An Improved Template Analysis Method Based on Power Traces Preprocessing with Manifold Learning
-
摘要: 能量数据作为模板攻击过程中的关键对象,具有维度高、有效维度少、不对齐的特点,在进行有效的预处理之前,模板攻击难以奏效。针对能量数据的特性,该文提出一种基于流形学习思想进行整体对齐的方法,以保留能量数据的变化特征,随后通过线性投影的方法降低数据的维度。使用该方法在Panda 2018 challenge1标准数据集进行了验证,实验结果表明,该方法的特征提取效果优于传统的PCA和LDA方法,能大幅度提高模板攻击的成功率。最后采用模板攻击恢复密钥,仅使用两条能量迹密钥恢复成功率即可达到80%以上。Abstract: As the key object in the process of template analysis, power traces have the characteristics of high dimension, less effective dimension and unaligned. Before effective preprocessing, template attack is difficult to work. Based on the characteristics of energy data, a global alignment method based on manifold learning is proposed to preserve the changing characteristics of power traces, and then the dimensionality of data is reduced by linear projection. The method is validated in Panda 2018 challenge1 standard datasets respectively. The experimental results show that the feature extraction effect of this method is superior over that of traditional PCA and LDA methods. Finally, the method of template analysis is used to recover the key, and the recovery success rates can reach 80% with only two traces.
-
表 1 向量矩阵计算算法
输入:能量数据${T_\alpha } = {\rm{\{ } }{T_i},0 \le i \le \alpha ,i \in N\}$,对齐参数$k$。 输出:对齐后的能量数据${T'_\alpha }$ (1) for j in range(α), do (2) 计算与${T_j}$ 欧式距离最近的$k$条能量迹${\rm{\{ }}{T_{j1}},{T_{j2}}, ··· ,{T_{jk}}\} $; (3) end (4) for j in range (α), do (5) 计算关系向量矩阵${ {{W} }_{{j} } } = \dfrac{ {\left( { {{C} }_i^{ - 1} \cdot { {{1} }_k} } \right)} }{ { { {{\textit{1} } } }_k^{\rm T} \cdot {{C} }_i^{ - 1} \cdot { {{{\textit{1}}} }_k} } }$,其中${ { C}_i} $为
${\rm{\{ }}{T_{j1}},{T_{j2}}, ··· ,{T_{jk}}\} $的协方差矩阵,${ {{{\textit{1}}} }_k}$为$k$维全1向量;(6) end (7) 计算矩阵${{M} } = ({{ {I} } } - {{W} }){({{I} } - {{W} })^{\rm{T} } }$; (8) 设$\beta = \alpha /2$从矩阵M中选择较小的$\beta $个特征值,记为${{{M}}_\beta }$,
计算${T'_\alpha } = T \cdot {{{M}}_\beta }$;(9) return ${T_\alpha }^\prime $。 表 2 PANDA 2018 Challenge1数据集预处理后方差(×104)表(汉明重量不同)
方差 0 1 3 7 15 31 63 127 255 0 4.08 10.99 14.31 16.61 9.80 15.80 18.32 13.02 10.19 1 10.99 2.67 12.49 8.83 7.34 9.50 11.48 5.00 6.33 3 14.31 12.49 8.53 13.62 15.21 12.67 11.73 13.00 15.81 7 16.61 8.83 13.62 3.62 16.24 8.13 11.60 4.99 10.73 15 9.80 7.34 15.21 16.24 4.23 12.21 12.85 9.23 9.84 31 15.80 9.50 12.67 8.13 12.21 4.17 11.62 8.86 9.61 63 18.32 11.48 11.73 11.60 12.85 11.62 4.54 9.26 9.73 127 13.02 5.00 13.00 4.99 9.23 8.86 9.26 1.97 5.23 255 10.19 6.33 15.81 10.73 9.84 9.61 9.73 5.23 4.26 表 3 PANDA 2018 Challenge1数据集预处理后方差(×104)表(汉明重量相同)
方差 7 11 13 14 19 35 67 131 224 7 3.62 11.23 23.70 12.19 13.35 13.52 11.55 14.04 9.86 11 11.23 2.60 18.80 11.73 12.07 11.85 12.43 10.97 10.21 13 23.70 18.80 31.91 23.04 27.09 22.52 23.58 56.33 19.22 14 12.19 11.73 23.04 3.89 12.54 9.52 14.47 14.96 12.70 19 13.35 12.07 27.09 12.54 4.78 13.86 15.33 17.68 11.98 35 13.52 11.85 22.52 9.52 13.86 3.15 15.07 15.10 10.67 67 11.55 12.43 23.58 14.47 15.33 15.07 4.98 17.73 9.50 131 14.04 10.97 56.33 14.96 17.68 15.10 17.73 37.04 20.31 224 9.86 10.21 19.22 12.70 11.98 10.67 9.50 20.31 3.91 表 4 PANDA 2018 Challenge1数据集PCA-20处理后方差(×104)表(汉明重量不同)
方差 0 1 3 7 15 31 63 127 255 0 33.00 27.97 30.58 29.58 28.96 30.91 29.07 31.04 31.06 1 27.97 13.72 15.97 16.05 15.23 16.10 15.99 20.49 14.26 3 30.58 15.97 13.79 16.97 15.97 17.57 15.58 23.60 16.56 7 29.58 16.05 16.97 17.04 16.70 17.60 17.34 22.65 17.31 15 28.96 15.23 15.97 16.70 14.53 16.83 16.07 21.60 16.43 31 30.91 16.10 17.57 17.60 16.83 16.64 16.65 22.57 17.06 63 29.07 15.99 15.58 17.34 16.07 16.65 15.41 22.27 16.76 127 31.04 20.49 23.60 22.65 21.60 22.57 22.27 24.36 22.35 255 31.06 14.26 16.56 17.31 16.43 17.06 16.76 22.35 13.91 表 5 PANDA 2018 Challenge1数据集LDA-20处理后方差(×104)表(汉明重量不同)
方差 0 1 3 7 15 31 63 127 255 0 0.95 1.21 0.93 0.99 1.07 1.09 1.08 1.12 1.13 1 1.21 1.13 1.07 1.17 1.20 1.11 1.24 1.15 1.20 3 0.93 1.07 0.65 0.90 0.99 0.93 1.00 1.05 1.01 7 0.99 1.17 0.90 0.84 0.97 1.02 1.10 1.09 1.06 15 1.07 1.20 0.99 0.97 0.92 1.08 1.17 1.16 1.11 31 1.09 1.11 0.93 1.02 1.08 0.89 1.10 1.10 1.02 63 1.08 1.24 1.00 1.10 1.17 1.10 1.07 1.18 1.15 127 1.12 1.15 1.05 1.09 1.16 1.10 1.18 0.98 1.15 255 1.13 1.20 1.01 1.06 1.11 1.02 1.15 1.15 0.97 -
KOCHER P, JAFFE J, and JUN B. Differential power analysis[C]. The 13th Annual International Cryptology Conference, Santa Barbara, USA, 1999: 388–397. doi: 10.1007/3-540-48405-1_25. ERNST D and MARTIN S. The common criteria for information technology security evaluation: Implications for China’s policy on information security standards[R]. East-West Center Working Papers, No. 108, 2010. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.2770146. VAN TILBORG H C A and JAJODIA S. Encyclopedia of Cryptography and Security[M]. Boston: Springer, 2011: 468–471. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-5906-5. CHARI S, RAO J R, and ROHATGI P. Template attacks[C]. The 4th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Redwood Shores, USA, 2002: 13–28. doi: 10.1007/3-540-36400-5_3. BRIER E, CLAVIER C, and OLIVIER F. Correlation power analysis with a leakage model[C]. The 6th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Cambridge, USA, 2004: 16–29. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-28632-5_2. BOGDANOV A. Improved side-channel collision attacks on AES[C]. The 14th International Workshop on Selected Areas in Cryptography, Ottawa, Canada, 2007: 84–95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-77360-3_6. RIVAIN M, PROUFF E, and DOGET J. Higher-order masking and shuffling for software implementations of block ciphers[C]. The 11th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2009: 171–188. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-04138-9_13. CORON J S and KIZHVATOV I. Analysis and improvement of the random delay countermeasure of CHES 2009[C]. The 12th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Santa Barbara, USA, 2010: 95–109. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-15031-9_7. 黄海, 冯新新, 刘红雨, 等. 基于随机加法链的高级加密标准抗侧信道攻击对策[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(2): 348–354. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171211HUANG Hai, FENG Xinxin, LIU Hongyu, et al. Random addition-chain based countermeasure against side-channel attack for advanced encryption standard[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(2): 348–354. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171211 LERMAN L, BONTEMPI G, and MARKOWITCH O. Power analysis attack: An approach based on machine learning[J]. International Journal of Applied Cryptography, 2014, 3(2): 97–115. doi: 10.1504/IJACT.2014.062722 ARCHAMBEAU C, PEETERS E, STANDAERT F X, et al. Template attacks in principal subspaces[C]. The 8th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Yokohama, Japan, 2006: 1–14. doi: 10.1007/11894063_1. STANDAERT F X and ARCHAMBEAU C. Using subspace-based template attacks to compare and combine power and electromagnetic information leakages[C]. The 10th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Washington, USA, 2008: 411–425. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-85053-3_26. HETTWER B, GEHRER S, and GÜNEYSU T. Applications of machine learning techniques in side-channel attacks: A survey[J]. Journal of Cryptographic Engineering, 2020(10): 85–95. doi: 10.1007/s13389-019-00212-8 王燚, 吴震, 蔺冰. 对加掩加密算法的盲掩码模板攻击[J]. 通信学报, 2019, 40(1): 1–14. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019007WANG Yi, WU Zhen, and LIN Bing. Blind mask template attacks on masked cryptographic algorithm[J]. Journal on Communications, 2019, 40(1): 1–14. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019007 CAGLI E, DUMAS C, and PROUFF E. Convolutional neural networks with data augmentation against jitter-based countermeasures: Profiling attacks without pre-processing[C]. The 19th International Conference on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Taipei, China, 2017: 45–68. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-66787-4_3. ZHOU Yuanyuan and STANDAERT F X. Deep learning mitigates but does not annihilate the need of aligned traces and a generalized ResNet model for side-channel attacks[J]. Journal of Cryptographic Engineering, 2020(10): 135–162. doi: 10.1007/s13389-019-00209-3 WANG Z. The data of PANDA challeng1[EB/OL]. https://github.com/kistoday/Panda2018/tree/master/challeng1, 2019. CRIMINISI A, SHOTTON J, and KONUKOGLU E. Decision forests: A unified framework for classification, regression, density estimation, manifold learning and semi-supervised learning[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Computer Graphics and Vision, 2012, 7(2/3): 81–227. doi: 10.1561/0600000035 HOMMA N, NAGASHIMA S, IMAI Y, et al. High-resolution side-channel attack using phase-based waveform matching[C]. The 8th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems - CHES 2006, Yokohama, Japan, 2006: 187–200. doi: 10.1007/11894063_15. GUILLEY S, KHALFALLAH K, LOMNE V, et al. Formal framework for the evaluation of waveform resynchronization algorithms[C]. The 5th IFIP WG 11.2 International Workshop on Information Security Theory and Practice. Security and Privacy of Mobile Devices in Wireless Communication, Heraklion, Greece, 2011: 100–115. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-21040-2_7. MATEOS E and GEBOTYS C H. A new correlation frequency analysis of the side channel[C]. The 5th Workshop on Embedded Systems Security, Scottsdale, USA, 2010: 4. doi: 10.1145/1873548.1873552. GIERLICHS B, LEMKE-RUST K, and PAAR C. Templates vs. stochastic methods: A performance analysis for side channel cryptanalysis[C]. The 8th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Yokohama, Japan, 2006: 15–29. doi: 10.1007/11894063_2. ZHANG Hailong and ZHOU Yongbin. Template attack vs. stochastic model: An empirical study on the performances of profiling attacks in real scenarios[J]. Microprocessors and Microsystems, 2019, 66: 43–54. doi: 10.1016/j.micpro.2019.02.010 -





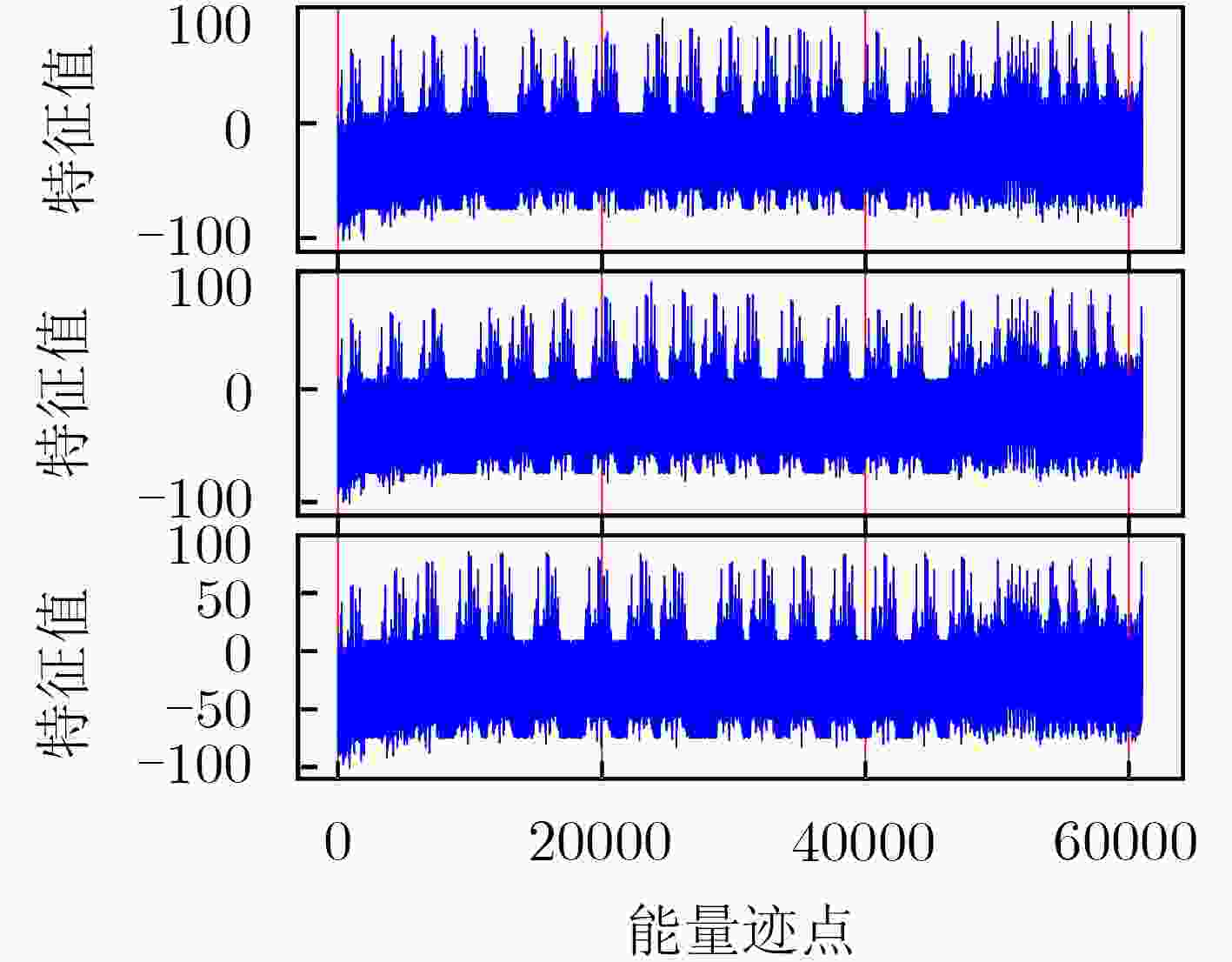
 下载:
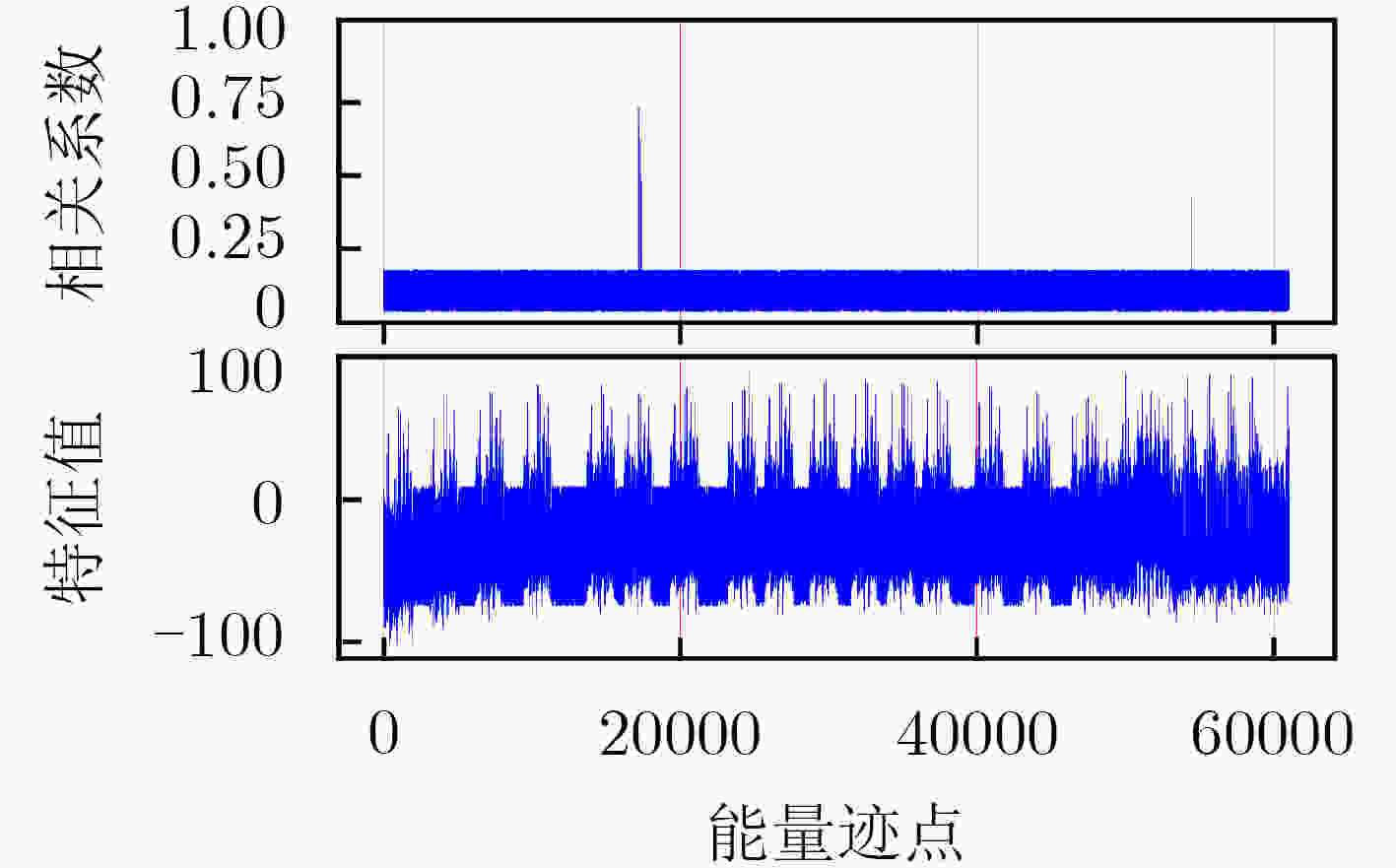
下载:
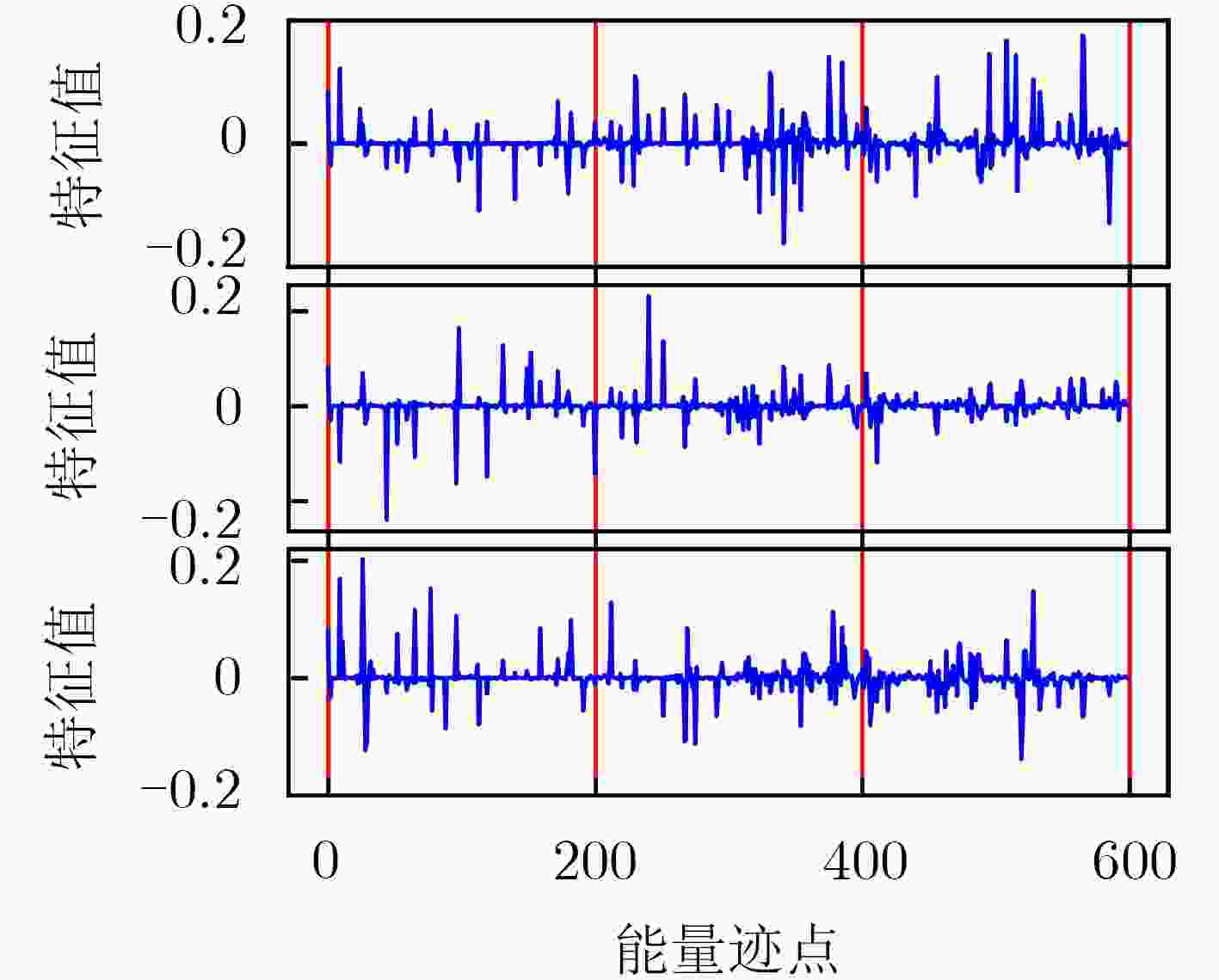
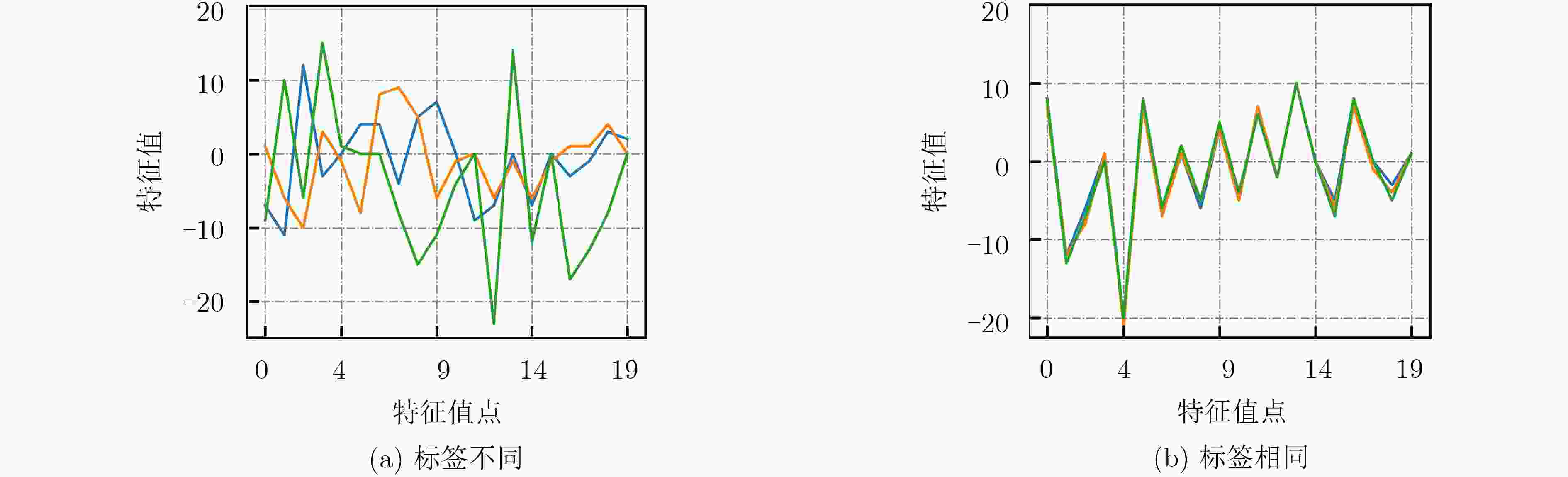


 下载:
下载:
