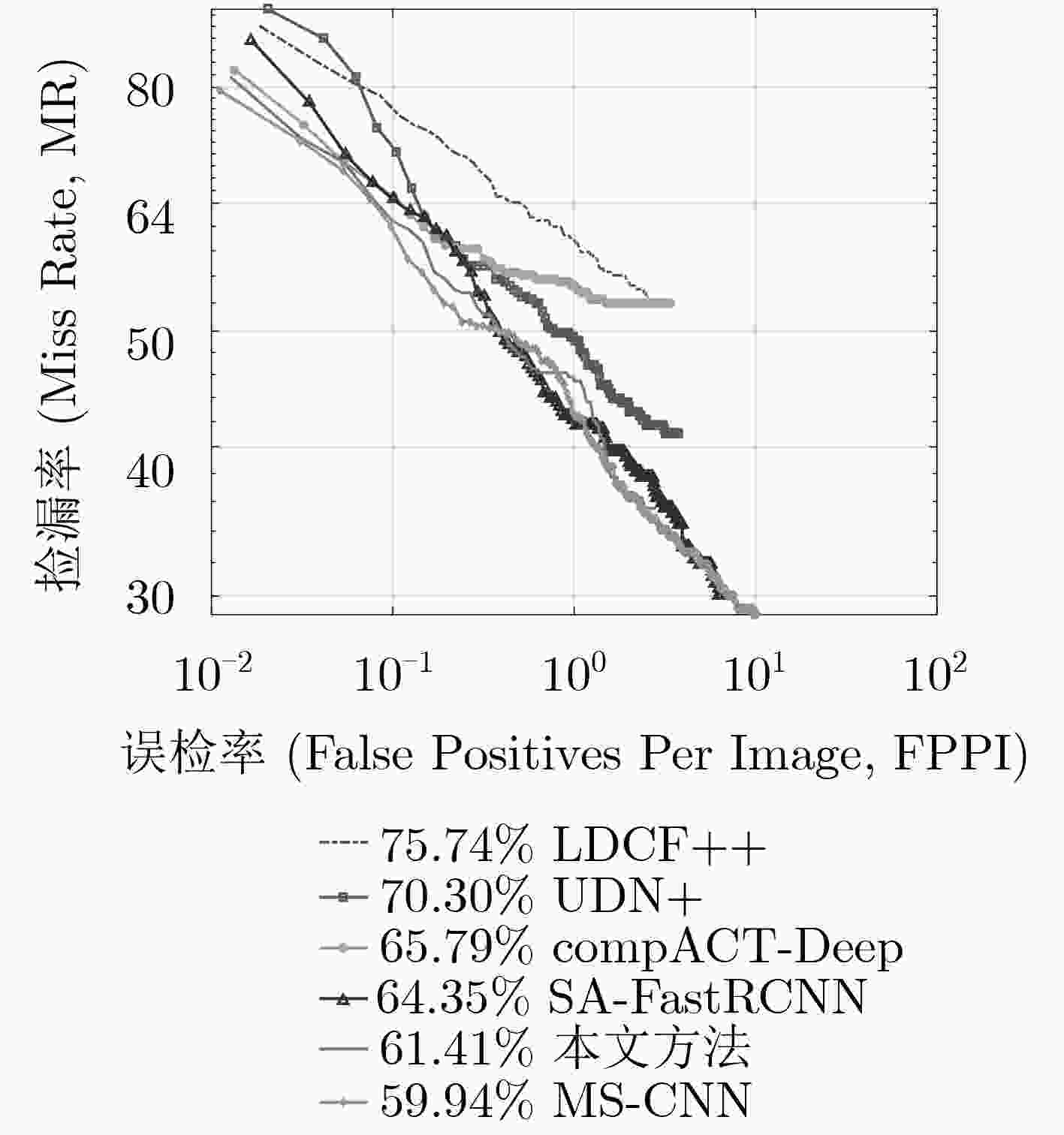
方法 主干网络 Reasonable Heavy Partial Bare 测试时间(s) OR-CNN[11] VGG-16 12.8 55.7 15.3 6.7 – FasterRCNN[21] VGG-16 15.4 – – – – ALFNet[8] ResNet-50 12.0 51.9 11.4 8.4 0.27 CSP[9] ResNet-50 11.0 49.3 10.4 7.3 0.33 CAFL[13] ResNet-50 11.4 50.4 12.1 7.6 – PedJointNet[14] ResNet-50 13.5 52.1 – – – TLL[20] ResNet-50 15.5 53.6 17.2 10.0 – RepLoss[23] ResNet-50 13.2 56.9 16.8 7.6 – 本文方法 ResNet-50 11.6 47.6 9.8 7.5 0.22 -
张功国, 吴建, 易亿, 等. 基于集成卷积神经网络的交通标志识别[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 31(4): 571–577. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2019.04.019ZHANG Gongguo, WU Jian, YI Yi, et al. Traffic sign recognition based on ensemble convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2019, 31(4): 571–577. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2019.04.019 种衍文, 匡湖林, 李清泉. 一种基于多特征和机器学习的分级行人检测方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2012, 38(3): 375–381. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.00375CHONG Yanwen, KUANG Hulin, and LI Qingquan. Two-stage pedestrian detection based on multiple features and machine learning[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(3): 375–381. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.00375 刘威, 段成伟, 遇冰, 等. 基于后验HOG特征的多姿态行人检测[J]. 电子学报, 2015, 43(2): 217–224. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2015.02.002LIU Wei, DUAN Chengwei, YU Bing, et al. Multi-pose pedestrian detection based on posterior HOG feature[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2015, 43(2): 217–224. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2015.02.002 REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]. 2015 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 91–99. LI Jianan, LIANG Xiaodan, SHEN Shengmei, et al. Scale-aware fast R-CNN for pedestrian detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 20(4): 985–996. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2017.2759508 王进, 陈知良, 李航, 等. 一种基于增量式超网络的多标签分类方法[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 31(4): 538–549. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2019.04.015WANG Jin, CHEN Zhiliang, LI Hang, et al. Hierarchical multi-label classification using incremental hypernetwork[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2019, 31(4): 538–549. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2019.04.015 GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440–1448. LIU Wei, LIAO Shengcai, HU Weidong, et al. Learning efficient single-stage pedestrian detectors by asymptotic localization fitting[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 618–634. LIU Wei, LIAO Shengcai, REN Weiqiang, et al. High-level semantic feature detection: A new perspective for pedestrian detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 5182–5191. ZHANG Shanshan, BENENSON R, OMRAN M, et al. How far are we from solving pedestrian detection?[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1259–1267. ZHANG Shifeng, WEN Longyin, BIAN Xiao, et al. Occlusion-aware R-CNN: detecting pedestrians in a crowd[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 637–653. OUYANG Wanli, ZHOU Hui, LI Hongsheng, et al. Jointly learning deep features, deformable parts, occlusion and classification for pedestrian detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(8): 1874–1887. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2738645 FEI Chi, LIU Bin, CHEN Zhu, et al. Learning pixel-level and instance-level context-aware features for pedestrian detection in crowds[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 94944–94953. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2928879 LIN C Y, XIE Hongxia, and ZHENG Hua. PedJointNet: Joint head-shoulder and full body deep network for pedestrian detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 47687–47697. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2910201 ZHANG Shanshan, YANG Jian, and SCHIELE B. Occluded pedestrian detection through guided attention in CNNs[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6995–7003. ZHU Chenchen, HE Yihui, and SAVVIDES M. Feature selective anchor-free module for single-shot object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 840–849. LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944. CHEN Long, ZHANG Hanwang, XIAO Jun, et al. SCA-CNN: Spatial and channel-wise attention in convolutional networks for image captioning[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6298–6306. WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. SONG Tao, SUN Leiyu, XIE Di, et al. Small-scale pedestrian detection based on topological line localization and temporal feature aggregation[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 536–551. ZHANG Shanshan, BENENSON R, and SCHIELE B. Citypersons: A diverse dataset for pedestrian detection[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4457–4465. DOLLAR P, WOJEK C, SCHIELE B, et al. Pedestrian detection: An evaluation of the state of the art[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(4): 743–761. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.155 WANG Xinlong, XIAO Tete, JIANG Yuning, et al. Repulsion loss: Detecting pedestrians in a crowd[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7774–7783. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
