A Kernel Normalization Decorrelated Affine Projection P-norm Algorithm Based on Gaussian Kernel Explicit Mapping
-
摘要:
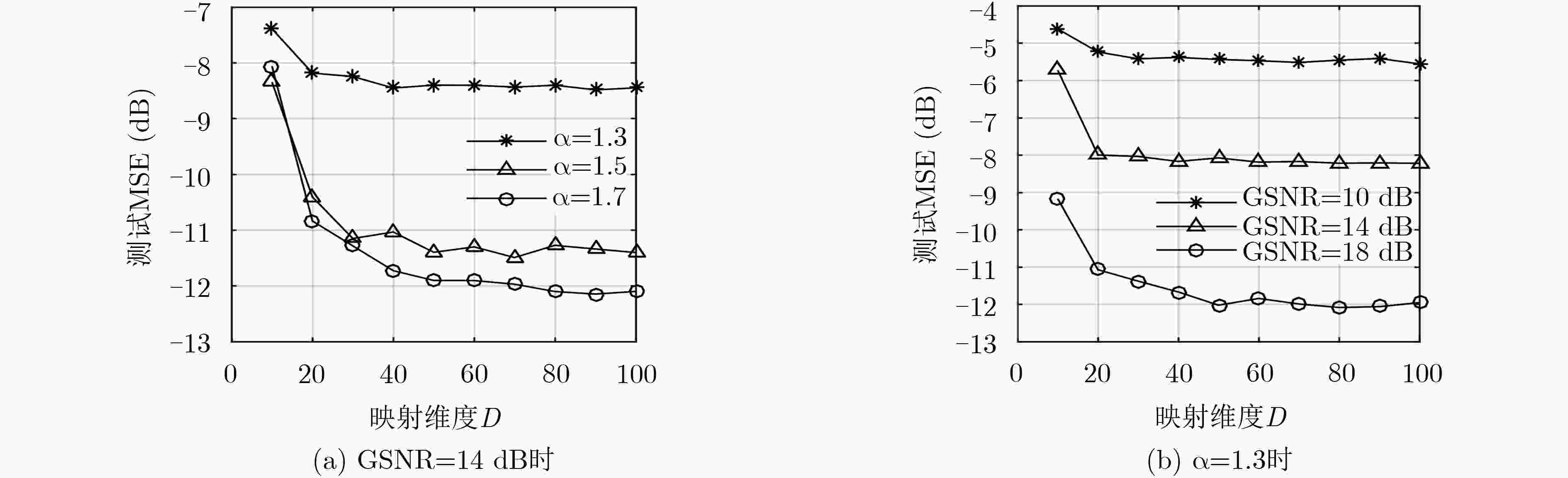
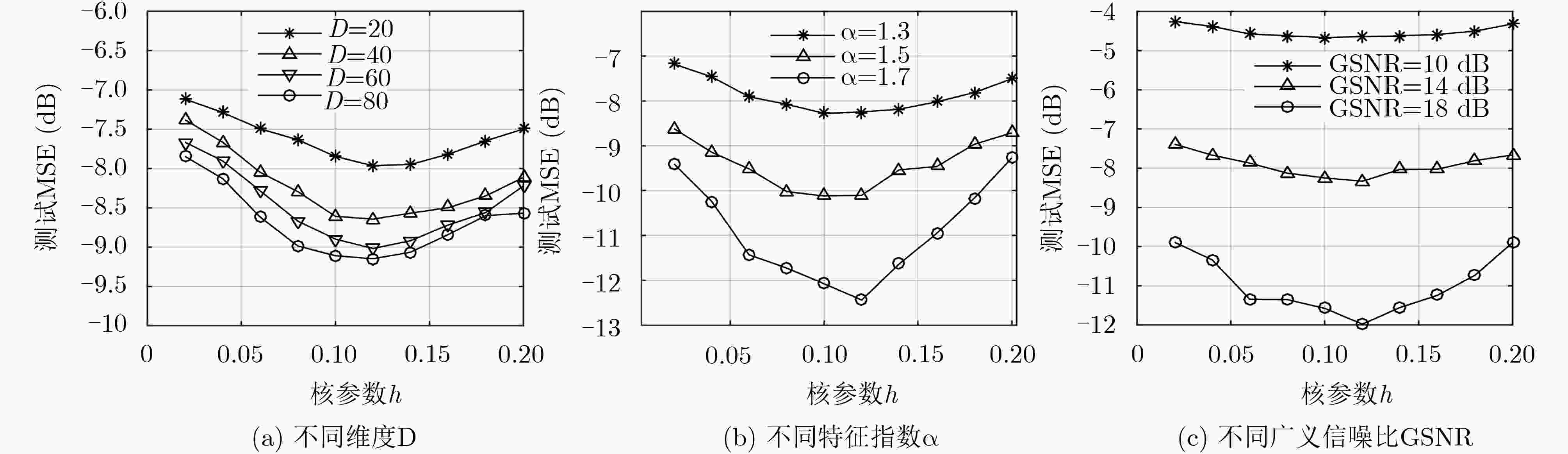
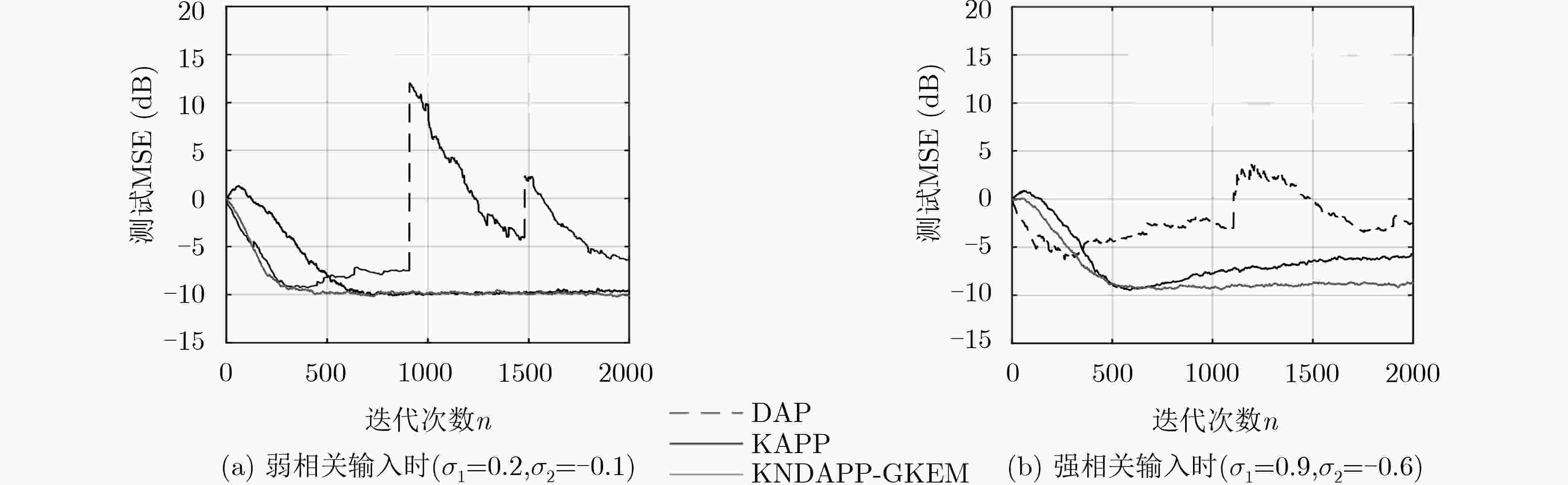
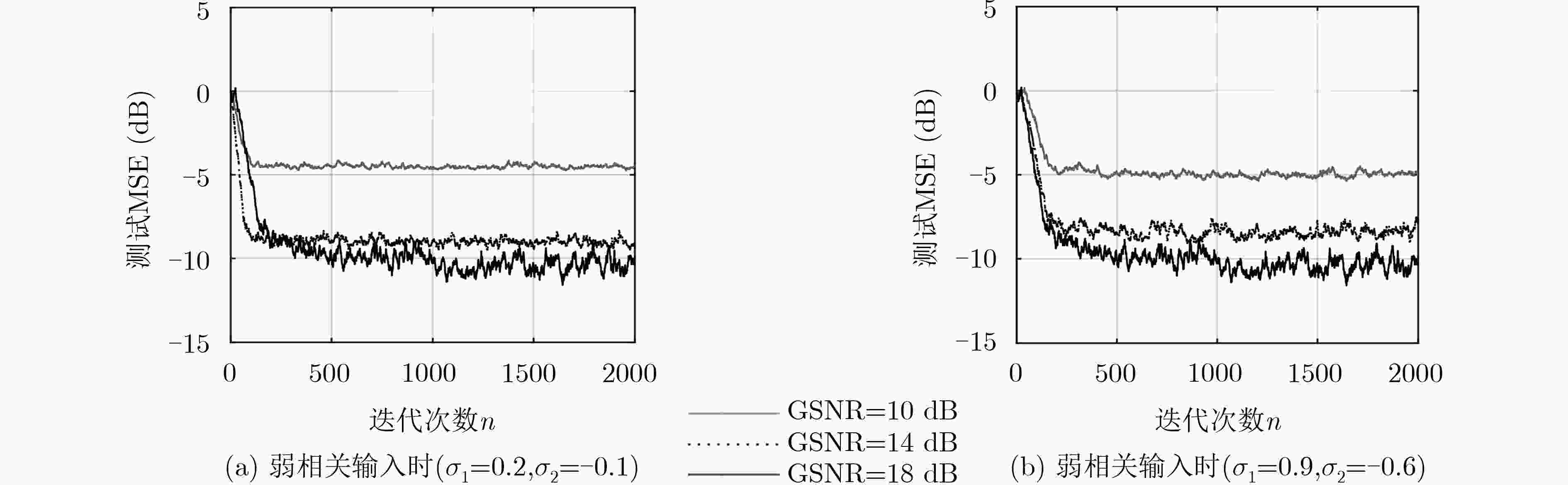
为了降低核仿射投影P范数(KAPP)算法的计算量和存储容量,提高在输入信号强相关时KAPP算法的收敛速度和稳态性能,该文提出基于高斯核显性映射的核归一化解相关APP(KNDAPP-GKEM)算法。该算法利用归一化解相关方法预先解除输入信号的相关性;利用高斯核显式映射方法近似得到显式核函数,消除了对历史数据的依赖,解决了KAPP算法因结构不断生长导致的计算量和存储容量过大的问题。α稳定分布噪声背景下的非线性系统辨识仿真结果表明,在输入信号强相关时KNDAPP-GKEM算法收敛速度快,非线性系统辨识稳态均方误差小,训练所需时间呈线性缓慢增长,有利于实际非线性系统辨识的应用。
Abstract:In order to reduce the computation complexity and storage capacity of the Kernel Affine Projection P-norm (KAPP) algorithm, and improve the convergence rate and steady-state performance of the algorithm when the input signal is strongly correlated, a Kernel Normalization Decorrelated Affine Projection P-norm algorithm based on Gaussian Kernel Explicit Mapping (KNDAPP-GKEM) is proposed. The correlation of the input signal is eliminated in advance by the normalized correlation method. The explicit kernel function is approximated by Gaussian kernel explicit mapping method, which eliminates the dependence on historical data and solves the problem that the computation and storage capacity of the KAPP algorithm are too high due to the continuous growth of structure. The simulation results of nonlinear system identification under α-stable distribution noise environment show that when the training data scale is large, the KNDAPP-GKEM algorithm still maintains a fast convergence rate and the low identification mean square error of nonlinear system. Moreover, its training time is linearly and slowly increased, which is more conducive to the practical application of nonlinear system identification.
-
表 1 KNDAPP-GKEM算法在n时刻的计算复杂度
迭代步骤 乘法运算次数 加法运算次数 计算复杂度 映射得到$\varphi ({{x}}(n)$ DL+D DL–D O(1) 归一化计算${{{Z}}_{\rm{N}}}(n)$ 2K3+3DK2+2D2K 3DK2+2D2K+2K3–D2–2DK–3K2 O(K3) 计算y(n), e(n)和ep(n) DK +K DK O(K) 更新权重${{w}}{\rm{(}}n{\rm{)}}$ DK+D+1 DK O(K) -
OZEKI K and UMEDA T. An adaptive filtering algorithm using an orthogonal projection to an affine subspace and its properties[J]. Electronics and Communications in Japan, 1984, 67(5): 19–27. doi: 10.1002/ecja.4400670503 王世元, 史春芬, 蒋云翔, 等. 基于q梯度的仿射投影算法及其稳态均方收敛分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(10): 2402–2407. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171125WANG Shiyuan, SHI Chunfen, JIANG Yunxiang, et al. Q-affine projection algorithm and its steady-state mean square convergence analysis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(10): 2402–2407. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171125 王兰, 杨育红, 李良山. 解相关变阶仿射投影窄带干扰抑制算法[J]. 信息工程大学学报, 2016, 17(3): 266–269, 280. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0673.2016.03.003WANG Lan, YANG Yuhong, and LI Liangshan. Decorrelating affine projection algorithm with variable order for narrowband interference suppression[J]. Journal of Information Engineering University, 2016, 17(3): 266–269, 280. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0673.2016.03.003 LIU Weifeng, PRÍNCIPE J C, and HAYKIN S. Kernel Adaptive Filtering: A Comprehensive Introduction[M]. Hoboken, USA: Wiley, 2010: 69–93. 李群生, 赵剡, 寇磊, 等. 一种基于多尺度核学习的仿射投影滤波算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 924–931. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190023LI Qunsheng, ZHAO Yan, KOU Lei, et al. An affine projection algorithm with multi-scale kernels learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 924–931. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190023 邱天爽, 张旭秀, 李小兵, 等. 统计信号处理: 非高斯信号处理及其应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2004: 131–171.QIU Tianshuang, ZHANG Xuxiu, LI Xiaobin, et al. Statistical Signal Processing: Non-Gauss Signal Processing and Its Application[M]. Beijing: Electronics Industry Press, 2004: 131–171. 金明明. 核自适应滤波算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 杭州电子科技大学, 2017: 48–54.JIN Mingming. The research on kernel adaptive filtering algorithms[D]. [Master dissertation], Hangzhou Dianzi University, 2017: 48–54. 刘勇, 江沙里, 廖士中. 基于近似高斯核显式描述的大规模SVM求解[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2014, 51(10): 2171–2177. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2014.20130825LIU Yong, JIANG Shali, and LIAO Shizhong. Approximate gaussian kernel for large-scale SVM[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2014, 51(10): 2171–2177. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2014.20130825 RAHIMI A and RECHT B. Uniform approximation of functions with random bases[C]. Proceedings of the 46th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, Urbana-Champaign, USA, 2008: 555–561. doi: 10.1109/ALLERTON.2008.4797607. BOROUMAND M and FRIDRICH J. Applications of explicit non-linear feature maps in steganalysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2018, 13(4): 823–833. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2017.2766580 HU Zhen, LIN Ming, and ZHANG Changshui. Dependent online kernel learning with constant number of random fourier features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(10): 2464–2476. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2387313 SHARMA M, JAYADEVA, SOMAN S, et al. Large-scale minimal complexity machines using explicit feature maps[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2017, 47(10): 2653–2662. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2694321 王迎旭. 基于随机特征的多核分布式协同模糊聚类算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 济南大学, 2019: 21–65.WANG Yingxu. Research of random feature based multiple kernel collaborative fuzzy clustering method in P2P distributed network[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Jinan, 2019: 21–65. LIU Yuqi, SUN Chao, and JIANG Shouda. A kernel least mean square algorithm based on randomized feature networks[J]. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(3): 458. doi: 10.3390/app8030458 王永德, 王军. 随机信号分析基础[M]. 3版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2009: 11.WANG Yongde and WANG Jun. Fundamentals of Random Signal Analysis[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Electronic Industry Press, 2009: 11. -






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
